i
THE EFFECTIVENESS BETWEEN SURVEY, QUESTION,
READ, RECITE, REVIEW (SQ3R) AND KNOW, WANT, LEARN
(KWL) STRATEGY
TO INCREASE STUDENTS’ READING
COMPREHENSION
(An Experimental Research of the Eleventh Grade Students of
MA Al-Bidayah Candi Bandungan Semarang Regency in the Academic Year of 2016/2017)
Submitted to the Board of Examiners in Partial Fulfillments of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd.) in English Education Department, Teacher Training
and Education Faculty, State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
By:
NUR TSAQIB
113-13-033
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
v MOTTO
“DO NOT LOSE HOPE, NOR BE SAD”
(Qur’an 3:139)
“DREAM, BELIEVE, AND MAKE IT HAPPEN”
(Agnesmo-Indonesian Singer)
“DARE TO LEAVE YOUR COMFORT ZONE AND LIFE
YOUR DREAMS”
vi
DEDICATION This graduating paper is whole heartedly dedicated to:
1. My beloved parents, father (Muslikhin) and my beloved mother (Suiyah), thanks all support, trust, finance, encouragement, praying and I just can say thank you, I love you so much. (God Bless You)
2. My beloved sisters Muslikhatun, Rosidah, Alfiyah, and Siti Munawaroh thanks for your support, kindness and togetherness.
3. My beloved brothers in law Ruwadi, As‟adi, Lukmanto, and Muthohiron thanks for your support and praying.
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, the most gracious, the most merciful, the lord of universe, because of Him, the researcher could finish this graduating paper as one of the requirement for Sarjana Pendidikanin English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga in 2017. Then, peace and salutation always be given to our prophet Muhammad
SAW who has guided us from the darkness to the lightness.
However, this success would not be achieved without those supports,guidance, advice, help and encouragement from individual and institution, and the researchersomehow realize that an appropriate moment for me to deepest gratitude for:
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd. the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN)Salatiga
2. Suwardi, S.Pd, M.Pd. as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty 3.Noor Malihah, S.Pd, M.Hum, Ph.D. as the Head of English Education Department
4. Rr. Dewi Wahyu Mustikasari, M.Pd. as the Counselor who has educated, supported, directed, and given the writer advice, suggestion, and recommendation for this graduating paper from beginning until the end
5. All of the Lecturers in the English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga
6. All of the Staff who have helped the writer in processing the graduating paper administration
7. All of staff and teachers of MA Al-Bidayah Candi Bandungan Semarang Regency
ix ABSTRACT
Tsaqib, Nur. 2017. “THE EFFECTIVENESS BETWEEN SURVEY, QUESTION, READ, RECITE, REVIEW (SQ3R) AND KNOW, WANT, LEARN (KWL) STRATEGY TO
INCREASE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION (An Experimental Study of the
Eleventh Grade Students‟ of MA Al-Bidayah Candi Bandungan Semarang Regency in the Academic Year of 2016/2017)A Graduating Paper English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. Counselor: Rr. Dewi Wahyu Mustikasari M.Pd
Keywords:SQ3R, KWL Strategy, Students’ Reading Comprehension
The objectives of the research were: 1) This research was conducted in order to find how effective was the improvement of students‟ reading comprehansion when using SQ3R and KWL strategy, 2) This research was conducted in order to find which strategy was more effective between SQ3R and KWL in improving students reading comprehansion. The subject of this research was the studentsof the senior high school consist of sixty four students of MA Al-Bidayah Candi, Bandungan, Semarang Regency.The researcher used a quasi experiment research as a method in this research. The methodology of this research used quantitative research. It was conducted in two classes treatment and comparative, each of class had three times treatment. Each treatment consists of planning, action, observation and reflection. The results showed that:1) The mean score pre-test of treatment class was 50.23 and for mean score pre-test of conmparative class was 48.88, where the mean post-test of treatment class was 84.90, and for mean post-test of comparative was 60.73. 2) The improvement of the students‟ reading comprehension was significant after applying SQ3R and KWL strategy, and
SQ3R was more effective strategy to improve students‟ reading skill or can be mentioned
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES ... iii
STATEMENT OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF TABLES ... xiii
LIST OF FIGURES... xiii
LIST OF CHARTS... xiv
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Limitation of the Research ... 6
C. Problemsof the Research... 6
D. Objectives of the Research ... 7
E. Significance of the Research ... 7
F. Definition of theKey Terms ... 9
1. SQ3R Strategy ... 9
2. KWL Strategy ... 10
xi
G. Hypothesis ... 13
H. Graduating Paper Outline…………....……….... 14
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW A. Previous Researches ... 15
B. SQ3R Strategy………... 18
C. KWL Strategy ………... 21
D. Advantages of Using Reading Strategy... 22
E. Similarity and Difference between SQ3R and KWL Strategy...23
F. Reading Comprehansion ... 24
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD A. Research Approach ... 27
B. Research Method ... 27
C. Research Design ... 28
D. Location of the Research ... 30
E. Subject of the Research ... 30
F. Role of the Researcher ... 30
G. Poulation ... 30
H. Sample ... 31
I. Time Schedule of the Research ... 33
J. Method of Data Collection ... 33
K. Research Instrument ... 34
L. Rubric of Tes ... 35
xii
N. Method of Data Analysis ... 40
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION A. Profile of the Students Before and After the Treatments for Both Treatment and Comparative Class... 43
1. Pre-test Analysis ...43
2. Treatments ...49
3. Post-test Analysis ...51
B. Findings 1. Analysis of Students‟ Improvement... 57
2. Paired Sample ... 59
a. SQ3R Strategy... 60
b. KWL Strategy... 61
3. Strategy Which is More Effective ... 62
CHAPTER V CLOSURE A. Conclusion ... 64
1. Profile of the Students‟ Reading Comprehansion Skill before and after Having Treatment by SQ3R and KWL Strategy ... 64
2. Significance Difference of the Students‟ Profile on Their Reading Comprehansion Skill after Having SQ3R and KWL Strategy ... 64
B. Suggestions ... 66 REFERENCES
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
a.Table 3.1 Students of MA Al-Bidayah Candi ... 31
b. Table 3.2Time Schedule of the Research... 33
c.Table 4.1Pre-test Result of Treatment Class ... 44
d. Table 4.2 Interpretation Pre-test Score of Treatment Class ... 45
e. Table 4.3Pre-test Result of Comparative Class ... 47
f. Table 4.4Interpretation Pre-test Score of Comparative Class ... 48
g. Table 4.5Post-test Result of Treatment Class ... 51
h. Table 4.6Interpretation Post-test Score of Treatment Class ... 53
i. Table 4.7Post-test Result of Comparative Class …... 54
j. Table 4.8Interpretation Post-test Score of Comparison Class ... 56
k. Table 4.9 Paired Sampel Test of SQ3R ... 58
l. Table 4.10 Paired Sampel Test of KWL ... 59
m. Table 4.11 Paired Samples Corelation ... 62
n. Table 5.1 Paired Samples Corelation ... 65
LIST OF FIGURES a.Figure 3.1Design of Quasi-Experimental Research ... 29
b. Figure 3.2Evaluation Criteria ... 35
xiv
LIST OF CHART
a.Chart 4.1 Performance Students‟ Reading Skill in Treatment Class by SQ3R Strategy
... 57
b. Chart 4.2Performance Students‟ Reading Skill in Comparative Class by KWL Strategy
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Research
Many people need English to support their goals in life since English becomes an international communication tool, It is important to learn English especially in education. “English as the International language serves many
people as a bridge into the worlds of higher education, science, international trade, politics, tourism or any other venture which interest them” (Edge, 2003, p.25). So that, English course becomes one of essential subjects to the students as a tool to communicate. In a school life, there are four skills that should be mastered by the students in learning English, which are listening, speaking, reading and writing. Here, the researcher is interested in observing the students‟ reading skill since it is one of the important skills that must be mastered by the students to get the writen information.
According to Achersold and Field (1997, p.15), “Reading is what
happens when people look at text and assign meaning to the written symbols in that text.” It can be described that reading is the interaction between the
2
information suggested by the written language, and the context of reading situation.”
To create an understanding mentioned, the students have to catch a meaning by reading carefully from the written information to understand the meaning clearly. (Phakiti, 2006, p.1) cites “Second language reading comprehension is known as a highly complex skill to master.”
Mastering reading is not easy, because every teacher has a series of problems in teaching, and learning reading skill. As stated by Carlston (2011), “One of the barriers to master reading comprehension is students‟
inability to engage the text when they do read. Ineffective reading may cause the students to find difficulty in comprehending the text.” Furthermore Shepherd & Selden, (2011) add “In addition, reading and literacy researchers
agree that reading activities always comprise both decoding process and comprehension.” It is the reason why reading comprehansion is one of several activities that has own difficulties on its process to overcome the students‟
obstacles in reading comprehansion.
The unsatisfactory of reading ability from the students might be caused by the following problems as stated by Gebhard (2000, p.186),
3
It can be inferred that the students will be passive learner if the teacher always writes and writes without giving any chances for the students, the students will get bored and cannot improve their self if the teacher use the impropriate teaching reading strategies, and it can makes the students unmotivated or less interest with the lesson. Accarding to MacKay and Tom (1999) as cited by Mustikasari (2014, p.16) “As an active participant in
learning process, the learner needs to have input in to both the content of the course and the way in which it is being taught,” it means that the teacher
should has a strategy to make the students understand it and enjoy to the learning-teaching process especially to the passive students.
Based on the pre-survey which were done by using the interview on Saturday, April 15th 2017, it could be inferred that the second year students of MA Al-Bidayah Candi Bandungan had some problems in reading comprehansion as follow : 1) Less dictionary in the reading class (most of the students did not have dictionary to be used in reading class by this reason the students could not look for unfamiliar vocabulary), 2) Less reading teaching strategy in the reading class ( the teacher did not provide reading strategy while taught reading skill by this reason the students got bored and did not have motivation to do reading activity). It can be informed that majority of the students had the problem on point 2.
4
interest in English major and to increase the students‟ skill in reading comprehansion.
There are several strategies of language teaching reading comprehension, but the researcher would like to compare between Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review (SQ3R) and Know, Want, Learn (KWL) as the strategies that applay to increase the reading comprehansion skill of the students.
As stated by Manitoba (2005, p.2) “You should try SQ3R, a reading
strategy designed to help students improve their comprehension (understanding), memory, and efficiency in reading.” SQ3R strategy is clasified in active learning strategy that consists some activities which one demanded the students to do an active learning process by this strategy, an active learning process is needed to achiev the goal of teaching-learning process easier. (Yuksel, 2012, p.5 ) “The prior knowledge activation
is one of the vital necessary components in establishing an effective learning.”
A number of studies on the use of SQ3R strategy have been conducted. (Carlston, 2011, p.11) “Study found that when students use SQ3R
5
(Lipson & Wixson, 2003) “SQ3R's origins can be traced back to the
early 1940s (Robinson, 1941), and it has recently earned the title "The grandfather of study strategies." This strategy, designed for use with expository text, is best-suited for textbook reading and assignments. SQ3R can be broken down into many different and separate skills, which are necessary for successful implementation.
The second strategy chosen by the researcher is Know, Want, Learn (KWL) strategy. To encourage students to develop effective reading skills, there are various teaching and learning strategies that can be used by the teachers in classroom. Most of the teaching and learning strategies usually focus on a particular strategy or skill. (Ogle, 1986, p.29) “KWL (Know,
Want, Learned) strategy is one of teaching and learning strategies used mainly for information text.” The aim is more diverse. It helps the readers
elicit prior knowledge of the topic of the text; set a purpose for reading; monitor their comprehension; asses their comprehension of the text; and expand ideas beyond the text. Ogle (1986, p.26) informs “Developed the
strategy for helping the students to access important background information before reading nonfiction.” The KWL strategy (accessing what I know,
determining what I want to find out, recalling what did I learned) combines several elements of approaches. The first two steps of KWL, the students and teacher engage in oral discussion.
6
purpose of reading is to learn an international language and search an information in a text which is English (3) SQ3R strategy is focused on communication, it is a great way to maximize reading skill since an important element of language, reading skill is also can applayed as communicate tools and to searh an information in a text wich is English (4) Both SQ3R and KWL strategies have some techniques which include interesting media and fun activities.
From the explanation above, the researcher decided to rise a title THE EFFECTIVENESS BETWEEN SURVEY, QUESTION, READ, RECITE, REVIEW (SQ3R) AND KNOW, WANT, LEARN (KWL) STRATEGY TO INCREASE THE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION.
B. Limitation of the Research
Limitation of the research is on the reading comprehension skill. The researcher limits the research on the reading comprehension which is discussed only on the narrative text.
C. Problem of the Research
Based on the limitation of the problem above, the problems of the research are formulated as follows:
1. How effective is the improvement of students‟ reading comprehension
when using SQ3R and KWL strategy?
2. Which strategy is more effective between SQ3R and KWL in improving students reading comprehension?
7
In accordance with the problems, the writer has some objectives of the research:
1. This research is conducted in order to know how effective is the improvement of the students‟ reading comprehension when using SQ3R
and KWL strategies
2. This research is conducted in order to know which strategy is more effective between SQ3R and KWL in improving students reading comprehension
E. Significances of the Research
The result of this research is expected to be useful in two dimensions, theoritically and practically:
1. Theoritically
a. Theoritically, this research is expected can describe about two reading strategies (SQ3R and KWL) and compare which one is more effective to increase the student‟s skill in reading
comprehansion.
b. The result of research paper can be used as an input in English teaching learning process especially for reading by using SQ3R or KWL strategy.
c. The result of research can be used as the reference for those who want to conduct a research in English teaching learning process. d. The results of the study can strengthen the knowledge of the theory
8 a. For the writer
The findings of the research can be used as a starting point in improving the writers teaching ability, especially in teaching reading comprehension.
b. For the students
This research can add the students‟ interest in English learning, so
English is not boring lesson for them anymore. The result of this research is beneficial for students as reference in english major learning related on the reading comprehansion. By studying the result of this research, hopefully the students will have better skill in reading comprehansion to decrease a mistake when the students search information in a text or essay.
c. For the teacher
Apart from that, this research is also beneficial for the teacher to knowing which one of two strategies (SQ3R and KWL) that more effective to improve reading skill of the students‟ in narrative text. The
result of this research is very important for english teachers. It also can help them in teaching learning process to choose more effective strategy in teaching reading comprehension.
d. For other researcher
The findings of the research can be used as one of the references in conducting a research on English Language Teaching, especially in the implementation of SQ3R and KWL strategy.
9
The terms of the title of this study will be explained to make understandable meaning as follows:
1. SQ3R Strategy
A number of studies on the use of SQ3R strategy have been conducted. Artis (2008, p.133) states the significance and usefulness of SQ3R as: “Because students can independently learn the basics of the
course via reading, it reduces the need for instructor monologues (passive learning) to cover that information.” It is comparable with the activities that applyed from SQ3R strategy to increase students‟ reading
comprehansion and retain more information by applaying five steps from SQ3R strategy.
SQ3R is a Reading or Study formula designed to help process and
increase retention of written information. As cited by Asiri and Momani (2017)
SQ3R consists of the following five steps.
S = SURVEY
Scan the piece of writing to establish its purpose and get the main ideas. Q = QUESTION
Write questions to give purpose and improve concentration. R = READ
Search for answers to your questions. Make notes and highlight main ideas that support the concept.
R = RECITE
10
It is important to review the material to understand and remember it. 2. KWL Strategy
(Ogle, 1986, p.37) “KWL (Know, Want, Learned) strategy is one
of teaching and learning strategies used mainly for information text.” It
helps the reader to find out the information of the information text quickly. According to Lenski et al. (1995, p.31) “KWL strategy helps children
become good readers by getting them to do many of the things that good readers do.” This strategy gets the students to read silently with
comprehension. In addition, the students relate new information to what they already know when they confirm or disconfirm the information in the
K column. Further, the students learn to set their own purposes for reading when they generate questions for the W column. Their reading to answer these questions helps them concentrate while they are reading as they more actively monitor their own comprehension.
(Dieu, 2015, p.487) Using a KWL chart in different phases of your teaching, you can monitor your students‟ reading process: 1) Before reading, ask students to complete the “I know” column. 2) After students have completed the “I know” column, ask students to complete the “What I want to know” column. 3) After reading, ask students to complete the “What I have learnt” column.
It can be concludes that KWL strategy has three steps of activity that can improve the students‟ skill in reading comprehansion.
3. Reading Comprehension
11
reading may cause the students to find difficulty in comprehending the text.
(Shepherd & Selden, 2011, p.21) “In addition, reading and literacy
researchers agree that reading activities always comprise both decoding process and comprehension.” Furthermore, Sheperd and Sheldon (2011,
p.23) state that research on comprehension indicates that good readers employ several strategies before, during, and after they read. It means that a structured reading strategy could help the reader to focus their reading aim on the comprehension of the text. Therefore, memory of the information from the text is achieved through understanding. Thus, the absence of reading strategies could lead the readers into ineffective reading activities.
Comprehension includes the correct association of meanings with word symbols, the selection of the correct meaning suggested by the context, the organization and retention of meanings, the ability to reason one‟s way through smaller idea. (Phakiti, 2006, p.15) “Second language
reading comprehension is known as a highly complex skill to master.” New words and diverse text structure may cause problems to EFL learners to acquire complete knowledge of the language. That is also the major challenge for a number of students of ESL. According to Celce-Murcia (1991, p.98) “Reading helps learners in successful functioning as well as giving them sense of efficacy when having access to information.” Poor
12
essential for the kind of knowledge society that one envisages in the globalized context. Therefore, the students of modern world must know how to learn from reading and how to get in the present educated society. A reader can lead others to light.
Comprehension is a thinking process it is thinking through reading. According to Sheperd and Sheldon as cited by Pribadi (2017, p.1) state that “Research on comprehension indicates that good readers employ
several strategies before, during, and after they read.” As such, it is dependent upon the learners, basic cognitive and intellectual skills, upon their background of experience (vocabulary, knowledge, concepts, and ideas) and upon their language skills (knowledge of morphology, syntax, and grammar).
G. Hypothesis
Hypothesis is a statement in quantitative research in which the investigator makes a prediction or a conjecture about the outcome of a relationship among attributes or characteristics. Traditionally used in experiments, they serve, like research questions, to narrow the purpose statement to specific predictions.
(Creswell, 2012, p.111) These predictions are not simply an “educated guess.” Rather, researchers base them on results from past research and literature where investigators have found certain results and can now offer predictions as to what other investigators will find when they repeat the study with new people or at new sites.
13
It states that there is no improvement students on reading skill when using SQ3R and KWL strategy as measured by pre-test and post-test and both SQ3R and KWL strategy are equal. “The symbolic
expression as illustrated by Schreiber and Asner-Self” (2011, p.244) looks like:
̅ ̅
2. Alternate hypothesis (Ha).
It states that there is an improvement on students on reading skill when using SQ3R and KWL strategy, and there is a strategy between them which is more effective. “The symbolic expression as illustrated by Schreiber and Asner-Self” (2011, p.244) looks like:
̅ ̅
H. Graduating Paper Outline
14
15
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Previous Researches
The researcher is inspired by other reaserches that using SQ3R and KWL strategy to teach reading comprehansion. There are several researches taken from some relevant sources related to this research exactly. However, the researcher picks four of them which are two reasearches inspired with SQ3R strategy and two other are inspired with KWL strategy.
16
The second research was done by Khaghaninejad, Saadabadimotlagh and Kowsari (2015). The objective study aimed at exploring the possible effects of strategy-based instruction of reading passages to undergraduate Iranian EFL learners. Then the researcher used clasroom action research as the methodology of this research. The study particularly explored the effects of using SQR3 and TPS reading strategies on learners‟ reading performance.
The learners in the first experimental group (SQR3) surveyed, questioned, read, reviewed and recited the reading passages while learners in the second experimental group (TPS) group thought about reading passages and shared their comprehensions with the classmates. However, learners in the control group followed the traditional method of translating reading passages to Persian for comprehension. The reading section of IELTS Test, as an internationally validated test, was applied as the pre- and the post-test of the study to further check learners‟ reading comprehension. As a result the
paired-samples t-test and ANOVA analysis of learners‟ performances indicated that SQR3 and TPS learners significantly outperformed on their post-tests compared with their peers in the control group. The results certified the efficacy of strategy-based approach of teaching reading passages, namely SQR3 and TPS, in promoting learners‟ reading comprehension in academic
Iranian EFL context.
17
reading comprehension. To prove the benefit of prior knowledge, K-W-L strategy was used as treatment in the experiment. In this research the researcher used classroom action reseach. The hypothesis was that the K-W-L strategy would help passive students improve their reading comprehension skill. The final target was trying to change students from negative attitudes to positive feeling towards reading class after the K-W-L strategy was used and to improve Vietnamese students‟ reading skill as well as catching the main
idea in the reading texts in order to have successful communication in English. As a result, the research has proved the effect of the treatment. It also suggested a way to control a reading class, to create an interesting and exciting atmosphere to improve students‟ reading comprehension skill.
Then the second previous research was done by Riswanto, et al (2014). There was a fact that most of the Secondary School students were still low in comprehending reading texts. Therefore, the main objective of this study was to see whether the use of KWL (Know, Want, Learned)” strategy
was effective in improving the students‟ reading comprehension achievement
in learning English as a Foreign Language. The researcher used classroom action research in this research. The data were collected by using multiple choice reading comprehension test. The data obtained were analyzed by using t-test formula. The result showed that KWL strategy was effective in improving the students‟ reading comprehension achievement. The
effectiveness was indicated by the result of the Stepwise Regression formula that the contribution of KWL strategy on students‟ reading comprehension
18
By considering those four previous researches above, the researcher made a conclussion that three of those researches above only used one strategy. Meanwhile only one research used two strategies but did not to be compared, all of those researches above used the strategy just to be exlored and knew how effective the strategy was in teaching reading comprehansion.
By some reasons above the researcher claims that this research is more spesific than the previous researches above. The researcher used two strategies of reading comprehansion to be applied and compared between SQ3R and KWL strategy in reading comprehansion, and the researcher find the improvement of both strategy and also finds which strategy is more effective.
B. Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review (SQ3R) Strategy
(Lipson and Wixson 2003, p.47) “SQ3R strategy is perhaps one of the
oldest and most widely strategy.” It applies most readily to textbooks and
formal reading assignments in wich readers are required to consume main points from expository writing. However, Manktelow (2007, p.47) explains that “SQ3R is a fives stage active reading strategy, they are survey, question,
read, recite, and review.” This strategy uses for fully absorbing written
19
reviewed else where the steps associated with the strategy are briefly.” The goal of the strategy is to increase the students‟ engagement with the text.
Although commonly taught, there is surprisingly limited regarding the impact of SQ3R. In addition, Shepard (2001, p.23) explains that “SQ3R is a five steps strategy thus are survey, question, read, recite, and review. It will help the students to identify the significant ideas, graps these ideas more readily, remember the essential points, and better prepared for exams.” Each step is symbol that will appear as a reminder at appropriate places throughout the text. The following explains how the S in SQ3R refers to survey; the Q refers to question; and 3R refers to read, recite, and review. This strategy identifies each of the five steps. (Carter 2007, p.156) “SQ3R stands for Survey,
Question, Read, Recite, and Review. As the reader move through the staages of SQ3R, the reader will skim and scan the text. Approach SQ3R as a flexible framework on which to build the study strategy.” When the reader bring personal learning styles and study preferences to the system, it will work better than if the reader follow it rigidly. They claim that the SQ3R has five steps, those are: survey, question, read, recite, and review, an it is elaborated bellow.
1. Survey
20 2. Question
After the students have surveyed the text, the next step is to ask questions about the assignment. The process of asking questions leads to discover knowledge, which is the essence of critical thinking as the students formulate some questions and then discover the answer in the text and the materials. It meant the students should make a note of any questions on the subject‟s mind, or particularly interest of the survey.
These questions can be considered almost as study goals understanding. 3. Read
In read, the students should read all points of the text that are relevant in order to make easier the students to answers the question because this steps will be particularly easy for the students, if there is a lot of dense and complicated information from the text. . Besides, when the students find the concept of reading, then they will able to answer and the questions based on the text that has been studied in reading comprehension.
4. Recite
In recite, the students response all of the questions by using their own words after they finish reading. Moreover, the students have to take a notes from the text to the information, read appropriate sections of the document, run through several items.
5. Review
21
it prepares for the exams. Furthermore, if the students close the book, after reading it once, the students will forget almost everything related to the material. However, if the students close the book, the students will remember all of the materials that have been studied before, (Kwanlent, 1996).
C. Know, Want, Learn (KWL) Strategy
(Ros & Vaughn, 2002, p.179) “Know-Want-Learn (KWL) is an instructional reading strategy that is used to activate the students‟ background
knowledge, assist students in setting purposes for reading, and help students to monitor reading comprehension by using graphic organizer.” In this definition, four important concepts of Know-Want-Learn (KWL) strategy are used. Firstly, Know-Want-Learn (KWL) is an instructional reading technique to aid the teaching of reading. It uses graphic organizer namely KWL chart to help the students record their thinking process before, during, and after reading. Secondly, Know-Want-Learn (KWL) strategy is designed to activate students‟ background knowledge. By using Know-Want-Learn (KWL)
strategy, the teacher can help the students recall the information stored in their mind which is related to the topic. Thirdly, Know-Want-Learn (KWL) strategy can assist students in setting purposes for reading. By the use of
Know-Want-Learn strategy, the teacher can encourage the students to determine why they are reading a specific text. Fourthly, (Ros & Vaughn, 2002, p.179) Know-Want-Learn (KWL) consists of three basic stages,
22
topic. 3) Learn: And finally assess what the students learn in the L stage or Learn, it means the students start to learning the topic that given by the teacher.
From the definition, Know-Want-Learn (KWL) strategy can be concluded as a strategy which has well-organized steps to be followed by the students. The strategy combines the use of reading strategies in the effort to improve reading comprehension.
D. Advantages of Using Reading Strategy
Rading strategy has some advantages that can help the students understand the text. Below, three advantages of reading strategy are presented.
1. Helping the students to check prior knowledge
The use of reading strategy in the teaching of reading helps the students check their prior knowledge of a topic, concept, or process before learning about it. With this prior knowledge, the brains of the students will recall what they already know about the topic.
(Cardenas, 2009, p.38) When the students get new information, the students will use their brains to join the old knowledge with the new information from the text. learners who start making connection about what they already know can create meaning of the text more easily.
2. Building the students‟ interest in reading
The second benefit of using reading strategy is to stir the students‟ interest in what students also want to know additionally about
the topic. By questions about the topic can increase the students‟ interest
23
text because they want to find the information or the topic of the text. (Cardenas, 2009, p.38) “The students are not only making use of their
prior knowledge but also are motivated to keep reading the text.” 3. Providing a chance for the students to assess what they have learned
The third benefit is to provide a chance for students at the end of a lesson to look back and assess what they have learned in the lesson, by reading strategy the students can easily remember what have they read. (Ros & Vaughn, 2002, p.179) “The students record the information they
get from the text. Here, the students can assess their own thinking process.”
E. Similarity and Difference between SQ3R and KWL Strategy
Based on explanation above, the researcher makes a conclussion that those both strategy SQ3R and KWL have a similarity and difference those are:
1. The similarities
a. SQ3R and KWL strategy have several parts or stages on its utilizing b. SQ3R and KWL strategy are active learning reading strategy
(student-centered)
c. As cited by Pribadi (2017, p.2) “SQ3R and KWL strategy can help the students to solve their problems in reading comprehension especially on senior high school.”
2. The differences
24
b. The last part of SQ3R is surveying wich is the same with giving feedbeck, the last part of KWL strategy is learning (there is no feedbeck).
F. Reading Comprehansion 1. Definition of Reading
In the conference‟s Eleventh Year Book, Spencer (1946) writes,
“In the broadest sense, reading is the process of interpreting sense stimuli.
Reading is performed whenever one experiences sensory stimulation.” It
means that reading is a process to interprate writen text or searches a meaning by combining word by word. Harris and Sipay (1975, p.5) define “Reading as the meaningful interpretation of written or printed verbal
symbols.” The reader interprates printed verbal symbol from the witer to
get a meaning or information. Gibson (2009) says that “Reading is receiving communication: it is making discriminative responses to graphic symbols it is decoding graphic symbols to speech; and it is getting meaning from the printed page.” As a reflection from writing, reading is a
reciving communication by this activity there is a relation between the writer and the reader. (Anderson et al, 1985) “Reading is the process of
25
same meaning that is conveyed by the writer and may be different from the other readers reading in the same text.
2. Definition of Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension as the process of simulatenously extracting and constructing meaning. In other word, the researcher recognize both challenges: figuring out how print represents word and engaging in the translation of print to sound accurately (extracting), at the same time formulating a representation of the information being presented, which inevitably requires building new meanings and integrating new with old information (constructing meaning).
Catherine (2003, p.3) adds that “comprehension entails three
elements: (1) The reader who is doing the comprehending, (2) The text
that is to be comprehended, and (3) The activity in which comprehension is a part.” As the comprehansion those three elements can not be sparated
because the reader needs to do a reading activity to understand the text. Grellet (1992, p.3) states that “reading comprehension understands
a written text and extracting the required is to catch the meaning from the text and to comprehend the information that is conveyed in the text.”
Comprehension is about the ability of people to understand something. There should be an interaction between the reader and the text. Kustaryo (1998, p.11-12) states that “reading comprehension means understanding what has been read.” Comprehension involves understanding the
26
organizing ideas, recognizing the author‟s purpose, making judgments and
evaluating.
It can be concluded that reading comprehension is a process which is conducted by the readers to understand extracting and constructing meaning of the text and to get information from the text. In reading comprehension should be interaction between the reader and the text, because reading comprehension is the process of making meaning from text. As cited by Clara (2011, p.56)
Reading comprehension is a process of making sense of a written text. However, it is not a passive one way decoding process. Instead, it is an active two way process in which the reader and text interact. The reader test clues from the text against his knowledge to arrive at an understanding of the text acceptable to the reader. Reading comprehension is not just reading with aloud voice but reading is established to understand the meaning of words, sentences, and paragraph as well as sense relationship among ideas. Simanjuntak (2011, p.57) “Whenever a student just read loudly but cannot understand the content of the text, it means that he fails in comprehending the passage.”
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
27
The researcher used quantitative approach in this research. According to Kothari (2004, p.3), “all the measurement of quantity or amount are the
basis of quantitative research.” All phenomenon that can be stated in terms of
quantity can be applied by using this approach. The quantitative research field holds a positive view of the world by mean that the researcher believed that there were truth out there. Moreover, Schreiber and Asner-Self (2011, p.13) add that “this approach focuses on objectivity and quantifying the phenomenon under investigation, assigning numbers to ideas or constructs of interest.”
Therefore, this research met the characteristics as a quantitative research as Creswell (2012, p.13) explains. Firstly, it described a research problem by explaining the relationship between variables. Secondly, it provided problem statements and hypotheses of the study. Thirdly, the problem statements and hypotheses were created in specific, narrow, measurable, and observable. Fourthly, it collected numeric data such as score of students‟ pre- and post-test by using instruments. Fifthly, it compared classes, control and treatment class, using statistical analysis. Finally, it was written using standard, fixed structures and evaluation criteria, and took objectives.
B. Research Method
A method was needed to accomplish this research so that the researcher gained the scientific knowledge to solve the problems of research. Darmawan (2013, p.127) “Explains the term „method‟ is derived from Greek word „methodos‟ that means way or steps. In scope of scientific studies, a
28
researcher determined the influences of a result by testing an idea, practice, or procedure.
As Creswell (2012, p.145) states that “The basis objective of an experimental method is to check the effect of an intervention on a result.” An experiment happened when the researcher wanted to verify possible cause and effect between independent and dependent variables.
C. Research Design
There are many research designs offered in experimental design. One of them is two groups pre-test and post-test design. The researcher decided to use the design by the reasons that the researcher would like to know of how far is the students‟ skill on reading comprehansion by pre-test survey and
would like to know the effectiveness of the strategies by post-test survey. One type of experimental research is called by quasi experimental research since it describes the two independent variables towards a dependent variable. (Sabarwal & White, 2014, p.6) “Quasi Experiment methods that involve the creation of a comparison group are most often used when it is not possible to randomize individuals or groups to treatment and control group.”
In this quasi experimental research, the researcher managed pre-test for both treatment and comparative class. After that, the treatment class was treated by SQ3R strategy while the comparative class was traeted by KWL strategy. The common design can be seen in this figure below as illustrated by Arikunto (2010, p.316):
Figure 3.1
29
Class Pre-test Independent
Variable
Post-test
T Y1 X1 Y2
C Y1 X2 Y2
It means:
X1
: Treatment by SQ3R strategy :
X2 : Treatment by KWL strategy
Y1 : Dependent variable before the manipulation of the independent variable X
Y2 : Dependent variable after the manipulation of the independent variable X
T : Treatment class C : Comparative class
D. Location of the Research
30
Same with usual research, this research also has subject as a participant and to help collect the data. In this research the subject was all of eleventh grade social-1 and social-2 students of MA Al-Bidayah Candi Bandungan Semarang Regency in the academic year of 2016/2017, there were 64 students as the subject of the research.
F. Role of the researcher
In this research, the researcher was also the participant. The researcher acted as the teacher in the class.
G. Population
As Kothari (2004, p.55) states that “Population is all pieces in any
field of research.” (Schreiber and Asner-Self, 2011, p.83) “All potential
respondents of research subject also called as population.” They add that population is a collection of all component linked to the process of point of interest. The population of this research was the eleventh grade of MA Al-bidayah Candi Bandungan in the academic year of 2015/2016 consisted of 91 students that divided in to three classes. Namely 30 students from social 1 class, 34 students from social 2 class, and 27 from science class.
H. Sample
The sample of this research is the eleventh grade social 1 and social 2 students of MA Al-Bidayah Candi, Bandungan in the academic year of 2016-2017. The total samples are 64 students. As Patel wrote (2009, p.80) “Sample
is part of the representative of population that is observed.” For clearer
31
Table 3.1
Students of MA Al-Bidayah Candi
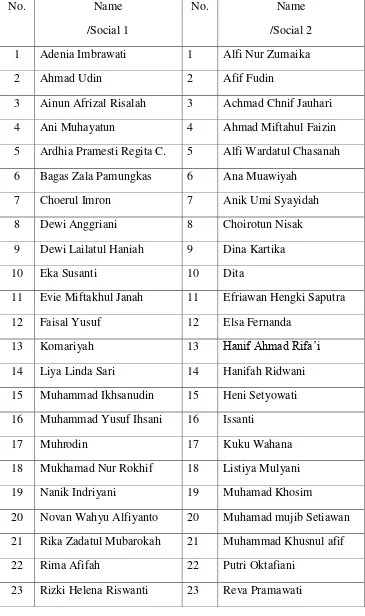
No. Name
3 Ainun Afrizal Risalah 3 Achmad Chnif Jauhari
4 Ani Muhayatun 4 Ahmad Miftahul Faizin
5 Ardhia Pramesti Regita C. 5 Alfi Wardatul Chasanah 6 Bagas Zala Pamungkas 6 Ana Muawiyah
7 Choerul Imron 7 Anik Umi Syayidah
8 Dewi Anggriani 8 Choirotun Nisak
9 Dewi Lailatul Haniah 9 Dina Kartika
10 Eka Susanti 10 Dita
11 Evie Miftakhul Janah 11 Efriawan Hengki Saputra
12 Faisal Yusuf 12 Elsa Fernanda
20 Novan Wahyu Alfiyanto 20 Muhamad mujib Setiawan 21 Rika Zadatul Mubarokah 21 Muhammad Khusnul afif
22 Rima Afifah 22 Putri Oktafiani
32
24 Siti Rina Aliyah 24 Riska Diana Sari 25 Salimatul Wahidah 25 Rosana Sriasih
26 Syaeful Anwar 26 Ruhmiyati
27 Ulfa Umami 27 Sulistyowati
28 Uswatun Khasanah 28 Tifani Oktavia 29 Vina Lilatus Sholkah 29 Unna Yurdanny
30 Tri Kusumawati 30 Wiwin Kurnianti
31 Agus Setyawan 32 Alfi hasanah 33 Khotimatus Sa‟adah 34 Nur Anisa Yulianti
A reason why the researcher choosed social 1 class and social 2 class is based on mean of daily score from the students. By the pre research observation the researcher asked the result of daily score of the students and knew that 88.28 is mean of science class, 81.67 is mean of social 1 class, and 83.02 is mean of social 2 class, the daily score is enclosed in appendices.
Based on the explanation above the researcher made a conclussion that the students of social 1 and social 2 are almost have some ability in english subject, based on that reason the researcher decided to choose the students from eleventh grade social 1 and social 2 of MA Al-Bidayah Candi Bandungan in the academic year of 2016/2017.
33
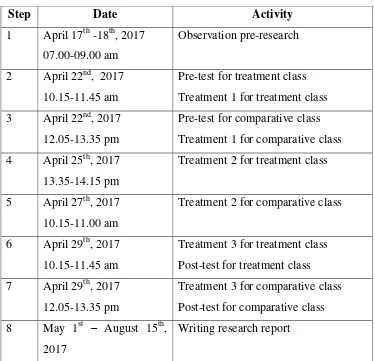
The researcher planned the time schedule in hope for the research was conducted smoothly. The research was done on August, 15th 2017. The table is shown below:
Table 3.2
Time Schedule of the Research
Step Date Activity
Pre-test for treatment class Treatment 1 for treatment class 3 April 22nd, 2017
12.05-13.35 pm
Pre-test for comparative class Treatment 1 for comparative class 4 April 25th, 2017
13.35-14.15 pm
Treatment 2 for treatment class
5 April 27th, 2017 10.15-11.00 am
Treatment 2 for comparative class
6 April 29th, 2017 10.15-11.45 am
Treatment 3 for treatment class Post-test for treatment class 7 April 29th, 2017
12.05-13.35 pm
Treatment 3 for comparative class Post-test for comparative class 8 May 1st – August 15th,
2017
Writing research report
J. Method of Data Collection
The researcher had two methods of collecting data to carry out the research. Kothari (2004, p.96) states that “The data can be collected through
34
this research, the researcher used test as the primary method. Then, documentation was the secondary method.
1. Test
a. Pre-Test
The researcher conducted pre-test. It aimed to know how far is the students‟ reading comprehansion ability.
b. Post-Test
After received the treatment by SQ3R strategy for the treatment class and KWL strategy for the control class. The students were asked for doing the post-test.
2. Documentation
The researcher used documentation as the secondary method to collect the data. As Kumar (2005, p.236) explaines that “Documentation organized the verbal data like correspondence, journal, memory report, and other that can be mutually responsible.” In this research, the researcher documented the students‟ test sheets, lesson plans, narrative text sheets, general condition of the school, school‟s document validaty sheets of lesson plan, validaty sheets of sylabus and photos report.
K. Research Instrument
35
excercises were about W-H Question. The researcher make same instrument between pre-test and post-test.
L. Rubric of Test
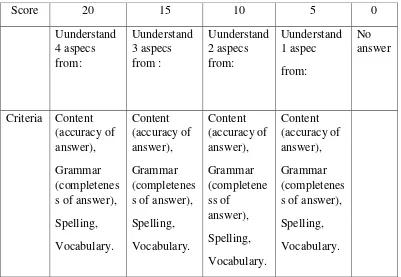
In addition, the researcher ranged the criteria of the students‟ competence namely: content, grammar, spelling, and vocabulary on both group the researcher classified as follows:
Figure 3.2
Criteria Content (accuracy of
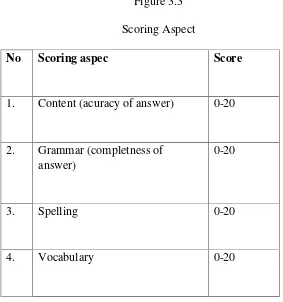
36 Figure 3.3 Scoring Aspect
No Scoring aspec Score
1. Content (acuracy of answer) 0-20
2. Grammar (completness of answer)
0-20
3. Spelling 0-20
4. Vocabulary 0-20
Guadiance of scoring 1. Number of question : 5
2. Each question has maximal score : 20 3. Maximal score is 5 x 20 = 100
4. KKM score is 73
5. E.g Siti got the answer that appropiate 4 aspecs by 3 questions and just appropiate 2 aspect for 2 questions, siti,s score is (3x20)+(2x10)= 80 M. Validity and Reliability
Dealing with this challannge of planning to assess reading comprehansion‟s report from the students, the researcher needed to be aware
37
teaching learning process. There were criteria that would be used to construct them. According to Schmitt & Messick (1989) in Richards (2001) as cited by Margiyanti (2014, p.20) “Validity (did the test really mesure what it was
supposed to mesure?), Reliability (did the past test perform consistently from one administration to the next?), Practicality (was the test practical to give and mark in particular setting?).”
1. Validity
Kimberlin and Winterstein (2008, p. 278) define
Validity is the extent to which an instrument measures what are purports to measure. Validity requires that an instrument can be reliable without being valid. While we speak of the validity of a test or instrument, validity is not a property of the test itself. Instead, validity is the extent to which the interpretations of the results of a test are warranted, which depends on the test‟s intended use.
To know how far a test is warranted, it always needs validity. In this research, the researcher used such kinds of validity:
a. Content Validity:
Kimberlin and Winterstein (2008, p. 279) state:
When we want to find out if the entire content of the behavior/construct/area is represented in the test we compare the test task with the content of the behavior. This is a logical method, not an empirical one.
38
researcher used fairy tales and legend that have familiar titles is students‟ head.
b. Face Validity:
Kimberlin and Winterstein (2008, p. 279) state: “Basically face
validity refers to the degree to which a test appears to measure what it purports to measure.” Keyword of face validity here is „degree‟ or
level. In order to qualify this face validity, the researcher adjusts the test with the indicator of 2016 curriculum and students‟ ability.
c. Criterion-Oriented or Predictive Validity:
Kimberlin and Winterstein (2008, p. 279) state:
When you are expecting a future performance based on the scores obtained currently by the measure, correlate the scores obtained with the performance. The later performance is called the criterion and the current score is the prediction. This is an empirical check on the value of the test – a criterion-oriented or predictive validation.
The keywords of this part are later performance (criterion) and current performance (prediction). There is a pre-test and post-test in this research. Which pre-test called by criterion and post-test is the prediction.
2. Reliability:
Kimberlin and Winterstein (2008, p. 276) define:
39
systematic or constant errors. Test-retest, equivalent forms and split-half reliability are all determined through correlation.
Reliability consists of: a. Test-retest Reliability
Test-retest reliability is the degree to which scores are consistent over time. It indicates score variation that occurs from testing session to testing session as a result of errors of measurement. Problems: Memory, Maturation, Learning.
b. Equivalent-Forms or Alternate-Forms Reliability
Two tests that are identical in every way except for the actual items included. Used when it is likely that test takers will recall responses made during the first session and when alternate forms are available. Correlate the two scores. The obtained coefficient is called the coefficient of stability or coefficient of equivalence. Problem: Difficulty of constructing two forms that are essentially equivalent. Both of the above require two administrations.
c. Split-Half Reliability
40
Spearman-Brown prophecy formula. Split-half reliability is a form of internal consistency reliability.
d. Rationale Equivalence Reliability
Rationale equivalence reliability is not established through correlation but rather estimates internal consistency by determining how all items on a test relate to all other items and to the total test.
e. Internal Consistency Reliability
Determining how all items on the test relate to all other items. Kudser-Richardson-> is an estimate of reliability that is essentially equivalent to the average of the split-half reliabilities computed for all possible halves.
f. Standard Error of Measurement
Reliability can also be expressed in terms of the standard error of measurement. It is an estimate of how often you can expect errors of a given size.
N. Method of Data Analysis
The researcher did some steps to analyze the data, they were: 1. Scored the students‟ test
The researcher scored the result of pre- and post-test from both experimental and comparative group. The researcher used point scale of 0-100 to measure the students answer.
41
After the students‟ test were scored, the researcher calculated the
data using t-test to determine whether there was significant difference before and after the treatment for both treatment and comparative class. “The researcher took the following steps as Sudijono (2010, p.305)
explains:
a. Calculated the mean (M) from each group using the following formula:
M = Mean ∑x = Total score
N = Number of students
b. Calculated the standard deviation difference (SDD)
√ ( )
SDD= Standard deviation
N = Number of students
D = Difference between pre- and post-test c. Calculated mean of difference (MD)
MD = Mean of difference
∑D= Total of difference between pre- and post-test
d. Calculated the standard error of mean difference (SEMD)
√
SEMD= Standard error of mean difference
42
N = Number of students e. Calculated t-value (to)
to = t-value of observation
MD = Mean of difference
SEMD= Standard error of mean difference f. Compared t-value (to) with t-table (tt)
Criteria of hypothesis accepted describes as follows:
to≥ tt = Reject null hypothesis (ho) and accept alternate hypothesis
43
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
C.Profile of the Students Before and After the Treatments for Both Treatment and Comparative Class
1. Pre-test Analysis
The researcher administered two kinds of test. They were pre-test and post-test. Pre-test was conducted before the treatment. It aimed to measure the students‟ reading comprehansion ability before having treatment by SQ3R
stratergy for treatment class and KWL strategy for comparative class. The researcher set the procedure of pre-test as follows:
a. The researcher as the teacher gave the test sheet to the students b. The teacher made rules for the students when they did the test c. The students submitted their test sheet as soon as they finished it d. The teacher gave scoring to the pre-test
Each correct answer was scored 20 if the students were able to answer all correctly would get 100 points.
44
After the pre-test was done, the researcher checked and gave score for the test. Then, the researcher could display the result of pre-test for treatment class as follows:
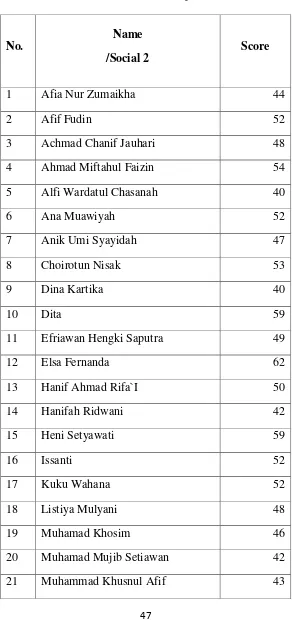
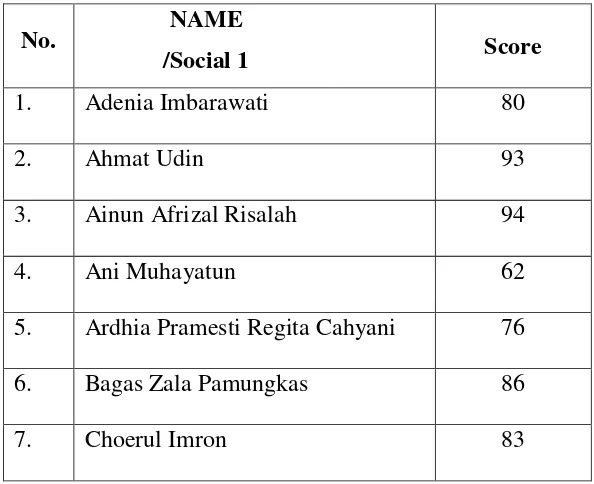
Table 4.1
Pre-test Result of Treatment Class
No.
Name
/Social 1 Score
1. Adenia Imbrawati 49
2. Ahmad Udin 56
3. Ainun Afrizal Risalah 47
4. Ani Muhayatun 46
5. Ardhia Pramesti Regita C. 49
6. Bagas Zala Pamungkas 47
7. Choerul Imron 44
8. Dewi Anggriani 49
9. Dewi Lailatul Haniah 49
10. Eka Susanti 45
11. Evie Miftakhul Janah 49
12. Faisal Yusuf 41
13. Komariyah 54
14. Liya Linda Sari 65
15. Muhammad Ikhsanudin 44
16. Muhammad Yusuf Ihsani 56
17. Muhrodin 41
18. Mukhamad Nur Rokhif 67
45
20. Novan Wahyu Alfiyanto 46
21. Rika Zadatul Mubarokah 45
22. Rima Afifah 51
23 Rizki Helena Riswanti 62
24 Siti Rina Aliyah 54
25 Salimatul Wahidah 50
26 Syaeful Anwar 29
27 Ulfa Umami 54
28 Uswatun Khasanah 54
29 Vina Lilatus Sholkah 52
30 Tri Kusumawati 50
Total (∑x1) 1507
N = 30
Mean (M) 50.23
Based on the table above, there were 30 students had done the pre-test. The highest score of treatment class was 67 while the lowest was 29. The mean of treatment class‟s pre-test score was 50.23.
b. Interpretation Pre-test Score of Treatment Class
After scoring the result of pre-test then the researcher could interpret the pre-test score for treatment class as follows:
Table 4.2
Interpretation Pre-test score of Treatment Class
Number of Student
Probable
Performance Category
46 B
ased on
the table above, it showed that from 30 students most of them gained enough category of their performance by the students of 15. Then 4 students gained good category and 10 students gained fair category. There was only 1 student gained poor category. At last, there was no student reached their excellent and very good performance on reading comprehension.
c. Pre-test Analysis of Comparative Class
Then, the researcher did the same step by displaying the pre-test result of comparative class. The distribution score table are as follows:
correct, 80% of correct answers - Very Good The students answer about 70% of
correct answers
4 Good The students answer about 60% of
correct answer
10 Fair The students answer about 50% of correct answer
15 Enough The students answer about 40% of correct answer
1 Poor The students‟ answers are mostly incorrect, less of 40% of correct answers
47
Table 4.3
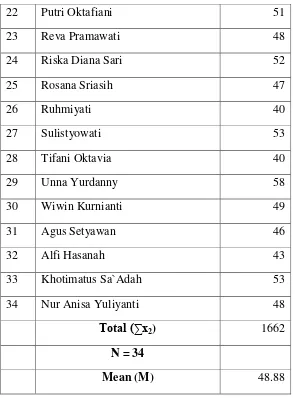
Pre-test Result of Comparative Class
No.
Name /Social 2
Score
1 Afia Nur Zumaikha 44
2 Afif Fudin 52
3 Achmad Chanif Jauhari 48
4 Ahmad Miftahul Faizin 54
5 Alfi Wardatul Chasanah 40
6 Ana Muawiyah 52
7 Anik Umi Syayidah 47
8 Choirotun Nisak 53
9 Dina Kartika 40
10 Dita 59
11 Efriawan Hengki Saputra 49
12 Elsa Fernanda 62
13 Hanif Ahmad Rifa`I 50
14 Hanifah Ridwani 42
15 Heni Setyawati 59
16 Issanti 52
17 Kuku Wahana 52
18 Listiya Mulyani 48
19 Muhamad Khosim 46
20 Muhamad Mujib Setiawan 42
48
22 Putri Oktafiani 51
23 Reva Pramawati 48
24 Riska Diana Sari 52
25 Rosana Sriasih 47
26 Ruhmiyati 40
27 Sulistyowati 53
28 Tifani Oktavia 40
29 Unna Yurdanny 58
30 Wiwin Kurnianti 49
31 Agus Setyawan 46
32 Alfi Hasanah 43
33 Khotimatus Sa`Adah 53
34 Nur Anisa Yuliyanti 48
Total (∑x2) 1662
N = 34
Mean (M) 48.88
Based on the table above, there were 34 students had done the pre-test. The highest score of comparative class was 62 while the lowest was 40. The mean of comparative class‟s pre-test score was 48.88.
d. Interpretation Pre-test Score of Control class
After scoring the result of pre-test then the researcher could interpret the pre-test score for comparative class as follows:
Table 4.4
Interpretation Pre-test Score of Comparative Class
49 Student Performance
- Excellent The students‟ answers are mostly correct, 80% of correct answers - Very Good The students answer about 70% of
correct answers
1 Good The students answer about 60% of correct answer
14 Fair The students answer about 50% of correct answer
19 Enough The students answer 40% of correct answer
- Poor The students‟ answers are mostly incorrect, less of 40% of correct answers
Total = 34
The table showed that from 34 students most of them got fair and enough category of their performance. 14 students obtained fair category and 19 got enough category. Then 1 student at good category.
The last, there was no student reached their excellent, very good and poor performance on reading comprehension.
2. Treatments
50
research, the researcher administered three times treatments for each class. The researcher used SQ3R for treatment and to be compared with KWL strategy to applayed in cmparative class. This strategy was a kind of way that could develop the students‟ reading competence.
The researcher did treatments by some steps as follows:
a. The researcher explained about narrative text it was consisted about definition, social function, generict structure, language fiture, and W-H question.
b. The researcher applied SQ3R strategy to improve students‟ reading competence, it consisted five activities such as : surveying, questioning, reading, reciting, reviewing.
c. The researcher gave feedbeck to the students.
For the first treatment, the researcher used fairytale narrative text entitled “Cinderella”, and for the second treatment, the researcher used legend
narrative text entitled “The Legend of Tangkuban Perahu Mountain”. Then
for the last treatment, the researcher used fabel narrative text entitled “The ant and the Grasshopper”.
Then the researcher mostly did the same steps for the comparative class as follows:
a. The researcher explained about narrative text it was consisted about definition, social function, generict structure, language fiture, and W-H questuin.