International Journal of Agriculture. Photon 125 (2014) 285-289
https://sites.google.com/site/photonfoundationorganization/home/international-journal-of-agriculture Original Research Article. ISJN: 7758-2463
International Journal of Agriculture
Ph ton
The phospate soluble capability of Pseudomonas sp. and Bacillus sp.
as Superior Solubilizing Phospate Exogenous Bacteria (SPB) on
Andisols as tea planting area
Mieke Rochimi Setiawatia*, Eko Pranotob
a
Agricultural Faculty, Padjadjaran University (UNPAD), Bandung-West Java, Indonesia
b
Soil and Plant Nutrition Division Research Institute for Tea and Cinchona (RITC), Bandung, Indonesia
The authors receive Thomas Edison Award-2014 in Agriculture for Inspiration and Knowledge Distribution among young research scholars.
Article history:
Received: 03 January, 2014 Accepted: 10 January, 2014 Available online: 12 February, 2014
Keywords:
Andisols, exogenous, solubilizing phosphate bacteria, soluble-P, tea planting area
Corresponding Author:
Setiawati M.R.*
Email: miekesetiawati@yahoo.com Phone: +628122147664 2
Pranoto E.
Email: ekogambung@gmail.com Phone: +62225928780
Abstract
In Indonesia, tea was planted dominant on uplands area with 52-55% from the total area on Andisols as soil of tea planting area. The range of pH was 4,5 - 5,6 made high retention of phosphate was the main problem on tea plantation. The used of Superior Solubilizing Phosphate Exogenous Bacteria (SPB)
was one of the problem solving. Laboratory-scale experiments have been conducted to test the phosphate soluble capability from SPB on Andisols. The inoculant source of SPB from agricultural food plants with elevation 600 - 800 m above sea level. The strain that used were: Pseudomonas cepaceae, P. malei, Bacillus mycoides, and B. subtilis. The experiment was using a Completely
Randomized Design with six treatments and four repeated. The ANOVA’s analysis was not significant in increase the soluble-P. Even it, the treatment D (Bacillus mycoides) was the highest soluble-P. The capability from solubilizing phosphate bacteria to increase P-soluble depend on the pH of soil. Even
Pseudomonas cepaceae, P. malei, Bacillus mycoides, and B. subtilis were the superior
solubilizing phosphate bacteria on agricultural food plants soil, but they have not significantly different on Andisols. So, for the better results, may use the indigenous isolate.
Citation:
Setiawati M.R., Pranoto E., 2014. The phospate soluble capability of Pseudomonas sp. and Bacillus sp. as Superior Solubilizing Phospate Exogenous Bacteria (SPB) on Andisols as tea planting area. International Journal of Agriculture. Photon 125, 285-289.
1. Introduction
Andisols are soils formed in volcanic ash and defined as soils containing high proportions of glass and amorphous colloidal materials, including allophane, imogolite and ferrihydrite. In the FAO soil classification, Andisols are known as Andosols. Because they are generally quite young, Andisols typically are very fertile except in cases where phosphorus is easily fixed. They can usually support intensive cropping areas such as tea, coffee or tobacco.
Landforms in volcanic regions are strongly influenced by the chemical and mineralogical composition of the materials that were deposited during eruptive phases. Volcanic
their silica contents in three main categories
that are Rhyolite (65-75% SiO2), Andesite
(65-55% SiO2) and Basalt (55-45% SiO2). The
mineralogical properties and chemical
composition (notably the contents of K2O,
Na2O and CaO) distinguish individual rock
types. The mineral contents from Andisols
such are Allophane, Ferrihydrite, and
are amongst the most fertile lands in the world and are, therefore, very intensively cultivated, even if the users are aware of the risks of volcanic outbursts (Neall, 2009).
In Indonesia, tea was planted dominant on uplands area with 52-55% from the total area on Andisols as soil of tea planting area. Tea is one of the kind of beverage with 37% market
segment (Notohadiprawiro, 2006) and
contribute around Rp. 1.2 trillion on Gross Domestic Product (0.3% from total Gross Domestic Product non oil and natural gas on 2010 (Indonesia Agricultural Ministry, 2010).
Depend on observation at volcanic soils in Europe, that were from Italy, Portugal (Azores), Iceland, Spain (Tenerife) and France concluse that the decomposition kinetics that the proportion of C in added plant material that would be mineralized is greater for soil microbial communities at later stages of development than at earlier stages, and also the efficiency of leaf litter decomposition increases with soil development (Hopkins and
Bartoli, 2004). The use of phosphate
solubilizing bacteria as inoculants
simultaneously increases P uptake by the plant and crop yield. Strains from the genera Pseudomonas, Bacillus and Rhizobium are
among the most powerful phosphate
solubilizers. The principal mechanism for
mineral phosphate solubilization is the
production of organic acids, and acid phosphatases play a major role in the mineralization of organic phosphorous in soil (Rodriguez and Fraga, 1999).
Solubilizing Phosphate Bacteria can
increasing the phosphate solubilizing by phosphatase enzyme and organic acid as its secondary metabolite. The ability of a few soil microorganisms to convert insoluble forms of phosphorus to an accessible form is an important trait in plant growth-promoting bacteria for increasing plant yields. The use of phosphate solubilizing bacteria as inoculants increases the P uptake by plants. Arthrobacter sp. (CC-BC03) was the highest phosphate solubilizing strain bacteria to produce soluble-P in 5 g of tricalcium phosphate medium after 72 hours incubation, and then in succession are Serratia marcescens (CC-BC14), Delftia sp. BC21), Arthrobacter ureafaciens (CC-BC02), Chryseo-bacterium sp. (CC-BC05),
Bacillus megaterium (CC-BC10)
Phyllobacterium myrsinacearum (CC-BC19), Rhodococcus erythropolis (CC-BC11), and Gordonia sp. (CC-BC07) (Chen et al., 2006). The solubilizing bacteria were screened for
their capacity in solubilizing inorganic and mineralizing organic phosphate using modified NBRIP media in vitro. Most isolates were able
to solubilize Ca3(PO4)2 with various
solubilization index in the first screening. Secondary screening using P sources with lower pH, further grouped these bacteria into :
(a) solubilizing inorganic Ca3(PO4)2 with pH mineralizing both P sources: Roseateles sp. CK15, Rhizobium sp. CK19, Enterobacter sp. CK23, and Erwinia sp. CK24 (Sitepu et.al, 2013).
The objective of research was to obtain solubilizing phosphate bacteria as inoculants that increasing the P uptake by tea plants. By using a variety of bacteria that has been known as phosphate solubilizing superior from rhizosphere of various plants, it will get a good chance to get a solubilizing phosphate bacteria that suitable for tea plants grown in Andisols where could solve the problem from a high phosphate retention.
2. Experimental
2.1 Preparation of Inoculant
This experiment used Superior Solubilizing Phospate Exogenous Bacteria (SPB) Isolates
from Padjadjaran University (UNPAD)’s
collection. The inoculant source of SPB from agricultural food plants with elevation 600 - 800 m above sea level. The strain that used was: Pseudomonas cepaceae, P. malei, Bacillus mycoides, and B. subtilis. Each of bacteria multiplied on Pikovskaya liquid medium. After five days incubation, the population of SPB was variated. Before applied in Andisol as in-vitro test, the population was made same each other with dilution, shown on Table 1.
2.2 Experimental Design
The research was done on UNPAD laboratoy’s in 06° 55’ 32” S dan 107° 46’ 16” E in March 2013. This experiment used Completely Randomized Design with six treatments and four repeated. The statistic analyxe used was Analyze of Variants (ANOVA) with Duncan different test. The dose each treatment was10% v/w, its mean 10 ml inoculant per 100
Table 1: The population of Solubillizing Phosphate Bacteria Strain of BPF Total Population
(1012 cfu/ml) before dilution
Dilution Total Population
(1012 cfu/ml) after dilution
Dose of Inoculant (ml)
Steril Aquadest (ml)
Pseudomonas cepaceae 1.09 1.0000 0.0000 1.09
P. malei 1.23 0.8831 0.1169 1.09
Bacillus mycoides 1.18 0.9189 0.0811 1.09
B. subtilis 1.57 0.6939 0.3061 1.09
Negative control mean no inoculant, just only 100 g steril Andisols. The Positive control mean only gave 10 ml steril liquid Pikovskaya. Each treatment was incubated for 5 days. The arrangement treatments were:
A. Negative control B. Positive control
C. Pseudomonas cepacea D. Bacillus mycoides E. Bacillus subtilis F. Pseudomonas mallei
The responses are:
a. Soluble-P with Bray methode
b. The water content of Andisol with gravimetric method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1 Soluble-P
After 5 days incubation, the soluble-P each treatment was measured and the result shown
on Table 2. Even the ANOVA’s analysis was not significant, the the treatment D (Bacillus mycoides) was the highest soluble-P. Even the strain from genera of Pseudomonas and Bacillus were the most powerful phosphate
solubilizers, but the major source of
phosphatase activity in soil is considered to be of microbial origin (Garcia et al., 1992; Xu and Johnson, 1995). Its mean that even the isolates was superior, the activity was influential by the environmental aspect like pH of soil. In Indonesia, tea growth well on pH 4.5 - 5.6 (Widayat et al., 2006). The isolated strains were inoculated on tea rhizosphere in specific media containing tryptophan produce growth regulating substances such as indole acetic acid (IAA) under in-vitro conditions (Sharma et al., 2012). The phosphate solubilizing bacteria grew rapidly in the liquid medium at pH 5 and 7 but almost no growth occurred at pH 3 (Islam et al., 2007).
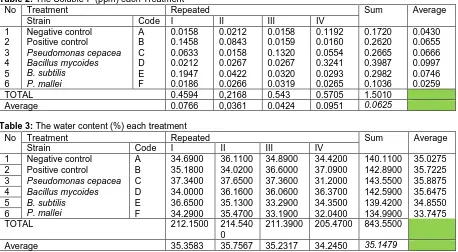
Table 2: The Soluble-P (ppm) each Treatment
No Treatment Repeated Sum Average
Strain Code I II III IV
1 Negative control A 0.0158 0.0212 0.0158 0.1192 0.1720 0.0430
2 Positive control B 0.1458 0.0843 0.0159 0.0160 0.2620 0.0655
3 Pseudomonas cepacea C 0.0633 0.0158 0.1320 0.0554 0.2665 0.0666
4 Bacillus mycoides D 0.0212 0.0267 0.0267 0.3241 0.3987 0.0997
5 B. subtilis E 0.1947 0.0422 0.0320 0.0293 0.2982 0.0746
6 P. mallei F 0.0186 0.0266 0.0319 0.0265 0.1036 0.0259
TOTAL 0.4594 0,2168 0.543 0.5705 1.5010
Average 0.0766 0,0361 0.0424 0.0951 0.0625
Table 3: The water content (%) each treatment
No Treatment Repeated Sum Average
Strain Code I II III IV
1 Negative control A 34.6900 36.1100 34.8900 34.4200 140.1100 35.0275 2 Positive control B 35.1800 34.0200 36.6000 37.0900 142.8900 35.7225
3 Pseudomonas cepacea C 37.3400 37.6500 37.3600 31.2000 143.5500 35.8875
4 Bacillus mycoides D 34.0000 36.1600 36.0600 36.3700 142.5900 35.6475
5 B. subtilis E 36.6500 35.1300 33.2900 34.3500 139.4200 34.8550
6 P. mallei F 34.2900 35.4700 33.1900 32.0400 134.9900 33.7475
TOTAL 212.1500 214.540
0
211.3900 205.4700 843.5500
Average 35.3583 35.7567 35.2317 34.2450 35.1479
3.2 Water Content
The average water content each treatment was 33 - 35%. Water content was measurable at the same times with soluble-P each treatment, that shown on Tabel 3.
solvent. A relatively low and uniform supply of water soluble phosphorus was maintained in some of the lime and avocado groves. Where this was done the trees were in excellent condition. While the trees showed no evidence of injury in areas of high water soluble phosphorus concentrations, they showed no benefit. On the average, the water soluble neutral, pH seems is the environment factor of Andisols that influence decreases the activity of PSB in phosphate solubilizing. Therefore it is recommended to use the PSB isolates derived from the tea plant Andisols. We expected the indigenous isolates not inhibited its activity on phosphate solubilizing because it has adapted to its environment.
4. Research Highlights
The main points in this research to know were: a. There are many microbes which can
increase the phosphate solubilizing by
phosphatase enzyme and organic acid as its secondary metabolite
b. Some microbes have an ideal condition to growth well and functioned. It’s better to used the superior microbe in each habitat
c. Bacillus mycoides was producing the
highest soluble-P than other superior
solubilizing phospate exogenous bacteria on Andisols as tea planting area in Indonesia. It’s arround 83.78% more than control (without solubilizing phospate bacteria).
Limitations
The important thing on this research was to calibrate the population of microbes. Because we used some and different microbes, so the growth and population different too. On Table 1 we calibrated the population of all microbes. So, the each microbe have the same population before inoculated on the soil, that
was around 1.09 x 1012 cfu/ml. Different
population will be confused us in interpretation of the data.
Recommendation
In every research by used microbe to compare
and know the capability or function, it should be done in same population. To do it, before application we should be to regeneration of microbe isolate and growth it on it’s medium. After someday incubation, please count the population and calibrated it, so we will have the same population.
Funding and Policy Aspects
One of the “green concept” on agricultural aspect was used some superior microbe as a biofertilizer. The huge population in each biofertilizer product make it dominant on the habitat which bio-fertilizer applied without know the capability on that habitat. This is the basic research to prove that the exogenous superior microbe can not significantly on other habitat, particulary on tea plantation area. So, the one of next research need to produce biofertilizer special from indigenous microbes of tea area.
Justification of Research
The objective of research was to obtain the phospate soluble capability from the superior solubilizing phosphate bacteria. The inoculant from agricultural food plants with elevation 600 - 800 m above sea level in Indonesia. The strain that used was Pseudomonas cepaceae, P. malei, Bacillus mycoides, and B. subtilis. In Indonesia, tea was planted dominant on uplands area with 52-55% from the total area on Andisols as soil of tea planting area. To know the capability of that superior exogenous microbe on Andisol, the research should be done.
Conclusion
The capability from solubilizing phosphate bacteria to increase P-soluble depend on the pH of soil. Andisols as a tea planting area in Indonesia had range of pH 4.5 – 5.6 that made
P retention more. Even Pseudomonas
cepaceae, P. malei, Bacillus mycoides, and B.
subtilis were the superior solubilizing
Author’s Contribution and Competing Interest
Mieke Rochimi Setiawati as a main author contributes on produce the inoculant. She was a lecturer on UNPAD with specialization on soil biotechnology, particulary microbe on agricultural food plants. Eko Pranoto as
co-author contributes in applied and
experimented it on Andisol as tea planting area. He was a researcher from Indonesia Research Institute for Tea and Cinchona.
References
Chen Y.P., Rekha P.D., Arun A.B., Shen F.T., Lai W.A.,Young C.C., 2006. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Applied Soil Ecology, 34, 33-41.
Garcia C., Fernandez T., Costa F., Cerranti B., Masciandaro G., 1992. Kinetics of phosphatase activity in organic wastes. Soil Biol Biochem Journal, 25, 361-365.
Hopkins D.W., Bartoli F., 2004. Size and activity of the soil microbial community from a range of European volcanic soils. Volcanic soil resources in Europe. Agricultural Research Institute. Reykjavik, Iceland. Rala Report, 214, 35-36.
Indonesia Agricultural Ministry (Welcome Speaking). 2010. Anually meeting of Indonesia tea board, Bandung.
Islam M.T., Deora A., Hashidoko Y., Rahman A., Ito T., Tahara S., 2007. Isolation and Identification of Potential Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria from the Rhizoplane of Oryza sativa L. cv. BR29 of Bangladesh. Verlag der Zeitschrift für Naturforschung Journal, Tübingen, 62c, 103-110.
Kapur S., 2010. Andosols. University of Çukurova. Departments of Soil Science and Archaeometry, Adana, Turkey,
Malcolm J.L., 1951. Water soluble phosphorus and potassium in the soil of lime and avocado groves in dade county. Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc, 64, 285-292.
Neall V. E., 2009. Volcanic soils. Land use and land cover. UNESCO-EOLSS, VII, 23-45.
Notohadiprawiro T., 2006. The limited concept on agricultural aspect; the serious constraint on national development. Soil Science and Environment Journal, 6(1), 63-70.
Rodriguez H., Fraga V., 1999. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnology Advances, 17, 319-339.
Sharma B.C., Subba R., Saha A., 2012. In vitro solubilization of tricalcium phosphate and production of IAA by phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from tea rhizosphere of Darjeeling Himalaya. Plant Sciences Feed Journal, 2(6), 96-99.
Sitepu, I.R., Hashidoko V., Santoso V., Tahara V., 2013. Potential of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from dipterocarps grown in peat swamp forest in central Kalimantan and their possible utilization for biorehabilitation of degraded peatland. [Online] Available :
http://www.geog.le.ac.uk/carbopeat/media/pdf/yogy apapers/p17.pdf
Widayat W., Santoso V., Martosupono V., Astika G.P.W., Dharmadi A., Kartawijaya W.S., Sukasman, Tobroni M., Suwardi E., Topani, Samudi J.B., 2006. Tea cultivation guideline. 3rd edition, Indonesia language. Indonesia Research Institute for Tea and Cinchona, Gambung, Indonesia.