262
PROBIOTIC BACTERIA AS YOGHURT STARTER AND ITS IMPLICATION EFFECT TO THE PATHOGENIC AND NON
PATHOGENIC BACTERIA IN MICE GASTROINTESTINAL
Lovita Adriani, Hendronoto A.W. Lengkey
Faculty of Animal Husbandry, University of Padjadjaran, Bandung, INDONESIA
The purpose of the research was to study the effect of bacteria consortium of Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophillus, Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacteria on the ecosystem of gastrointestinal in mice.The aim of this study was to explore the differences between yoghurt content from different consortium, with 1,25% dosage; in mice during three until five weeks. Also, the effect on the number of population of non pathogenic bacteria (Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacteria ) and the total pathogenic bacteria in the segment of the mice gut (jejunum, ilium and colon). Results indicated that the bacteria mixture have a good implementation in microbial intestine of mice, which increased the population of non pathogenic and decreased of pathogenic bacteria.
Keywords: total numbers of bacteria, pathogenic bacteria, and non‐pathogenic bacteria.
According to the previous studies, some genera of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria make an extremely important group of probiotic bacteria. Microflora of the gastrointestinal tract of human or animal, they offer considerable potensial as probiotic because of their history of save use and the general body of evidence that supports their positives role (Björkstén, et al, 2001, Guarner and Malagelada, 2003a, Sears,2005 and Steinhoff , 2005). Namely probiotics are microorganism which had been included in food without any adverse effects and which were present in the gastrointestinal tract for health. At present, these microorganism, called probiotics, have been selected from mostly lactic acid bacteria, e.g. Lactobacillus acidophilus. Bifidobacteria is a part of the normal intestinal microflora of human, since the microorganism are indigenous to the colon. The importance of an indigenous microflora in the gastrointestinal tract as a natural resistance factor against potential pathogenic microorganism was already recognised by Metchnicoff. Probiotic strain can be used only , if the microorganism active in the body of the host if the fulfill a large number of criteria. On the other side, lactic acid and acetic acid caused intestine acidity and can prevented the growth of pathogenic bacteria. Those acids reduce absorbsion of ammonia and amine since the large number of ammonia and amine can rise blood pressure, cholesterol,and cancer because of nitrosamine.
Lactobacillusis a group of gram‐positive anaerobic colonic bacteria that produce lactic acid. Supplementation withLactobacillusand the resultant increased colonic levels of this
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Raw milk used for making yoghurt, from farm animal at the faculty. The bacteria are pure cultivated Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. The identification of the cultures was based on the characteristics of lactobacilli and streptococci as described in Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology (Holt et al, 1994).
120 mice, from a commercial hatchery.
The experimental design were Completely Randomized Design (CRD), with six treatment and four replication. Every cages was filled with five mice.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Total non pathogenic bacteria in each segment of 6 weeks Mice Gastro Intestinal (cfu/ml).
In Table 1, presents the total non pathogenic bacteria in each segment of 6 weeks mice gastro intestinal (cfu/ml).
In Table 1 , the total of non pathogenic bacteria in the colon are higher than the total bacteria in the stomach, jejunum and ileum, especially with ration + Bifidobacteria starter (R3, R4 and R5). Helpful bacteria prevent the growth of pathogenic species by competing for nutrition and attachment sites to the epithelium of the colon. Symbiotic bacteria are more at home in this ecological niche and are thus more successful in the competition. Indigenous gut floras also produce bacteriocins which are proteinacious toxins that inhibit growth of similar bacterial strains, substances which kill harmful microbes and the levels of which can be regulated by enzymes produced by the host (Guarner and Malagelada, 2003a). The resident gut microflora positively control the intestinal epithelial cell differentiation and
proliferation through the production of short‐chain fatty acids. They also mediate other
264
Notes :
Lb = Lactobacillus bulgaricus, La = Lactobacillus acidophilus
R0 = Controle ration (without yoghurt) R2 = Controle ration + Lb, St and La starter R4 = Controle ration + Lb, St, La and B starter
St = Streptococcus thermophilus, B = Bifidobacterium spp.
R1 = Controle ration + Lb and St starter R3 = Controle ration + Lb, St and B starter R5 = Controle ration + La and B starter
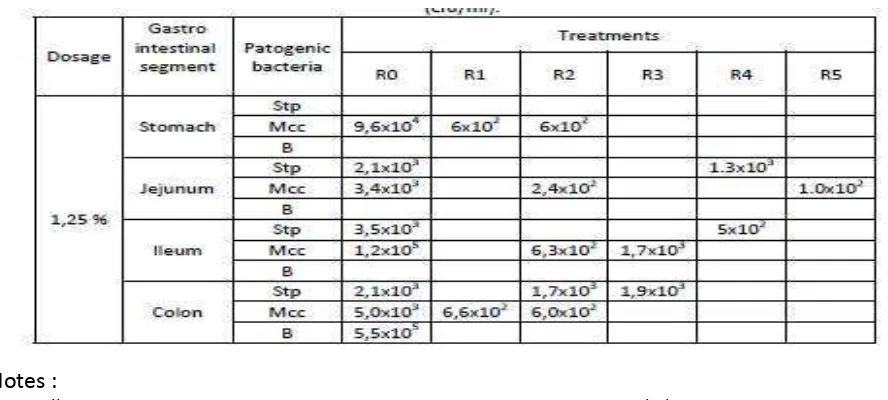
Total pathogenic bacteria in each segment of 6 weeks Mice Gastro Intestinal (cfu/ml).
In Table 2, presents the total pathogenic bacteria in each segment of 6 weeks mice gastro intestinal (cfu/ml).
Tabel 2. Total pathogenic bacteria in each segment of 6 weeks Mice Gastro Intestinal
Notes :
B = Bacillus, Mcc = Micrococci, Stp = Staphylococcus aureus.
R0 = Controle ration (without yoghurt) R1 = Controle ration + Lb and St starter R2 = Controle ration + Lb, St and La starter R3 = Controle ration + Lb, St and B starter R4 = Controle ration + Lb, St, La and B starter R5 = Controle ration + La and B starter
From the data from Table 2, the mice that have been feed with R5, has reducing the
pathogenic bacteria especially in the colon. This fact are agree with Beaugerie and Petit (2004) that fermentation process, since it produces lactic acid and different fatty acids, also serves to lower the pH in the colon, preventing the proliferation of harmful species of bacteria and facilitating that of helpful species. The pH may also enhance the excretion of carcinogens.
Metabolic function
266
Lucrări Științifice – vol 53 seria Medicină Veterinară
great importance to our body as this would help in prevention of such tumors that are difficult to avoid. The macrocomponents consists of the excessive intake of fat and sodium chloride which can later promote tumors such as in breasts and colons from fat and gastric carcinogenesis from sodium chloride(Guarner and Malagelada , 2003b)
CONCLUSION
The yoghurt with consortium starters with Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium spp. with 1.25% dosage of mice body weight have been raised the non pathogenic population and decreased the pathogenic bacteria in colon.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Beaugerie L, Petit JC (2004). "Microbial‐gut interactions in health and disease. Antibiotic‐associated diarrhoea".Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol18(2): 337–52. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2003.10.002.
2. PMID 15123074. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1521691803001276
3. Bettelheim KA, Breadon A, Faiers MC, O'Farrell SM, Shooter RA (1974). "The origin of O serotypes of Escherichia coli in babies after normal delivery".J Hyg (Lond)72(1): 67–70. PMID 4593741.
4. Björkstén B, Sepp E, Julge K, Voor T, Mikelsaar M (2001). "Allergy development and the intestinal microflora during the first year of life". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 108 (4): 516–
20.doi:10.1067/mai.2001.118130. PMID 11590374.
http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0091‐ 6749(01)96140‐8
5. Guarner F, Malagelada JR (2003a). "Gut flora in health and disease". Lancet 361 (9356): 512–9.
doi:10.1016/S0140‐6736(03)12489‐0. PMID 12583961.
http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140‐6736(03)12489‐0
6. Guarner F, Malagelada JR (2003b). "Role of bacteria in experimental colitis". Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17 (5): 793–804. doi:10.1016/S1521‐6918(03)00068‐4. PMID 14507589. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1521691803000684
7. Holt, J.G., N.R. Krieg, P.H.A. Sneath, J. T. Staley, and S. T. Williams, 1994. Bergey’s Manual of determination Bacteriology, 9th ed. Williams and Williams. Baltimore. p. 566.
8. Junjie Qin; et al (2009), "A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic
sequencing", Nature (464): 59–65, doi:10.1038/nature08821,
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v464/n7285/full/nature08821.html, retrieved 2010‐03‐06
9. O'Hara AM, Shanahan F (2006). "The gut flora as a forgotten organ". EMBO Rep. 7(7): 688–93. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400731. PMID 16819463. Schwiertz A, Gruhl B, Löbnitz M, Michel P, Radke M, Blaut M (2003). "Development of the intestinal bacterial composition in hospitalized preterm infants
in comparison with breast‐fed, full‐term infants". Pediatr. Res. 54 (3): 393–9.
doi:10.1203/01.PDR.0000078274.74607.7A. PMID 12788986.
http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt‐core/templatejournal/
lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0031‐3998&volume=54&issue=3&spage=393
10. Sears CL (2005). "A dynamic partnership: celebrating our gut flora". Anaerobe 11 (5): 247–51.
doi:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2005.05.001. PMID 16701579.
http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1075‐9964(05)00068‐5
1. Steinhoff U (2005). "Who controls the crowd? New findings and old questions about the intestinal microflora". Immunol. Lett. 99 (1): 12–6. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2004.12.013. PMID 15894105.
http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0165‐2478(05)00005‐2
2. Tap J, Mondot S, Levenez F, Pelletier E, Caron C, Furet JP, Ugarte E, Muñoz‐Tamayo R, Paslier DL, Nalin