1. Introduction
Brunei Darussalam is the country with the smallest population in ASEAN with about 0.4 million people in the nation. In terms of urbanization, over 70 percent of its population are living in urban areas (refer to Table 1). In terms of transportation modes, Brunei has one airport and one national airline. In addition to that, the country has three ports: Muara, Bandar Seri Begawan and Kuala Belait port. Besides that, it has developed paved road over 77 percent in the country in 2005 (refer to Table 2). This paper will discuss on the transportation development in the Sultanate. In order to fully understand the development, the paper will explain the development of three modes of transportation (land, air and sea) in Brunei Darussalam by decades from 1970s to 2010s. In addition to that, the paper will suggest some recommendation to the problems encountered during these transportation developments.
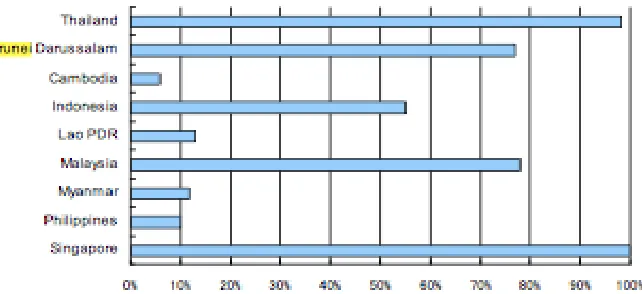
Table 1: Population residing in urban areas by ASEAN countries (%)
Source: World Urbanization Prospects: The 2009 Revision
Table 2: Percentage of paved road in 2005 in ASEAN countries
2. Literature Reviews (from the Unhabitat, 2013)
In accordance to the Global Report on Human Settlements 2013 by Unhabitat, despite the increasing level of urban mobility worldwide, access to places, activities and services has become increasingly difficult. Sustainable mobility extends beyond technicalities of increasing speed and improving the effectiveness and efficiency of transport systems, to include demand-oriented measures. While the speed and efficiency of travel are important, more critical however, is the ease of reaching those destinations in terms of proximity, convenience as well as positive externalities. Mobility is not only a matter of developing transport infrastructure and services, but also of overcoming the social, economic, political and physical constraints to movement. Globally, the transport bias of urban mobility is demonstrated by the dominance of private motor vehicles.
The Unhabitat (2013) also reported that the most advanced public transport systems in the world include all dimensions of quality that is travel time, reliability, safety and security, comfort and user information to provide a very attractive alternative to car and motorcycle use. Funding for capital investments in high-capacity public transport requires the participation of local, regional and national governments. Therefore, integration is important for public transport systems to be efficient and sustainable. The most efficient systems are those that have achieved route integration; integration with other public transport systems; integration with private motorized transport; integration with non-motorized modes; and fare integration.
3. The Developments by Decades
In regards to the Report on Brunei in 1904 by McArthur, during that time, the country possesses no roads, only rough tracks used chiefly by the “Kadayans” in bringing goods to native markets, which is held periodically at convenient “pengkalans”. All travelling is in consequences done by water. Fortunately, there are numerous waterways and tributary streams, which make access to most parts of Brunei. The capital of the state is distant 42 miles from Labuan. A local ship the steamship “Taganac” calls twice a month to bring in cargoes of sundries and taking out exports, chiefly cutch.
JPD (n.d) stated that in 1907, the first footpath has been built between Residency and Brunei Town at Jalan Subok. In 1914, a 60 miles distance pilot scheme has been constructed to communicated Brunei Town and Kuala Belait. In 1924, the Road Traffic Regulations were first introduced under Chapter 68 of Brunei Laws called “Traction Engines and Motor Cars Enactment 1924”, which is then in 1954 has been amended and known as “The Road Traffic Enactment 1954”. By 1960, a total of 7992 vehicles have been registered and 7519 driving licenses have been issued.
According to the Brunei’s Department of Civil Aviation (n.d), in 1953, the first commercial air transport in Brunei, connecting Bandar Seri Begawan with Anduki in the Belait district. Airport services were operated from the Berakas area at an old runway site built by the Japanese during World War 2 which then known as Brunei Airport. The airport became operational in 1974.
Marine Department of Brunei first operated as Department of Custom and Marine, which is in 1948. The main services then was to provide transportation of passengers and mail 3 times a week to Labuan. Also, during that time, it only operated 8 outboards and 6 vessels as maritime transportations (Marine Department, n.d).
Muara port, which is situated about 27 kilometers to the northeast of the capital, is the largest of the country’s harbors as the bulk of imports and exports go through it. Meanwhile, Bandar Seri Begawan port has existed since before the Second World War. Currently, it serves the needs of passenger vessels ferrying commuters to and from the various neighboring Malaysian towns apart from carrying bulk cargoes for direct delivery. Lastly, Kuala Belait port is located at the mouth of the Belait River. The port, which is 61 meters long, serves the Belait district and caters to cargo vessels from the neighboring countries.
3.1 Developments in 1970s
All information regarding the developments in 1970s is found in Annual Report: Brunei (1977) and Brunei (1978-1981).
3.1.1 Department of Land Transport
The number of new vehicle license registration in 1977 was 4,942, an increase of 1,000 from 1976. In addition to that, a total of 5,513 driving test had been held but the result was not satisfying because there was only 48.6 percent of them passed the test. Thus, the Department of Land Transport is required to organize an even firmer test in order to maintain and enhance the quality of driving in the nation. The next year, 43,844 vehicles are registered and 46136 driver who has driving license. The department accumulated $1,167,826 profits that year of 1978. The Road Safety Council was established in 1978, as an effort to promote road safety consciousness among motorists.
3.1.2 Department of Civil Aviation
3.1.3 Marine Department/ Port Department
The Ports Department reported a generation of profits of $127,895 in 1977, 17 percent increase from last year. During this year, the department has requested one tractor or loader to help the sender transferring heavy loads to its storage area. By the end of this year, a 90,000 square feet warehouse will complete its construction and will be able to accommodate more loads to prevent congestions.
3.2 Developments in 1980s
All information regarding the developments in 1980s is found in Brunei (1982), Brunei Darussalam (1983-1984), (1985-1986), (1987), (1988), and (1989).
3.2.1 Department of Land Transport
By the end of 1981, 62,047 vehicles were registered and 49,500 driver who has driving license. The department accumulated $2,470,631 profits that year. At the end of 1982, a total of 8,358 drivers took their driving test, out of which only 4,057 passed. By 1984, 77,680 motorized vehicles were registered. Driving tests continued to be stringent in order to maintain the country’s high driving standards. The number of tests totaled 11,494 in 1985 and 8157 the following year with passes averaging around 64 percent only. Apart from that, road taxes, and the fees for vehicle registration, examination and driving test continued to be among the lowest in the world. The number of licensed motor vehicles in use during 1989 was estimated at 72,291 made up of 62,418 private motorcars, 7,540 commercial vehicles including buses and taxis, 333 motorbikes and scooters. The figures do not include government and military vehicles. Also, the number of passes (of driving test and highway code test) has slightly improved since the creation of a legislation that enabled the official establishments of a driving school in September 1987.
3.2.2 Department of Civil Aviation
At the end of 1984, a third B-737 was added to the national flag carrier, Royal Brunei Airlines (RBA). The third aircraft is intended to reduce the average use of aircraft in which the previous two aircrafts have reached maximum average use. In that year, RBA had also offered twice-weekly fly to Jakarta and Darwin. With this addition, RBA is set to offer all ASEAN’s cities destination. During 1985 and 1986, RBA achieved another milestone when it took delivery of three new Boeing 757 aircrafts. Airport Development Project (ADP) that began in November 1984 was completed in September 1987 at an overall cost of more than $52 million. The ADP has not only enhanced the existing facilities of the Brunei International Airport but has also given it a host of new ones including a sterile transit hall capable of accommodating 1,000 passengers at a time and six aero-bridges connecting the aircraft to the terminal.
In 1989, Royal Brunei (RB) celebrated 15th anniversary of its foundation. The year also saw RB joining five other airlines as part owner of a new US$100 million regional computerized reservation system called ABACUS, enabling agents to book and confirm customers’ ticket on a ‘real time’ basis from data to a broad range of carriers – all by a simple keyboard entry on an Abacus terminal. The system also provides many other services, including hotel and car rental bookings. During the year, express check-ins was introduced at the Brunei International Airport; and the airlines’ second B737 was sold after 14 years’ service, leaving Royal Brunei with three B757s and one B737.
3.2.3 Marine Department/ Port Department
The following year, the Marine Department set up the Commercial Vessel Licensing Board to smoothen furthers the administration and regulation of vessel registration and licensing. The department registered a total of 28 vessels with a combined Gross Register Tonnage of 5,828 tonnes and 143 licensed vessels in 1987. Under the Five Year National Development Plan (NDP), the department purchased two vessels, one was for the installation and maintenance of buoys costing more than $1.4 million and the other a dredger costing nearly $2 million. Also during that year, an allocation of $10 million for the construction of the department’s headquarters which has been entrusted to a consultant to design and supervise its implementation.
In 1988, there were 600 applications for permits to operate water taxis in Kampong Ayer (water village), the Belait River, and between Bandar Seri Begawan (BSB) and Bangar in the Temburong District. In addition, applications for permits to run ferries to destinations outside the State such as BSB to Labuan and Limbang were received. After a study, three permits for the BSB/Labuan destination were issued to local operators. The year under review saw the department taking delivery of the port maintenance and inspection vessel, which was built in Hong Kong at a cost of $1.8 million.
3.3 Developments in 1990s
All information regarding the developments in 1990s is found in Brunei Darussalam (1990), (1991), (1992), (1993), and (1994-1995).
3.3.1 Department of Land Transport
3.3.2 Department of Civil Aviation
The year 1990 show the number of passengers who passed through the International Brunei Airport were 244,802 inbound; 243,742 outbound; and 8,796 transit, thus recording increases of 5.11 percent; 7.8 percent; and 29.73 percent respectively over 1989. During that year, RBA opened two new routes, namely Frankfurt and London’s Gatwick. The year also saw the delivery of the first of two new B767s to extended range, wide-bodied aircraft and last of RBA’s original fleet of B737s being sold to Aloha Airlines. The year after, RBA won the prestigious “Koala Award” in the best airline category for its innovation, commitment and contribution to Australian tourism. During 1992, RBA purchased three B767-300 extended range aircraft in addition to its existing fleet of three B757ERs.
In 1993, its network of routes comprised Singapore, Manila, Kuching, Kota Kinabalu, Hong Kong, Bangkok, Kuala Lumpur, Jakarta, Darwin, Taipei, Dubai, Frankfurt, London, Perth, Jeddah, Abu Dhabi, Bali, Bahrain, Zurich, Beijing, and Cairo. In accordance with the practice of many airlines of other Muslim countries, RBA does not serve pork or alcohol on board. The year also saw it taking delivery of one of two Boeing 767-300 Extended Range (ER) it ordered from United States. This brought the total to seven aircraft in active service during 1993. Between 1994 and 1995, there were several projects undertaken by the DCA. One of the most notable and significant of these was the upgrading of the Air Traffic Services Communications and Surveillance facilities at the Brunei International Airport, which is scheduled to be completed and fully operational by early 1997. The DCA’s annual revenue amounted to $9.8 million in 1994 and $11.2 million the following year. Among other things, the State flag carrier celebrated two decades of achievement and established six new destinations namely Balikpapan, Miri, Labuan, Osaka, Brisbane and Culcutta.
3.3.3 Marine Department/ Port Department
In 1990, a total of 821 vessels were called at Muara port, 10 percent less than 1989; in Bandar Seri Begawan port the number of vessels arrived rose by 9 percent from 266 in 1989 to 291; and Kuala Belait port handled 238 vessels which is down by 45 percent. In 1991, the Government officially formed the Merchant Shipping Licensing Board (MSLB). Its functions include considering applications for the setting up of a marine transport business; determining the number of vessels to be licensed; and finding ways to solve any problem that might arise from such enterprise.
Since joining the International Maritime Organization, the level of maritime safety has been further raised with the signing and enforcement in 1992 of the International Convention on Civil Liability for Oil Pollution Damage 1969; and International Convention on the Establishment of International Fund for Compensation for Oil Pollution Damage 1971. In comparison of last year’s figures, the import show a rise of 16 percent and exports a decrease of 37 percent due to reduction of timber products being sent through the Tanjong Selirong anchorage in 1993. In 1994, a joint project with Japan to keep oil spills in check was carried out.
3.4 Developments in 2000s
All information regarding the developments in 2000s is found in Brunei Darussalam Statistical Yearbook (2004), (2005), (2008), and (2009).
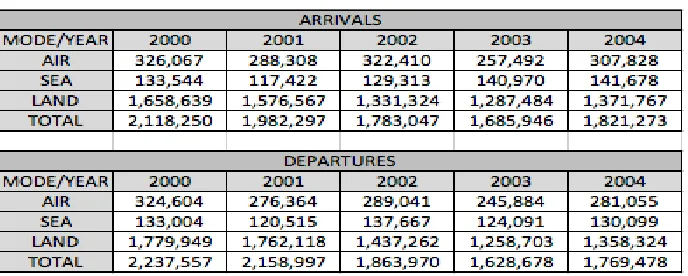
Table 3: Arrivals and Departures by air, sea and land (2000-2004)
Source: Immigration and National Registration Department, Ministry of Home Affairs
Table 4: Arrivals and Departures by air, sea and land (2005-2009)
Source: Immigration and National Registration Department, Ministry of Home Affairs
3.4.1 Department of Land Transport
Table 6: Number of Newly Registered Vehicles (2000-2008)
Source: Land Transport Department, Ministry of Communication
Table 7: Length of Roads (1999-2003) and (2005-2009)
Source: Public Works Department, Ministry of Development
3.4.2 Department of Civil Aviation
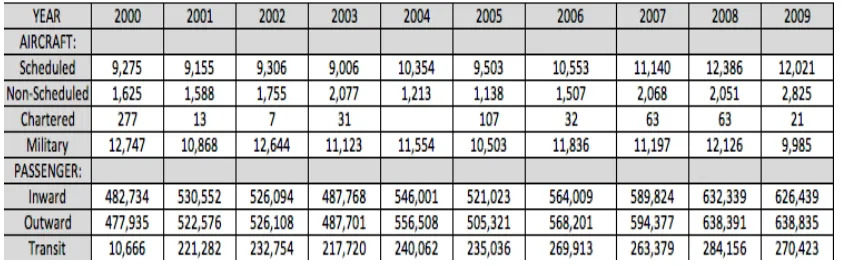
The Department reported that both the number of aircraft movement and passenger displayed an increasing number from the year 2000 to 2004, excluding the year 2003 which showed slight decline (refer to Table 8). In addition to that, the number of scheduled, non-scheduled and military aircraft movement increased throughout the years under review from 2005 to 2008; and the figures for scheduled and military aircraft movement fell in 2009 compared to the previous year. Also, in 2009, the number of inward and transit passengers slightly down from 632,339 in 2008 to 626,439 in 2009 and 248,156 in 2008 and 270,423 in 2009. The number of outward passengers slightly increased in 2009 compared to the previous year.
Table 8: Aircraft Movement and Passenger (2000-2009)
3.4.3 Marine Department/ Port Department
Table 9 shows the yearly number of boats licensed. During the periods between 2000 and 2004, in terms of passenger boats, the figures are declining meanwhile the government vessels that were registered are increasing. In 2009, the Marine Department recorded 9 cargo boats, 147 passenger boats, 43 fishing boats, 36 leisure crafts and 44 government vessels were licensed.
Table 9: Number of Boats Licensed (2000-2009)
Sources: Marine Department, Ministry of Communication
3.5 Developments in 2010s
All information regarding the developments in 2010s is found in Brunei Darussalam Statistical Yearbook (2010), (2011), and Quarterly Statistical Indicators: Negara Brunei Darussalam (Quarter 4, 2012).
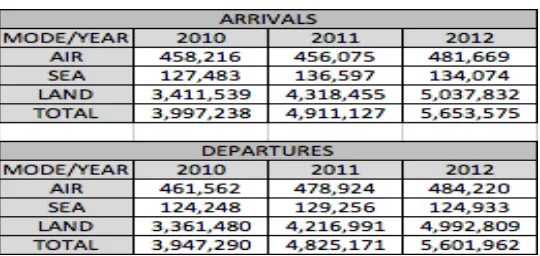
The number of both arrivals and departures (by air, sea and land) in 2012 shows an increase from 3,997,238 in 2010 to 5,653,575 in 2012 and from 3,947,290 in 2010 to 5,601,962 in 2012 accordingly.
Table 10: Arrivals and Departures by air, sea and land (2010-2012)
3.5.1 Department of Land Transport
In 2011, the number of newly licensed registered vehicles was 15,900 with an increase of 5.5 percent as compared to 2010 (refer to Table 11). In 2012, it also increased to 18,562 non-government vehicles and 89 government vehicles, which give a total of 18,651 newly, registered vehicles. The length of road in 2011 increased from 3,028.11 kilometers in 2012 to 3,127.35 kilometers in 2011.
Table 11: Number of Newly Registered Vehicles (2010-2012)
Source: Land Transport Department, Ministry of Communication
3.5.2 Department of Civil Aviation
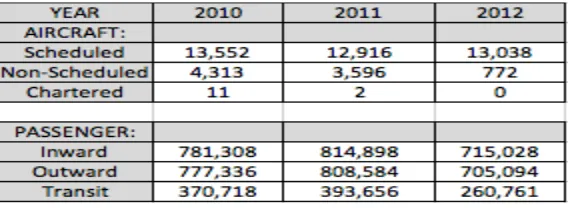
Table 12 shows that the number of aircraft movement (excluding scheduled) and passengers fell down in 2012 as compared to 2011.
Table 12: Aircraft Movement and Passenger
Source: Civil Aviation Department, Ministry of Communications
3.5.3 Marine Department/ Port Department
In 2011, 8 cargo boats; 145 passenger boats; 45 fishing boats; 21 leisure crafts; and 54 government vessels were licensed as compared to 2010: 11 cargo boats; 125 passenger boats; 42 fishing boats; 30 leisure crafts; and 45 government vessels.
4. Recent Major Projects
Improved road connectivity between logistics hubs, including 2.7 kilometers bridge to link the Pulau Muara Besar port and manufacturing center with the mainland. Other projects include Temburong Bridge and bridge in Sg. Brunei, which connect Jalan Rsidency in Bandar with Kg. Sg. Kebun in Lumapas to reduce transit times (this project costs about 139 millions).
A project in Brunei Airport costs 150 million to support 3 million passengers a year (which almost reached the maximum capacity). Between 2011 and 2012, tenders proposed out to revamp bus system, which includes features for disability access, communication radios, CCTV, onboard ticket machine and luggage compartments. Apart from that, Proposed Integrated Public Transit System of light rail transit system. However, research found out that it would bring losses if implemented. In 2013, Telisai-Lumut dual carriageways of 18.6 kilometers were constructed.
In 2014, Government allocated 19.79 percent of its national budget for 2014/2015 $226.6 millions for road, bridges and civil aviation. The national carrier is requested to increase short haul travel like Malaysia from five times a week to twice a day. In addition to that, four 787 Dreamliner for long haul routes are in operations. With these, they can have extended range with a lot of options in North Asia and Indian sub-continents. Four primary highways of Muara-Tutong are being joined now by 18.6 kilometers Telisai-Lumut highway. Once Temburong Bridge is completed in 2018, travel distance will be 30 to 40 minutes, which significantly improve, compare to two hours by boat and multiple border crossing via Sarawak on land.
5. Recent Technological Developments
The long awaited demerit point system, officially launched in October known as SiKAP (Sistem Keselamatan Amalan Pemandu) in a major effort to reduce the high rate of road accidents in the country. Under this system, motorists will be issued three demerit points for lesser driving offences such as parking haphazardly, dangerously or illegally, and up to 24 points for reckless driving cause death. Additionally, motorists who accumulate 24 or more demerit point within a two-year period will have their driving license suspended for a period of time. A third suspension will lead to the driving license being revoked for a year.
At the end of February this year (Analisa Amu, 2015), the minister of Ministry of Communications stated more than 60 drivers accumulated 21 demerit points. He further added that the demerit point system has been effective in reducing road fatalities and preventing serious injuries. The number of road fatalities dropped 25 percent in 2014 form the previous year. It was also previously reported that there were 24 deaths in 2014, down from 32 in 2013. Severe and minor injuries resulting from road accidents decreased 35 percent and 12 percent respectively.
Another initiative organized by the Land Transport Department is the JPD online apps for smartphones, which is available in both App Store and Google Play. The apps consist of SiKAP demerit point’s details, driving license renewal and vehicle license renewal to produce an effective system and efficient service to the public. Working online from home and through mobile phones will further enhance the department’s productivity, the people and a positive effect on the country’s productivity.
Apart from that, this year also saw that the online applications for vehicle and driving licenses could be done and processed in one day, requiring only one visit to the Land Transport Department’s Headquarter in Beribi.
The app would also help people reach the airport at the right time. In addition to that, it offers information on safety rules and services available at the Brunei International Airport. The Ministry of Communications in a statement (DCA, 2014) said iFlyBrunei is in line with the DCA’s initiatives to better its services and provide easier options for users to gain information through their mobile devices. It also upholds the ministry’s vision: Towards a Smart Society and Excellence in Communication for Enhancing National Competitiveness by 2017.
6. Recommendations
In my honest opinion, it is crucially important to improve the efficiencies of the public transport in order to reduce the number of registered vehicles (of non-government). The importance of having efficient and effective public transportation system help to reduce traffic congestion, fuel consumption, carbon emission and pollution, and the number of newly registered vehicles. In some sense, this helps to achieve sustainable transportation in social, economic, environment, infrastructure development and wealth creation. Instead of subsidizing the car fuels, the amount of subsidies can be used to subsidies the fare of public transportation for instances buses and taxis. Hence, the use of public transportation can be common in the country. However, in order to achieve such success, three important factors need to be taken into consideration: improve buses and taxis services, road accessibility for public transportation, and subsidies the fares for public transportation.
Secondly is the road accessibility of the public transportation such as the buses. There should be adequate place for bus waiting point instead of just having few selected area. In other words, the routes for each bus should be reduced to improve efficiency and time promptness. When each area is maximized, shorter distance and more accurate time arrival can be achieved. For instance, buses for Rimba area. The bus can accommodate for residents in Rimba to go the schools, universities and supermarket. And from there, another bus with another route can bring the residents outside their area. In my case, Lambak area has many zones like Lambak Kanan, Lambak Kiri, Lambak Tengah and so forth. Having each zone to have each bus or one specific bus to go around this area can help to improve efficiencies of the public transport. From there, another bus can bring students to go universities area (in Rimba) for example. By having this kind of improved and precise road accessibility would help to encourage more public to use the buses instead of using private vehicles.
Thirdly, if the fares of the public transportation are reduced or subsidies by the government, it would probably help to encourage more people to use public transport. The high amount of subsidies for fuel can be used for public transportation’ subsidized fares. When there are many people using the public transportation, it means that continuous improvements in its structure or system are needed. Failure to adhere to such needs would let the public back to use private vehicles instead of public transportation.
Other recommendations include the improvements in online system in transportation such as renewal of driving license, and the speed of procedures in transportation-related transaction and activities. Apart from that, Brunei Airport needs to be developed into better and improved place such as calling for more international brands to put their foot in the airport terminals like in the Changi Airport in Singapore. In terms of marine and ports, the government is required to put priorities on investing advanced equipment in the port area. These advancements will help more containers and vessels to visit the airport and make business transactions.
7. References
Analisa Amu (2015). Keep your driving record clean, check SiKAP mobile app. Retrieved from:
http://www.bt.com.bn/frontpage-news-national/2015/02/25/keep-your-driving-record-clean-check-sikap-mobile-app Last accessed 15th March 2015
Annual Report Brunei (1977). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei (1978-1981). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei (1982). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam (1983-1984). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam (1985-1986). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam (1987). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam (1988). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam (1989). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam (1990). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam (1992). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam (1993). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam (1994-1995). Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam Statistical Yearbook 2004. Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam Statistical Yearbook 2005. Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam Statistical Yearbook 2008. Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam Statistical Yearbook 2009. Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam Statistical Yearbook 2010. Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei Darussalam Statistical Yearbook 2011. Department of Statistics, Department of Economic Planning and Development, Prime Minister’s Office.
Brunei’s Department of Civil Aviation (n.d). History. Retrieved from:
http://www.civil-aviation.gov.bn/index.php/about-dca/introduction?id=72 Last
Accessed 10th March 2015
DCA (2014). iFlyBrunei app launched to assist air travellers. Retrieved from:
http://www.civil-aviation.gov.bn/index.php/news-highlights/212-iflybrunei-app-McArthur, M.S.H (1987). Report on Brunei in 1904. Ohio University Press, Center for Southeast Asian Studies.
Quarterly Statistical Indicators: Negara Brunei Darussalam (Quarter 4, 2012). Rabiatul Kamit (2013) SiKAP aims at reducing road mishaps. Retrieved from:
http://www.bt.com.bn/news-national/2013/10/02/sikap-aims-reducing-road-mishaps
The Report: Brunei Darussalam (2008). Oxford Business Group The Report: Brunei Darussalam (2010). Oxford Business Group The Report: Brunei Darussalam (2011). Oxford Business Group The Report: Brunei Darussalam (2013). Oxford Business Group