THE USE OF SNAKE AND LADDER GAME AND
COOPERATIVE LEARNING TO IMPROVE STUDENTS'
SPEAKING SKILLS
(A Classroom Action Research of the Tenth Grade Students of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran in the Academic Year of 2018/2019)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd.)
By:
MUHAMMAD ARIF
NIM. 1131407
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
MOTTO
“You never fail until you stop trying”
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is dedicated to:
1. My beloved parents Muhyiddin (Alm) and Arumi, thanks for the prayer, support, and motivation.
2. My siblings: Halimah and her family, Muh. Abdul Ghoni and his family, Zuhroh and her family, Muhammad Malkan and his family, Muhammad Muhtar, Laila Maghfiroh and her husband, Muhammad Abdul Azis, Muhammad Hilmi Amarudin, and Nafisatun Ni‟mah, who always
motivate, support and help me.
3. My brothers and sisters in Nurul Islam boarding school, thanks for your love, help, and motivation.
4. My great friends: Muhammad Misbakhul Munir, Muhammad Mukhlis, Nurul Alfiatun K., and Siti Fatimah, thanks for your guidance and your inspiring life.
5. My friends in campus, thanks for your motivation.
6. My friends in CEC (Communicative English club), thanks for your big support.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
In the name of Allah, the Most Gracious and the Most Merciful. All praises due to Allah SWT who always blesses and helps the researcher, so the researcher can finish the graduating paper as the requirements for Sarjana Pendidikan in English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. bless and Mercy also be given to Muhammad SAW for his guidance that leads the researcher to the truth.
However, this paper will not be finished without guidance, support, advice, help, and encouragement from individual and institution. Hence, the researcher would like to express special thanks to:
1. Mr. Dr. H. Rahmad Hariyadi, M.Pd. the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
2. Mr. Suwardi, M.Pd. as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
3. Mrs. Noor Malihah, Ph.D. as the Head of English Education Department 4. Mr. Faizal Risdianto, M.Hum. as the counselor who has given countless
hours of reading and revising this graduating paper, thanks a lot for your guidance
ABSTRACT
Arif, Muhammad. 2018. The Use of Snake and Ladder and Cooperative Learning
to Improve Students’ Speaking Skills (A Calssroom Action
Research of the Tenth Grade of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran in the Academic Year of 2018/2019). A Graduation Paper. Teacher Training and Education Faculty. English Education Department. State Institute for Islamic Studies Salatiga. Counselor: Faizal Risdianto, S.S., M.Hum.
Key Words: Snake and Ladder Game, Cooperative Learning, Speaking
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR‟S NOTE ... iii
STATEMENT OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENT ... x
LIST OF TABLES ... xiii
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiv
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Problems of The Research ... 5
C. Objectives of the Research ... 5
D. Benefits of the Research ... 6
E. Hypothesis and Success Indicator ... 7
F. Research Methodology 1. Research Design ... 7
2. Research Subject ... 10
4. Data Collection Method and Research Instrument ... 13
5. Data Analysis Techniques ... 15
G. Graduating Paper Organization ... 18
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Supporting Theories ... 19
1. Concept of Snake and Ladder Game ... 19
2. Concept of Cooperative Learning ... 24
3. Concept of Speaking ... 28
B. Previous Researches ... 32
CHAPTER III IMPLEMENTATION OF RESEARCH A. Procedures of The Research in Cycle I ... 34
1. Planning ... 34
2. Action ... 35
3. Observation ... 35
4. Reflection ... 37
B. Procedures of The Research in Cycle II ... 37
1. Planning ... 37
2. Action ... 38
3. Observation ... 38
4. Reflection ... 40
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
A. Research Findings ... 41
1. Cycle I ... 41
2. Cycle II ... 47
B. Discussion ... 53
1. Cycle I ... 58
2. Cycle II ... 66
CHAPTER V CLOSURE A. Conclusion ... 76
B. Suggestions ... 77 BIBLIOGRAPHY
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1.1 List of the Students ... 10
Table 1.2 Research Schedule ... 12
Table 1.3 Teacher‟s Field Note Checklist ... 14
Table 1.4 Students‟ Field Note Checklist ... 15
Table 4.1 Teacher‟s Field Note Checklist of Cycle 1 ... 45
Table 4.2 Students‟ Field Note Checklist of Cycle 1 ... 46
Table 4.3 Teacher‟s Field Note Checklist of Cycle 2 ... 51
Table 4.4 Students‟ Field Note Checklist of Cycle 2 ... 52
Table 4.5 Rubric of Speaking... 53
Table 4.6 Pre-test Score in Cycle 1 ... 58
Table 4.7 Grade of Pre-test Passing Grade in Cycle 1 ... 60
Table 4.8 Post-test Score in Cycle 1 ... 60
Table 4.9 Grade of Post-test Passing Grade in Cycle 1 ... 62
Table 4.10 Differen Square of Pre-test and Post-test Score in Cycle 1 ... 63
Table 4.11 Pre-test Score in Cycle 2 ... 66
Table 4.12 Grade of Pre-test Passing Grade in Cycle 2 ... 68
Table 4.13 Post-test Score in Cycle 2 ... 69
Table 4.14 Grade of Post-test Passing Grade in Cycle 2 ... 70
Table 4.15 Differen Square of Pre-test and Post-test Score in Cycle 2 ... 71
LIST OF FIGURES
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Research
In the globalization era, English plays a very significant role as an international language and people are required to be proficient in both oral and written English. People also consider that English is the window of the world. It means that we are able to know everything in the world by the mastery of English.
English has many functions, one of them as being stated in the curriculum 2013 that English has a great role to convey the ideas over Indonesia and understand ideas derived from abroad (Widya, Furaidah, & Rohmah, 2016). In education, English is also as a means for the students to develop culture and art, and the final objective of its teaching and learning process is the students are expected to master four skills of language. They are listening, speaking, reading, and writing. But one of the four language skills which this research focuses is speaking skill.
are required to make the process of their understanding more easily. But in the fact that students often find problems in developing speaking skill.
Many problems happen in the teaching and learning process of speaking. In this case, Indonesian students learn English as a foreign language. The students do not speak English in their daily life. The students only learn it at the school. To make the students able to speak English, the teacher takes a big part to stimulate the students to be brave of speaking English. "No matter what is the teacher role in the classroom, the teacher always acts the central focus of the students' attention” (Mustikasari, 2011:155). All of the activities of the teacher will be the students' attention. What the teacher says and does will be the important part of teaching and learning process. To know the problems in teaching and learning process on speaking in X-1 of MA Nurul Islam, the researcher conducts an interview.
cannot improve her teaching and learning skills. Wright, Betteridge, & Buckby stated that "games also help the teacher to create a context in which the language is useful and meaningful” (Wright, Betteridge, & Buckby, 1994:1).
The second speaking problem is from the students. The researcher found that in the X-1 class, most of the students are afraid of speaking English because they are afraid of speaking incorrectly. They are afraid of making mistake when they speak English and being laughed by their friends. They prefer to answer with Indonesian and others are only silent because of lack of vocabulary that they have.
From those problems, the researcher provides some ways to make learning English become fun and joy. The students express their ideas using English in front of many students without any doubt. The researcher has two ways. The first way is using a game. Game is one of the effective ways to develop students' speaking ability.
Wright, Betteridge, & Buckby stated that "games also help the teacher to create a context in which the language is useful and meaningful” (Wright, Betteridge, & Buckby, 1994:1). Besides having many advantages to the students, game also can give advantages to the teacher. The game can make the teacher more creative. It will make the teacher think to connect the game and the material. The teacher must prepare the things for the game. The teacher also has to learn and master the game well before the teacher asks the students to play. It can train the teacher to be a good planner. To sum up, the game is highly motivating because it is amusing and interesting. A game can also be used to give practice many types of communication.
There are many advantages of using a game, the game can give relaxation and fun to the students and usually involve friendly competition and interested in learning. According to Puspita & Surya (2017), a game provides an interesting environment where students must follow the rules previously describes and strive to achieve challenging goals (Puspita & Surya, 2017:292). This creates the motivation for the students of English to get involved and participate actively in learning activities. A game is used to deliver the materials in order to be more fun for the students in a learning process, so they will be enthusiastic to join the activity. It is important to use the game as an alternative way to teach speaking.
„best practices' in education” (Cohen, Brody, & Shevin, 2014:3).
Cooperative learning is an appropriate method to encourage the students to speak up. It can develop their confidence in front of their friends. Cohen, Brody, & Shevin also stated that "Cooperative learning is effective in reducing prejudice among students and in meeting the academic and social needs of students at risk for educational failure" Cooperative learning is not only about working together, but also supporting each other. One and other students become one team. The important thing in this cooperative learning is not only about they finish the task, but it is about the process of how they complete the task.
Based on the explanation above, the researcher proposes a research entitled, "THE USE OF SNAKE AND LADDER GAME AND COOPERATIVE LEARNING TO IMPROVE STUDENTS' SPEAKING SKILLS (A Classroom Action Research of the Tenth Grade Students of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran in the Academic Year of 2018/2019)”
B. Problems of the Research
Based on the above phenomenon, this research tries to answer a problem.
To what extent is the improvement of snake and ladder game and cooperative learning to improve students‟ speaking skills in X-1 of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran?
Based on the statement of the problem of the research, the objective of the research is as follow:
To measure what extent is the improvement of snake and ladder game and cooperative learning to improve students‟ speaking skills of X-1 of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran.
D. Benefits of the Research
The researcher expects that the result of this research can give a contribution to academic field and practice field, as follows:
1. Theoretically
a. The students know more about snake and ladder game and cooperative learning.
b. The results of the research can be used to develop teaching speaking.
c. The result of the research can be reference for other researchers to conduct further research.
2. Practically a. Students
This research can motivate the students to improve their speaking skills through snake and ladder game and cooperative learning. b. Teachers
This research can be used as a consideration in selecting the appropriate media and method in teaching and learning process.
c. School
The result of the research improve the institution‟s quality in English teaching and learning process.
E.
Hypothesis and Success IndicatorBy conducting this research, the researcher proposes a hypothesis: Using snake and ladder game and cooperative learning can improve students' speaking skill at the tenth grade of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran in the academic of year 2018/2019.
The success indicator of this research is taken from the passing grade (KKM) of English lesson in MA Nurul Islam Tengaran. The passing grade is 70 and the target of the passing grade is 85%.
F. Research Methodology 1. Research Design
In this research, the researcher uses Classroom Action Research (CAR). There are some definitions of action research from experts. According to Pelton, “Action research is best seen as way you
“Action research is a form of inquiry that enables practitioners
everywhere to investigate and evaluate their work” (McNiff & Whitehead, 2006:7). It is used to evaluate the teachers‟ work and found the solution from every problem happened in the classroom. Therefore, the teachers could improve their ways to teach the students. According to Kemmis, McTaggart, & Nixon (2014:11), “Classroom action research typically involves the use of qualitative,
interpretative modes of enquiry and data collection by teachers (often with help from academic partners) with a view to teachers making judgments about how to improve their own practices.”
Kemmis, McTaggart & Nixon stated
This Lewinian view of action research and what, in earlier conditions of the Planner, we called “a spiral of cycle of self -reflection” or “the self-reflective spiral” over-simplified the process, and, we now think, gave too much significance to the individual steps of planning, acting, observing, reflecting, re-planning, (and so on) and their reiteration (Kemmis, McTaggart & Nixon, 2014:9).
Based on Kemmis and Mc Taggart as quoted in Burns (2010:8) the procedures of each cycle are as follows:
1. Planning
In this step, the activities are:
a. Preparing materials, making a lesson plan, and design the step in doing action
b. Preparing a list of students' name and scoring c. Preparing teaching-aids
d. Preparing sheets for students and teachers observation sheet e. Preparing a test for pre-test and post-test
2. Acting
b. Teaching material.
c. Giving chance for students to ask any difficulties. d. Giving post-test for students.
3. Observing
This phase involves the researcher in observing systematically the effects of the action and documenting the context, actions, and opinion of those involved. It is a data collection phase where you use open-eyed and open-minded tools to collect information about what is happening.
4. Reflecting
At this point, the researcher will reflect on, evaluate and describe the effects of the action in observation to make sense of what has happened and to understand the issue you have explored more clearly. The researcher may decide to do further cycles of action research to improve the situation even more, or to share a story of four researches with others as part of your ongoing to professional development.
The researcher will become the observer, and the practitioner will be the teacher of X-1.
2. Research Subject
The subject of this research is the students of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran. The researcher only focuses on the tenth grade. There are two classes of tenth grade, but the researcher uses X-1. There are 29 students in X-1.
Table 1. 1 the List of the Students in X-1
No Name
1 A. M. A.
2 A. Y. J.
3 C. M.
4 F. A.
5 I. H.
6 K. R. M.
7 M. H. I. L.
8 M. F. R.
9 M. I. S.
11 M. T.
12 M. I. A.
13 R. F. F.
14 W. H. A. I.
15 Y. A.
16 A. H. F.
17 A. R. Z. 18 A. A. H.
19 D. A. P. D.
20 I. N. A.
21 J. I. A.
22 L. F.
23 M. D.
24 M. F. A.
25 M. I. A.
26 M. S.
27 M. T. H.
29 S. I. M. K
3. Research Steps
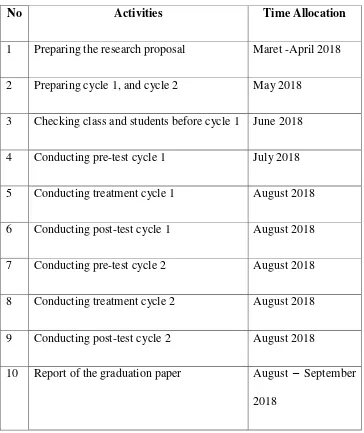
In conducting the research, the researcher carries out the steps which summarized in the following research schedule. The research schedule is shown below:
Table 1.2 Research Schedule
No Activities Time Allocation
1 Preparing the research proposal Maret -April 2018
2 Preparing cycle 1, and cycle 2 May 2018
3 Checking class and students before cycle 1 June 2018
4 Conducting pre-test cycle 1 July 2018
5 Conducting treatment cycle 1 August 2018
6 Conducting post-test cycle 1 August 2018
7 Conducting pre-test cycle 2 August 2018
8 Conducting treatment cycle 2 August 2018
9 Conducting post-test cycle 2 August 2018
4. Technique of Collecting Data and Research Instrument
To carry out the research, the researcher has several techniques of collecting data. The techniques of collecting data are test, observation, and documentation. The researcher uses test as the main method and observation to get data.
1. Test
The researcher uses test to assess the students‟ speaking skills.
Test is done by some purposes. One of the purpose is to know the students‟ speaking development. There are two tests, a pre-test and
a post-test. a) Pre-Test
Before conducting the cycle 1 and cycle 2, the researcher gives the pre-test for each cycle. The purpose is to know the speaking ability of the students before they get treatment in the cycle 1, and cycle 2. The research records the students‟ speaking. The researcher observes the pre-test
to get data analysis. b) Post-Test
2. Observation Kothari stated
The observation method is the most method especially in studies relating to behavioral sciences. In a way we all observe things around us, but this sort of observation is not scientific observation. Observation becomes a scientific tool and the method of data collection for the researcher, when it serves a formulated research purpose, is systematically planned and recorded and is subjected to checks and controls on validity and reliability (Kothari, 2004:96).
Therefore, in this research, the researcher observes the research using field note checklist. The researcher collaborates with the English teacher of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran. The researcher will become the observer. There are two kinds of field note checklist. Those are field note checklists for the teacher and the students.
Table 1.3 Teacher’s Field Note Checklist
No Teacher’s activities
1 Greeting students before the lesson begins
2 Praying before the lesson begins
3 Checking students‟ attendance
4 Reminding previous materials
5 Preparing and giving the materials
7 Giving explanation for the question
8 Guiding students‟ activity
9 Giving feedback after the lesson
10 Giving motivation for students
Table 1.4 Students’ Field Note Checklist No Students’ activities
1 Answer the teacher‟s greeting before the lesson begins
2 Praying before the lesson
3 Paying attention to the material delivered by the teacher
4 Giving question about the teacher
5 Working on group
6 Playing the game with rules
7 Taking conclusion from the lesson
3. Documentation
In this research, the researcher uses photo, recordings, and videos as the documentation of the research.
The researcher conducts the Classroom Action Research (CAR) in improving the students‟ speaking skills through snake and ladder
game and cooperative learning for the tenth grade students of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran. In analyzing the data, the researcher uses mixed method. It means that the research involve mixing of qualitative and quantitative data.The researcher would like to analyze the data using mixed method as follow:
1. Qualitative data
According to Creswell (2016:4) the qualitative data is a method for exploring and understanding the meanings that some individuals or groups of people attribute to problems of sociality or humanity. This research applies an inductive way of looking at the research, focusing on the meaning of the individual, and translating the complexity of a problem.
The most important data in the action research is the description behavior of the students. The analysis of qualitative data is taken from observation, test, and documentation.
2. Quantitative data
The procedure of the data analysis is done by analyzing the results of the test. According to Sudijono (2010:81-85) formula: a. Mean of Pre-test and Post-test
M=
Explanation:
M = Mean of the students‟ score
∑x = Sum of the students‟ score
N = Total number of the students b. Calculated mean difference
MD =
Explanation:
MD = Mean of difference
∑D = Total of difference between pre-test and post-test
N = Total number of the students c. Standard Deviation Calculation
SDD = √ ( )2
Explanation:
SDD= Standard Deviation
D = Difference Pre-test and Post-test N = Number of students
Explanation:
=Standard error of mean ef difference
= The difference of standard deviation
N = The total number of the students
e. Looking for to by using the following formula :
to =
to= t-value of observation MD = Mean of difference
SEMD= Standard error of mean difference
db. = N-1
G. Graduating Paper Organization
This research paper is divided into five chapters; each chapter has different elements as follows:
Chapter I is an introduction. It covers the background of the research, the problem of the research, the objective of the research, the benefits of the research, the hypothesis, the research methodology, and organization of graduating paper.
Chapter II describes theoretical framework which consists of supporting theories and previous researches. Supporting theories consists
1 D MD
SD SE
N
of a concept of snake and ladder game, concept of cooperative learning, and concept of speaking.
Chapter III discusses research implementation which consists of a description of teaching and learning in each cycle.
Chapter IV presents research findings and discussion. The first part is research findings which describes about the steps of each. The next part describes the discussion.
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Supporting Theories
1. Concept of Snake and Ladder Game a. Definition of Snake and Ladder Game
In Science and Technology Education book, “snakes and ladders is a popular game for children in many countries of the world. It is an ancient Indian board game regarded today as a worldwide classic game. It is easy to make from basic materials and can be adapted to suit many learning situations.”
According to Albab who adapted from Lowe (1988:27) that this game also “can assist in developing basic arithmetic such as
counting, addition and subtraction, communication, as well as the concept for which a game has been developed.”
Koninklijke (2012) stated that snake and ladder game is a game for 2 -5 players, who need to end their way around the board to get the finish.
According to Shitiq and Mahmud who adapted from Avedon (2003), “the snake and ladder game is believed to have
originated in 2nd century India. The game was developed by teachers and marked as a children game.”
b. The Rule of Snake and Ladder Game
1) Two, three, four or five people may play.
2) Each player throws the die or spins the spinner. The player who has the highest number starts the game by throwing the die and moving his/her counter, starting at space 1.
3) If a player scores a six, he/she throws the die or spins the spinner again.
4) If a counter stops on the head of snake the, player must side the counter down the snake until it gets to the tail. Then carries on from that point. If a counter lands at the foot of a ladder the player moves it to the top and carries on from there.
5) The first player to reach the square which has the highest number on it is the winner.
c. The application of Snake and Ladder Game
1) Teacher‟s Role
In this step, the teacher has to consider the strategies before presenting the game. There are four teacher‟s roles in playing
snake and ladder game. They are preparing the media, preparing the students, explaining learning skills, and managing the classroom.
by themselves. For example, the teacher can make board game from the big sheet of paper. The board should be large enough so all students can see. And the teacher can download from the internet directly and then print it or the teacher can draw by themselves.
The second important part in teacher‟s role is preparing the
students. The teacher has to prepare the students in order to make the students confidence to learn the material. Next, they also need to prepare the topic in general and activity in particular.
The following role of the teacher is explaining the skills in choosing the language item. The teacher has to explain briefly about what the students have to do. As facilitator, the teacher has to help the students to create the activity where the students do not only use the language, but also understand the reason of knowing something.
The last teacher‟s role in playing Snake and Ladder Game
is managing the classroom. The teacher has to make the students feel comfort in the classroom. After that the teacher guides the students to speak freely in the classroom.
Media is important tool to play it because media is the first impression for the students to be interested to the game. Preparing the students and explaining the skills are also important for the teacher. If the students can be conductive, and learning skills is explained well, the game will run well. Over all, teacher has to manage the classroom, classroom is not only about building, but also about the students and atmosphere. 2) Students‟ Role
The students have the role as active speakers. If the students are passive, the game will not run effectively. In this game, the students will work in group. Students will cooperate in their group to play the game. It is expected that students can practice English well during playing the game. If the students are active and obey the rules, the playing will be successful. 3) How to Play the Game
The teacher needs a large snake and ladder board and dice. The steps of the game are:
a) The students are divided by some groups and every group consists of 4-5 students.
c) To decide who goes first, each player must shake the dice. Who gets the highest number of the dice will be the first and continued by the next players.
d) Every square has its challenge, it is a picture. For example: When the player throws the dice and gets number 5, so the player moves to five squares. The player sees the picture which the player gets then describe the picture in the square.
e) When the player describes the picture, another player pays attention whether the player‟s description right or not based on the structure and grammatically.
f) Another player corrects if the player who is getting chance gets wrong.
g) If a counter stops on the head of snake the, player must side the counter down the snake until it gets to the tail. Then carries on from that point. If a counter lands at the foot of a ladder the player moves it to the top and carries on from there.
h) The first player who reaches the finish is the winner.
for children but it can be adabted to suit many learning situations. It means that snake and ladder game can be played in many levels depends on the necessary and consideration, such as this research that using snake and ladder game for senior high school students because of the learning material and the purpose.
2. Concept of Cooperative Learning a. Definition of Cooperative Learning
There are some definitions of cooperative learning from the experts, they are:
The first, according to Jolliffe (2007:3), cooperative learning requires pupils to work together in small groups to support each other to improve their own learning and that of others.
The second, according to Marr (1997), cooperative learning encourages mutual respect and learning among students with varying talents and abilities, languages, racial, ethnic background.
The third, according to Kristiawan (2013:86), cooperative learning is the key to deal with children with various abilities and diverse area of intelligences.
the lesson and this method grown students‟ ability to collaborate
and compare with others.
b. Key Elements of Cooperative Learning
Jolliffe (2007:3) stated that most researchers agree that to be truly cooperative learning should consist of key elements and two of these are particularly vital:
1) Positive Independence
This requires each pupil in a small group to contribute to the learning of the group. Pupils are required to work in a way so that each group member needs the others to complete the task. It is a feeling of „one for all and all for one‟.
2) Individual Accountability
This means that each member of the group is accountable for completing his or her part of the work. It is important that no one can „hitchhike‟ on the work of others. It requires each
pupil in the group to develop a sense of personal responsibility to learn and to help the rest of the group to learn.
is the key elements of cooperative learning which have not been mentioned:
1) Group Processing
Processing means giving pupils time and procedures to analyses how well their groups are functioning and using the necessary skills. This reflection ships among members. Feedback from the teacher and or students observers on how well they observed the groups working may help processing effectiveness.
2) Small-group and Interpersonal Skills
Pupils do not come to school with the social skills. They need to collaborate effectively with others, so teachers need to teach the appropriate communication, leadership, trust-building, decision-making, and conflict management skills to students and provide the motivation to use these skills in order for the groups to function effectively.
3) Face-to-face Interaction
discussion. Oral summarizing, giving and receiving explanations, and elaborating (relating what is being learned to previous learning) are important types of verbal interchanges.
c. Types of Cooperative Learning
Jolliffe (2007:43) stated that cooperative learning utilizes three types of cooperative learning, they are:
1) Formal Cooperative Learning
These last from on lesson to a few weeks and need to consist of the following to work effectively:
a) Team-building activities to establish team identify and cohesion
b) Specific teamwork skills highlighted each lesson and/or week
c) Teacher monitoring and support for task and teamwork skills
d) Evaluation of learning and teamwork by pupils and teacher. 2) Informal Cooperative Learning Group
These last from a few minutes to work a whole lesson and usually consist of „turn to your partner‟ discussion or
think/pair/share and can be extended from pairs to fours or eights.
These usually last for a term or a school year and consist of heterogeneous cooperative learning groups with stable membership to build on support and encouragement to each other. The elements described in formal cooperative learning groups above will need to be incorporated and built on.
3. Concept of Speaking a. Definition of Speaking
There are some definitions of speaking from the experts. According to Luoma, “speaking forms a part of the shared social
activity of talking” (Luoma, 2004:20). Byrne (1997:8) described “Oral communication is a two way process between speaker and
listener and involves the productive skill of speaking and receptive skill of listening.”
According to Noor Malihah (2010:88), speaking skill is an ability to orally express, opinion, thought, and feeling to other people both directly and indirectly. While. According to Setia Rini (2014:226), speaking is a skill that can be mastered through continuous practices, this can not be generated genetically.
According to Harmer (2001:269-271), there are two elements of speaking. They are language features and metal/social processing. He says on his book that the ability to speak fluently presupposes not only knowledge in language features, but also ability to process the information and language „on the spot‟.
1) Language features
According to Harmer (2001:269-270) sum up the necessary elements for spoken language are:
The first is connected speech. Connected speech means effective speakers of English need to able to produce the individual phonemes of English. In connected speech sound are modified (assimilation), omitted (elision), and added (linking). It is for this reason that we should involve students in activities designed specifically to improve their connected speech.
The second is expressive devices. It is about the native speakers of English change the pitch and stress of particular part of utterance, vary volume and speed, show by their physical and non-verbal means how they are feeling.
The last is negotiation language. In spoken, people also have to negotiate to make effective speaking. People use to seek clarification and show the structure of what are saying.
From those four elements, the students can use all elements to speak among the students. All of them are important to be applied in conversation. The conversation is not complete if students only use one element of language features. For example, the students only use right lexis and grammar in conversation without considering expressive device. The conversation will be flat and the listener will not interest to continue the conversation.
2) Mental or social processing
Mental or social processing according to Harmer (2001:271) is about the speaker‟s productive ability involves the knowledge
of language skills and dependent upon the rapid processing skills that talking necessitates. There are three types of mental or social processing, they are:
propositionally appropriate sequences. The purpose is to help the students develop habits of rapid language processing in English.
The second is interacting with others: most speaking involves interaction with one or more participants. The effective speaking also involves a good deal of listening, an understanding of how the other participants are feeling, and a knowledge of how linguistically to take turns or allow others to do.
The third is information processing: the speakers need to be able to process the information they tell to the listeners.
c. Kind of Speaking Activity
Harmer (2001:271) stated “Many of classroom speaking activities which are currently in use fall at or near the communicative end of the communication continuum.” Harmer
(2001:271-275) explained that there are seven speaking activities in the classroom, but in this research, the researcher takes only two speaking activities. The first is communication games and the second is discussion.
1) Communication Games
“Games which are designed to provoke communication
picture, or things in the right order, or find similarities and differences between pictures (Harmer, 2001:272).”
Games are one of the effective and fun ways to be applied in teaching and learning process. By playing games, the students feel challenging.
2) Discussion
“One of the best ways of encouraging discussion is to
provide activities which force students to reach a decision or a consensus, often as a result of choosing between specific alternatives (Harmer, 2001:273).”
One of the reasons why discussion fail is that students are reluctant to give an opinion in front of the class. Having group discussion has good role for the students, in the group, students can decrease their anxiety and increase their confidence in front of the group. So they dare to speak in front of the class.
B. Previous Researches
students‟ writing pre-test, post-test and observation checklist analysis. The
result of the calculation showed that students taught by using Snake and Ladder Game had higher achievement than those who were taught without Snake and Ladder Game.
The second previous research was from Hajriyani. Her research was about “the effectiveness of cooperative learning in improving students‟ skill in writing recount text. She concluded that based on the
research toward the comparative research of students‟ writing skill in recount text between experiment class and control class at the tenth grade of SMAN 1 Beruntung Baru is the students‟ written test score, the writing
mastery of control class is in very good category.
The third previous research was from Hanifah. Her research was about improving students‟ speaking skills through story telling using
puppet. She concluded that using puppets could help the students mastering English skills and also develop their vocabulary to arrange the sentences. As differentiation, the researcher used pictures. So, the students could produce sentences into a conversation. This step was useful to increase students‟ speaking skills.
From the first previous research, the researcher found the similarity and difference from this research. Both of the researches used snake and ladder game, but Albaniyah‟s paper focused on the implementation of
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH IMPLEMENTATION
A. Procedures of the Research in Cycle I
The researcher collaborated with the English teacher of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran. The researcher planned the cycle and consulted with the teacher. The researcher became the observer and the teacher taught the class. The research planned cycle as below:
1. Cycle 1 a. Planning
In planning stage, the researcher planned what action would be done. The activities in the planning were presented as below:
1) Preparing syllabus about descriptive text, lesson plan, rubric, material, and media.
2) Preparing the students attendance list, and the students‟ scoring list.
3) Preparing the teacher‟s and the students‟ field note checklist.
4) Preparing tools of learning in the class. 5) Preparing pre-test and post-test.
7) Preparing the camera to take the picture and videos. The media which was used in this research such as PowerPoint Presentation, picture, and board game. The preparation was prepared in order to reach the purpose of teaching and learning process.
b. Acting
In acting stage, the teacher did the planning which was presented as below:
1) Presenting the PowerPoint Presentation about descriptive text.
2) Giving opportunity for the students to give question about the material.
3) Giving opportunity for the students to work individually.
4) Explaining about rules of playing snake and ladder game.
5) Giving opportunity for the students to play the game. 6) Giving feedback, reinforcement, and motivation for the
students. c. Observing
researcher collected the score of the students. The researcher used field note checklist to observe the teacher and the students. The field note checklist of the teacher‟s activity was listed below:
1) Greeting students before the lesson begins 2) Praying before the lesson begins
3) Checking students‟ attendance 4) Reminding previous materials 5) Preparing and giving the materials 6) Giving opportunity for asking 7) Giving explanation for the question 8) Guiding students‟ activity
9) Giving feedback after the lesson 10)Giving motivation for students
The field note checklist of the students‟ activities were
listed below:
1) Answer the teacher‟s greeting before the lesson begins
2) Praying before the lesson
3) Paying attention to the material delivered by the teacher
6) Playing the game with rules 7) Taking conclusion from the lesson d. Reflecting
The teacher reflected the lesson plan that was arranged by the researcher. The researcher evaluated how the teacher taught the students, and calculated score of the students. If the score of the students were less than the passing grade (KKM), the researcher would conduct the next cycle. B. Procedures of the Researchin Cycle 2
This cycle would be conducted if cycle 1 could not achieve the passing grade. As like in cycle 1, in cycle 2 the researcher became the observer and the teacher taught the class. The research planned cycle as below:
a. Planning
In planning stage of cycle 2, the researcher planned several activities. The activities in the planning were presented as below:
1) Preparing syllabus about descriptive text, lesson plan, rubric, material, and media.
2) Preparing the students attendance list, and the students‟ scoring list.
4) Preparing tools of learning in the class. 5) Preparing pre-test and post-test.
6) Preparing the mobile phone to record the speaking. 7) Preparing the camera to take the picture and videos.
The media which was used in this research such as PowerPoint Presentation, picture, and board game. The preparation was prepared in order to reach the purpose of teaching and learning process.
b. Acting
In acting stage of cycle 2, the teacher did the planning which was presented as below:
1) Presenting the PowerPoint Presentation about descriptive text.
2) Giving opportunity for the students to give question about the material.
3) Giving opportunity for the students to work individually.
4) Explaining about rules of playing snake and ladder game.
5) Giving opportunity for the students to play the game. 6) Giving feedback, reinforcement, and motivation for the
The researcher observed the teacher how the teacher taught the students. The researcher also observed the students, and it started from pre-test until post-test. The researcher collected the score of the students. The
researcher used field note checklist to observe the teacher and the students. The field note checklist of the teacher‟s activities were listed below:
1) Greeting students before the lesson begins 2) Praying before the lesson begins
3) Checking students‟ attendance 4) Reminding previous materials 5) Preparing and giving the materials 6) Giving opportunity for asking 7) Giving explanation for the question 8) Guiding students‟ activity
9) Giving feedback after the lesson 10)Giving motivation for students
The field note checklist of the students‟ activities were listed below:
1) Answer the teacher‟s greeting before the lesson begins 2) Praying before the lesson
5) Working on group
6) Playing the game with rules 8) Taking conclusion from the lesson d. Reflecting
The teacher reflected the lesson plan that was arranged by the researcher. The researcher evaluated how the teacher taught the students, and calculated score of the students. The researcher evaluated the result of cycle 1 and cycle 2. After conducting the cycle 2, researcher also expected 85% students could pass the passing grade (KKM). When the result of cycle 2 was less than 85%, the researcher would conduct cycle 3.
C. The Minimal Standard of Successful
The students‟ success and failure in doing the activities planned
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
A. Research Findings
This research consisted of two cycles, which each cycle consisted of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. The whole steps of this research were described below:
1. Cycle 1 a. Planning
In this cycle, the researcher planned some activities such as: 1) Preparing the syllabus about describing tourism place, lesson
plan, rubric, material, and media.
2) Preparing students‟ attendance list and scoring list. 3) Preparing students‟ and teacher‟s field note checklist. 4) Preparing tools for learning.
5) Preparing pre-test and post-test.
b. Implementation of the Action
The cycle 1 was conducted on July 21st, 2018. The cycle 1 was divided into three parts. The first was pre-test which was conducted on July 21st, 2018. The pre-test was about describing tourism place.
In the pre-test, the teacher gave every student a minute for preparation and two minutes for speaking, so the expectation was every student had three minutes. But in reality, the students could spend a minute on preparation and one to one and a half minute for speaking.
During pre-test, many students got the same difficulties such as grammar, pronunciation, and filler. When conducting the pre-test, the researcher found students saying, “it have...”. The correct one was "it has". The students did not understand the difference between "have and has" for a singular subject. The researcher also found students saying “there is six tower”, and the
correct one was “there are six towers”. The students also had not understood about plurality and singularity.
Besides grammar, the students also got some pronunciation errors. For example, in the word mosque, the correct phonetic symbol is /mask/. But, the students pronounced what it is, “/mosque/”. The next difficulty which students got was filler.
a....a...a.. or they combined with Bahasa such as “the mosque di kelilingi (is surrounded ) many trees”.
The second part is treatment. It was conducted on Wednesday, August 1st, 2018. In this part, the teacher came to the class and started greeting the students and asked about the students‟ condition, “How are you to day?”, then, the students
answered, “I am fine”. But the students did not give feedback by questioning the teacher's condition. The teacher tried to stimulate the students to ask about the teacher‟s condition by saying, “Why
don’t you give me feedback by asking “what about you, Miss?”,
then the students asked,“What about you, miss”, “I am fine, thank
you”the teacher said.
Next, the teacher opened the class, after opening the class the teacher forgot to check the students‟ attendant list. Because it
was the second meeting for the students and the previous was the first meeting which was about an introduction, so the teacher did not remind the previous lesson.
responded, “Good! And how does it look like?”, he said, “It is scary, Miss.”
After that, the teacher explained the descriptive text included definition, generic structure, and its characteristics. In explaining the characteristics of descriptive text, the teacher explained the mistakes which students made in pre-tests such as grammar and pronunciation. In addition, the teacher made sure of students‟ understanding by asking the students‟ one by one. The
following activity was the teacher showed an example of descriptive text and had students read and translate together. After translating, the teacher divided the students to be four groups then showing a picture which the students had to discuss and describe cooperatively.
In addition, the next activity was playing the snake and ladder game. The teacher explained the rule of playing this game then the teacher had students play. The students really enjoyed playing the game. After playing the game. The teacher gave feedback about the mistakes the students did by saying, “When
Jundi said that Monas is locate in Jakarta is not correct and the correct one is "Monas is located in Jakarta". Then, the teacher closed the class.
described Masjid Agung Jawa Tengah. As like in pre-test that every student got a minute for preparation before starting to speak. The students did better for the post-test, so the students had an improvement. In the pre-test, the students could spend one to one and a half for speaking, but in post-test, the students could spend one and a half to two minutes even more.
In the pre-test, the many students said, "It have", and the students said, "it has" in post-test; in the pre-test, the students said, "there is six tower", and the students said, "there are six towers" in post-test. Most of the students had tried to use correct grammar, pronunciation, and proper vocabulary and decreased the filler, but the teacher still found some mistakes which students made such as some students still said mosque, it have etc.
c. Observation
Observer observed the process of teaching and learning in the class. The observer observed not only the teacher but also the students by using a field note checklist.
The field note checklists of the teacher‟s activities were listed
below:
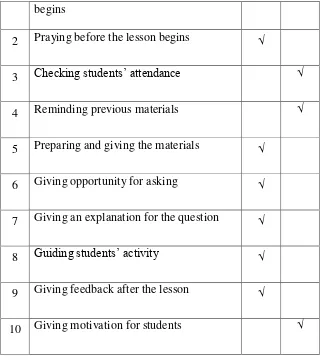
Table 4.1 Teacher’s Field Note Checklist of Cycle 1
No Teacher’s Activities Yes No
begins
2 Praying before the lesson begins √
3 Checking students‟ attendance √
4 Reminding previous materials √
5 Preparing and giving the materials √
6 Giving opportunity for asking √
7 Giving an explanation for the question √
8 Guiding students‟ activity √
9 Giving feedback after the lesson √
10 Giving motivation for students √
In the cycle 1, the teacher forgot to check the students‟
attendance list and give motivation for the students.
The field note checklists of the students‟ activities were listed
below:
Table 4.2 Students’ Field Note Checklist of Cycle 1
No Students’ activities Yes No
1 Answer the teacher‟s greeting before the
lesson begins
2 Praying before the lesson √
3 Paying attention to the material delivered by the teacher
√
4 Giving question about the material √
5 Working on group √
6 Playing the game with rules √
7 Taking conclusion from the lesson √
d. Reflection
After analyzing the result of cycle 1, the researcher inferred that there was an improvement in students' score. It could be seen from the average score between pre-test and post-test. But in this cycle, the researcher still found many students who still did mistakes.
The target of the passing grade was 85%, but only 44% of the students could reach the target, it showed that there were still many students who did not pass. Seeing the result, the researcher would conduct the cycle 2 to reach the target of the passing grade. 2. Cycle 2
In this cycle, the researcher planned some activities such as: 1) Preparing a syllabus about describing tourism place, lesson plan,
rubric, material, and media.
2) Preparing students‟ attendance list and scoring list. 3) Preparing students‟ and teacher‟s field note checklist. 4) Preparing tools for learning.
5) Preparing pre-test and post-test.
In the second meeting, its material was about describing a person. The media which was used in this research such as PowerPoint Presentation, and board game. All preparations were prepared to reach the purpose of teaching and learning process. b. Implementation of the Action
The cycle 2 was conducted on August 3rd, 2018. The cycle 2 was divided into three parts. The first was the pre-test which was conducted on August 3rd, 2018. The pre-test was about describing a person.
During the pre-test, many students got the same difficulty such as grammar, pronunciation, and filler. When conducting the pre-test, the researcher found a few students still saying, “he have...”. The correct one was “he has”. There were three students said “I will to describe”, the correct one was “I will describe”.
Many students pronounced the word “Brown” by “/bron/”, and the
correct one is “/braun/”. The next difficulty in cycle 2 which
students got was filler. The researcher still found some students a....a...a.. But in cycle 2, the mistake was lesser than in cycle 1.
The second part is treatment. It was conducted on Wednesday, August 8th, 2018. In this part, the teacher came to the class and started greeting the students and asked about the students‟ condition. Then, the students answered the teacher's
question, then the student s gave feedback by questioning the teacher's condition. Next, the teacher opened the class, after opening the class the teacher checked the students‟ attendant list. The following activity was the teacher reminded the previous lesson.
continued to ask, “What is his name?”, the students said, “Cristiano Ronaldo”. “Have you ever met him?” teacher asked, then the students siad, “No, never”. “So, who is your favorite football player?” the teacher asked again, some students answered such as Radian, he answered, “Moh. Salih”, and Catur, he said, “Messi”. The teacher keep stimulating the students to speak by asking,“Who says Moh. Salih as your favorite football player? And why?”, then Radian raised his hand and said,“Because he is a Moslem, he is religious”, and Hilmi intrupted by saying,“Because, good skill”, and the teacher said,“Yes, he has good skill”.
After that, the teacher showed a picture. Then, the teacher asked students to read together, after that the teacher called students one by one to translate one sentence by one sentence. The next, the teacher explained descriptive text such as a generic structure and its characteristics based on the reading text.
The teacher explained the mistakes which students made in pre-tests such as grammar and pronunciation. And the teacher made sure of students‟ understanding by asking the students one by
one. The following activity was the teacher gave an individual task for every student, after that the teacher showed a picture and asked the students to discuss and describe cooperatively in a group.
teacher had students play. The students really enjoyed playing the game. After playing the game. The teacher gave feedback by saying, “Last time, there were some students saying that he is beautiful and the correct one is she is beautiful, the correct one is his name is Sule, not his name Sule, the correct one is he is an
comedian, not he is pelawak ” and then, the teacher closed the
class.
And the last part in this cycle was post-test. It was conducted on Thursday, August 9th, 2018. In this part. The students described Joko Widodo. The students did better for the post-test, so the students had an improvement. Because most of the students could describe the picture for two minutes to four minutes.
In pre-test, the students said, “he have”, and the students said, “he has” in post-test; in pre-test, the students said, “bron”, and the students said, “braun” in post-test; in pre-test, the students said, “I will to describe”, and the students said, “I will describe”. Most
of the students had tried to use correct grammar, pronunciation, and proper vocabulary and decreased the filler, but the teacher still found some mistakes which students made such as some students still said, “He wear”, and the correct one is “He wears”.
Observer observed the process of teaching and learning in the class. The observer observed not only the teacher but also the teacher by using field note checklist.
The field note checklists of the teacher‟s activities were listed
below:
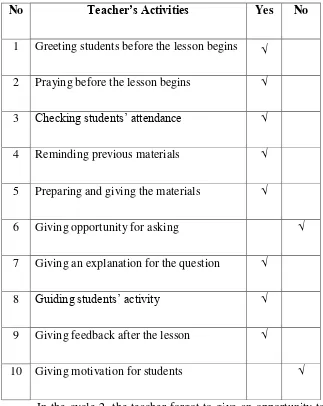
Table 4.3 Teacher’s Field Note Checklist of Cycle 2
No Teacher’s Activities Yes No
1 Greeting students before the lesson begins √
2 Praying before the lesson begins √
3 Checking students‟ attendance √
4 Reminding previous materials √
5 Preparing and giving the materials √
6 Giving opportunity for asking √
7 Giving an explanation for the question √
8 Guiding students‟ activity √
9 Giving feedback after the lesson √
10 Giving motivation for students √
The field note checklists of the students' activities were listed below:
Table 4.4 Students’ Field Note Checklist of Cycle 2
No Students’ activities Yes No
1 Answer the teacher‟s greeting before the
lesson begins
√
2 Praying before the lesson √
3 Paying attention to the material delivered by the teacher
√
4 Giving a question about the material √
5 Working on group √
6 Playing the game with rules √
7 Taking conclusion from the lesson √
d. Reflection
In the learning process, the teacher missed some activities such as not giving the opportunity for students to ask, but some students were active, the students asked questions before the teacher offered, and not giving motivation to the students. So when all activities were done, the teacher closed the class directly.
The passing grade was 70, and the target was 85%. And 88% of the students could reach the target. It showed that most of the students could pass the passing grade. Therefore, the students achieved the target of the passing grade, so the researcher stopped the research until cycle 2.
B. Discussion
The researcher collected the data of cycle 1 and cycle 2 from the students. They consisted of 29 students from X-1 of MA Nurul Islam Tengaran. The researcher only took data from 25 students because 4 students did not attend the class completely.
In scoring pre-test and post-test of the students, the researcher used rubric which was adapted from Oller (1979). Rating of the speaking scale was described below:
Table 4.5 Scoring Rubric of Speaking
No Competency Description Scores
accent make understanding difficult, require frequent repetition
3. “Foreign accent” requires concentrated listening and mispronunciation lead to occasional misunderstanding and apparent errors in grammar or vocabulary
3
4. Marked “foreign accent” and occasional
mispronunciations which do not interfere with understanding
4
5. No conspicuous mispronunciations, but would not be taken for a native speaker
5
6. Native pronunciation, which no trace of
“foreign accent” 6
2 Grammar 1. Grammar almost entirely inaccurate
except in stock phrases
1
2. Constant errors showing control of view major patterns and frequently preventing communication
2
3. Frequent errors showing some major patterns uncontrolled and causing occasional irritation and misunder-standing
4. Occasional errors showing imperfect control of some patterns but no weakness that causing misunderstanding
4
5. Few errors, with no patterns of failure 5 6. No more than two errors during the
interview
6
3 Vocabulary 1. Vocabulary inadequate for even the simplest conversation
1
2. Vocabulary limited to basic personal and
survival areas (time, food,
transportation, family)
2
3. Choice of words sometimes inaccurate, limitation of vocabulary prevent
discussion of some common
professional and social topics
3
4. Professional vocabulary adequate to discuss special interest; general vocabulary permits discussion of any non-technical subject with some circumlocutions.
4
5. Professional vocabulary broad and price; general vocabulary adequate to copy with complex practical problems and
varied social situation
6. Vocabulary apparently as accurate and extensive as that of an educated native speaker
6
4 Fluency 1. Speech is so halting and fragmentary that conversation is virtually impossible
1
2. Speech is very slowly and uneven expect for short or routine sentences
2
3. Speech is frequently hesitant and jerky; sentences may be left uncompleted
3
4. Speech is occasionally hesitant, with some unevenness caused by rephrasing and grouping for words
4
5. Speech is effortless and smooth, but perceptibly non-native in speed and evenness
5
topic; requires constant repetition and rephrasing
3. Understand carefully, somewhat simpli-fyied speech directed to him, with considerable repetition and rephrasing
3
4. Understands quite well normal educated speech directed to him, but requires occasional repetition and rephrasing
4
5. Understand everything in normal educated conversation except for every colloquial or low-frequency items, or exceptionally rapid or slurred speech
5
6. Understands everything in both formal and colloquial speech to be expected of an educated native speaker
6
From the rubric above, the researcher got the score of students‟
pre-test and post-test in cycle 1 and cycle 2 which were described below:
1. Cycle 1
In cycle 1, the researcher calculated the pre-test, post-test, mean, standard deviation, and t-test.
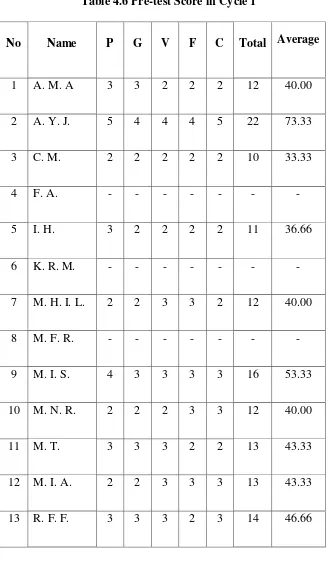
The score was from pronunciation (P), grammar (G), vocabulary (V), fluency (F), and comprehension (C). The researcher calculated the total and the average score.
Table 4.6 Pre-test Score in Cycle 1
No Name P G V F C Total Average
1 A. M. A 3 3 2 2 2 12 40.00
2 A. Y. J. 5 4 4 4 5 22 73.33
3 C. M. 2 2 2 2 2 10 33.33
4 F. A. - - - -
5 I. H. 3 2 2 2 2 11 36.66
6 K. R. M. - - - -
7 M. H. I. L. 2 2 3 3 2 12 40.00
8 M. F. R. - - - -
9 M. I. S. 4 3 3 3 3 16 53.33
10 M. N. R. 2 2 2 3 3 12 40.00
11 M. T. 3 3 3 2 2 13 43.33
12 M. I. A. 2 2 3 3 3 13 43.33
14 W. H. A. I. 3 3 3 3 2 14 46.66
15 Y. A. 4 3 3 4 4 18 60.00
16 A. H. F. 3 3 4 3 3 16 53.33
17 B. R. Z. 4 4 4 5 4 21 70.00
18 A. A. H. 5 4 5 5 5 24 80.00
19 D. A. P. D. 2 3 2 2 2 11 36.66
20 I. N. A. 3 3 3 3 3 15 50.00
21 J. I. A. 3 3 3 3 4 16 53.33
22 L. F. - - - -
23 M. D. 2 2 3 3 3 14 46.66
24 M. F. A. 4 3 3 3 4 17 56.66
25 M. I. A. 2 2 2 2 2 10 33.33
26 M. S. 4 3 3 3 4 17 56.66
27 M. T. H. 4 3 3 4 4 18 60.00
28 R. I. 3 2 2 3 3 13 43.33
From the individual student‟s average score of pre-test in
cycle 1, the researcher could calculate the grade of the students who could pass the passing grade.
Table 4.7 Grade of Pre-test Passing Grade in Cycle 1
Criteria Grade Presentation
>70 2 8%
70 1 4%
<70 22 88%
Total 25 100%
From the data, the researcher could conclude that the students who could pass the passing grade were just two students. b. Post-test
The score was from pronunciation (P), grammar (G), vocabulary (V), fluency (F), and comprehension (C). The researcher calculated the total and the average score.