Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Philip J. Pratt
- Mary Z. Last
- Sekolah: Grand Valley State University
- Mata Pelajaran: Database Management
- Topik: Concepts of Database Management
- Tipe: textbook
- Tahun: 2014
- Kota: Boston
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction to Database Management
This chapter introduces the foundational concepts of database management, including the essential terminology and the advantages and disadvantages of using database management systems (DBMS). It sets the stage for understanding the role of databases in modern organizations by examining the case of TAL Distributors, a company transitioning from spreadsheet management to a more robust database system. The chapter emphasizes the importance of data organization and retrieval efficiency, which are crucial for effective decision-making in businesses.
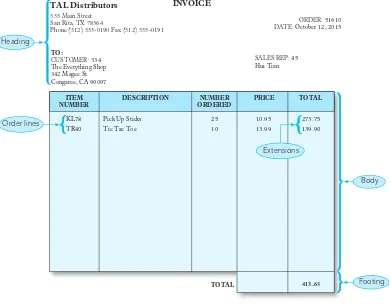
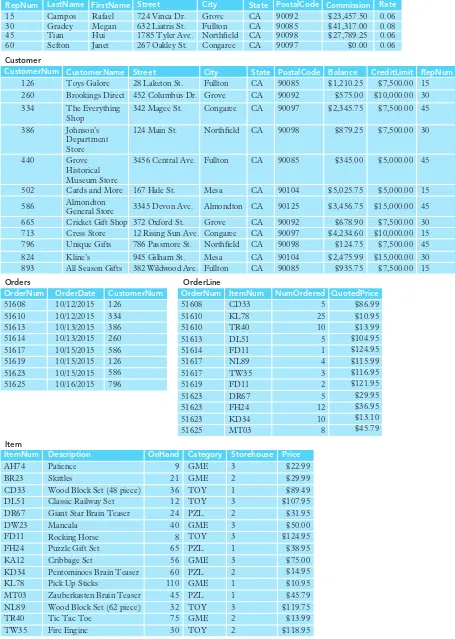
1.1 TAL Distributors Background
TAL Distributors serves as a case study to illustrate the challenges faced by organizations relying on spreadsheets for data management. The chapter outlines the limitations of spreadsheets, such as data redundancy and difficulty in accessing related information, highlighting the need for a more structured approach to data management. This section emphasizes how the growth of TAL Distributors necessitated the transition to a database system to enhance data integrity and operational efficiency.
1.2 Database Background
The section provides a definition of a database, explaining its structure and the types of information it can store. It introduces key database concepts such as entities, attributes, and relationships, which are fundamental for understanding how databases function. This background sets the foundation for later discussions on database design and management, illustrating the critical role that databases play in organizing and relating different categories of information.
1.3 Database Management Systems
This subsection discusses the various types of database management systems available, their functionalities, and the significance of selecting the appropriate DBMS for an organization. It highlights the features that a robust DBMS should offer, including data integrity, security, and support for concurrent access. Understanding these elements is crucial for students as they prepare to work with databases in real-world scenarios.
1.4 Advantages of Database Processing
The advantages of database processing are explored in detail, focusing on benefits such as reduced data redundancy, improved data integrity, and enhanced data sharing capabilities. The chapter emphasizes how databases facilitate better decision-making by providing accurate and timely information, which is vital for business operations. This understanding is essential for students to appreciate the value of database systems in organizational contexts.
1.5 Disadvantages of Database Processing
In this section, the potential drawbacks of database processing are examined, including the complexity of database systems, the cost of implementation, and the necessity for skilled personnel. By addressing these challenges, students gain a balanced view of database management, preparing them for practical considerations they may encounter in their future careers.
1.6 Introduction to Database Cases
The chapter concludes by introducing two additional case studies: Colonial Adventure Tours and Solmaris Condominium Group. These cases are utilized throughout the text to reinforce learning by providing practical examples of database management concepts in action. This approach helps students connect theoretical knowledge with real-world applications, enhancing their understanding of database systems.
II. The Relational Model: Introduction, QBE, and Relational Algebra
This chapter delves into the relational model, a foundational concept in database management. It introduces Query-By-Example (QBE) and relational algebra, which are essential for manipulating data within relational databases. By understanding these concepts, students learn how to formulate queries and retrieve data effectively, which is a crucial skill in database management.
2.1 Relational Databases
The section explains the structure of relational databases, emphasizing the organization of data into tables and the relationships between them. It details how data is stored in rows and columns, enabling efficient data retrieval and manipulation. This foundational knowledge is critical for students as they learn to design and implement relational databases.
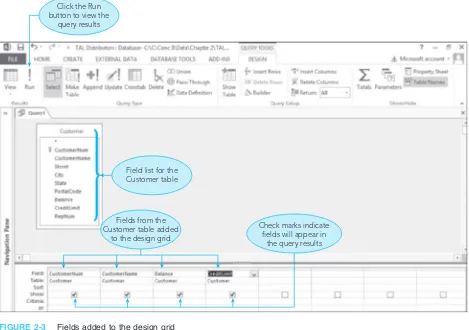
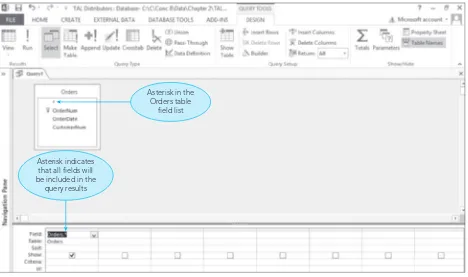
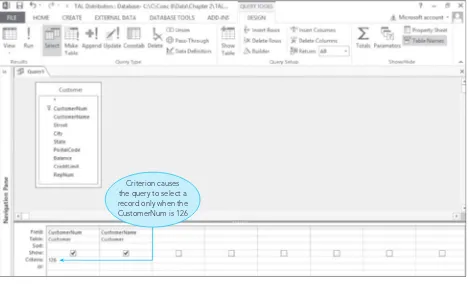
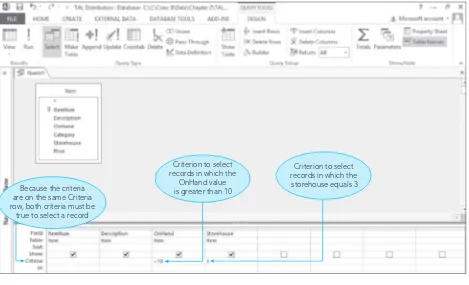
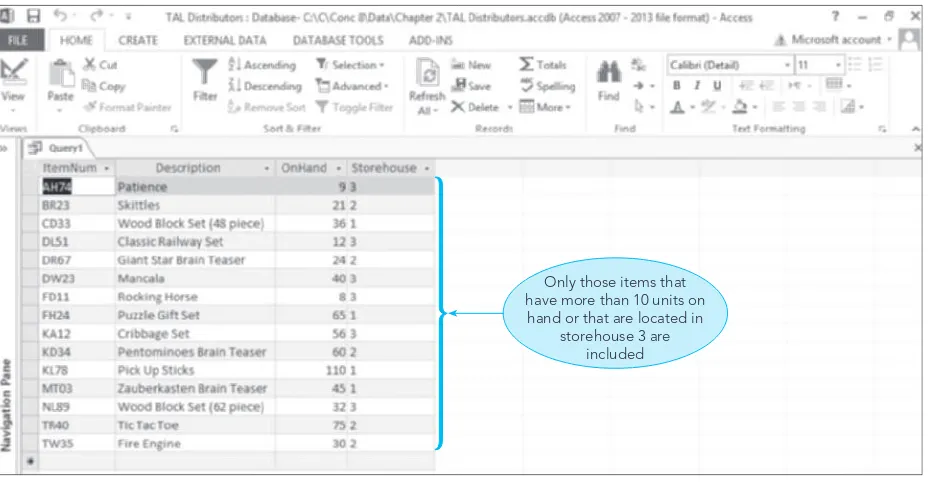
2.2 Query-By-Example (QBE)
QBE is introduced as a user-friendly method for querying databases. The chapter provides examples of simple and compound queries, illustrating how users can extract specific information without needing to write complex SQL statements. This approach enhances accessibility for students who may not have a programming background, making database management more approachable.
2.3 Simple Queries
This subsection focuses on constructing simple queries using QBE. It includes practical exercises that allow students to practice retrieving data based on specific criteria, reinforcing their understanding of how to interact with databases effectively.
2.4 Advanced Query Techniques
The chapter progresses to more advanced query techniques, including computed fields, grouping, and sorting data. These concepts are crucial for students to master as they prepare for more complex database interactions and data analysis tasks.
2.5 Relational Algebra
The introduction of relational algebra provides students with a theoretical framework for understanding database operations. It covers fundamental operations such as selection, projection, and join, which are essential for manipulating and retrieving data from relational databases. This theoretical grounding is important for students as they advance in their studies.
III. The Relational Model: SQL
This chapter is dedicated to Structured Query Language (SQL), the standard language for interacting with relational databases. It covers the syntax and structure of SQL commands, enabling students to perform various database operations, including data retrieval, insertion, updating, and deletion.
3.1 SQL Basics
The section introduces the basic syntax of SQL, focusing on essential commands such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. Understanding these commands is fundamental for students as they learn to manipulate data within a database.
3.2 Advanced SQL Queries
Building on the basics, this subsection explores advanced SQL queries, including the use of joins, subqueries, and aggregate functions. These concepts are critical for students to master as they prepare for real-world database management tasks.
3.3 SQL Functions
The chapter discusses built-in SQL functions that enhance data manipulation capabilities. Students learn how to use functions for calculations and data transformations, which are essential skills in database management.
3.4 SQL Data Manipulation
This section focuses on data manipulation techniques using SQL, including how to update and delete records. Practical exercises reinforce learning, allowing students to apply their knowledge in hands-on scenarios.
3.5 SQL Best Practices
The chapter concludes with best practices for writing efficient SQL queries. Emphasizing the importance of performance and optimization, this section prepares students to write effective queries that minimize resource usage.
IV. The Relational Model: Advanced Topics
This chapter covers advanced topics in the relational model, including views, indexes, and integrity rules. Understanding these concepts is essential for students as they learn to design and manage complex databases.
4.1 Views
The section explains the concept of views in databases, highlighting their benefits for data security and abstraction. Students learn how to create and manage views, which are essential for controlling data access.
4.2 Indexes
Indexes are discussed as a means to improve database performance. The chapter covers how to create and utilize indexes effectively, preparing students to optimize data retrieval processes.
4.3 Security and Integrity
This subsection focuses on database security measures and integrity rules, including entity and referential integrity. Students learn the importance of maintaining data accuracy and consistency, which are critical for effective database management.
4.4 Advanced Database Features
The chapter concludes with a discussion of advanced features such as stored procedures and triggers. These concepts enhance students' understanding of how to implement complex logic and automate tasks within a database.
V. Database Design: Normalization
This chapter introduces the process of normalization, a critical step in database design that ensures data integrity and minimizes redundancy. Students learn the different normal forms and how to apply them to their database designs.
5.1 Functional Dependence
The section explains the concept of functional dependence, which is foundational for understanding normalization. Students learn how to identify functional dependencies in their data models.
5.2 Normal Forms
This subsection covers the various normal forms, including first, second, and third normal forms. Students learn how to transform unnormalized tables into normalized forms, reducing redundancy and improving data integrity.
5.3 Common Normalization Errors
The chapter discusses common errors encountered during the normalization process, providing students with strategies to avoid these pitfalls in their database designs.
5.4 Application to Database Design
Students are guided on how to apply normalization principles to real-world database design scenarios, reinforcing their understanding through practical examples.
VI. Database Design: Design Method
This chapter outlines a systematic approach to database design, incorporating user views and entity-relationship diagrams. Students learn how to gather requirements and model their databases effectively.
6.1 User Views
The section emphasizes the importance of understanding user requirements and perspectives in the design process. Students learn how to incorporate user views into their database designs.
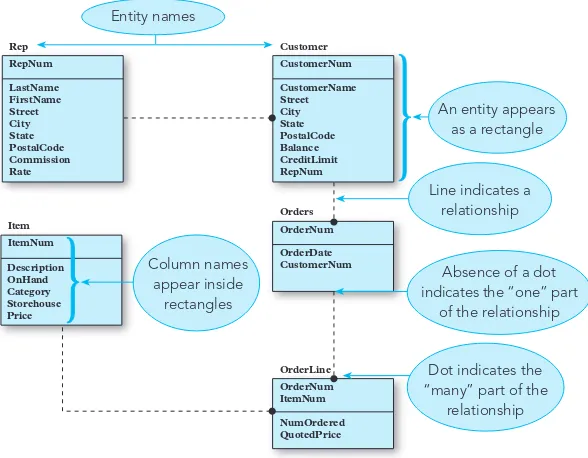
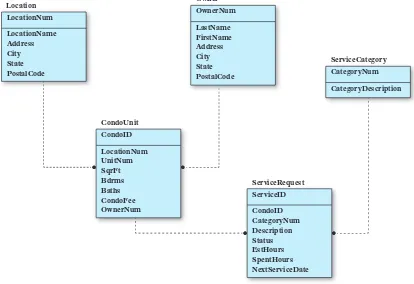
6.2 Entity-Relationship Diagrams
Entity-relationship diagrams are introduced as a tool for visualizing database structures. Students learn how to create and interpret these diagrams, which are essential for effective database design.
6.3 Database Design Language (DBDL)
This subsection covers the use of Database Design Language (DBDL) in documenting database designs. Students learn how to communicate their design intentions clearly.
6.4 Physical-Level Design
The chapter concludes with a discussion of physical-level design considerations, preparing students to translate their logical designs into practical implementations.
VII. DBMS Functions
This chapter explores the various functions provided by database management systems, including data updating, retrieval, and security services. Students gain insight into how DBMSs facilitate efficient data management.
7.1 Data Update and Retrieval
The section discusses how DBMSs support data updating and retrieval processes, highlighting the importance of efficiency and accuracy in these operations.
7.2 Catalog Services
This subsection covers catalog services provided by DBMSs, which help manage metadata and facilitate data access. Students learn the significance of catalogs in database management.
7.3 Security Services
The chapter focuses on security features within DBMSs, emphasizing the importance of data protection and user authentication. Students learn about various security measures that can be implemented.
7.4 Data Integrity Features
Students explore the integrity features of DBMSs, including constraints and validation rules that help maintain data accuracy and consistency.
VIII. Database Administration
This chapter addresses the critical role of database administration, covering topics such as policy formulation, access privileges, and disaster planning. Students learn the responsibilities of a database administrator and the importance of effective database management.
8.1 Database Policy Formulation
The section discusses the formulation and enforcement of database policies, emphasizing the need for clear guidelines to govern database usage and security.
8.2 Access Privileges
This subsection focuses on managing access privileges within a database, highlighting the importance of restricting access to sensitive data and ensuring compliance with security protocols.
8.3 Disaster Planning
The chapter covers disaster planning strategies, preparing students to implement measures that protect data integrity and availability in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
8.4 DBMS Evaluation and Selection
Students learn about the process of evaluating and selecting a database management system, considering factors such as functionality, scalability, and cost.
IX. Database Management Approaches
This chapter provides an overview of various database management approaches, including distributed databases, client/server systems, and object-oriented databases. Students gain exposure to advanced topics that are increasingly relevant in the field of database management.
9.1 Distributed Databases
The section discusses the characteristics and advantages of distributed databases, preparing students to understand how data can be managed across multiple locations.
9.2 Client/Server Systems
This subsection explores client/server architectures, highlighting the benefits of this approach for database management and application development.
9.3 Data Warehouses
Students learn about data warehouses and their role in data analysis and reporting, emphasizing the importance of effective data management strategies for decision support.
9.4 Object-Oriented DBMSs
The chapter concludes with an introduction to object-oriented database management systems, providing students with insights into this evolving area of database technology.