DESIGNING REALIA TO TEACH VOCABULARY FOR THE SEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMP TAMAN DEWASA YOGYAKARTA
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Yanuar Emiko Purnomo Student Number: 061214018
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHING TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
2010
“Every big
step starts
with an inch.”
(Anonymous)
I
dedicate
this
thesis
to
all
teachers
and
students
and
also
to
my
parents
and
family
ABSTRACT
Purnomo, Yanuar Emiko. 2010. Designing Realia to Teach Vocabulary for the Seventh Grade Students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Department of Language and Arts Education, Faculty of Teachers Training and Education, Sanata Dharma University
Realia as a useful medium to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students of Junior High School can be used to motivate the students learn English. Moreover, realia makes the students easier to memorize vocabularies through various pictures. The combination between realia and games can also avoid boredom in the classroom. Learning English will be more meaningful if the students can learn through experience. By using realia, the students can see, touch, and observe the things directly.
This study was aimed to help the Junior High School teachers to design the realia to teach vocabulary especially for the seventh grade students in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. There were two problems to solve in this study: 1) What is the design of realia as the media to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta? and 2) What are the effects of the design on the students learning?
This study was done by conducting the steps of Kemp’s instructional design model which was put under the umbrella of Borg and Gall’s R&D cycle. This study also considered relevant theories related to vocabulary, realia, learners’ characteristics, Direct Method, and Communicative Language Teaching.
This study has found the answers to the formulated problems above. First, the design of realia as the media to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta is realia design which includes the identification of learners’ characteristics and needs, the statement of competence standard, basic competence, topics, and objectives, the list of subject content which is based on the purpose of the design and the related theories, realia design, and also the experts’ validation and evaluation for the design revision.
Second, to obtain the answer to the second question, this design had been implemented in the real classroom. The effects of realia that affects the students learning can be concluded as follows. First, the students stated that they could enrich their vocabulary through the realia especially from the various pictures given. Second, the students could remember vocabularies easily because they experienced to see the real shape. Third, the students were motivated to learn English. Last, the students could study and play at the same time so that they did not feel bored when they were learning English, especially vocabulary.
ABSTRAK
Purnomo, Yanuar Emiko. 2010. Designing Realia to Teach Vocabulary for the Seventh Grade Students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta: Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni, Fakultas Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Realia sebagai media yang berguna untuk mengajarkan kosa kata Bahasa Inggris bagi siswa SMP kelas tujuh dapat digunakan untuk memotivasi siswa dalam belajar Bahasa Inggris. Selain itu, realia memudahkan siswa dalam mengingat perbendaharaan kata yaitu dengan bermacam-macam gambar. Kombinasi antara realia dan permainan juga dapat mengatasi kebosanan di dalam kelas. Belajar Bahasa Inggris akan jauh lebih bermakna jika para siswa bisa belajar melalui pengalaman. Dengan menggunakan realia siswa dapat melihat, menyentuh, dan mengobservasi sesuatu secara langsung.
Studi ini bertujuan untuk membantu para guru di sekolah untuk mendesain realia untuk mengajar kosa kata Bahasa Inggris bagi siswa kelas tujuh di SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. Terdapat dua permasalahan untuk dipecahkan dalam studi ini, yaitu 1) Seperti apa desain realia sebagai media untuk mengajarkan kosa kata Bahasa Inggris bagi siswa kelas tujuh SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta? dan 2) Apa pengaruh realia bagi pembelajaran siswa?
Studi ini diselesaikan dengan menerapkan langkah-langkah dari model desain materi Kemp yang dimasukkan ke dalam langkah-langkah metode penelitian dan pengembangan pendidikan (R&D) Borg dan Gall. Studi ini juga menggunakan teori-teori yang berkaitan dengan vocabulary, realia, karakteristik siswa, metode langsung, dan pengajaran bahasa yang komunikatif.
Studi ini telah menemukan jawaban atas permasalahan yang telah dirumuskan di atas. Pertama, desain realia sebagai media untuk mengajar kosa kata Bahasa Inggris bagi kelas tujuh SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta adalah desin realia yang mencakup adanya identifikasi kebutuhan dan karakteristik siswa, pernyataan tujuan desain, standar kompetensi, kompetensi dasar, topic, dan tujuan khusus, daftar materi berdasarkan tujuan desain dan teori terkait, desain realia, dan juga validasi dan evaluasi dari para ahli untuk merevisi desin tersebut.
Kedua, untuk memperoleh jawaban atas pertanyaan yang kedua, desain ini telah dipraktikkan di kelas yang sesungguhnya. Pengaruh realia bagi pembelajaran siswa dapat disimpulkan sebagai berikut ini. Pertama, siswa dapat memperkaya perbendaharaan kata Bahasa Inggris melalui realia, khususnya dari bermacam-macam gambar yang diberikan. Kedua, siswa dapat mengingat perbendaharaan kata dengan mudah. Ketiga, siswa termotivasi untuk belajar Bahasa Inggris. Terakhir, siswa dapat belajar sambil bermain pada saat yang bersamaan sehingga mereka tidak merasa bosan ketika sedang belajar.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to thank God for giving me this beautiful life. I’m grateful for His mercy and guidance in giving me full strength to complete this thesis. Even facing difficulties in completing this thesis, God never stops giving me His miracles.
I would also thank and express my appreciation to my thesis sponsor, Gregorius Punto Aji, S.Pd., M.Hum for the support, advice, and guidance in helping me to finish this thesis. I would also thank Ani Qri Handayani, S.Pd.; Ag. Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A. and Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, S.Pd., M.Ed. sincerely for their willingness to give suggestion, criticism, and correction on the design. Special appreciation to the seventh grade students of Junior High School in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta, especially Class A for their willingness to participate in the survey analysis and design implementation.
I would like to address my deepest gratitude to my family: M. Eko Joeni Purnomo, S.Pd, Sudarmini and Daniko Purnomo for their love, care, and especially for their great support and motivation. My thankfulness goes to Ana Anggraini, S.Pd., M.Hum, Elisabeth Kurnia and Asuan for their willingness in giving criticism and suggestion to my thesis.
My appreciation goes to Concetta English Course members; Prisca, Diyan, Editha, Ida, Oda, Jalu and Bang Gon for their encouragement to finish the thesis and also for the incredible experiences and beautiful moments in my life.
Last but not least, my very special thanks go to Topaz Feizal Bagaskoro for his patience, love, and support during the process of my thesis.
With love,
Emiko
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ABSTRAK ... vii
PUBLICATION PAGE ... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... xi
LIST OF TABLES ... xiv
LIST OF FIGURES ... xv
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xvi
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ……… 1
A. Research Background ……….... 1
B. Problem Formulation ………... 3
C. Problem Limitation ……… 3
D. Research Objectives ………... 4
E. Research Benefits ……….. 4
F. Definition of Terms ………... 4
1. Media ………. 5
2. Vocabulary ……… 5
3. Realia ………. 5
4. Junior High School ……… 6
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ……….. 7
A. Theoretical Description ………. 7
1. Instructional Design ……… 7
2. Educational Research and Development ……… 13
3. Vocabulary ………. 15
a. The Importance of Vocabulary ……….. 15
b. Vocabulary Teaching Technique ………... 15
4. Realia ………. 17
a. Realia as the Media of Learning ……… 17
b. The Advantages and Limitations of Realia ………… 17
c. The Examples of Realia ………. 18
5. Learners’ Characteristics ……… 19
6. Direct Method ……… 20
7. Communicative Language Teaching ………. 21
8. The Grammar Translation Method ………... 23
B. Theoretical Framework ……… 24
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY ……….... 28
A. Research Method ... 28
B. Research Participants ... 30
C. Research Instruments ... 31
D. Data Gathering Technique ... 32
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 34
F. Research Procedure ... 35
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 38
A. The Design of Realia to Teach Vocabulary for the Seventh Grade Students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta …….. 38
1. Learners’ Characteristics ……… 39
2. Competence Standard, Basic Competence, Topic, and Indicator ……….. 42
3. Subject Content ……….. 47
4. Realia ………. 50
5. Feedback from the Product Validation ……….. 59
6. Product Revision ………... 62
B. The Effects of Realia on the Students Learning ………….. 64
1. Description on Field Testing of Realia……… 64
2. Discussion on the Effects of Realia on the Students Learning ………. 66
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ……….. 72
A. Conclusions ………... 72
B. Suggestions ………... 73
REFERENCES ………... 75
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
3.1 Data Needed ... 34
4.1 Summary of Learners’ Characteristics ... 41
4.2 Competence Standard, Basic Competence, Topic, and Indicator of the Design ... 43
4.3 Subject Content of the Design ... 50
4.4 Learners’ Interest ... 51
4.5 The Realia ... 57
4.6 Description on the Preliminary Testing Respondents ... 59
4.7 Strengths and Weaknesses of the Design ... 62
4.8 Revision of the Design ... 63
4.9 Students’ Opinion on the Main Field Testing ... 67
4.10 The Effects of Realia on the Students Learning ... 70
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
2.1 Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ... 12 2.2 The Steps of Designing Realia Adapted from Kemp’s Model ... 27 3.1 The Researcher’s R&D cycle completed with Kemp’s Model ... 37
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix Page
1. List of Questions for Needs Analysis Interview ... 76
2. Result of Needs Analysis Interview ... 78
3. Questionnaire ... 80
4. Sample of the Questionnaire ... 81
5. List Questions for Design Validation Interview ... 86
6. Result of Product Validation Interview ... 87
7. Questionnaire for Main Field Testing ... 89
8. Sample of Main Field Testing Questionnaire ... 90
9. The Designed Realia ... 95
10.Documentation of Design Implementation ... 124
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter elaborates the research background, problem formulation, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits and definition of the terms.
A. Research Background
Language has been a part of our life since it is used for many purposes; to communicate, to convey information, to deliver speech, and also to express feeling. Learning a new language is not easy. It needs effort in order to master a foreign language. Moreover, English becomes an obligatory subject to be taught in Junior High School so the learners have to learn and use it to communicate. English is also expected to ease the learners to communicate fluently in facing the global era.
The most important thing that the learners need to acquire in learning English is vocabulary. Learning vocabulary is the main part of mastering English because it is the basic language element. The learners will have many difficulties in speaking, reading, writing, and listening if they do not know the vocabularies and their meanings.
Considering the learners’ age, 11-15 years old, commonly they want to know and learn something which is considered interesting but they are easy to be influenced by their peers. They tend to change their mood easily and become very active sometimes hyperactive when they are facing something new. Meanwhile, it is not easy for them to remember all new vocabularies, write, and pronounce them correctly at once time.
Realia is supposed to motivate the learners to learn vocabulary and improve their skills in reading, writing, speaking, and also listening. Realia is real objects or models which are effective in showing meanings (Lado, 1964: 125). By using realia, the learners can touch, see, and learn at the same time as hearing new words (Jo Budden, 2008). As a result, their learning experience will be more memorable.
The researcher has chosen one of Junior High Schools in Yogyakarta namely SMP Taman Dewasa as the research area. The observation was conducted in 8 to 29 August 2009. The seventh grade students became the research participants in this study. The researcher chose this level because it is the secondary level where the Basic English of vocabulary is taught. In this level, the learners focus on the various vocabulary items which still deal with our daily life, such as personal introduction, things around us, things around school, shopping, professions, family life, story, and hobby.
the media for the learners to learn vocabulary, such as colorful pictures/flashcards, pops up, a map, and others.
Concerning the previous phenomena, the researcher would design the realia to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students. The realia designed would be based on the book which was used in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta in order to help the learners to learn vocabulary.
B. Problem Formulation
In this study, the researcher would like to answer the questions as follows: 1. What is the design of realia as the media to teach vocabulary for the seventh
grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta? 2. What are the effects of the design on the students learning?
C. Problem Limitation
D. Research Objectives
The objectives of the study can be stated to answer the problems formulated: 1. To design realia as the media to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students
of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta.
2. To know the effects of the design on the students learning.
E. Research Benefits
The benefits of the study can be stated as follows: 1. The students
The realia is expected to help them to enrich the vocabulary and increase their motivation to learn English.
2. The teachers
The realia is expected to help the teachers in teaching vocabulary creatively and inspire them to create the same media.
3. The researcher
This study helps the researcher learns and knows better on how to apply her knowledge and ability to develop learning media through realia.
F. Definition of Terms
1. Media
The term media often refers of any device that brings information from the source of message to the destination (Prihatin, 2007). Rowntree (1979) states “by mode I mean the kind of stimulus presented to the student. Thus, written symbols represented one mode. The vehicle carrying stimulus mode is the medium.” According to Gerlach and Ely (1980), a medium is any person, material, or event that establishes condition which enable the learner to acquire knowledge, skills, and attitudes. In this study, realia is used as one of media to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta.
2. Vocabulary
Vocabulary means list of words that are used as the basic element of communication. It is important to be mastered in order to support the learners in the acquisition of English as the target language. Vocabulary can be defined, roughly, as the words we teach in the foreign language (Carter, 1998). Vocabulary in this research is words which are taught in the seventh grade level of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta.
3. Realia
4. Junior High School
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter provides information and discusses the theories related to the study. A theoretical framework is included in this chapter to the relationship between the study and theories applied.
A. Theoretical Description
In the theoretical description, the researcher provides some theories which would be used as the guidance to design realia as the media of learning. They are instructional design, educational research and development, vocabulary, realia, learners’ characteristics, Direct Method, and Communicative Language Teaching.
1. Instructional Design
Instructional design becomes the basis information required to be the guidance in designing the learning activities. Instructional design is the entire process of analysis of learning needs and goals and the development of a delivery system to meet the needs; includes the development of instructional materials and activities; and tryout and revision of all instruction and learner assessment activities (Briggs, 1977: xx).
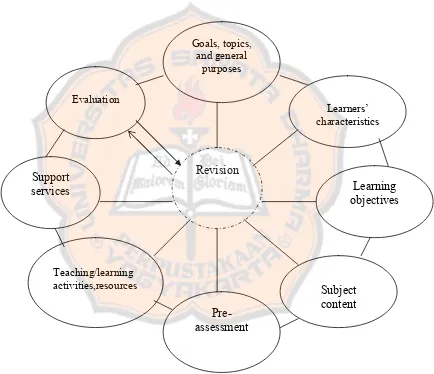
The researcher uses the theory of instructional design which was brought by Jerrold E. Kemp. The theory is well known as the Kemp’s model. In this model, system approach is provided to adjust and improve the design through its goal and
evaluation. “System approach means the overall plan of the instructional design compiled in order” (Kemp, 1977:6).
According to Kemp (1997: 8), the model is designed to supply answers to three questions which may be considered the essential elements of instructional technology :
1. What must be learned? (Objectives)
2. What procedures and resources will work best to reach the desired learning levels? (activities and resources)
3. How will we know when the required learning has taken place? (evaluation) In brief, those questions above reflect the existence of objectives, activities and resources as well as evaluation as the basis to create an instructional design which is considered as the essential elements of instructional technology (Kemp, 1977: 8).
In Kemp’s model design, the plan consists of eight important parts as follows. 1. Considering goals, listing topics, and stating general purposes
2. Identifying the learners’ characteristics
To make the students success in the educational program, they should learn at their own pace, on their own schedule, and with their own selection of learning experiences and materials. In other words, the designer must obtain information about the learner’ capabilities, needs, and interests.
When designing an instructional plan, the designer must decide his/her characteristics of the students. There are two factors to understand their characteristics. The first is academic factor. It includes academic background; grade-point average; level of intelligence; reading level; scores on standardized achievement and aptitude tests; study habits; ability to work alone; background in the subject or topic; motivation for studying the subject; expectation of the course, vocational and cultural aspirations. The second factor is social factor. It includes age; maturity; attention span; special talents; physical and emotional handicaps; relations among students; socioeconomic situation. Other factors such as learning conditions and learning styles should be taken into account when planning, as well.
3. Specifying the learning objectives
The learning objectives should be stated clearly in order to promote the learning itself. This consideration is based on the idea that learning requires active efforts from the learners. To engage actively in the learning activities, the learners need to know and understand the objectives of the learning process that they experience.
psychomotor domain. It includes objectives that care for the skills requiring the use and coordination of skeleton muscles, as in the physical activities of performing, manipulating and constructing. The third is affective domain. It includes objectives such as attitudes, appreciations, values, and all emotions.
4. Listing the subject content that supports each objective
A student’s learning experience must involve subject content. The content must closely relate to the objectives and to the student’s need. Subject content means the material consists of specific knowledge (facts and information), skills (step-by-step procedures, conditions, and requirements), and topics (Kemp, 1977: 44).
5. Developing pre-assessment
Pre-assessment aims to know two major points. The first is to determine the students’ background and present level of knowledge about the topic being presented. The second is to determine which of the objectives that the students have already achieved.
6. Selecting teaching-learning activities and resources
7. Specifying support services for implementing activities and producing materials Support services include matters related to budget, facilities, equipment, and personnel whose time must be scheduled for participation in the instructional plan (Kemp, 1977: 84). The support services must be considered at the same time when the instructional plan is made and materials are selected.
8. Evaluating students’ learning in terms of their accomplishment of objectives The designer should evaluate the students’ learning in terms of their accomplishment of the objectives. The evaluation should indicate the objectives from each domain. There are three domains such as: cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domain.
The eight parts of Kemp’s model comprise a flexible process. There is interdependence among them. One element may affect others and vice versa. It is the planners’ choice to start wherever he/she wants to start and move back and forth to other steps (Kemp, 1977: 9). The model of Kemp’s instructional design can be seen in Figure 2.1
Goals, topics, and general
purposes
Evaluation
Learners’ characteristics
Revision Support
services Learning
objectives
Teaching/learning
activities,resources Subject
content
Pre-assessment
2. Educational Research and Development
Educational research and development (R&D) is a process used to develop and validate educational products (Borg and Gall, 1983: 772). It consists of a cycle in which a version of the product is developed, field-testing, and revised on the basis of field-test data. The goal of R&D is to take the research knowledge and incorporate it into a product that can be used in the schools. In a sense, the purpose of R&D is to bridge the gap that frequently exists between educational research and educational practice. There are various steps of R&D which are known as R&D cycle. There are 10 major steps in the R&D cycle:
1. Research and information collecting
It includes review of related literature, classroom observation, and preparation. 2. Planning
It includes defining skills, stating objectives determining course sequence, and small scale feasibility testing.
3. Develop preliminary form of product
It includes preparation of instructional materials, handbooks, and evaluation devices.
4. Preliminary field testing
5. Main product revision
In main product revision, the data obtained from the preliminary field testing are compiled and analyzed. The collected data are used as feedback in developing and improving the educational product.
6. Main field testing
The purpose of this step is to determine whether the educational product under development meets its performance objectives. Furthermore, it is also used to collect information that can be used to improve the course in its next revision. Therefore, the questionnaire and interview data should be obtained from all participants in the main field testing.
7. Operational product revision
This part compiled the revision of product as suggested by the main field-test results.
8. Operational field testing
The purpose of this step is to determine whether an educational product is fully ready to be used in the schools without the presence of the developer or his staff. 9. Final product revision
10.Dissemination and implementation
Dissemination refers to the process of helping potential users to become aware of R&D product. Implementation refers to the process of helping the adopter of R&D product to use it in the way it is intended by the developers.
3. Vocabulary
a. The Importance of Vocabulary
Burton (1982: 98) states that the larger our vocabulary is the better our performance will be in all aspects of English language work. A large vocabulary helps the learners to express their ideas precisely and vividly because vocabulary really supports learners to learn the skills of the target language.
Considering the importance of vocabulary for the students’ learning, the students must master and develop this element. If it is not done, the vocabulary mastery of the students will be very limited and as a result they will have difficulties in learning the skills of language.
b. Vocabulary Teaching Technique
Gairns and Redman (1986) suggest the following types of vocabulary presentation techniques:
1. Visual techniques
Zebrowska (1975: 452) states that learners remember better material that has been presented by means of visual aids. Visual techniques lend themselves well to presenting concrete items of vocabulary-nouns; many are also helpful in conveying meanings of verbs and adjectives.
2. Verbal explanation
This pertains to the use of illustrative situations, synonyms, opposites (Gairns and Redman, 1986: 74), definition (Nation, 1990: 58) and categories (Allen and Valette, 1972: 116).
3. Use of dictionaries
Using dictionaries is another technique to find out meanings of unfamiliar words and expressions. Students may use a variety of dictionaries: bilingual, monolingual, pictorial, and the like.
4. Using games
4. Realia
a. Realia as the Media of Learning
Realia as the media of learning for the students can be used to teach in the classroom at any time. A teacher can use many kinds of media to teach the students to attract their attention in learning something. According to Rowntree (1979) through the realia, the students may do direct observation of things, people, and events. Furthermore, the students are expected to work less with the realia and more with the symbolism that represents it. The ability to manipulate this symbolism is vital part of the individual’s cognitive growth and gives him/her powerful tool for communication. In this activity, the students are encouraged to communicate and observe real things which may trigger their ideas to come out.
b. The Advantages and Limitations of Realia
In the book Instructional Technology for Teaching and Learning, Newby (2000: 111) also states the advantages and limitations of realia.
The advantages are:
1. Less abstract and more concrete
Real objects provide hands-on learning experiences and emphasize real world applications.
2. Readily available
Materials are readily available in the environment, around school, and at home. 3. Attract students’ attention
The limitations are: 1. Storage
Large objects can pose special problems. Caring for living materials such as plants and animals can take a lot of time.
2. Possible damage
Materials are often complex and fragile. Parts may be lost or broken. c. The Examples of Realia
Lado (1964: 125) in his book Language Teaching states that Realia as the media of learning can be in the form of these categories:
1. Visual sources
The examples of visual sources are things that can be seen by the students such as photos, cards, map, and pictures.
2. Real things
The examples of real things that can be brought in the classroom are book, pencil, pen, ruler, flag, etc.
3. Real people
The examples of real people may use the student, teacher, and/or foreign people as the media to teach vocabulary.
4. Real animals
The examples of real animals such as elephant, frog, dog, cat, etc can be used as the media to teach vocabulary of animals.
5. Real events
5. Learners’ Characteristics
The students of Junior High School are in the age of 11 to 15 years old. According to Hurlock (1980: 185), those students are in the stage age of teenagers. Hurlock in Psikologi Perkembangan (1980: 207) also says that adolescence is a transition period that is the period of time in the individuals’ life when they develop from a child into an adult.
In social aspect, adolescent is an intensely social period in the developmental continuum. The social experiences they have as teens are accompanied by a large psychological differences namely “an enormous self-consciousness” (Hamachek, 1990: 117). The adolescents feel that they are always being watched by others all the time. Thus, they tend to monitor their appearance and action. Additionally, “many adolescent activities are doing in group, and sub groups or cliques with the groups (Hamachek, 1990: 117). It bounds the teacher’s role since peer approval may be considerably more important for the student than the attention of the teacher (Harmer, 1988: 39). Therefore, the individuals will get more influence to their behavior, attitude, interest and appearance from their friends rather than their family (Hurlock, 1980: 213). They also put themselves in the “freedom area”. They do not like if somebody dominate their life.
6. Direct Method
According to Diller (1978) the very basic rule of the Direct Method is translation is not allowed. Its name derives from the fact that meaning is to be conveyed directly in the target language through the use of demonstration and visual aids with no recourse to the students’ native language. Teachers who use the Direct Method intend that students learn how to communicate in the target language. In order to do this successfully, students should learn to think in the target language. Although the teacher directs the class activities, the relation between the teacher and the students is more like partners in the teaching-learning process. Teachers who use the Direct Method believe students need to associate meaning and the target language directly. The teacher introduces a new target language word or phrase then demonstrates its meaning through the use of realia, pictures, or pantomime; the teacher never translates it into the students’ native language. Grammar is taught inductively; that is, the students are presented with examples and they figure out the rule or generalization from the examples. An explicit grammar rule may never be given. Students practice vocabulary by using new words in complete sentence.
There are some techniques of the Direct Method: a. Reading aloud
Students take reading sections of a passage, play, or dialog out loud. At the end of each student’s turn, the teacher uses gestures, pictures, realia, examples, or other means to make the meaning of the section clear.
b. Getting students to self-correct
The teacher of this class has the students self-correct by asking them to make a choice between what they said and an alternative answer he supplied. For example, a teacher might simply repeat what a student has just said; using questioning voice to signal to the student that something was wrong with it.
c. Map drawing
The students are given a map to give directions such as the following, ‘Find the mountain range in the West. Write the words “Rocky Mountains’ across the mountain range.’ Then the teacher gives instructions for all the geographical features of the United States so that students will have a completely labeled map if they follow the instruction correctly.
7. Communicative Language Teaching
CLT refers to a varied set of principles which reflect a communicative view of language and language learning and which can be used to support a wide variety of classroom procedures (Richards and Rodgers, 2001:172). It includes some principles, they are:
b. the goal of classroom activities is at authentic and meaningful communication; c. fluency is an important aspect of communication;
d. the integration of different language skills is involved in the communication; e. learning is a process of creative construction and involves trial and error.
Meanwhile, in CLT, the teacher plays role as the facilitator of learning (Littlewood, 1981: 92). In this kind of role, the teacher must be able to facilitate communication process between all participants in the classroom, as well as between these participants and the various activities. Breen and Candlin (1980: 99) add that teacher also plays role as an independent participant within the learning-teaching group. Another role of teacher is that teacher should act as a researcher and a learner at the same time.
In CLT, the practitioners view the instruction materials as ways of influencing the quality of classroom interaction and language use (Richards and Rodgers, 2001: 168). The materials, then, should promote communicative language use in the classroom. There are three kinds of materials that are commonly used in CLT, they are: text-based, task-based, and realia.
communication practice, cue-card and student-interaction practice booklets. Another type of material is realia type. The realia materials make use of authentic materials which are based on actual life experiences. The materials include the use of: signs, magazines, advertisement, newspaper and other visual sources like symbols, charts, pictures and maps.
8. The Grammar-Translation Method
The Grammar Translation Method derived from traditional approaches to the teaching of Latin and Greek in the nineteenth century. It is “a way of studying a language that approaches the language first thought detailed analysis of its grammar rules, followed by application of this knowledge through the task of translating sentences and text into and out of the target language” (Richards and Rogers, 2002). The principal characteristics of the Grammar Translation Method were these:
a. The goal of foreign language study is to learn a language in order to read its literature or in order to benefit from the mental discipline and intellectual development that result from foreign language study. “The first language is maintained as the reference system in the acquisition of the second language” (Stern, 1983: 455).
b. Reading and writing are the major focus; little or no systematic attention is paid to speaking or listening.
c. Vocabulary selection is based solely on the reading texts used, and words are taught through bilingual word lists, dictionary study, and memorization.
e. Accuracy is emphasized. f. Grammar is taught deductively.
g. The student’s native language is the medium of instruction.
B. Theoretical Framework
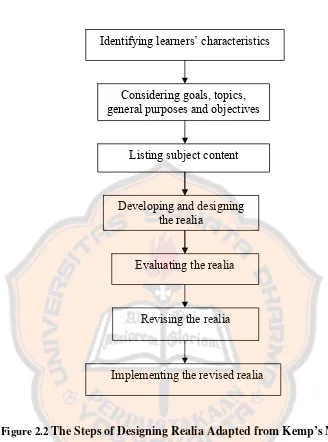
The researcher adapted the steps from Kemp’s model to conduct the research. The second step used in this study combined the first and third steps of Kemp’s Instructional Design since there was correlation among them. So, the researcher stated goals, topics, general purposes, and objectives in succession. Identifying learners’ characteristics was conducted first in order to state the goal of the study. After stating the goal, the researcher chose the topics based on basic competence in the curriculum of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. Then, the researcher could state the indicators from each topic developed from the basic competence.
There are seven major adapted steps of the Kemp’s model to design the realia as follows.
1. Identifying learners’ characteristics
2. Considering goals, topics, general purposes, and objectives
This step included defining the goals, stating general purposes and objectives based on the curriculum and the syllabus that are used in the school.
3. Listing subject content
The researcher made lists of topic or the subject content based on the identified learning objectives. Furthermore, the researcher also developed the pre-design realia by applying the findings from the needs analysis and also by applying salient principles of related theories which supported the study such as: the theory of vocabulary and realia. The vocabulary theory became the guidance for the researcher to choose the appropriate vocabulary teaching technique. The realia theory also became the guidance to design the appropriate realia based on the students’ need. 4. Developing and designing the realia
The researcher designed the realia based on the students’ needs and interests. The theory of Grammar Translation Method used as the guidance to design the smart compass realia where the translation of the first language was put on it.
5. Evaluating the realia
6. Revising the realia
The researcher conducted the revision based on the evaluation from the experts. After that, the researcher prepared to implement the product in a real classroom.
7. Implementing the revised realia
Identifying learners’ characteristics
Considering goals, topics, general purposes and objectives
Listing subject content
Developing and designing the realia
Evaluating the realia
[image:43.610.140.468.97.539.2]Revising the realia
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the methodology which was applied in this study. This chapter is divided into six parts, they are: research method, research participant, research instrument, data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
As stated in the problem formulation, this research was conducted in order to design realia to teach vocabulary in the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. In this research, the researcher used observation, library study, interview checklist, and questionnaire as the research instruments.
The researcher applied Research and Development (R&D) since the research was an educational research to develop and validate the educational products. There are some steps of R&D that can be followed which are usually called as R&D cycle. It consists of several parts as follows.
1. Research and information collecting
In this step, observation and reviewing related to literature were conducted to collect pertinent information and knowledge related to the research. The researcher used questionnaires in the observation. The seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta became the subjects of the questionnaire.
2. Preliminary Product Developing
In this step, the researcher focused on designing realia based on pertinent information and knowledge gathered from the previous step. After collecting the data from the questionnaire, the researcher started to design realia for the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta.
3. Preliminary Field Testing
In this step, the design was evaluated by the experts in English teaching. The researcher had chosen the English teacher and the PBI lecturers to be the participants of the preliminary field testing step. The feedback and evaluation from them became the first version to the design that had been developed by the researcher.
4. Product Revision
In this step, the gathered feedback from the preliminary field testing was compiled and analyzed. The result from the preliminary field testing was used as the revision to develop the designed product into the suitable product which was needed by the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta.
5. Main Field Testing
B. Research Participants
The research applied purposive sampling where the researcher chose participants who were considered as the representative of the elements needed in this study.
1. The participants in research and information collecting step
The purpose of this step was to collect the information needed to design media for the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta such as the learner characteristics, the weakness of learners in learning vocabulary items, the facilities, etc. In order to obtain all the information required, the researcher observed the school and also interviewed the English teacher. The seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta also became the participants in the needs analysis. The researcher expected to find out their interests which were related to the study. They filled the questionnaire about their interests and needs in enhancing the vocabularies.
2. The participants in preliminary field testing step
consideration of choosing the same English teacher and the second lecturer was the fact that the researcher would know what was and what was not suitable for the students because both the teacher and lecturer knew the students’ characteristics and needs.
3. The participants in the main field testing step
The purpose of this step was to implement the design and obtain feedback from the students. The seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta were chosen to be the participants and all of them were asked to fill in the questionnaire to give their opinion about the realia.
C. Research Instruments
In this study, the researcher applied some research instruments to obtain the information and data needed. The instruments are elaborated in these categories:
1. Instrument for research and information collecting step
The researcher also applied questionnaire as the instrument to obtain the information about the students’ needs and interests. The researcher used open-ended questions type because there were a great number of possible answers from the students.
2. Instrument for preliminary field testing step
The researcher applied the same instruments conducted to obtain the information. The interview was aimed to collect feedback from the English teacher in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta and PBI lecturers of Sanata Dharma University on the realia.
3. Instruments for the main field testing step
The researcher distributed questionnaires with open-ended questions to the students of the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta to obtain feedback in the form of evaluation from revised design which was conducted in the classroom.
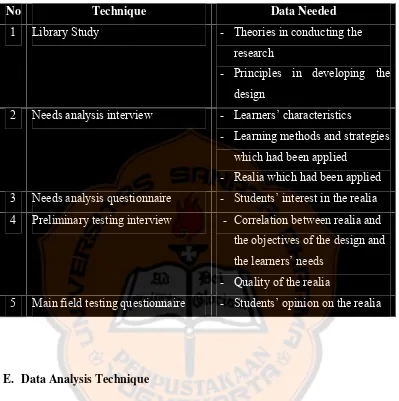
D. Data Gathering Technique
The researcher obtained data and information related to the study by conducting three techniques. First, the researcher conducted library study to obtain any information related to designing realia for the seventh grade students from books in the library and articles in the internet. By conducting literature study, the researcher expected to obtain theories, other knowledge and information to design the product.
would cover the questions about the learners’ characteristics, learning activities, materials, facilities, methods and also teacher and learners’ difficulties in the teaching learning activities. Other interviews were also conducted to obtain feedback on the design. The interviews were directed to the English teacher and PBI lecturers. In this interview, the researcher found feedback, evaluation on the objectives and realia quality.
Table 3.1 Data Needed
No Technique Data Needed
1 Library Study - Theories in conducting the
research
- Principles in developing the
design
2 Needs analysis interview - Learners’ characteristics
- Learning methods and strategies which had been applied
- Realia which had been applied 3 Needs analysis questionnaire - Students’ interest in the realia
4 Preliminary testing interview - Correlation between realia and
the objectives of the design and the learners’ needs
- Quality of the realia
5 Main field testing questionnaire - Students’ opinion on the realia
E. Data Analysis Technique
The researcher collected the data and information from the library study, interviews, and the questionnaire. All the data needed were analyzed through qualitative data analysis.
F. Research Procedure
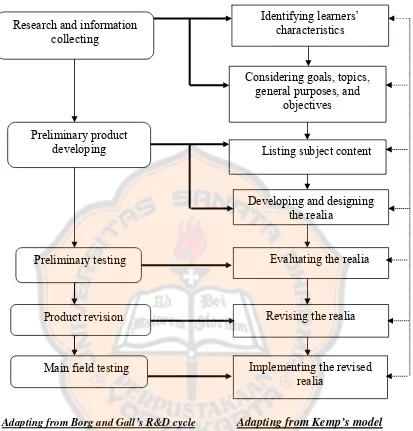
The procedures conducted in this study were based on the integration between R&D and Kemp’s model. The researcher put Kemp’s model under the framework of R&D. The listed procedures of this study are as follows:
1. Research and information collecting
a. The researcher limited the research area. b. The researcher stated the general purposes. c. The researcher stated the objectives.
d. The researcher conducted the library study to find out some books and articles for literature review to guide the study.
e. The researcher designed the research instruments in form of interview checklist and questionnaire to obtain the needs analysis data.
f. The researcher asked permission to the headmaster and the English teacher in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta to conduct the research.
g. The researcher interviewed the English teacher to obtain the needs analysis data.
h. The researcher analyzed the needs analysis data to create and develop the realia.
2. Preliminary Product Developing
a. The researcher chose and listed the subject content that were appropriate for the seventh grade students.
3. Preliminary Testing
a. The researcher interviewed the English teacher of SMP Taman Dewasa IP to evaluate the realia.
b. The researcher interviewed PBI lecturers to evaluate the realia. 4. Product Revision
a. The researcher analyzed the data collected from preliminary testing. b. The researcher revised the product.
5. Main Field Testing
a. The researcher implemented the product in the real classroom
b. The researcher distributed questionnaire to obtain feedback from the students to see how well the product facilitated the students’ learning.
To obtain clearer idea on the theoretical framework which is applied in this study, the researcher’s theoretical framework is presented in Figure 3.1.
[image:53.610.112.525.113.544.2]
Adapting from Borg and Gall’s R&D cycle Adapting from Kemp’s model
Figure 3.1 The Researcher’s R&D cycle completed with Kemp’s Model continuing to (next step)
providing the basis for feedback line
Research and information collecting
Preliminary product developing
Considering goals, topics, general purposes, and
objectives
Listing subject content
Developing and designing the realia
Evaluating the realia
Revising the realia
Implementing the revised realia
Main field testing Product revision
Preliminary testing
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the research result and discussion of realia as the media to teach vocabulary for students in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. This chapter answers the two questions stated in the problem formulation. There are two main parts in this chapter. The first part is discussion on the design of realia to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. The second part is discussion on the effects of realia on the students learning.
A. The Design of Realia to Teach Vocabulary for the Seventh Grade Students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta
This part presents the result of the design of realia to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. The researcher followed the procedures of scientific study to present the realia. The theories of Educational Research and Development (R&D) from Borg and Gall (1983) and instructional design from Kemp (1977) became the procedures to design the product. Those theories were applied as the main procedure guideline of the study. Besides those theories, the study also required more theories which provide knowledge and information related to the process of designing the product. The theories about vocabulary, realia, learners’ characteristics, Direct Method, and Communicative Language Teaching were collected to support the design of realia to
teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta.
The followings present the detailed components of the designed realia to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta.
1. Learners’ Characteristics
This part discusses the knowledge and information related to learners’ characteristics which were obtained by conducting need analysis interview and questionnaire. The interview was conducted to obtain the information about learners’ characteristics and information related to the realia. The questionnaires were distributed to the students to know their needs in learning vocabulary.
The researcher had interviewed the English teacher who was responsible to teach English for the seventh grade students in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. This interview had been conducted in the 9th of March 2010 at 10.30 a.m. The interview was aimed to obtain the information about learners’ characteristics. After interviewing the English teacher, the researcher obtained the important data about learners’ characteristics of the seventh grade students. The data were about the general description of learners’ academic achievement and motivation in the classroom.
grades of National Examination. The students obtained mainly under twenty out of thirty. Moreover, this school receives inclusive students who need special attention from the teachers. The English teacher added that the inclusive students mean the students who need extra attention, guidance, and encouragement from the teacher during the lesson because they cannot absorb and follow the lesson easily. In other words, they are different from the other students in terms of the way they absorb the knowledge taught in the classroom.
The willingness of the students to response the learning depended on the way the teacher conveyed the learning materials.
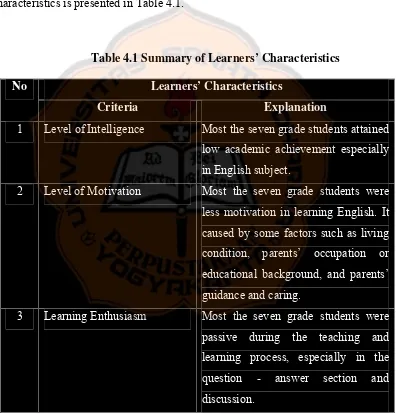
[image:57.610.122.519.256.670.2]Based on the data gathered in the 9th of March 2010, there were three classes for the seventh grade students. Each class consisted of thirty one students. There were nineteen boys and twelve girls in each class. The summary of learners’ characteristics is presented in Table 4.1.
Table 4.1 Summary of Learners’ Characteristics Learners’ Characteristics
No
Criteria Explanation
1 Level of Intelligence Most the seven grade students attained
low academic achievement especially in English subject.
2 Level of Motivation Most the seven grade students were
less motivation in learning English. It caused by some factors such as living condition, parents’ occupation or educational background, and parents’ guidance and caring.
3 Learning Enthusiasm Most the seven grade students were
2. Competence Standard, Basic Competence, Topic, and Indicator
This part discusses the competence standard, basic competence, topic, and indicator of the design. Realia was designed for the seventh grade students in order to help them learn the vocabulary easier and encourage them to communicate. School based curriculum is used as the main curriculum in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. The researcher applied the second step of designing realia from Kemp’s model which was considering goals, general purposes, and objectives. The general purposes of the design in this study were based on the basic competence in the syllabus while the objectives of the design were based on the indicators in the syllabus.
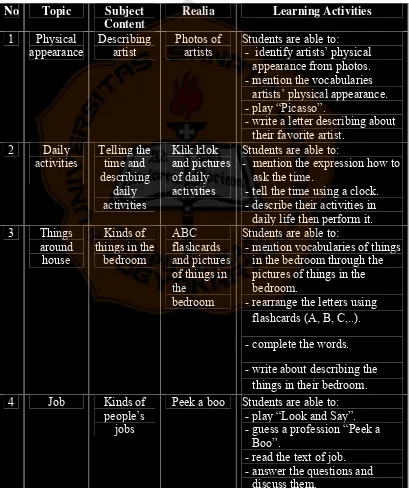
As stated in the syllabus for the seventh grade students of semester one used in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta, the researcher chose eight units to design, they are: (1) physical appearance; (2) daily activities; (3) things around house; (4) job; (5) things around school; (6) hobby; (7) clothes; and (8) shops. Each topic spent four meetings. Each meeting taught one or two skills which lasted for eighty minutes. Competence standard, basic competence, topics and indicators in the syllabus for the seventh grade are presented in Table 4.2.
Table 4.2 Competence Standard, Basic Competence, Topic, and Indicator of the Design
1) Unit 1
Skill Writing
Competence
Standard
6. To express the meaning in short functional written text to interact with the closest environment.
Basic Competence 6.1 To express the idea in short functional written text using language accurately, fluently, and acceptably
to interact with the closest environment. Topic Physical Appearance
Indicator 1. Students are able to mention the vocabularies of artists’ physical appearance.
2. Students are able to identify artists’ physical appearance from photos.
3. Students are able to write a letter telling about their best friend.
2) Unit 2
Skill Speaking
Competence Standard 4. To express the meaning in the short functional oral text to interact with the closest environment. Basic Competence 4.1 To express the meaning of short functional spoken
text accurately, fluently, and acceptably to interact with the closest environment.
Topic Daily Activities
Indicator 1. Students are able to mention the expression how to ask the time.
2. Students are able to tell the time using a clock. 3. Students are able to make a sentence based on the
3) Unit 3
Skill Writing
Competence Standard 6. To express the meaning in short functional written text to interact with the closest environment.
Basic Competence 6.1 To express the idea in short functional written text using language accurately, fluently, and acceptably
to interact with the closest environment. Topic Things around House
Indicator 1. Students are able to mention vocabularies of things in the bedroom.
2. Students are able to rearrange letters. 3. Students are able to complete the words.
4. Students are able to describe the things in their bedroom.
4) Unit 4
Skill Reading
Competence Standard 5. To understand the meaning in the short functional written text to interact with the closest environment. Basic Competence 5.2 To respond to the meaning of short functional
written text accurately, fluently, and acceptably to interact with the closest environment.
Topic Jobs
Indicator 1. Students are able to guess the jobs by using peek a boo.
5) Unit 5
Skill Speaking
Competence Standard 4. To express the meaning in the short functional oral text to interact with the closest environment.
Basic Competence 4.1 To express the meaning of short functional spoken text accurately, fluently, and acceptably to interact with the closest environment.
Topic Things around School
Indicator 1. Students are able to mention kinds of school equipments.
2. Students are able to pronounce the vocabularies. 3. Students are able to make sentences using the
school equipments.
4. Students are able to make a dialog based on the situations given.
6) Unit 6
Skill Speaking
Competence
Standard
4. To express the meaning in the short functional oral text to interact with the closest environment.
Basic Competence 4.2To express the meaning in short functional spoken text accurately, fluently, and acceptably to interact with the closest environment.
Topic Hobbies
Indicator 1. Students are able to mention kinds of hobbies.
2. Students are able to match the pictures of
7) Unit 7
Skill Speaking
Competence Standard 4. To express the meaning in the short functional oral text to interact with the closest environment.
Basic Competence 4.1 To express the meaning of short functional spoken text accurately, fluently, and acceptably to interact with the closest environment.
Topic Clothes
Indicator 1. Students are able to mention kind of clothes and accessories through the smart compass.
2. Students are able to make sentences through the smart compass.
8) Unit 8
Skill Listening
Competence
Standard
2. To understand the meaning in the short functional oral text to interact with the closest environment.
Basic Competence 2.1To respond to the meaning of spoken act in short functional text accurately, fluently, and acceptably to interact with the closest environment.
Topic Shops
Indicator 1. Students are able to mention the expression how to give direction.
2. Students are able to ask and give direction to the shops.
In conclusion, realia was aimed to facilitate the seventh grade students to learn vocabulary and encourage them to communicate. Realia was adjusted to the competence standard, basic competence, topics, and indicators so that it would be more appropriate to be applied for the seventh grade students.
3. Subject Content
Subject content consists of the appropriate topics which are chosen to facilitate the students learning in the classroom. Based on the research procedure, subject content was chosen and listed in the preliminary product developing step. Listing the subject content should be based on the purpose of the design, related theories, and the curriculum used in the school. The researcher stated some topics to be developed into the realia to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. The learning process was going to be conveyed through realia, therefore the topics chosen should be derived from the curriculum used in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. Here below, the topics will be discussed further in order to get clearer idea.
The second topic was daily activities. The subject content was telling the time and describing daily activities. The skill taught was speaking. The students were expected to be able to express how to ask the time, tell the time using “klik klok”, create a sentence using pictures of daily activities, and describe their daily activities using “klik klok” and pictures of daily activities orally. The realia to be used to support the vocabulary learning about time and describing daily activities was “klik klok” and pictures of daily activities.
The third topic was things around house. The subject content was kinds of things in the bedroom. The skill taught was writing. The students were expected to be able to mention vocabularies of things in the bedroom through pictures, rearrange the letters using ABC flashcards, complete the words, and then describe the things in their bedroom in written. The realia to be used to support the vocabulary learning about things in the bedroom was ABC flashcards and pictures of things in the bedroom.
The fourth topic was job. The subject content was kinds of people’s job. The skill taught was reading. The students were expected to be able to guess kinds of jobs through “Peek a Boo”, read the simple text about job, identify the parts of the text, and answer questions related to the text. The realia to be used to support the vocabulary learning about kinds of people’s job was “Peek a Boo”. Through “Peek a Boo”, the students could read the description about the name of the job. They could find the answer through the picture behind the cover of “Peek a Boo”.
able to mention kinds of school equipments through the magic bag, pronounce the things correctly, and then make the dialog based on the situation given. The realia to be used to support the vocabulary learning about school equipments was the magic bag. The magic bag contained of school equipments or stationeries.
The sixth topic was hobby. The subject content was about kinds of hobbies. The skill taught was speaking. The students were expected to be able to mention kinds of hobbies through the dice, match the pictures with the appropriate words, guess kinds of hobbies through pantomime, and then make a short dialog. The realia to be used to support the vocabulary learning about kinds of hobbies was the dice. Each part of the dice contained of a picture of hobby.
The seventh topic was clothes. The subject content was kinds of clothes and accessories. The skill taught was speaking. The students were expected to be able to mention all kinds of clothes and accessories through the smart compass and create a sentence. The realia to be used to support the vocabulary learning about clothes and accessories was the smart compass.
Table 4.3 Subject Content of the Design
NO SKILL TOPIC SUBJECT CONTENT
1 Writing Physical appearance Describing artist
2 Speaking Daily activities Telling the time and describing
daily activities
3 Writing Things around house Kinds of things in the bedroom
4 Reading Job Kinds of people’s jobs
5 Speaking Things around school School equipments
6 Speaking Hobby Kinds of hobbies
7 Speaking Clothes Kinds of clothes and
accessories
8 Listening Shops Asking and giving directions
4. Realia
A further development on the design would be discussed further in this part. After listing the topics of the design, the researcher needed some important information related to the students’ interest on the realia. Furthermore, the theories of realia, Direct Method, and Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) were considered as the underlying knowledge to present the design.
was considered as the representative from the seventh grade students of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. They were asked about the media which they liked and which they did not like to be applied in the learning process. The summary of the learners’ interest on the media to learn vocabulary is presented in Table 4.4.
Table 4.4 Learners’ Interest No Learners’ interest in the learning media
1 The media expected to be
applied in learning vocabulary.
• Using pictures
• Using real things
• Contain of games
• Using Computer
2 The undesirable media to be
applied in learning vocabulary.
• No pictures
• Many difficult words
• No translation
• Long sentences
difficult words, no translation, and there were many long sentences included in the media.
From the information collected through the open questionnaires, it showed that the students liked to learn through pictures, real things, and computer which contained games. The rejection on the difficult words and sentences which did not provide the translation showed that the students preferred to translate it through things or fun activities rather than to be translated by the English teacher or dictionary. It is also added by the English teacher in the interview that demonstrating things applied in the learning activity gave a good feedback for the students. The students felt being involved in the learning activities especially when the lesson included fun games.
In order to obtain the information about the media, the researcher conducted the interview with the English teacher who was responsible to teach the seventh grade in SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. The interview questions were about the media used to teach English, especially vocabulary.
From the interview with the English teacher, the researcher obtained the information needed. The English lesson was held twice a week in class 7A, every Monday and Tuesday. On Monday, the English lesson started at 7.30 a.m. to 8.50 a.m. and Tuesday at 11.40 a.m. to 1.00 p.m. which lasted for eighty minutes in every meeting. The sources learning which were provided for the students to learn English were dictionaries and text books.
pictures drawn on the whiteboard were aimed to give a stimulus to the students. Through the pictures and real things, the students wanted to know and learn about it. As a result, the media would bring the students to be actively involved in the learning process.
When dealing with method and strategy which were applied to teach vocabulary for the seventh grade students, the English teacher stated the Direct Method was suitable for the students’ characteristic in the seventh grade of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta. Using pictures and demonstration were applied to attract the students’ attention and maintain the students’ interest.
Based on the interview with the teacher, the school did not provide the media to teach English. The school only provided English text books and dictionaries of English-Indonesia and Indonesia-English to support the learning. Although the school provided computer facility, it was only used for Technology Informatics Learning (TI). Since the media of teaching-learning English had not been provided by the school, the researcher planned to develop the media which were expected could facilitate the teaching-learning process. Realia was chosen as the media to be developed to support the teaching-learning process in the seventh grade of SMP Taman Dewasa Yogyakarta.
combined with fun activity like games because it could release stress and the students could absorb the vocabulary and remember it without any force.
Besides the suggestion from the English teacher about the realia as the media of learning, the theory of realia from Newby in the book Instructional Technology for Teaching and Learning (2000) about the advantages and limitations of realia also becomes the important aspects in developing the realia. The advantages of realia are less abstract and more concrete; readily available in the environment, around school, and at home; and attract students’ attention. While the limitations are it takes a lot of time for the large objects and possible damage.
After knowing the students’ interest and the suggestion on the developing of realia from the English teacher and the theory of realia, the researcher started to develop the realia based on the learners’ characteristics, learners’ need and the subject content. There were eight media for eight subject contents. The following paragraphs discussed the realia.
1) Photos
2) Klik klok and pictures of daily activities
Klik klok and pictures of daily activities were aimed to attract students’ attention to learn about time and the activities in daily life. The klik klok was made from ivory and carton papers. It was made in bigger size than the real clock in order to make the students could see it clearly when it was applied in front of the class. The pictures of daily activities were used to support the students in learning vocabulary and later they would be able to describe their own daily activities through klik klok and the pictures.
3) ABC flashcards and pictures of things in the bedroom
ABC flashcards and pictures of things in the bedroom were aimed to make the students learn vocabulary easily. The ABC flashcards were made from the ivory paper. The flashcards consisted of letters from A to Z. The magnet was put behind the flashcard to be put on the magnet board. By using the ABC flashcards, the students would be able to rearrange letters and complete the missing letters in a word. The pictures of things in the bedroom were used to show to the students about things in the bedroom.
4) Peek a Boo
question-answer section and discussion, they tended to be very noisy when they did no