PARTICIPATIVE LEADERSHIP AND JOB STRESS AS THE PREDICTOR TO THE EMPLOYEES’ JOB SATISFACTION IN THE COMPANY OF CENTRAL JAVA
By : Sutarto Wijono
Faculty of Psychology in Satya Wacana Christian University, Salatiga, Indonesia
Abstract
This reseaarch is to find out a participative leadership and job stress as a predictor to the production workers in the company located in Central Java. The subject of the research consists of 93 people working in the company of Central Java. A participative leadership scale is resulted from Newston and Davis (1993). A job stress index by Wolfe, Quinn, Snoek and Rosental (in Mustapha, 1994) is to measure a job stress. The scale of Brayfield and Rothe (in Wijono, 2011) is applied to measure a job satisfaction. The SPSS/PC+ is used to analize the collected data. The Statistic method used to analize is Multiple Regression. The result of the research finds out that the participative leadership and job stress are as the predictor to job satisfaction (F = 16,583; t.s.<0.05)
Key words : participative leadership, job stress, and job satisfaction to people working in production (production workers) in a company located in Central Java.
INTRODUCTION
employees shall do demonstration and strike in the organisation. This statement indicates that the strike is caused by disagreement and unsatisfaction on organisation policy such as self development, potency and competence of employees in the organisation. (Davis & Newstroom, in Wijono , 2011).
Therefore an organisation also needs to be a motivator which can develop its employees’ potency and competency , so that the workers can get a job satisfaction (Herzberg, 1959). Meanwhile Locke (Wagner III and & Hollenbeek, 1995, page 206 – 207) explains that job satisfaction is “a pleasure feeling the results from the perception that one’s job fulfills or slows for the fulfillment of one’s importance job value”. In line with this Robbins (2001) states that suppporting co-workers, personality harmony with job and opportunities from their jobs are factors of workers’ satisfaction. On one opportunity Nilvila (in Dhama, 2009) states that employees’ job satisfaction is one of the important aspects needing paying attention to increase human resource capability in an organisation, because through the job satisfaction employees can work optimally; so can production workers. To make those working in production field work more productively to the expected target the company should consider its workers’ job satisfaction. In another word when the production workers gain a job satisfaction they shall gain maximum production result as targetted by the company.
Generally a job satisfaction is influenced by several factors such as leadership style and job stress. This statement is supported by Fang’s finding (2009)stating that leadership style is an important topic in management study as it has significant impact on employees’ job perfromance and job satisfaction, which is also closely related to the success or failure of an oreganisation. Several experts’ finding also shows that participative leadership is also found to be positivelu related to employees’job satisfaction (Jamal & Xie, as cited in Huang et al.,2006; Drucker, Lickjert, Daley, &Bernstein, as cited in Kim, 2002). Then this finding is supported ny the statement which says that participation has an effect on both satisfaction and productivity but participation anad productivity strongly influence pon satisfaction rather than productivity (Miller & Monge, in Magsood, S, et all, 2006). Meanwhile Magsood , S. Et all (2013) also finds that in our study we focussed on three emerging leaqdership styles among various styles i.e participative, bureaucratic and directive. It has been ascertained out
In another chance , there is a statement saying that job satisfaction is influenced by job stress. The research results supporting this statement as done by Alberto (1995), and Praptini (200) shows that factors influencing job satisfaction, one of which is job stress, Asyidatur’s research result (in Dhama, 2009) also shows that a change variation occuring in satisfaction variable is influienced by job stress. Psychological tension and social support from the leader. He also says that the behaviour styles like job stress relate with the job satisfaction among the employees working in a formal sector. Then, Robbins (2003) says that the impact of job stress shall cause a psychological symptom. Besides that, stress caused by a job can cause a satisfaction or unsatisfaction in the job itself. On tyhe contrary Cooper Roden (1985) having done a research on the tax employees found signs of stress symptoms like experiencing a
quick heart beat level and headache .
This job satisfaction can also be related with psychological effect felt when job stress appears. This means that if job stress increases and followed by tension feeling , the job satisfaction will decrease (Brief et all., 1981). This statement is upported by Henry’s finding (2007) who says that there is a negative and significant relation between job stress and job satisfaction. It means if the employees’ job stress is high it shall result in employees’ job satisfaction to decrease. Another finding showing that the job stress influences the job satisfaction has been found by Sullivan and Bhagat, (1992), and Fraser (in Leila, 2002; Brewer & Landers, 2003, & Anitawidanti, 2010). Besides that , there are several researches showing that thye cause of high stress and low job satisfaction simultanuously indicates there is a tiredness in job. This finding is supported by (Ahmadi and Alireza, 2007, Ahsan, Abdullah & Young Gun Fie, 2009).
Baased on the explaination of phenomena and result of the research found by the former researchers the writer is interested in doing a research through quantitative approach on whether both factors, participative leadership and job stress, shall give an influence simultanuously on production workers’ job satisfaction in the company located in Central Java ? The problem formulations which would be tested and found answers are: Are participative leadership and work stress a predictor to the production workers’ job satisfaction in the Central Java company ?
RESEARCH METHOD a. Research Subject
The research subject was found from the production section of the private company in Central Java. We found 93 respondents consisting men and women with education level from high school up to university. Subject choice was chosen randomly in choosing research subject. 120 questionnaires were shared to the production workers , but only 93 questionnaires returned. Only 93 people were used for the interest of the research.
b. Research Measure Tool
The measure scale of participative leadership style in this research was designed to 3main features of partyicipative leadership style of Newstorm and Davis (1993) namely: mental and emotional complicity , motivation to contributing and responsibility acceptance. Under the writer’s guide Khahita (2011) formulated the measure scale of participative leadership style of Newstorm and Davis into several indicators arranged into 30 items in Likert scale. This scale was used together by Khahita and Wijono (2013) in a different research.
The research tool used to measure job stress is questionnaires which consist of 15 items, arranged by Wolfe, Quinn, Snoek and Rosenthal (1964)well-known as Job Related Tension Index. This tool has been translated into Malaysian langusge and used by Lem Boon (1983), Hasan (1992), and Mustyhapa (1994)with Back Translation technique. The items of the job stress questionnaires have been modified into Indoinesian language by the writer for the interest of this investigation. The choices given to the subject are 5 possibilities of answers. They are never, seldom,
sometimes, rather often and often.
Thelast but not least is the measure tool in form of questionnaires about job
Experiment Results of Validity and Reliability on the Measure Tool
Validity and reliability of every measure tool based on cronbach alpha on the significancy level of 5% with N=93, are as follows:
1) Participative Leadership
Correlation Coefficient Values on the items of the style measure scale on the participative leadership are about 0,318 and 0,632. Of 30 items after being analized 7 items failed. They were 1, 11, 13, 14, 18, 24, and 26. After rearranging only 23 items of participative leadership scale were considered valid with the score above
0,03. Then the experiment result of the statistical analisis on the participative leadershipship measure tool was with the formulation cronbach alpha resulting in
reliability score 0,823. 2) Job stress
Correlation Coefficient of the job stress measure ranges from 0,333 and 0,589. From 15 items after analization 2 items failed namely no. 6 and 11. After the two failed items were thrown away , then analized again and with the score was above 0,03. This means the items in this scale were considered valid. The job stress measure tool from the result of the
statistical analisys with the formulation cronbach alpha was gained reliability score 0,828.
3) Jo b satisfaction
The measure correlation coofficient on the job satisfaction ranges from 302 upto 602. The experiment on the validity and reliability was found that of 18 items 6 items of job satisfaction failed namely no. 3, 4, 8, 10, 13 and 18. After remanaging 12 items were stated valid with the score above 0,30. The statistical experiment result on the job satisfaction using cronbach alpha was gained reliability score 0,808.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
1.Result of Experiment on Multiple Regressison
Description of the hypothesis experiment result shows that participative leadership and job stress become a predictor to the job satisfaction of production workers. Therefore this
hypothesis is proved to be accepted. This is as in tables 1, 2 and 3 as follows:
Table 1
Correlation between Participative leadership style and job stress to job satisfaction
Model R R Square
Adjusted R Square
Std. Error of the
Estimate Durbin-Watson
1 .519a .269 .253 4.692 1.950
a. Predictors: (Constant), Participative leadership style, Job stress b. Dependent Variable: Job satisfaction.
Value R = 0,519 on the above table showed a correlation between tha participative leadership and job stress simultanuously become a pedictor to the job satisfaction with determinate coefficient (R ) 0,269 ( note: determination coefficient used to know the percentage of the free variable influences to tied variable changes). Therefore it can be concluded that the influence of participative leadership variable and job stress become a prodictor simultanuously to variable Y2 (job satisfaction)and is 26,9% while the rest 73,1% is influenced by the other variable.The standard of estimation error is 4,692. This is caused by both variables which are influencial simultanuously and become a prodictor to the workers job satisfaction .
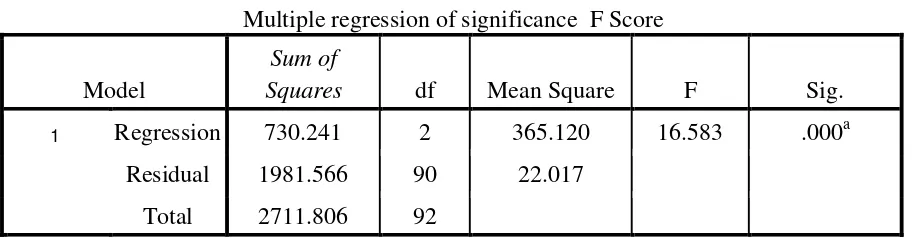
Table 2.
Multiple regression of significance F Score
Model
Sum of
Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
1 Regression 730.241 2 365.120 16.583 .000a
Residual 1981.566 90 22.017
Total 2711.806 92
a. Predictors: (Constant), Participative leadership, job stress_ b. Dependent Variable: Job satisfaction
Based on the table Anova it was found out value F counting 16.583 with df1 ( countifyer
[image:6.595.71.528.463.582.2]leadereship and job stress simultanuously influencial as a predictor to the workers’ job satisfactio in the production section is accepte.
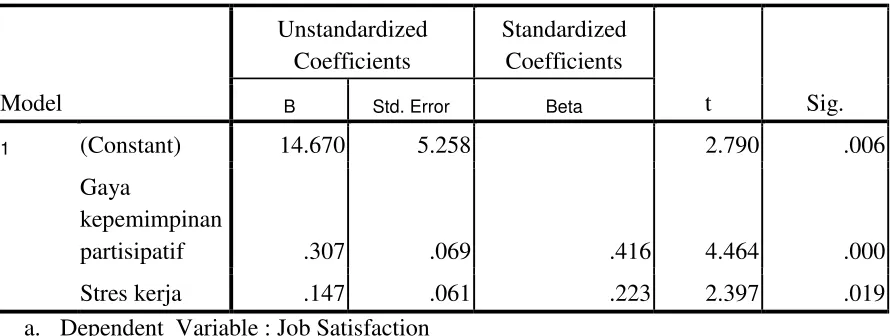
Table 3.
The effects of Participative leadership and Job stress to Job satisfaction
Model
Unstandardized Coefficients
Standardized Coefficients
t Sig.
B Std. Error Beta
1 (Constant) 14.670 5.258 2.790 .006
Gaya
kepemimpinan
partisipatif .307 .069
.416
4.464
.000
Stres kerja .147 .061 .223 2.397 .019
a. Dependent Variable : Job Satisfaction
Similarity of linier regression resulted from this analysis is as follow:
Y1 = +14,670+0.307x1-0.147x2
When the research was viewed partially, it was found out that the t test value to the participative leadership was 4,464 (significance), job stress was 2.397 (significance), so individually X1 was influential to the change Y1, and also X2 was influential to the change Y1.
2. Discussion
variation happening in the variable of job satisfaction is influenced by job stress, psychological tension and social support from their leaderes.
Yet the result of the research partially is found that there is a significant influence to the participative leadership on a job satisfaction (t test = 4,464; p<0,05). This means that the participative leadership variable has a role to the cause of variable change on job satisfaction. There are possibilities that the participative leadership variable is influential to the job satisfaction , such as : first, the production workers have accepted the participative leadership style well that they feel happy with it and thus is positively influencial to their job satisfaction. The result of the finding is opposite with Rahman’s (2012) finding the different thing that there is no a significant relationship between leadership participation and job satisfaction. Second, every worker has been able to adapt himself with the participative leadership styles of his leaders that they can experience a higher job satisfaction than their job productivity they achieve. This is supported by the finding result saying that participation has effect on both satisfaction and productivity but participation strongly influences on satisfaction rather than productivity (miller & Monge, in Magsood, S. Et all, 2006)
Partially this research has also found out that there is an effect of the job stress on the workers’ job satisfaction (t test = 2,397; p<0,05). There are several other findings showing that job stress influences job satisfaction. This statement is stated by Sullivan and Bhagat (1992). The say that there are research results showing that job stress is influencial on job satisfaction in an organisation. In one event Farber (1983) found that stress arose due to unification of famili and professional life like military pilot such as relationship with wife, communication with children, family interaction , financial management, family conflict, friends, and marriage between couples can cause a highest stress in pilot family group and influence so much on their job satisfaction.Besides that job stress continuously shall disturb or hamper individual’s achievement and capability to work and this shall influence his job satisfaction. Then Ismael, Yao and Yunus (2009) in their research to 80 employees in Klang city , Malaysia. They found that job stress (fisiologycally and psychologically) had a positive signnificant correlation with the workers’ job satisfaction. The result of the same finding was also found by Gole (2008) and Lee (2008). This research result was also supported with the
finding of pustaka research by Fairbrother and Warn, (1993); Stacciarini, (2004), and Guleryuz et all, (2008) showed that job stress was influencial on job satisfaction.
Conclusion
Both of the variables , participative leaqdership and job stress , partially give effect on the production workers’ job satisfaction . Generally this research found that the participative leadership and job stress partially can also be called important variables in influencing job satisfaction of the workers. Therefore either participative leadership or job stress can become variable influencial partially on the job satisfaction in this research. Besides that it can be said that both of the variables , participative leadership and job stress, simultanuously still can be a predictor to the production workers’ job satisfaction. Perhaps other factors such as personality , locus of control, job climate, and organisation culture can still be considered as a free variable and moderator to the workers’ job satisfaction.
Suggestions
Management Field
Management party is supposed to be aware that both of the variables namely participative leadership and job stress are supposed to be prodictor to the workers’ job satisfaction in the company. Therefore anticipative steps need implementing as follows :
1) The leaders are expected to participate in doing tasks with their subordinates. This thing is important to do that management participates actively in controlling moderate job stress through various ways such as simulation or making a competitive competition with a moderate stress level
2) Giving a participative leadership training to supervisors and their subordinatesto be able to create a conducive atmosphere in facing a competition with a moderate stress level in order to achieve a job satisfaction.
Research Field
2) The research about the job satisfaction is suggested to use more samples especially among executives in service or manufacturing company organization. But we need to consider demography factors such as city area by considering genders, education levels and age.
DAFTAR PUSTAKA
Ahmadi, K. & Alireza, K. (2007). Stress and job satisfaction among air force military pilots. Journal of Social Sciences. 3, (3), 159-163.
Ahsan, N; Abdullah, Z; Young Gun Fie, D., & Alam, S.S. (2009). A study of job stress on job satisfaction among university staff in Malaysia: empirical study. European Journal of Social Sciences. 8, (1).
Alberto. (1995). A comparison of organizational structure, job stress, and satisfaction in audit and management. All Bussiness
Anitawidanti, H. ( 2010). Hubungan stres kerja dengan kepuasan kerja karyawan berdasarkan gender. Studi pada PT Transindo Surya Sarana Semarang. Skripsi. Semarang: Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Diponegoro.
Brewer, E. and Landers, J. Mc. (2003). The Relationship Between Job Stress and Job Satisfaction Among Industrial and Technical Teacher Educators. E-Journals JVER. 28, (2), 37-50
Brief, A.P., Schuler, R.S., & Sell, M.V. (1981). Managing job stress. Boston: Litle, Brown and Company.
Cooper, C.L. & Roden, J. (1985). Mental health and satisfaction among tax officers. Social Science and Medicine, 21, (3), 741-751.
Dhania, D.R. (2009). Pengaruh beban kerja dan stress kerja terhadap kepuasan kerja. (studi pada medical representative di kota Kudus). Tesis. Salati ga: Program Pascasarjana. Universitas Kristen satya Wacana.
Fang, Y. W. (2009). The relationship between leadership styles and foreign English teachers job satisfaction in adult English cram schools: Evidences inTaiwan. The Journal of American Academy of Business, Cambridge, 14 (2), 75-82. Retrieved August 5, 2010, from ProQuest database.
Farber, BA, (1983), Stress and Burnout in the Human Service Professions, Pergamon Press, Inc. USA
Fairbrother, K,, & Warn, J. (1993). Workplace dimention, stress & job satisfaction. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 18, (1), 8-21.
Guleryuz, K., Guney, S., Aydin, F.M., & Asan, O. (2008). The mediating effect of job satisfaction between emotional intelligence and organizational commitment of nurses, a queationnaire survey. Internasional Journal of Nursing studies, 45, 11,1625-1635.
Hasan, S.A. (1992). Tekanan kerja dan hubungannya dengan kepuasan kerja dan kekerapan merokok di kalangan pekerja. Latihan Ilmiah. Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia.
Henny. (2007). Hubungan stres kerja dan kepuasan kerja karyawan bagian customer care pada PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia Tbk Bekasi. Skripsi. Bogor: Fakultas Ekonomi dan Manajemen. Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Huang, X., Shi, K., Zhang, Z., & Cheung, Y. L. (2006). The impact of participative leadership behavior on psychological empowerment and organizational commitment in Chinese state-owned enterprises: the moderating role of organizational tenure. Asia Pacific J Manage, 23, 345-367. Retrieved August 24, 2010, from ProQuest database.
Herzberg, F., Mausner, B, dan Snyderman, B. (1959). The Motivation to Work. New York: John Wiley & Sons.Inc.
Ismail, A., Yao, A. & Yunus, N.K.Y. (2009). Relationship between occupational stress and job satisfaction: an empirical study in Malaysia. The Romanian Economic Journal. 4 : Year XII, 34.
Ivancevich, J.M., Matteson, M.T., dan Preston. (1982). Occupational stress, type A a behavior, and psychological well being. Academy of Management Journal. 25, 2, 373-391.
Khatika, O. (2011). Gaya kepemimpinan partisipatif dan produktivitas kerja di P.T. Garudafood Putra Putri Jaya. Skripsi. Salatiga: Fakultas Psikologi. Universitas Kristen Satya Wacana.
Kim, S. H. (2002). Participative management and job satisfaction: Lessons for management leadership. Public Administrative Review, 62(2), 231-241. Retrieved August 10, 2010, from EBSCOhost database.
Leila, G. (2002). Stres dan Kepuasan Kerja. Jurnal USU Digital Library.
Lem Boon. (1983). Hubungan di antara tekanan kerja, kepuasan kerja dan prestasi kerja di kalangan pekerja-pekerja di sebuah syarikat tempatan. Latihan ilmiah. Universitati Kebangsaan Malaysia.
Maqsood, S., Bilal, H., Nazir, S., & Baig, R. (2013). Manager’s leadership styles and employee’s job satisfaction. Human and Social Science Research. 1 (2), 139-144. Journal webpage: http://www.oricpub.com/hssr-journal
Ilmiah. Bangi: Jabatan Psikologi Fakulti Sains Kemasyarakatan dan Kemanusiaan. Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia.
Newstrom, J.M. & Davis, K., (1993). (Ninth Ed). Organizational behavior: Human behavior at work. McGraw-Hill Inc.
Praptini. (2000). Pengarus stress kerja terhadap kepuasan kerja tenaga edukatif tetap fakultas ilmu social. Skripsi. Surabaya: Airlangga University library.
Rad, A.M.M., Yarmohammadian, M.H.,“A Study of Relationship between Managers’ Leadership Style and Employees’ Job Satisfaction”, Leadership in Health Service,. 19 (2), 11-28.
Robbins, S.P. (2001). Organizational Behavior. Second Ed. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall International.
Robbins, S.P. (2003). Perilaku Organisasi. Jilid 2. PT Indeks. Jakarta.
Stacciarini, J.M.R. (2004). Occupational stress and constructive thingking, health and job satisfaction. Journal of Advanced Nurcing, 46 (5), 480-487.
Sullivan, R. Bhagat. (1992). Organizational stress, job satisfaction, and job performance. www.google.com.
.Wagner III, J.A. & Hollenbeck, J.R. (1995). Management of Organizational Behavior. Second Ed. New Jersey: Englewood Cliffs, Prentice Hall.
Wijono, S. (2011). Stres kerja di balik makna dan dampaknya dalam organisasi. Pidato pengukuhan guru besar psikologi UKSW. Di Salatiga, 7 Oktober 2011.
Wijono, S. (2011). Stres kerja dan ketegangan psikologis sebagai prediktor terhadap kepuasan kerja karyawan. Jurnal Fakultas Psikologi NOETIC, 1 (3), 178-194. Salatiga: Universitas Kristen Krida Wacana.