Lessu, Deasy Natalia. 2017. The Ideologies of Anti-Authoritarianism and Social Movement in Anti-Flag’s Protest Song Lyrics: A Critical Discourse Analysis, Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Music especially punk rock is ideological. It has a basic belief about DIY (Do-It-Yourself) which presents their subculture (counterculture). It sets themselves as the outer group of the society. The belief of DIY sets the punk rock to life in liberty. Thus, they have tendency to rebel against authority. They see the traditional culture; the submissiveness of society to the power holders as the significant issue that need to be resisted. Thus, the song lyrics are not merely showing protest but the calling to do revolution as well. Through their music, specifically song lyrics, they act as the speaker to persuade the listeners. In the purpose of gaining up the critical awareness of the listeners about the role of punk rock music in carrying the protest about the social issues, the study will conducted by using Critical Discourse Analysis (CDA).
The study has aim to answer two research questions. The first question is How the linguistic features employed in Anti-Flag‘s protest song lyrics reveal the ideology? While the second question is What are the main ideologies conveyed in Anti-Flag’s protest song lyrics?
The study is about CDA, thus, the study will be guided by the framework of CDA. It helps to present concept about the ideology, how the ideology works in discourse and how the ideology constructs power. To discover the existence of ideology in the discourse, - the text, the concepts of the ideology, the special terms describe the ideology and the social issues which support the actuality of the ideology will be used. To do the analysis of the linguistic representation, the Systemic Functional Grammar will be applied. It represents the ideology through the linguistic units such as transitivity analysis, modality analysis and pronoun analysis.
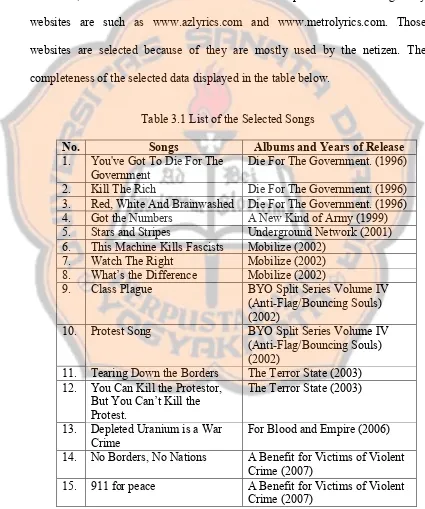
The data derives from the Anti-Flag song lyrics. It is as much as 15 song lyrics. This punk rock band is considerably consistent and committed in sounding protest about the social issues. The data used are for analyzing first questions attained from the lexical items used in the song lyrics and the literature data to support the concept and the social issues of the ideology. The data used for the second questions taken from the clauses in the song lyrics. It is done by the analysis of transitivity to present the frequent process which represents the ideology and the modals and pronouns analysis to present speaker’s intention and judgments about the ideology.
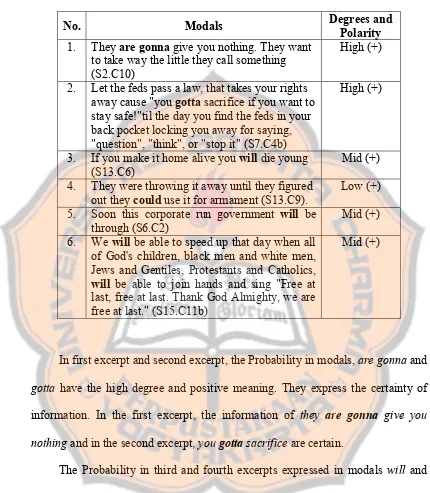
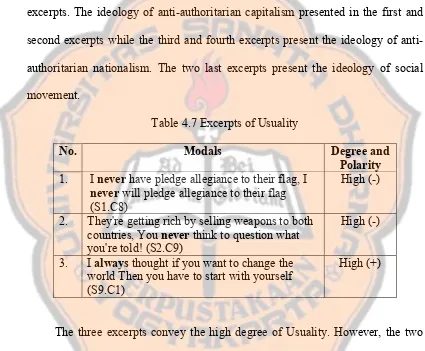
frequent type. The probability and obligation appears mostly in anti-authoritarianism. They indicate the certainty and probability and the obligation of the authority works. The ability appears in social movement expresses the skill of doing the revolution. About the pronoun analysis, the anti-authoritarianism mostly appears in pronoun you and they. It means that Anti-Flag is as the part of punk subculture persuade (and protest as well) society and protest government. It sets position of Anti-Flag as the out-group; not belong to society. The social movement mostly carries we as the pronoun. It means that Anti-Flag is in-group with society to do the movement.
It is recommended for the future researchers to conduct similar study on song lyrics, especially the punk rock music to enrich and raise their critical awareness of the use music as the protest medium. It is also recommended to explore more on the textual analysis especially theme-rheme since the usage of the theory might cause different interpretation.
Lessu, Deasy Natalia. 2017. The Ideologies of Anti-Authoritarianism and Social Movement in Anti-Flag’s Protest Song Lyrics: A Critical Discourse Analysis, Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Musik khususnya punk rock memiliki ideologi. Punk memilik prinsip dasar yaitu DIY (Do-It-Yourself) yang merepresentasikan cara hidup mereka, kebiasaan dan ide-ide dari kelompok mereka sebagai kelompok yang berbeda dari kelompok masayarakat pada umumnya. Prinsip DIY mengatur para anggota punk untuk hidup dalam kebebasan. Oleh karena itu, mereka mempunyai kecenderungan untuk melawan kekuasaan. Mereka memandang budaya yang telah menjadi tradisi dalam masyarakat seperti penundukan masyarakat terhadap para penguasa sebagai isu penting yang harus dilawan. Untuk itu, lirik-lirik lagu mereka tidak sekedar menyatakan protes tetapi juga mengajak untuk melalukan revolusi. Melalui musik, khususnya lirik lagu, mereka berperan untuk melakukan propaganda kepada penikmat musik secara khusus dan secara umum kepda masyarakat. Dalam rangka meningkatkan critical awareness dari para penikmat musi tentang peran musik punk rock sebagai pembawa pesan tentang isu sosial, penelitian ini akan dilakukan dengan mengimplementasikan Critical Discourse Analysis (CDA).
Penelitian ini bertujuan utnuk memberi solusi terhadap dua pertanyaan. Pertanyaan pertama Bagaimana unsur-unsur linguistik di dalam lirik-lirik lagu protes Anti-Flag mengungkapkan ideologi? Sementara pertanyaan kedua adalah Apa ideologi-ideologi utama yang diusung Anti-Flag dalam lirik lagu protes mereka?
Penelitian in adalah tentang analisa wacana kritis (CDA) dengan demikian penelitian ini akan mengikuti kerangka teori CDA. Teori ini membantu memberikan konsep tentang ideologi, kaitan ideologi dengan wacana dan bagaimana ideologi memiliki power. Untuk menemukan keberadaan ideologi di dalam teks, konsep tentang ideologi-ideologi utama, isitilah-istilah yang terkait dengan ideologi-ideologi tersebut serta isu-isu social yang mencerminkan aktualisasi dari ideologi-ideologi tersebut akan dibahas. Untuk menganalisa representasi linguistik, Systemic Functional Grammar dipakai. Teori ini menunjukkan representasi ideologi melalu analisa transitivity, modality dan pronoun.
pembicara (Anti-Flag) tentang ideologi-ideologi yang dibahas.
Dari analisa, ditemukan dua ideologi utama yang diusung oleh Anti-Flag adalah Anti-authoritarianism dan Social Movement. Anti-authoritarianism dibedakan kedalam Anti-authoritarian Capitalism dan Anti-authoritarian Nationalism. Hasil dari analisa transitivitymenunjukkan kedua ideologi dibentuk dengan material processes dan relational processes. Proses pertama menunjukan aksi dari actor sementara proses kedua menunjukan identitas dan karakter dari actor. Dari analisa modality ditemukan bahwa probability, obligation dan ability. muncul sebagai modals meaningyang dominan. Probabilitydan obligation sering muncul di ideologi anti-authoritarianism. Ini menunjukkan kepastian dan kepatuhan tentang dan terhadap pekerjaan para penguasa. Abilitysering muncul di ideologi social movement menunjukkan kekuatan dan kemampuan Anti-flag dan masyarakat untuk melakukan perubahan. Dari analisa pronoun ditemukan bahwa pronoun you dan they banyak muncul di idelogi Anti-authoritarianism. Hal ini berarti Anti-Flag berada di out-group yang memungkinkannya melakukan protes kepada pemerintah dan masyarakat. Pronoun we banyak ditemukan di ideologi social movement. Hal ini memposisikan Anti-Flag di in-group. Bersama-sama dengan masyarakat, Anti-Flagmemberi perlawanan terhadap para penguasa.
Untuk penelitian ke depan, direkomendasikan untuk melakukan penelitian yang sama pada lirik lagu, terlebih khusus lirik lagu punk rock untuk meningkatkan critical awareness terhadap penggunaan musik sebagai media protes. Selain itu direkomendasikan juga untuk mengeksplorasi textual analysis khususnya pada theme-rheme sebab penerapan teori yang berbeda dapat menghasilkan interpretasi yang berbeda pula.
i
MOVEMENT IN ANTI-FLAG’S PROTEST SONG LYRICS: A CRITICAL DISCOURSE ANALYSIS
A THESIS
Presented to the Graduate Program in English Language Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree of Magister Humaniora (M.Hum.) in English Language Studies
by
Deasy Natalia Lessu
Student Number: 116332032
THE GRADUATE PROGRAM IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE STUDIES
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
vi
In the very beginning, I would like to glorify my Awesome Lord, Jesus
Christ who started with me, worked with me and finished this thesis with me.
I would also like to reveal my biggest honor and thanks to those who have
helped me to accomplish this thesis.
BapakDr. B. B. Dwijatmoko, M.A. as my linguistics lecturers and my thesis
advisor for his patience, kindness, ideas, helps and supports.
Bapak Dr. G. Budi Subanar, S.J as the Graduate Program Director of Sanata
Dharma University. Bapak Paulus Sarwoto, Ph.D. as the Head of the
Graduate Program in ELS.
Bapak FX. Mukarto, Ph. D., Bapak Dr. E. Sunarto, M.Hum. and Bapak
Paulus Sarwoto, Ph.D. as my thesis examiners for their questions, ideas,
advices, inputs and revision since my thesis review until my thesis defence.
The lecturers in English linguistics of Graduate Program; Bapak Dr. Fr. B.
Alip, M.Pd., Bapak Prof. Dr. Soepomo Poedjosoedarmo, Bapak Dr. B. B.
Dwijatmoko, M.A., Bapak Barli Bram M.Ed., Ph.D. for the lecturers, the
knowledges, the ideas, the wisdom, the attitudes, the happiness and the laugh
you have shared with me.
Lectures in the Graduate Program, Ibu Dra. Novita Dewi, M.S., M.A
(Hons.)., BapakDr. J. Bismoko and all lecturers I cannot mention. My special
thanks for BapakDr. F.X. Siswadi, M.A. for his sharing and supports.
GondeszRuslinah a.k.aInul as my soulmate, my classmate and my supporter.
vii the end of our study.
My Gradute Program classmates, Mbak Fransisca, Mbak Ayu, Nitha,
Rindang, Ika Daru, Mas Windu, Mbak Sri, Mas Yanu, Fendy, Pak Ahsan
Mbak Susie and Satrio, Mbak Fahma, Diah, Christo and also my senior, Usi
Ariyana Pattiwael. Thank you for all we have been through together.
Graduate Studies’ staffs, Mbak Lely, Mbak Marni, Mbak Dita and Pak Mul.
Thank you for the helps and supports.
My family, Papa Ot and Mama Mery, my sisters, Jeane and Injili, my
brother, Mario, my cousin, Natalia and my extended family. Thank you for
being patient, praying, loving, blessing and supporting. Especially for my
papaand mama, thank you so much for believing me.
My brother and sisters of GKB Jubilee, especially, Breakthrough cell-group.
Special to Kak Yopie and Kak Helen. Thank you for all the blessing you have
shared with me.
My spiritual family, Chosen Generation Ministry in Ambon. Thank you for
the supports and prayers
My lecturers and friends of English Department, Pattimura University
Ambon. Thank you for the supports and carings.
Other people such as my best friend, Niko Harefa for his kindness and
viii “FAITH”
And being not weak in faith, she considered not her own body now dead, ... she staggered not at the promise of God through unbelief; but was strong in faith, giving glory to God; And being fully persuaded that, what God had promised, God was able also to perform.
21---ix
TITLE PAGE ... i
ADVISOR’S APPROVAL PAGE ... ii
DEFENSE APPROVAL PAGE ... iii
STATEMENT OF ORIGINALITY ... iv
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT... vi
1.1 Background of the Study... 1
1.2 Problem Formulation ... 6
1.3 Objectives of Study ... 6
1.4 Benefits of the Study... 8
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW... 10
2.1 Review of theories... 10
2.1.1 Ideology ... 10
2.1.1.1 Ideology and Discourse ... 14
2.1.1.2 Ideology and Power ... 15
2.1.1.3 Ideology of Punk ... 17
2.1.2 Critical Discourse Analysis... 19
2.1.3 Systemic Functional Grammar ... 22
2.1.3.1 Ideational Function and Meaning ... 23
2.1.3.2 Interpersonal Function and Meaning... 29
2.1.4 Protest Music ... 32
2.2 Review of Related Studies ... 34
2.3 Theoretical Framework ... 37
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY... 39
3.1 Type of study ... 39
3.2 Data of the Study... 40
3.3 Data Analysis Procedures ... 43
CHAPTER 4 ANALYSIS RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ... 48
4.1 Linguistic Features use in Anti Flag Protest Song Lyrics... 49
x
4.1.1.2 Modality Analysis ... 66
4.1.1.3 Pronoun Analysis... 74
4.1.2 The Lexical Features... 78
4.2 Ideologies in Anti Flag’s Protest Song Lyrics. ... 85
4.2.1 Concept of the Ideologies ... 86
4.2.1.1 The Concept of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism ... 87
4.2.1.2 The Concept of Anti-Authoritarian Nationalism... 88
4.2.1.3 The Concept of Social Movement ... 89
4.2.2 Social Issues ... 90
4.2.2.1 Social Issues of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism... 91
4.2.2.2 Social Issues of Anti-Authoritarian Nationalism ... 93
4.2.2.3 Social Issues of Social Movement... 95
4.2.3 Ideologies Representation ... 95
4.2.3.1 Representation of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism ... 95
4.2.3.2 Summary of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism Representation ... 114
4.2.3.3 Representation of Anti-Authoritarian Nationalism... 115
4.2.3.4 Summary of Anti-Authoritarian Nationalism Representation ... 131
4.2.3.5 Representation of Social Movement ... 132
4.2.3.6 Summary of Social Movement Representation ... 141
CHAPTER 5 ... Appendix 1: Transitivity Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism ... 152
Appendix 2: Transitivity analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Nationalism ... 159
Appendix 3: Transitivity Analysis of Social Movement ... 167
Appendix 4: Modality Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism... 174
Appendix 5: Modality Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Nationalism ... 174
Appendix 6: Modality Analysis of Social Movement... 175
Appendix 7: Pronoun Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism... 177
Appendix 8: Pronoun Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Nationalism ... 181
Appendix 7: Pronoun Analysis of Social Movement... 183
Appendix 9: The Distribution of Transitivity Processes in the Ideologies ... 185
Appendix 10: The Distribution of Modals in the Ideologies………...186
Appendix 11: The Distribution of Pronoun in the Ideologies... 186
Appendix 12: Anti-Flag Selected Song Lyrics. ... 187
xi
Table 3.1. List of Anti Flag Selected Song Lyrics... 42
Table 4.1 Excerpts of the Material Processes………... 50
Table 4.2. Excerpts of the Relational Processes ………...…………... 57
Table 4.3. Excerpts of the Mental Processes ……...………... 61
Table 4.4. Excerpts of the Verbal Processes... 64
Table 4.5. Excerpts of the Existential Processes ………..… 65
Table 4.6. Excerpts of Probability……….... 67
Table 4.7. Excerpts of Usuality…... 69
Table 4.8. Excerpts of Obligation…...……….…………. 70
Table 4.9. Excerpts of Inclination…... 72
Table 4.10. Excerpts of Ability …...………... 72
Table 4.11. Excerpts of Pronoun I…...………..….……. 75
Table 4.12. Excerpts of Pronoun You... 75
Table 4.13. Excerpts of Pronoun We... 77
Table 4.14 Excerpts of Pronoun They………... 78
Table 4.15. Excerpts of Word-Choice 1 ………....…………... 79
Table 4.16 Excerpts of Word-Choice 2 ……...………... 81
Table 4.17. Excerpts of Word Choice 3 ... 83
Table 4.18. Distribution of Transitivity ………...………..… 65
Table 4.19. Distribution of Modality ………... 67
xii
Appendix 1: Transitivity Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism ...Error! Bookmark not defined.
1. Material Processes...Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Relational Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Mental Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 4. Verbal Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 5. Existential Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Appendix 2: Transitivity Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Nationalism ...Error! Bookmark not defined.
1. Material Processes...Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Relational Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Mental Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 4. Verbal Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 5. Existential Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Appendix 3: Transitivity Analysis of Social Movement ...Error! Bookmark not defined.
1. Material Processes...Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Relational Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Mental Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 4. Verbal Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. 5. Existential Processes ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Appendix 4: Modality Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism...Error! Bookmark not defined.
Appendix 5: Modality Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Nationalism ...Error! Bookmark not defined.
Appendix 6: Modality Analysis of Social Movement...Error! Bookmark not defined.
Appendix 7: Pronoun Analysis of Anti-Authoritarian Capitalism...Error! Bookmark not defined.
xiii Bookmark not defined.
Pronoun I(Anti Flag)...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun You (Government) ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun You (Society) ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun We(Anti Flag) ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun We (Anti Flag & Society)...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun We (Government) ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun They(Government)...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun They(Society)...Error! Bookmark not defined. Appendix 7: Pronoun Analysis of Social Movement...Error! Bookmark not defined.
Pronoun I(Anti Flag)...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun You (Government) ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun You (Society) ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun We(Anti Flag) ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun We (Anti Flag & Society)...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun We (Government) ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun They(Government)...Error! Bookmark not defined. Pronoun They(Society)...Error! Bookmark not defined. Appendix 9: The Distribution of Transitivity Processes in the Ideologies ....Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.10The Distribution of Transitivity Processes in the Ideologies.Error! Bookmark not defined.
Appendix 10: The Distribution of Modals in the IdeologiesError! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.11The Distribution of Modals in the Ideologies ...Error! Bookmark not defined.
Appendix 11: The Distribution of Pronoun in the Ideologies...Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.12 The Distribution of Pronoun in the Ideologies ..Error! Bookmark not defined.
Appendix 13: Anti-Flag Selected Song Lyrics. ...Error! Bookmark not defined. Song 1:"You've Got To Die For The Government"...Error! Bookmark not defined.
xiv defined.
xv
Lessu, Deasy Natalia. 2017. The Ideologies of Anti-Authoritarianism and Social Movement in Anti-Flag’s Protest Song Lyrics: A Critical Discourse Analysis,
Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Music especially punk rock is ideological. It has a basic belief about DIY (Do-It-Yourself) which presents their subculture (counterculture). It sets themselves as the outer group of the society. The belief of DIY sets the punk rock to life in liberty. Thus, they have tendency to rebel against authority. They see the traditional culture; the submissiveness of society to the power holders as the significant issue that need to be resisted. Thus, the song lyrics are not merely showing protest but the calling to do revolution as well. Through their music, specifically song lyrics, they act as the speaker to persuade the listeners. In the purpose of gaining up the critical awareness of the listeners about the role of punk rock music in carrying the protest about the social issues, the study will conducted by using Critical Discourse Analysis (CDA).
The study has aim to answer two research questions. The first question is How the linguistic features employed in Anti-Flag‘s protest song lyrics reveal the ideology? While the second question is What are the main ideologies conveyed in Anti-Flag’s protest song lyrics?
The study is about CDA, thus, the study will be guided by the framework of CDA. It helps to present concept about the ideology, how the ideology works in discourse and how the ideology constructs power. To discover the existence of ideology in the discourse, - the text, the concepts of the ideology, the special terms describe the ideology and the social issues which support the actuality of the ideology will be used. To do the analysis of the linguistic representation, the Systemic Functional Grammar will be applied. It represents the ideology through the linguistic units such as transitivity analysis, modality analysis and pronoun analysis.
The data derives from the Anti-Flag song lyrics. It is as much as 15 song lyrics. This punk rock band is considerably consistent and committed in sounding protest about the social issues. The data used are for analyzing first questions attained from the lexical items used in the song lyrics and the literature data to support the concept and the social issues of the ideology. The data used for the second questions taken from the clauses in the song lyrics. It is done by the analysis of transitivity to present the frequent process which represents the ideology and the modals and pronouns analysis to present speaker’s intention and judgments about the ideology.
xvi
frequent type. The probability and obligation appears mostly in anti-authoritarianism. They indicate the certainty and probability and the obligation of the authority works. The ability appears in social movement expresses the skill of doing the revolution. About the pronoun analysis, the anti-authoritarianism mostly appears in pronoun you and they. It means that Anti-Flag is as the part of punk subculture persuade (and protest as well) society and protest government. It sets position of Anti-Flag as the out-group; not belong to society. The social movement mostly carries we as the pronoun. It means that Anti-Flag is in-group with society to do the movement.
It is recommended for the future researchers to conduct similar study on song lyrics, especially the punk rock music to enrich and raise their critical awareness of the use music as the protest medium. It is also recommended to explore more on the textual analysis especially theme-rheme since the usage of the theory might cause different interpretation.
xvii
Lessu, Deasy Natalia. 2017. The Ideologies of Anti-Authoritarianism and Social Movement in Anti-Flag’s Protest Song Lyrics: A Critical Discourse Analysis,
Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Musik khususnya punk rock memiliki ideologi. Punk memilik prinsip dasar yaitu DIY (Do-It-Yourself) yang merepresentasikan cara hidup mereka, kebiasaan dan ide-ide dari kelompok mereka sebagai kelompok yang berbeda dari kelompok masayarakat pada umumnya. Prinsip DIY mengatur para anggota punk
untuk hidup dalam kebebasan. Oleh karena itu, mereka mempunyai kecenderungan untuk melawan kekuasaan. Mereka memandang budaya yang telah menjadi tradisi dalam masyarakat seperti penundukan masyarakat terhadap para penguasa sebagai isu penting yang harus dilawan. Untuk itu, lirik-lirik lagu mereka tidak sekedar menyatakan protes tetapi juga mengajak untuk melalukan revolusi. Melalui musik, khususnya lirik lagu, mereka berperan untuk melakukan propaganda kepada penikmat musik secara khusus dan secara umum kepda masyarakat. Dalam rangka meningkatkan critical awareness dari para penikmat musi tentang peran musik punk rock sebagai pembawa pesan tentang isu sosial, penelitian ini akan dilakukan dengan mengimplementasikan Critical Discourse Analysis (CDA).
Penelitian ini bertujuan utnuk memberi solusi terhadap dua pertanyaan. Pertanyaan pertama Bagaimana unsur-unsur linguistik di dalam lirik-lirik lagu protes Anti-Flag mengungkapkan ideologi? Sementara pertanyaan kedua adalah Apa ideologi-ideologi utama yang diusung Anti-Flag dalam lirik lagu protes mereka?
Penelitian in adalah tentang analisa wacana kritis (CDA) dengan demikian penelitian ini akan mengikuti kerangka teori CDA. Teori ini membantu memberikan konsep tentang ideologi, kaitan ideologi dengan wacana dan bagaimana ideologi memiliki power. Untuk menemukan keberadaan ideologi di dalam teks, konsep tentang ideologi-ideologi utama, isitilah-istilah yang terkait dengan ideologi-ideologi tersebut serta isu-isu social yang mencerminkan aktualisasi dari ideologi-ideologi tersebut akan dibahas. Untuk menganalisa representasi linguistik, Systemic Functional Grammar dipakai. Teori ini menunjukkan representasi ideologi melalu analisa transitivity, modality dan
pronoun.
Data yang dipakai dalam penelitian ini berasal dari lirik-lirik lagu
xvii
i
tanggapan dan tujuan pembicara (Anti-Flag) tentang ideologi-ideologi yang dibahas.
Dari analisa, ditemukan dua ideologi utama yang diusung oleh Anti-Flag
adalah Anti-authoritarianism dan Social Movement. Anti-authoritarianism
dibedakan kedalam Anti-authoritarian Capitalism dan Anti-authoritarian Nationalism. Hasil dari analisa transitivitymenunjukkan kedua ideologi dibentuk dengan material processes dan relational processes. Proses pertama menunjukan aksi dari actor sementara proses kedua menunjukan identitas dan karakter dari
actor. Dari analisa modality ditemukan bahwa probability, obligation dan ability.
muncul sebagai modals meaningyang dominan. Probabilitydan obligation sering muncul di ideologi anti-authoritarianism. Ini menunjukkan kepastian dan kepatuhan tentang dan terhadap pekerjaan para penguasa. Abilitysering muncul di ideologi social movement menunjukkan kekuatan dan kemampuan Anti-flag dan masyarakat untuk melakukan perubahan. Dari analisa pronoun ditemukan bahwa pronoun you dan they banyak muncul di idelogi Anti-authoritarianism. Hal ini berarti Anti-Flag berada di out-group yang memungkinkannya melakukan protes kepada pemerintah dan masyarakat. Pronoun we banyak ditemukan di ideologi
social movement. Hal ini memposisikan Anti-Flag di in-group. Bersama-sama dengan masyarakat, Anti-Flagmemberi perlawanan terhadap para penguasa.
Untuk penelitian ke depan, direkomendasikan untuk melakukan penelitian yang sama pada lirik lagu, terlebih khusus lirik lagu punk rock untuk meningkatkan critical awareness terhadap penggunaan musik sebagai media protes. Selain itu direkomendasikan juga untuk mengeksplorasi textual analysis
khususnya pada theme-rheme sebab penerapan teori yang berbeda dapat menghasilkan interpretasi yang berbeda pula.
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
This introductory section categorized into four sections containing
background of the study, problem formulation, objectives of the study and
benefits of the study. The first section, background of the study, explicates the
depiction of the topic of the study and the reasons of studying it. The second
section is problem formulation. It elaborated with the purpose of clarifying what
matters that the study has to answer. The third section is the objectives of study
that expresses the process of doing the study based on the practical theories. The
fourth section provides the importance of the study and benefits obtained from the
study.
1.1 Background of the Study
Music and society are always powerfully intimate. Whenever people do
anything either individually or socially for any reason, music is there. In politics,
for example, the candidates use music to achieve number of supports from the
society during their campaign. The common reason underlies the existence of
music in society is it acts as a means of developing and negotiating interpersonal
relationship. Juslin & Sobloda 2001 (in Cross 2006) state, “music can be used by
individuals to modulate and regulate their own moods, and may be used in group
contexts to modulate collective mood”. Hence, music can easily unite people, or
The importance of music in the society has revolutionized. Such kind of
artwork is not only for entertaining people but also employed as a medium of
communication to produce a change and a revolution in some areas of human
culture. One of them is as a medium of protest. The use of music in protesting
recognized as the protest music or protest song. The protest song according to
Denisoff (1972) is “a socio-political statement designed to create an awareness of
social problems and which offers or infers a solution which is viewed as deviant
in nature.” Thus, the protest songs gain society’s awareness and support for the
being captured issue.
Commonly, the protest rises due to the government’s regulations or, actions
that are contradictive to the society’s expectation. Clearly stated by Boulding
(1967: 50), “protest arises when there is strongly felt dissatisfaction with existing
programs and polices of government or other organization…“. In the relation to
the protest, the protesters work to change or prevent the changes of a matter. At
least, they try to persuade others to change their ideas by criticizing or protesting
something wrong or unfair. Indirectly, through the protest, the society is eager to
show their power against the government. Lipsky (1965) in Porta and Diani
(2006) state that, protest is a political resource of the powerless.
Anti-Flag is a punk rock band. It has been totally stuck with their capacity
as the activist through their music. Since their first debut in 1996 until their latest
album in 2012, Anti-Flag is likely to criticize the government’s administration.
Their albums published during the era of three United States presidential such as
(2009-2016). One the protest issue is about the Bush's decision to wage a
preventive war in Iraq which becomes the trigger to arouse another issue such as
endangering the social security, increasing the tax, causing unemployment,
inflation, poverty etc. The protest revealed in the lyrics is such as the following
clauses.
(S6.C2) This scene will not fall victim to your violence or lies (Material Process).
(S6.C3) Our values are nothing but your values excuses to start fights
(Relational Process).
(S14.C2) So, if the heads of the state want to end terrorism, they should go and kill themselves. (Mental Process).
Through the clauses, the existence of government presents using noun, the
heads of the stateand the pronoun, your violenceand your values. The protest is
visible through the processes. For example, in clause S6.C3, the use of will not
indicates the willingness to fight against the government’s violence or lies. It is
clear that in the song lyrics, Anti-Flag as the speakers try to communicate or send
the message to the society about the social issue and to counter authority.
Music facilitates communication that goes beyond word, which people use
to share their emotions, intentions, and meanings. Thus, the language used in
musical lyric is powerful to influence the people. According to Wodak (2007:1)
“Language ... be seen as a driving force directed at changing politics and society”.
This is what Anti-Flag intend to spread through the message inside their lyrics.
However, language only gains power in the hands of the powerful: language is not
in power per se. A specific language symbolizes the group or person in power.
Generally, the term “ideology” refers to the hidden message inside the
language. Therefore, the song lyrics stand as the medium to advance its
ideological stance on language. Van Dijk in his writing about Ideological
Discourse Analysis states that “Ideologies may in fact be the same as the
representation a group has of itself (and of the relations with the relevant other
groups, e.g. the opponents) in the social structure”. Moreover, he also states that
as the member of a group, the language users supposedly will speak, write, or
understand from a specific social position. In here, Anti-Flag as the punk rock
band recognized as the member of the punk group. The ideologies will represent
their group itself as to counter the ideology of the government – the opponent.
Relating to the study, the analysis examines what ideologies are typically
associates with that position.
To do the study, Critical Discourse Analysis is considerably helpful to
support. CDA is a three dimensional framework of text analysis which involves
the analysis of the social practice, the discourse practice, and the text itself. The
analysis of the social practice dealt with the society in which the writer of the text
lives. The analysis of discourse practice refers to the process of the text
production, distribution and consumption while the text analysis deals with the
uncovering the underlying ideology that prompts the text production. Fairclough
(1995: 1-2) points out that “a range of properties of text considered potentially
ideological through the features of vocabulary and metaphors, grammar,
presuppositions and implicatures, politeness conventions, speech-exchange
Principally, CDA is an interdisciplinary approach to the study of discourse,
which views "language as a form of social practice" (Fairclough, 1989). As one of
its central objectives, CDA considers the linguistic choices. A text producer
makes the linguistic choices as a potential medium through which the ideological
import of a particular discourse situation can be reproduced. Fairclough and
Wodak (1997) usefully translate this into the "working assumption" that "any part
of any language text, spoken or written, simultaneously constitutes
representations, relations, and identities". That is, discourse represents particular
views of world, particular social relations between people, and particular social
identities according to the purpose, context, and addressees of the text.
Since the linguistics choices are considered in CDA, the Systemic
Functional Grammar (SFG) by Halliday will be an applicable to work with. The
SFG has three metafunctions: ideational, interpersonal, and textual functions.
They will be the tools to analyze clauses that represent the ideology. The
cooperation of both theories, CDA and SFG, will support each other to see how
the social issues transferred into the language and how the ideology of the speaker
1.2 Problem Formulation
The present study investigates the problems presents in the following
research questions:
1) How the linguistic features employed in Anti-Flag‘s protest song lyrics
reveal the ideology?
2) What are the main ideologies conveyed in Anti-Flag’s protest song lyrics?
1.3 Objectives of the Study
The study has three objectives. They related to the field of linguistics,
Critical Discourse Analysis and musical art.
The first objective is to reveal the ideologies in Anti-Flag song lyrics. The
objective intends to find out the concept of ideology and power conveyed by
Anti-Flag as the punk rock band. To achieve the objective, the macrostructures analysis
by van Dijk will be employed. The analysis focuses on the use of special terms
and the social issues which support the ideologies. They special terms present the
existence of topics related to the ideologies in the lyrics. On the other side, the
social issues provide information and knowledge about the reality of the topics. In
other words, they connect the text with the context.
The second objective is to find out the representation of the ideologies
through the use of linguistics units. The objective is achievable by using Systemic
Functional Grammar. It provides metafunctions analysis: ideational, interpersonal,
and textual functions. They help to show the relation between the lexical and
The study focuses on ideational and interpersonal function. By means of
transitivity analysis, the ideational function will be analyzed. It states that a clause
has meaning as a representation of some processes in ongoing human experiences.
The transitivity system is applicable to reveal the representation of people, events,
or issues in the text because it has a function to infer the author’s experience in the
texts. On the other side, the interpersonal function is analyzed by the use of
modality and pronoun analysis. The ideational function presents the interaction
between the speakers to the listener. The observation on those functions might
show the systemic characteristic of language in use. Moreover, to determine the
clause represents a certain ideology is to consider the basic concept of the
ideology itself. By doing so, the characteristics of each ideology will be clear.
Therefore, it will be easier and more correct to group the clauses into an ideology.
The third objective is to give appreciation to the musical art especially the
punk rock music. The use of music as the object of discourse analysis is less if
compare to the use of newspaper, speeches or literary works. To appreciate the
musical art is not merely about the musical notes of a song but to pay more
attention to the lyric of a song. The study of song lyrics by linguistics analysis
helps to understand the personal thoughts and feelings of the person who wrote it.
1.4 Benefits of the Study
The substance of a study is having benefits. The study hopefully equips
good contribution for all readers not merely for the certain parties.
Tthe study serves a purpose for the language learners who are interested in
linguistics, Critical Discourse Analysis (CDA) and Systemic Functional Grammar
(SFG). It provides knowledge and awareness on how to apply CDA approach in
analyzing song lyrics as type of discourse and SFG in textual analysis. For the
study presents song lyrics as the particular text therefore it might be a good
example on how to scrutinize language features on the song lyrics. Hopefully, the
study might raise critical analysis and awareness on the covert meaning (ideology)
of the song lyrics and on the linguistics comprehension.
Tthe study presents the importance to conceive the song lyrics. For the
music listeners, the study points out that music is more worthy if it is not merely
listened but understood the messages concealed in its lyrics. Music, especially
punk rock not merely affiliated with the noisy and awful sounds, which for few
people is annoying. Thus, people will come up with the negative perceptions
about the genre. On the other side, few people consider the punk rock music as an
interesting music that helps them to release their emotions, such as anger. Hence,
they merely appreciate the music instead of its lyrics. Lyrics are not just the part
of the total package of the music. In punk rock music, the lyrics contain
significant information, ideas, opinions, or images about the social issues. People
are lead to be conscious for the social problems especially about the socio-politics
Ultimately, through the study, It is proposed that perhaps readers, society
-may benefit from a deeeper understanding of punk rock counterculture idelogy.
Instead of just paying attention to the lyrics and musical sounds, people will see
culture, values, ideology, and messages. Public is hoped to be conscious that
music as the artwork can be an applicable medium of protest to do a revolution or
social movement. In a wider perspective, the study is hopefully might arouse
public response towards the social issues; capitalism and nationalism. It is about
how to make a stand to resist against social injustice. Public not only listening to
the punk rock music and absorb the significant points in the lyrics but to act. The
protest through song is propagandist to get people support. Despite this, the
intention of doing the protest is for the real action. Listening to punk rock music,
especially Anti-Flag, people will notice their existence as the part of drivers of
CHAPTER 2
LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter consists of three sections namely review of theories, review of
related studies and theoretical framework. The review of theories examines the
theories applied to conduct the study, the review of related studies provides
insights for the study and the theoretical framework clarifies the contribution of
the theories in solving the problem formulation.
2.1 Review of Theories
The section presents the theories exercised in the study. The first section
talks about ideology as it is what the study about. It presents the concept of
ideology, ideology and discourse, ideology and power and ideology of punk. The
second section is about the method of the study, Critical Discourse Analysis. It is
the general framework of the study. By reviewing the theory, the study is led to
reveal the ideology and power imbalance in practice in a society. The third section
is about the concept of protest songs. It provides the concept of how the songs
used as the protest medium. The fourth section is about the Systemic Functional
Grammar from Halliday (2004) elaborated with other experts. It presents concept
of transitivity, modality and pronoun. It used as the tool to observing data.
2.1.1 Ideology
The term, ideology is controversial. It is because there are many definitions
The ideology was used by Antonine Loues Claude Destutt de Tracy in 1796 for
the first time. The term used to officially states the ideas of a particular group of
scholars in France. The idea is about the new empiricist ‘science of ideas’ (the
studies of how people think, speak, and argue). Simply, ideology is about the
origins of the ideas. The ideas addressed to young people due to their minds are
not full of the ‘fixed ideas’ compared to the minds of established scholars
therefore it is not difficult to change. People who support the idea are in a group
called themselves as the ideologists. Parson (1951: 39) asserts that ideology is “a
system of beliefs held in common by the members of a collectivity”. From the
explanation, two main points can be taken out are the ‘system of beliefs’ and the
‘members of collectivity’.
The two main points above considered as the basic notion to understand the
concept of ideology. The system of beliefs might define as ‘the set of principles’
while the members of collectivity defined as ‘the group of people who shared the
same ideology and essentially have been controlled by the ideology. Thus, the
ideology is about a theory or set of beliefs or principles that underlie the group. A
group could be a political group, party, or organization. However, the existence of
an ideology might have relevancy to other ideologies. Nazism, National
Socialism, for example, has relevant beliefs to nationalism and racism. The
Nazism held racial theories based upon the belief of the existence of an Aryan
master race that was superior to all races. Nazi ideology was developed by intense
nationalists whose only interests were the future of Germany and
“a member of the National Socialist (Workers’) Party led by Adolf Hitler which
controlled Germany from 1933 to 1945” (CALD3).
The ideology is not merely descriptive but it is practical as well. It is not
only about a number of very general ideas that are the basis of group members’
specific beliefs about the world that guide their interpretation of events but it also
influences their social practice. According to Fairclough (2003: 9), “Ideologies are
representation of aspects of the world which can be shown to contribute, to
establishing, maintaining, and changing social relations of power, domination, and
exploitation”. Thus, ideology is practical as the power holders use the belief to
control the powerless people.
Ideology is the power and domination, which owned by a group who have
positions, attitudes, beliefs, and perspectives. Government is a group of people
who has power and domination since they are officially controlled a country. In
relation to the Nazism, Nazi has power and domination to control Germany
because of the position of Adolf Hitler as the leader of nation. He is hegemonic;
he has position of being the strongest and most powerful and therefore can control
others. The control itself is about the order, limit or rule people’s actions or
behavior. In a country, laws and policies become government’s tools to control
people.
The ideology may be more or less positive and negative depending on our
point of view or group membership. Marx and Engels define ideology in a
negative sense. They state, “Ideologies are systems of false ideas representing the
A negative connotation addressed to an ideology when it creates injustice. The
injustice here refers to the way the power holders treat the powerless in a relation.
There are three relations can be used; government-society, society-society and
society-government. In government-society relation, government has power to
create policies, which disappointedly has tendency to cause suffering to the
society. In society-society relation, the rich has power to bring misery to the poor.
In relation of society-government, the rich or big business have power to
influence and control the government. Basically, the power holders have tendency
to use their power and domination to obtain advantages for themselves by
disregarding the powerless groups. For that reason, groups of people come up to
counter negative ideology.
The opposition to the common ideologies normally contains the
disapproving opinions or suggestions that the ideologies are not good or not
important. Moreover, it is due to the negative impacts of the ideology to the social
life. As like a common ideology called Nazism, it has counter-ideology so-called
anti-Nazism. However, to spread the ‘anti-ideology’ is not that easy. Inferior
surely are unable to directly sounding protest or criticism to the superior as they
lack of power and domination. They need to collect members to support them.
Their ideology delivered through a medium that is easily to unify people. One of
the media is the music, folk song. It is used under the consideration of music is
well-liked and respected by common people. Moreover, it is potential to regulate
mood. The counter ideology either implicitly or explicitly filled in the song lyrics,
2.1.1.1 Ideology and Discourse
Ideology might be abstract and general. It can only indirectly emerge in talk
and text; it emerges in a discourse as the communication in speech; talk and
writing; text. Thus, it can be simply said that the discourse might attributes the
specific and fixed ideological contents. Moreover, the discourse is the
re-contextualization of concept of world through a speaker or writer’s point of view
that is presented in speech and writing. Therefore, the discourse is shaped by and
might present the ideology of the speaker or writer. They, the speaker or writer
has intention to propagate the listener or reader. Principally, they have power to
control people perception about the world. Fairclough (1995: 73) clarifies that the
“discourse is shaped by structures also contributes to shaping and reshaping them,
to reproducing and transforming them”. He says that the structures are the
combination of the elements of text such orders of discourse, codes and their
elements such as lexical and grammatical elements but also the mediated form
political and economic structure and relationships; relation in the market, relation
with the state and relation with society.
Talking about discourse and its relation to ideology is conceptually wide.
Van Dijk (2000) states that, the study about the notions of ideology and
discourses are not adequate in a discipline. They require the elaboration of all
disciplines such as humanities and social sciences. For that reason, he proposes to
stick with three main clusters; discourse, cognition and society. According to him,
the ‘discourse’ relates to the study of language use, text and other
relations with opinions and knowledge and the status as socially shared
representations. The ‘society’ relates to the aspects of social, political, cultural and
historical, group-based nature and the roles in reproduction of dominance or
resistance against dominance. The three main clusters help to find out how the
language use of ideology shared by the speaker influence the listener.
2.1.1.2 Ideology and Power
Ideology that owned by a specific social group might be different to the other
social group. The difference symbolized the identity of the group itself. The
identity is categorized into the in-group and the out-group. The standard
determination of a group generally defines by a sense of belonging. Some reasons
prescribes the belonging could be such as being in the same position in society.
The reasons are such as involving in the specific social issue and having the same
perception or opinion about a matter.
The sense of belonging contains the term of solidarity. Such solidarity may
contain positive attributes as foundations for a shared identity; groups also have a
tendency to define themselves in juxtaposition to others who manifestly do not
belong because they are different. Cultures thus often end up with a bipolar vision
of ‘us’ versus ‘them’ with the former being a representation of what it means to be
human, and latter implying something less than human. Groups define their
collective self by presuming superiority over the other whom they do not allow to
The superiority over the other groups presents the power of the ideology of the
group. It specifically defines power as the domination. For this notion, Gramsci
(as cited in Mayr 2008: 13) uses concept of hegemony.
“Hegemony highlights the mechanism through which dominant groups in society succeed in persuading subordinate groups to accept their own moral, political and cultural values and their institutions through ideological means”.
The position of being the strongest and most powerful and therefore provides
wide chances to control others. For the practice of power, Mayr (2008: 14) has a
notion that “hegemony operates largely through language”. He further explains
that the dominant cultural group generates the discourse represent them as
‘natural’ therefore people consent to the discourse with the particular formations
of power. Linguistically, the ideology in a text is written in speech act or an act of
writing (statement, question, command, promise, threat, giving of advice. etc.) has
potential to enforce people’s interests (Wodak 1989). Wodak (1989: 82) moreover
states that “certain types of speech act are associated with the special supporting
conventions”, for instance, the military commands. He further asserts that the type
of speech act in principle suitable for enforcing the interests of power. The notion
can be taken from the description is that the ideology is persuasive.
The power in the ideology used as propaganda. As the power is
dominating, the further idea is to use the domination for a specific purpose. It is to
persuade. The persuasion delivered with the intention of influencing people’s
2.1.1.3 Ideology of Punk
Punk is considered as a ‘counterculture’ or ‘subculture’. The term refers to
the way of life, customs and ideas of of a particular group of people within society
which are diferent from the rest of that society (CALD3). The subculture of punk
emerged at the first time in England. By the 1970’s in England, the subculture
were understood to be the groups of youths who practiced a wide array of social
dissent through shared behavioral, costume and musical orientations.
From the three mentioned orientations; behavioural, costume and musical,
the punk existence as the subculture may be clearly potrayed. The behaviour of
punk is often revolting. It means they refuse to be controlled or ruled and take
violent action against authority. The behaviour is clearly seen in Do-It-Yourself
(DIY) ethic. The ethich presents the core value of punk which are the freedom
and thinking for yourself. The implementation of the ethic depicted in their ability
to produce and distribute ideas and art without the interference of major
corporations. The common costume orientation presents in the way they dress up
by wear the the trashy cut-up clothes, the spiky hair and the acccessories such as
offsensive body jewelry, such as safety pins as earrings and face rings, swastikas
and crosses as pins and painted emblems.
The musical form adopted by punk rock instrumentally presents itself as
direct and straightforward, in a clear line from the so-called ‘classic’ style of rock
n roll music. The music employed a limited range of chords and heavy rhtymic.
Musically, the style is agrresive in feel and musician played in a seemingly
innovation of punk rock at the level of musical sound, since it sounds like noisy as
it somewhat full of screams. In the case of lyrics, they are realistic. The lyrics
presents the social issues. Stuart Borthwich and Ron May (as cited in Ferdinandi,
2010: 17) explains that punk “places a lyrical emphasis on exposing
working-class dissatisfaction with ‘normal’ society, and frequently focuses upon concerns
that are particular to young people. Not merely about it, the punk’s lyrics present
their invitation for listeners to a revolution.
The counterculture, again, is the rebellion against the traditional culture.
Hebdige (as cited in Ferdinandi, 2010: 15) says that the “subculture tends to
presented as independent organism, functioning outside the larger social, political
and economic contexts”. According to Brake (1985), subcultures arise as the
attempts to resolve collectively experience problems resulting in contradiction in
the social structure. Therefore, punk is not merely about the being; behave like
punk, costume like punk or enjoy the punk music. However, punk is about doing;
the loyality to the cultural sentiment that makes up the punk movement. Fox
(1987: 379) clarifies that, the “the contempt for authority and the conventional
culture was in fact, such an essential values for punk that if one expressed
prosystem sentiments or support for the present administration, one would not be
considered a member, no matter how well one looked the part.”
Punk’s ideology can be seen in the lyrics. In punk rock, there is an atraction
to telling the truth about the world in the sort of language. In the song, God Save
the Queen by Sex Pistols which has sevent times repetition of lyric, ‘there is no
or apathy. It’s counter idealism is expression of opposition. The songs stories the
major economic depression that occured in the United Kingdom during the late
1970s left an entire generation on welfare without hope for steady employement.
The issues of the British class sytem, instituonalized poeverty and unemployment
become the background of the song. The oppositional idealism has voices fierce
and passionate opposition to a wide array of social realities. The lyric presents
opposition can be seen in Ant-Flag song lyric entitled, Stars and Stripes. The
lyric, ‘don’t fly those stripes, those stars and stripes for me’ repeats 14 times. The
‘stars and stripes’ are refers to American flag. Since the flag symbolizes the
nation, hence, the lyrics presents the rejection of nationalism, anti-nationalism.
As the like culture has its counterculture, so does the ideology. The word,
anti in anti-nationalism above indicates as counter-ideology. The punk rock
ideology is proposed to fight the well-being ideology. Like nationalism, where
netizen has to submit themselves for the nation, anti-nationalism refuse the –ism.
The emergence of the idealism is also due to the reality exist in the nation. It
could be the social disappointment for nation that cannot support the citizen
needs and expectations.
2.1.2 Critical Discourse Analysis
Critical Discourse Analysis (CDA) is the part of Discourse Analysis (DA).
The point, which distinguishes the DA and CDA, is the term “critical”. The term
“critical” means the analysis of discourse is not only about what written or spoken
connections and causes. In other word, CDA is not only dealing with study the
surface of the text but the deep of it. CDA refers to the use of language in society
or in context, rather than in isolation, as discourse. Van Dijk (2008) defines
discourse to be a specific communicative event, in general, and a written or oral
form of verbal interaction of language use, in particular. Hodge (2012: 2) states,
“Analyses for the discourse ‘critically’ means to breaking up something,
loosening bonds”. Further, he says that when the critical combined with the
analysis thus it creates a ‘destructive approach’ that means a detailed analysis.
Based on the explanation above, it states that the focus of doing
critical-analysis is the discourse. In Cambridge Advance Learner’s Dictionary, discourse
defines as “communication in speech or writing.” In the case of communication in
writing, it absolutely deals with the text; the language and linguistic. However,
Fairclough (2003) argues that the discourse analysis is not merely the linguistic
analysis through the text. According to him, the discourse is also about the social
practices. Nevertheless, he further adds that, looking closely to the people’s
speech or writing also needed in understanding the social effects of discourse. In
conclusion, Fairclough states that,
Therefore, CDA called as interdisciplinary study. This study interlinked the way
language is functioned in the social practices such as exercising power, organizing
social institutions or constituting and transmitting knowledge (Wodak and Meyer
2001, p.11).
Talking about CDA is talking about examining the connection between
discourse, power, dominance, and social inequality. CDA concern with power as
it is the central condition in social life. The power exists, as there is the
dominance of a particular person or group to the others in society. Wodak and
Meyer (2001) explain, “Power is about relation of difference, and particularly
about the effects of differences in social structures”. It means people in the high
social structure tend to be powerful than the low social class. Indirectly, the power
or power abuse which exist in the social practice arouse the condition of social
inequality. In line with discourse, the distribution of power, the dominancy or the
social inequality clearly entwined with the language. It does not naturally define
that power derives from language, “but language can be used to challenge power,
to subvert it, to alter distributions of power in short and long term” (Wodak and
Meyer, 2001).
The powerfulness of language is not on the language itself but by how
powerful one uses it. This statement indicates that the language user has ideology.
In CDA, the ideology recognized as the core point to establish or maintain
unequal power relation. As Paul (2005) defines that, a central component of the
critical linguistic creed is the conviction that language reproduces ideology.
use. CDA regards language as a kind of social practice and an inseparable part of
social construction among which ideology serves as indispensable part.
Furthermore, the critical linguistics also assumes that as an integrated form of
social behavior, language will inevitably and inextricably tied up with the
socio-political context in which it functions (Paul, 2005). The analysis of CDA hardly
separated from the socio-political situations in which language produced.
Relating to the research, the CDA is applicable as the study focuses on the
discourse that contains power, ideology, and social inequality. This study sees the
song lyrics as the discourse that contains the ideology of the powerful actor,
Anti-Flag. Through the discourse, the speakers depict the socio-political situation about
the social injustice as the effect of the superior’s powerful action or decision
towards the inferior.
2.1.3 Systemic Functional Grammar
CDA as a concept of textual analysis needs to select a tool of analysis.
Fairclough (1995) mentions that the tool has to be functional theory of language
oriented to the question of how language structured to tackle its primary social
functions. Systemic functional grammar which is proposed by Halliday is suitable
to cooperate with the concept of CDA, as suggested by Halliday (1985) that it is
able to work with the view of language as a social semiotic which incorporated an
orientation to map relations between language (texts) and social structures and
relations. He defines that functional grammar is conceptual framework on which it
that it designed to account for how language is used. Everything that is written or
spoken has shaped the system. Language has developed to fulfill human needs
and it organized by functions to these needs. Functional grammar is purely
‘natural’ grammar that everything explains with reference to how language is
used.
Halliday developed a theory of the fundamental functions of language, in
which he analyzed lexico-grammar into three broad metafunctions: ideational,
interpersonal, and textual. Each of the three metafunctions is about a different
aspect of the world, and is concerned with a different mode of meaning of clauses.
The ideational metafunction is about the natural world in the broadest sense,
including our own consciousness, and is concerned with clauses as
representations. The interpersonal metafunction is about the social world,
especially the relationship between speaker and hearer, and is concerned with
clauses as exchanges. The textual metafunction is about the verbal world,
especially the flow of information in a text, and is concerned with clauses as
messages.
2.1.3.1 Ideational Function and Meaning
The ideational function is one of the metafunctions in SFG that concerns the
processes, participants, and circumstances found in the clause. Halliday (2004)
defines that the ideational function is the function that the speaker or writer
embodies language in his experience of the phenomena of the real world. This
consciousness through his reactions, cognitions, and perceptions, and also his
linguistic acts of speaking and understanding (Halliday, 2004). Zhuanglin (as
cited in Wang 2010) adds that the ideational function not only specifies the
available options in meanings but also determines the nature of their structural
realizations.
In order to analyze the ideational function, transitivity is the appropriate tool
to conduct. Transitivity aims at identifying the participants or things that are
involved, the actions and event taking place, and any relevant surrounding
circumstances (Morley cited in Wang 2010). In the transitivity system, the
meaningful grammatical unit is the clause since it expresses what is happening,
what is being done, what is felt and what the state is and so on (Wang, 2010). In
this system, the meaningful grammatical unit is clause, which expresses what’s
happening, what’s being done, what’s felt and what the state is and so on (Cheng
Yumin, in Wang 2010).
Transitivity system specifies the different types of processes that recognized
in the language and the structures by which they are expressed (Halliday, 1985).
He also asserts that the semantic categories explain how the real world
represented as linguistic structures are the concepts of process, participants and
circumstances. Eggins (2004) asserts that in analyzing transitivity structure, there
are aspects of clause that need to be considered: the selection of a process, the
selection of participants, and the selection of circumstances.
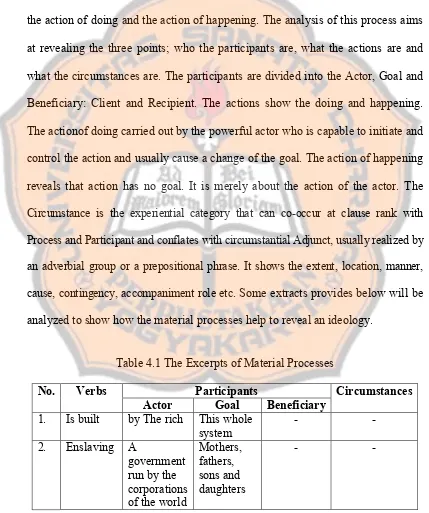
The term, ‘process’ refers to the doing, happening and being. ‘Participants’