MEMAHAMI PROBLEM
KUALITAS AIR SUNGAI
Ir. Moh Sholichin, MT. Ph.D
Tanaman wetland di
tepian sg Pasig
Di
Konsep Utama
Tipe pencemar, sumber pencemaran, efek dari
pencemaran air thd kesehatan.
Problem 2 utama pencemaran air permukaan
Problem 2 utama pencemaran air tanah
Pengurangan dan Pencegahan Pencemaran Air
Air adalah
kehidupan
1. Point Source Pollution (PSP)
(Sumber Pencemaran titik )
2. Nonpoint Source Pollution (NPSP)
(
Sumber Pencemaran bukan titik/ menyebar)2 Tipe Utama
Sumber Pencemaran : Titik
Berasal dari sumber yg pasti, seperti pipa
pembuangan
Pabrik, kawasan
industri, Kawasan IPAL
Sumber pencemaran: Bukan-titik
Nonpoint Source (NPS) Pollution adalah
pencemaran yang terbawa melalui air limpasan hujan.
NPS tidak dapat di
Contoh-contoh NPS
oil & grease from cars
fertilizers
animal waste
grass clippings
septic systems
sewage & cleaners from
boats
Mekanisme Transpor Polutan
• NPS pollutants berlangsung selama musim kemarau
Atmospheric deposition
Pemakaian pupuk kimia
Kotoran hewan/peternakan
Tumpahan minyak
Sumber Pollutant terjadi dan mengalir
bergantung pada land use.
Imperviousness increases runoff
Keterkaitan Landuse dengan Kualitas Air
Apa itu Penutup Kedap Air?
Jalan raya
Atap rumah
Parking Area
Cor beton
Penutup kedap air
• Menyebabkan adanya akumulasi polutan
menyebabkan
peningkatan limpasan tercemar dan banjir
Dampak pencemaran Sumber Bukan-titik
fish and wildlife
recreational
water activities
commercial
fishing
tourism
drinking water
Muatan Polutan dalam Runoff
Sediment
Soil particles
transported from their source
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
● Oxygen depleting material
Leaves
Organic material Toxics
● Pesticides
Herbicides
Fungicides
Insecticides
● Metals (naturally occurring in soil, automotive emissions/ tires)
Lead
Zinc
Mercury
● Petroleum Hydrocarbons (automotive exhaust and fuel/oil)
Debris
Litter and illegal dumping
Nutrients
● Various types of materials that
become dissolved and suspended in water (commonly found in fertilizer and plant material):
Nitrogen (N)
Phosphorus (P)
Bacteria/ Pathogens Originating from:
● Pets
● Waterfowl
● Failing septic systems
Sumber Polutan di Kawasan Permukiman
Nutrients: Fertilizers and septic systems
Pathogens: Pet waste and septic systems
Sediment: Construction, road sand, soil erosion
Toxic: Pesticides, household products
Debris: Litter and illegal dumping
Polutan dari pertanian
Sediment
Nutrients
Pathogens
Polutan Penting
Sediment reduces light penetration in stream, clogs gills of fish and aquatic invertebrates.
Nutrients act as fertilizer for algae & aquatic plants which can cause highly varying dissolved oxygen levels. At low DO levels, the aquatic life has the
potential to be harmed.
Toxics can impact life and contaminate drinking water supplies.
Apa Pencemaran Air?
PP 82 2001.
Pencemaran air yaitu
Apa pencemaran air?
WHO:
•
3.4 million premature
deaths each year from
waterborne diseases
•
1.9 million from
diarrhea
•
U.S. 1.5 million
illnesses
Apa pencemaran air?
Infectious Agents: bacteria and viruses often
from animal wastes
Oxygen Demanding Wastes: organic waste that
needs oxygen often from animal waste, paper
mills and food processing.
Inorganic Chemicals: Acids and toxic chemicals
often from runoff, industries and household
Apa pencemaran air?
Organic Chemicals: oil, gasoline, plastics, detergents
often from surface runoff, industries and cleaners
Plant Nutrients: water soluble nitrates, ammonia and
phosphates often from sewage, agriculture and urban
fertilizers
Sediment: soils and silts from land erosion can disrupt
photosynthesis, destroy spawning grounds, clog
rivers and streams
Bagaimana Kualitas Air?
Bacterial Counts: Fecal coliform counts from intestines of animals
• None per 100 ml for drinking
• >200 per 100 ml for swimming
Sources: human sewage, animals, birds,
Bagaimana mengukur kualitas air?
Dissolved Oxygen: BOD Biological Oxygen
Demand…the amount of
oxygen consumed by aquatic decomposers
Chemical Analysis: looking for presence of inorganic or
organic chemicals
Bagaimana mengukur Kualitas air?
Indicator Species:
organisms that give an
idea of the health of the
water body.
Tipe, Efek dan Sumber Pencemaran Air
Point sources
Nonpoint sources
Sumber Pencemaran: Titik dan Bukan-Titik
NONPOINT SOURCES
Urban streets
Suburban development
Wastewater treatment plant
Rural homes
Cropland
Factory Animal feedlot
Sumber Pencemaran Air
Agriculture: by far the leader
• Sediment, fertilizers, bacteria from livestock, food processing, salt from soil irrigation Industrial: factories and
powerplants
Pencemaran Air Sungai
Flowing streams can recover from moderate level of degradable water pollution if their flows are not reduced.
• Natural biodegradation process
• Does not work if overloaded or stream flow reduced
Pencemaran Sungai
Kurva Kantong oksigen Faktor yang mempengaruhi recovery
Dua Dunia
Developed Countries
U.S. and other developed countries sharply reduced point sources even with population and economic growth
• Nonpoint still a problem
• Toxic chemicals still problem
Dua Dunia
Developing Countries:
Serious and growing problem
• Half of world’s 500 major
rivers heavily polluted
• Sewage treatment minimal $$$
• Law enforcement difficult
• 10% of sewage in China treated
Sungai Gangga India
• Holy River (1 million take daily holy dip)
• 350 million (1/3rd of pop) live
in watershed
• Little sewage treatment
• Used for bathing, drinking etc.
• Bodies (cremated or not) thrown in river
Pencemaran Danau Air Tawar
Dilution as a solution in lakes less effective
• Little vertical mixing
• Little water flow (flushing) Makes them more vulnerable
• Toxins settle
• Kill bottom life
• Atmospheric deposition
Biomagnifications of PCBs in an aquatic food chain
Eutrofikasi Danau
Eutrophication: nutrient enrichment of lakes mostly from runoff of plant nutrients (nitrates and phosphates)
• During hot dry weather can lead to algae blooms
• Decrease of photosynthesis
• Dying algae then drops DO levels
Pencemaran Danau
Eutrofikasi Danau
Penyelesaian masalah:
• Advanced sewage treatment (N, P)
• Household detergents
• Soil conservation
• Remove excess weed build up
Studi Kasus: The Great Lakes
•Pollution levels dropped, but long
AIR TANAH = Groundwater
•
Why is groundwater pollution a serious
problem?
•
What is the extent of the problem?
Groundwater
Groundwater DAPAT TERKONTAMINASI:
• No way to cleanse itself
• Little dilution and dispersion
• Out of sight pollution
• Prime source for irrigation and drinking
Pencemaran Groundwater
Low flow rates
Few bacteria
Cold temperatures
Coal strip mine runoff
Pumping well
Waste lagoon
Accidental spills
Groundwater flow
Confined aquifer Discharge
Leakage from faulty casing
Hazardous waste injection well Pesticides
Gasoline station
Buried gasoline and solvent tank
Sewer
Cesspool septic tank De-icing
road salt
Groundwater
• Pollution moves in plumes
• Soil, rocks, etc. act like sponge
• Cleansing does not
work (low O, low flow, cold)
Pencegahan
lebih efektif
Pencegahan Pencemaran Groundwater
Monitor aquifers
Leak detection systems
Strictly regulating hazardous waste disposal
Store hazardous materials above ground
Pencemaran Laut
•
Toleransi pencemaran laut
•
Coastal zones: How does pollution affect
coastal zones?
•
What are major sources of ocean
pollution and what is being done?
Pencemaran Laut
Oceans can disperse and
break down large
quantities of degradable
pollution if they are not
overloaded.
• Pollution worst near heavily populated coastal zones
• Wetlands, estuaries, coral reefs, mangrove swamps
• 40% of world’s pop. Live
Pencemaran Laut
• Large amounts of
untreated raw sewage (viruses)
• Leaking septic tanks
• Runoff
• Algae blooms from nutrients
• Dead zones NO DO
• Airborne toxins
Preventing and reducing the flow of pollution
from land and from streams emptying into the ocean is key
TUMPAHAN MINYAK
Sources: offshore wells, tankers, pipelines and storage
tanks
Effects: death of organisms, loss of animal insulation
and buoyancy, smothering
Significant economic impacts
Mechanical cleanup methods: skimmers and blotters
Pencegahan dan Reduksi
•
How can we reduce surface water
pollution: point and also nonpoint.
•
How do sewage treatment plants work?
•
How successful has the U.S. been at
Penyelesiaan: Mencegah dan Mereduksi
Pencemaran Air Permukaan
Nonpoint Sources
Point Sources
Reduce runoff
Buffer zone
vegetation
Reduce soil erosion
Clean Water Act
Water Quality Act
Sumber Pencemaran Nonpoint
Sumber Pencemaran Nonpoint
Sumber pencemaran Nonpoint
Sumber Pencemaran: Titik
Most developed countries
use laws to set water
pollution standards.
Federal Water Pollution
Control Act (Clean Water
Act 1972, ’77, ’87)
•
Regulates navigable
Peraturan Air Bersih
•
Sets standards for key
pollutants
•
Requires permits for
discharge
•
Requires sewage treatment
•
Require permits for
wetland destruction
•
Does not deal with
nonpoint sources well
Teknologi: Sistem Septic
Memerlukan tanah dan perawatan
•
¼ of all U.S. homes
have Septic tanks
•
Can be used in
Combined sewer
overflow is a
problem in many
older towns
•
EPA: 1.8 M to
3.85 M sick from
swimming in
water
contaminated by
sewer overflows
Pendekatan Teknologi: Pengolahan Air
Limbah
Primary: removes 60% of
solids and 30-40% oxygen
demanding wastes
(physically)
Secondary: uses biological
processes to remove up to
90% of biodegradables
Tertiary: advanced
techniques only used in 5%
of U.S. $$$$
Disinfection: chlorine,
ozone, UV
Technological Approach: Advanced
(Tertiary) Sewage Treatment
Uses physical and chemical processes
Removes nitrate and phosphate
Expensive
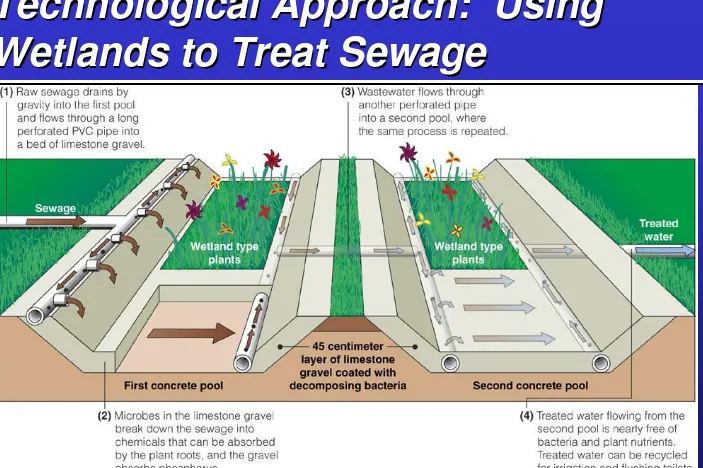
Technological Approach: Using
Wetlands to Treat Sewage
Berita Baik
Largely thanks to CWA: • Between 1972 – 2002
fishable and swimmable streams 36% to 60%
• 74% served by sewage treatment
• Wetlands loss dropped by 80%