ABSTRACT
da Costa, Marlyne Sandie Claudia. (2016). Spoken English Materials to improve Young Learners’ Multiple Intelligences. Yogyakarta: English Education Language Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
This final paper discussed spoken English Materials which could improve kindergarten students’ multiple intelligences through English. The writer conducted the Research and Development in order to design the materials and to
solve students’ speaking problems in English in the classroom.
In this final paper, the writer had one research question, namely: how are
spoken English materials used to improve young learners’ Multiple Intelligences?. The writer discussed how the materials can help young learners to increase their multiple intelligences using spoken English and how it can be useful in teaching English as second language for young learners or kindergartens.
The writer showed through practical examples how multiple intelligences can be used as the target to develop good pronunciation of English through spoken English materials and how the designed materials can show the greatness of the young learners eight Multiple Intelligences.
Finally the paper presented and aimed to explore how spoken English materials for Young Learners can be adapted to suit a particular theme or part of the curriculum a teacher might wish to teach and develop the eight Multiple Intelligences of them.
ABSTRAK
da Costa, Marlyne Sandie Claudia. (2016). Spoken English Materials to Improve Young Learners’ Multiple Intelligences. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris. Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Tugas Akhir (Makalah) ini memuat materi spoken English yang dapat mengembangkan kecerdasan majemuk atau Multiple Intelligences pada siswa di usia belia melalui bahasa Inggris. Penulis menggunakan Research and Development (R&D) dalam membuat atau mendesain materi dan mengatasi masalah berbicara atau speaking siswa dalam berbahasa Inggris di kelas.
Dalam makalah ini, penulis menjawab pertanyaan yang menjadi permasalahan yaitu: penggunaan spoken English dalam mengembangkan kecerdasan majemuk siswa pelajar di usia belia. Penulis membahas bagaimana desain materi ini dapat membantu meningkatkan kecerdasan majemuk pada siswa Taman Kanak-kanak melalui spoken English dan bermanfaat dalam mengajar bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa kedua atau English as Second Language.
Penulis menunjukkan bahwa lewat contoh latihan atau praktek, kecerdasan majemuk bisa digunakan sebagai sasaran dalam mengembangkan pengucapan atau pronunciation yang baik dan benar dalam berbahasa Inggris melalui materi spoken English.
Akhir kata, makalah ini dipersembahkan dan ditujukan untuk menjelajahi atau menyelidiki bagaimana desain materi ini dapat disesuaikan dengan beberapa tema atau bagian dari kurikulum yang sudah ada bagi guru yang akan mengajar dan mengembangkan kecerdasan majemuk siswa taman kanak-kanak.
i
A Sarjana Pendidikan Final Paper on
SPOKEN ENGLISH MATERIALS
TO IMPROVE YOUNG LEARNERS’
MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES
Prepared and Presented by
Marlyne Sandie Claudia da Costa
Student Number: 101214190
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that the final paper, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, January 8, 2016
The Writer,
v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Marlyne Sandie Claudia da Costa
Nomor Mahasiswa : 101214190
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
SPOKEN ENGLISH MATERIALS
TO IMPROVE YOUNG LEARNERS’ MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengolahnya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistrubusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 21 Januari 2016 Yang menyatakan
vi
ABSTRACT
da Costa, Marlyne Sandie Claudia. (2016). Spoken English Materials to improve
Young Learners’ Multiple Intelligences. Yogyakarta: English Education Language Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
This final paper discussed spoken English Materials which could improve kindergarten students’ multiple intelligences through English. The writer conducted the Research and Development in order to design the materials and to solve students’ speaking problems in English in the classroom.
In this final paper, the writer had one research question, namely: how are spoken English materials used to improve young learners’ Multiple Intelligences?. The writer discussed how the materials can help young learners to increase their multiple intelligences using spoken English and how it can be useful in teaching English as second language for young learners or kindergartens.
The writer showed through practical examples how multiple intelligences can be used as the target to develop good pronunciation of English through spoken English materials and how the designed materials can show the greatness of the young learners eight Multiple Intelligences.
Finally the paper presented and aimed to explore how spoken English materials for Young Learners can be adapted to suit a particular theme or part of the curriculum a teacher might wish to teach and develop the eight Multiple Intelligences of them.
vii
ABSTRAK
da Costa, Marlyne Sandie Claudia. (2016). Spoken English Materials to Improve
Young Learners’ Multiple Intelligences. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris. Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Tugas Akhir (Makalah) ini memuat materi spoken English yang dapat mengembangkan kecerdasan majemuk atau Multiple Intelligences pada siswa di usia belia melalui bahasa Inggris. Penulis menggunakan Research and Development (R&D) dalam membuat atau mendesain materi dan mengatasi masalah berbicara atau speaking siswa dalam berbahasa Inggris di kelas.
Dalam makalah ini, penulis menjawab pertanyaan yang menjadi permasalahan yaitu: penggunaan spoken English dalam mengembangkan kecerdasan majemuk siswa pelajar di usia belia. Penulis membahas bagaimana desain materi ini dapat membantu meningkatkan kecerdasan majemuk pada siswa Taman Kanak-kanak melalui spoken English dan bermanfaat dalam mengajar bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa kedua atau English as Second Language.
Penulis menunjukkan bahwa lewat contoh latihan atau praktek, kecerdasan majemuk bisa digunakan sebagai sasaran dalam mengembangkan pengucapan atau pronunciation yang baik dan benar dalam berbahasa Inggris melalui materi spoken English.
Akhir kata, makalah ini dipersembahkan dan ditujukan untuk menjelajahi atau menyelidiki bagaimana desain materi ini dapat disesuaikan dengan beberapa tema atau bagian dari kurikulum yang sudah ada bagi guru yang akan mengajar dan mengembangkan kecerdasan majemuk siswa taman kanak-kanak.
viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to glorify my all-in-all, the Lord Jesus Christ, who has given strengths and patience even in my worst time. I realized that without His favor and His blessings, surely I could not complete and finish this final paper.
Second, I would like to express my greatest gratitude to my major sponsor,
Drs. Barli Bram, M.Pd., Ph.D. because of his patience and guidance, careful
correction, advice, criticism, and encouragement so I could finish my final paper. My sincere gratitude is also addressed to all lecturers at the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University for their participation as the reader and parents at campus to support this final paper until I could finish it well. I would like to let them know how much I appreciate their help and participation and guidance too. My thanks are also addressed to all off the PBI staff and library staff.
I would like to thank the lecturers, Drs. Pius Nurwidasa P., M.Ed., Henny
Herawati S.Pd., M.Hum., Yuseva Ariyani Iswandari, S.Pd., M.Ed., and Patricia
Angelina, S.Pd., M.Hum. for their love, extreme patience, and willingness to help
and support me pass through hard times in completing the requirements for my final paper. I would like to let them know that I admire and value their extraordinary advice and guidance very much. With them I can grow better in my campus.
My deepest gratitude goes to my beloved Mother, Father, Cornel, Dave,
Alckie, and Vincent for their unending and fantastic affection. I would like to let
them know that they are everything to me and my happiness. I do really love them forever.
Finally, my gratitude goes to my discussion group Vita, Dee and Priska and all PBI 2010 till 2013 students for the wonderful friendships. I would like to give my great thanks to them for spending the precious time together and for their worth saying.
ix
However to anyone who does not work but trusts God who justifies the ungodly, their faith is credited as righteousness. -Romans 4:5
Harapan adalah sebuah bisikan dalam hati yang berkata
MUNGKIN bahkan ketika seluruh isi dunia berkata TIDAK.
-Andree
Chris-DEDICATION PAGE
-
I dedicated this final paper, my little piece of hard work as the gift for my Lord
Jesus Christ and these beloved people:
♥ My lovely parents, Bapak Donnie and Ibu Susan ♥ My beloved husband, Cornel
♥ My wonderful son, Dave
♥ My dearest brothers, Alckie and Vincent
♥ My fund sponsored and spiritual guidance, Tante Netty and Om Samuel ♥ My spiritual guidance, Bapak Eben, Ibu Lina, Om Yanto and Tante Marlini
♥ My lovely big family, da Costa fam, Tangkilisan fam, and so on ♥ My dearest bestfriend, Vita, Dee, Priska, and all of my friends.
♥ and everyone who has given me many experiences and many things to be conscious and courageous.
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... iv
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ABSTRAK ... vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... viii
DEDICATION PAGE ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background ... 1
B. Research Method ... 15
CHAPTER II. DISCUSSION ... 21
A.Spoken English ... 21
B.The Spoken English Designed Materials Improves Young Learners’ Multiple Intelligences ... 38
CHAPTER III. CONCLUSION ... 43
REFERENCES ... 44
xi
LIST OF TABLES
[image:13.612.103.516.222.558.2]xii
LIST OF APPENDICES
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the writer presents the background of the study, information and rationale of the study undertaken such as, investigated problems, the importance of the study, overview of the study strategy, the focus objectives of the paper, the significance of the study, and solving the problems.
A. Background
English is one of difficult languages to learn particularly in the beginning for many people, but it is very important in this era. It is an important language because when go abroad, at least we must use English or be familiar with English, as the global language to survive overseas. It is not only as the direct global language but also as the technology language terms of many electronics or gadget. In reality, the general difficulties are the grammar and pronunciation.
2
Speaking skill is the one of the skills that is important for someone to master in learning or studying English and built good English as the global language in the world. Speaking might be one of the hardest skills to learn for many people. The general meaning of speaking is a process of building and sharing meaning through the use of verbal and non-verbal symbols. Yet in this case, speaking English is crucial part of foreign or second language learning and teaching in Indonesia.
These problems also happen to children, mostly found by the writer in Indonesia. The children‟s language acquisition is learning to speak but over three or four years they can master the grammar of the language. According to Crystal (1979), the language acquisition of children is not only about producing sounds, but also about being able to perceive sounds and understand the meaning. So, in summary the children produce many things not in adult grammar which is still need to be revised by the adult.
However, nowadays, every school requires English teaching to improve
students‟ communicative skills because that is the way students can express themselves and learn how to use an authentic language easily. Authentically here means that the language strongly founded and connected to the fact or daily life. In Urban dictionary, the definition of authentic is to describe an experience as a reality outside of a classroom. So, the language learning of the students will provide an authentic language used in the classroom.
3
language by copying or imitating the teacher as their model. Some of the students will instantly make their own language which is sometimes awkward but we still can get the meaning. So, as the primary model in the learning center, we have to be very careful and do not forget to revise their speech but no need to say that they were wrong.
Speaking skill is an important requirement in a speech which consists of the use of words even sentences while having conversations in daily life without any misunderstanding. Then it could be understood well, so they can be more confident in speaking English. Speaking skill also has big roles to lead the students to their academic and non-academic success. It means that English is the International standard. Many people use these qualities as part of everyday conversation. The solution is learning how to consciously apply these qualities to a public speech. They need to be learned as skills. Mastery of these skills in a speech delivery will make someone more confident. Then confidence will enable us to better use these qualities. The result will be speech mastery. In truth, this skill plays a part of many influences such as, influence the speech and confidence.
4
According to Liliard (2005), Montessori schools are too strict, meaning the children should be allowed more freedom. She stated that children need freedom and
limits, so the teacher concern watching over children‟s ever move and correcting it by
order but striking the balance. Children do a good deal that develop language when they work with the appropriate materials. In education for children, Maria Montessori (1949-1974) advised that learning should be an engaging, inspiring activity, so schooling could be looked on with joy. The reconstruction of education in school must be brought by giving the children system that is adapted to their nature and that are better suited to how children learn. (Liliard, 2005)
Spoken English is an English language which is easy as the portable language or authentically founded and usually uses in every time and every type of conversation in daily life. It will be effectively used for children to learn English. This paper is going to analyze and answer the problems above by using spoken English design which is appropriate for the children as the young learners.
The research problem or question is:
1. How are spoken English materials used to improve young learners‟ Multiple Intelligences?
5
relatively distinct from each other and that each person has some level of each of these seven intelligences. More recently, he has added an eighth intelligence to his list (Educational Leadership, 1997). There are Bodily-kinaesthetic, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal, Linguistic, Logical-mathematical, Musical, Naturalistic, and Spatial.
These ideas of multiple intelligences are also very important to help the educators or the teachers to identify differing strengths and weaknesses in students and also contradicts the idea that intelligence can be measured through IQ. Here are the description of the eight types of multiple intelligences, namely:
1. Linguistic: Involves sensitivity to spoken and written language, ability to learn languages, and the capacity to use language to accomplish certain goals. (Howard, 1999, p. 41) For example reading, writing, speaking, and conversing in one's own or foreign languages.
2. Logical: Involves the capacity to analyze problems logically, carry out mathematical operations, and investigate issues scientifically (Howard, 1999, p. 42). Number and computing skills, recognizing patterns and relationships, timeliness and order, and the ability to solve different kinds of problems through logic.
6
4. Bodily-Kinesthetic: Physical coordination and dexterity, using fine and gross motor skills, and expressing oneself or learning through physical activities. 5. Musical: The ability of perceive and create pitch and rhythmic patterns.
Understanding and expressing oneself through music and rhythmic movements or dance, or composing, playing, or conducting music.
6. Interpersonal: Denotes a person‟s capacity to understand the intentions motivations, and desires of other people and, consequently, to work effectively with others. (Howard, 1999, p. 43). For example, understanding how to communicate with and understand other people and how to work collaboratively.
7. Intrapersonal: Involves the capacity to understand oneself, to have an effective working model on oneself-including one‟s own desires, fears and capacities
-and to use such information effectively -and regulating one‟s own life
(Howard, 1999, p. 43). Understanding one's inner world of emotions and thoughts, and growing in the ability to control them and work with them consciously.
8. Naturalist: Involves natural world of plants and animals, noticing their characteristics, and categorize them; it generally involves keen observation and the ability to classify other things as well.
7
intrapersonal, and naturalist. The first claim is that all human beings have all of these intelligences. The second claim is that, both because of our genetics and our environment, no two people have exactly the same profile of intelligence, not even identically twins, because their experiences are different.
In this paper, the writer conductseight multiple intelligences that are going to support the design of spoken English Materials for young learners or kindergartens. They are Linguistic, Logical-mathematical, Spatial, Bodily-kinesthetic, Musical, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal and Naturalist.
Teaching-learning process needs an appropriate media of teaching to make the class or learning center lively and interactively. Nasab (2014), states that, educational media is defined terminologically as medium, device, the intermediate material, and linkage between two interfaces, median, and finally the transmission route. Learning strategies are methods and techniques that students used in their learning endeavors in order to achieve the desired educational goals.
8
A lot of vocabularies are needed as the pillar for speaking English more bravely. Mastering the vocabularies well and how to pronounce it well will increase your confidence to apply English better by the time. According to Beasley (2008), English has become a language when no native speakers could survive by learning from the native speakers through listening and speaking to increase the new vocabulary and built good spoken English.
The problem with most English course material is that it is not strictly focused on teaching spoken language. Students who learn from these materials often end up sounding strange and like they are reading from a textbook. In addition, most students practice with each other and not with native speakers which results in mispronunciations and bad habits that leave little room for progress. Then to improve the speaking skill, we need to practice, observe, critique, and learn. To be fair it should be noted that some skills and speech challenges will require greater expertise to learn. As Karen Famen stated, language compatibility and well communication are needed to reach what people expect as for making good atmosphere in the world as the target of achievement through the communication.
9
According to Deiner (2010), the techniques of teaching early childhood
education must adapt to meet the children‟s learning need. The children are active in
learning, so the TESL teacher need appropriate techniques in order to raise the goal become meaningful on every meeting in classroom. It is the challenges for the TESL teacher in a developmentally appropriate way and meet recognized standard (Deiner, 2010, p. 87).
In an education development, this paper is beneficial for the teachers who
want to improve young learners‟ English become good English speaker at the very
early stage. By learning listening and speaking skill then reading and writing skill sufficiently, the young learners or kindergarten students can easily understand the English, exactly if the TESL teacher uses interesting, authentic and appropriate English materials to be learned by the young learners or kindergartens. The simple materials for their level is increasing the listening and speaking skill. Listening skill is to make the students more be familiar with the language and then the speaking skill is to make them implement the new language.
There are many media used in the teaching learning process. The media is used to teach English to young learners in terms to make and build the teaching-learning process to be move interesting and enjoyable in classroom. TESL can use many media in teaching English such as songs, rhymes chants, flashcards, worksheet features and games (Brewster, 2002).
10
sitting in the front and the back of the classroom. To make sure that everyone can see the letters on the card, it is better to write words with capital letters. Both sides of the flash cards should be used in teaching vocabulary. On the one side, the new word is written in L2 and perhaps with a picture beside it and on the other side is the translation. It can be seen that flash cards have been used for teaching a variety of purposes during the history of language teaching.
An example is to teach sounds of the alphabet using them (Young, Hecimovic & Salzberg, 1983). It is relevant to be used because student can focus on one vocabulary at a time and they can memorize it by repeating the pronounced word with the guidance of their teacher. Young learners tend to observe a lot because they are processing information in their head. Pictures paired with colors make the brain easier to memorize each vocabulary because our brain works better with shapes and different spectrum of colors.
11
fun way. When teacher uses a correct technique and tools, they can make their students understand faster and better.
According to Richard-Amato (1996), even though games are often associated with fun, we should not lose sight of their pedagogical values, particularly in second language teaching. Games are effective because they provide motivation, lower students' stress, and give them the opportunity for real communication. Using
educational games can improve student‟s motivation and response toward learning
English. They are one of many techniques that is used as a way to use the language in the context of game. The benefits of using games in the learning process are students will get rid of their boredom from learning through monotonous textbook and they can enjoy learning English with the same goal but in a fun way which is by contributing in such interesting activities set by the teachers. Thereby it is not only a break from the normal learning process but it can also provide better activities for the students to learn English in a different way.
Those activities above are very commonly used in the early years of English language learner simply because it makes the learning activities a lot more interesting. Young learners tend to be more focused on drawing or pictures, responds to song by singing along, simply because that is how children learn. They adapt to the new things by observing and listening and those have something to do with how the brain works.
12
must become authentic for the pupils. Most of them regard that the speaking skill is a difficult task than listening, reading or writing skill. Furthermore, the fact shows the young learners are good in imitating but sometimes some of them are not able to pronounce it well.
Therefore, this paper will help the TESL and provide the great spoken English materials become authentic and useful in teaching-learning process for the young learners. They have unique ability which is called MI (Multiple Intelligences). Through the MI descriptions, the writer will follow it as the spoken English materials design that will be catchy for the kindergartens and will attract them to learn English every day.
All of the children need not only a simple instruction but also authentic concept. It means that the children as the young learner go for meaning so the materials especially English language should be authentic in the class every time. In order to conduct the classroom, the educators or the teachers should be productive. Here are the benefits of spoken English materials through multiple intelligences for young learners or kindergarten students.
13
and widespread of the speech or conversation (The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the English Language, 2003).
In this paper, the writer defines the terms of young learners as kindergarten students. Children as the young language learners, have the natural abilities and characteristics to learn a new or foreign language (Moon, 2005, p. 3). According to Jean Brewster, the young learners have their own way and build their own language by listening and repeating or imitating the adult, or in this case from the TESL. They can learn faster and good in imitating then spend their time practicing the language.
In learning, the motivation of the students depends on the teacher style or ways. The TESL must not explain because the children go for meaning. It should be meaningful then they will try bit by bit. How the children think and learn should be placed at the center of planning and teaching to make them interested and to their needs because they are different.
Because the children are different, so the way to teach is different too, especially in teaching L2. It needs great effort and takes quality time to get the target language. Based on Brewster, Ellis and Girard‟s theory (2004, p.27), how the children as the young learners think and learn are different from older learners, because they are:
1.Excellent mimics 2.Emotionally excitable
3.Still developing literacy in their first language
14
5.Can be easily distracted but also very enthusiastic
6.Get bored easily but can concentrate for a surprisingly long time if they interested
7.Learn more slowly and forget things quickly
8.Tend to be self-oriented and preoccupied with their own world 9.Have a wide range of emotional needs
10.Have a lot of physical energy and often need to be physically active
Children need exercises and the TESL should express or show facial expression. In early childhood education, the easy and effective model of teaching for the kindergarten students is TPR (Total Physical Response) and CLT (Communicative Language Teaching) methods. The children as the young learners tend to develop their language and build their communication skills. Erickson (1997) stated that the children aim to develop feeling of competence, rather than inability. During the late childhood ranges from 5-12 years, they show greater attention and gains rapidly in strength, but still need accomplishment regardless of ability.
15
B. Research Method
This paper conducts library research or library study. George (2008) stated
that library study „involves identifying and locating sources that provide factual information or personal/ expert opinion on a research question‟ (p. 6). There were several steps in library study used in this paper which were locating information, collecting information from sources, and organizing information. In locating information, a list of keywords about the topic of this research paper has been made makes easier. Several books and journals that were relevant to the paper had been gathered from library and websites. The books and journals that have been located were read afterwards in order to collect the information that can be used to support the arguments in this paper. Then, the collected information was organized according to the topics.
The method is known as qualitative research as the discussion of the topics. According to York (1998), a major focus in qualitative research approach is on the observation of similarities and differences in social behaviour across social situation. The writer also does not base the research on the pre-determined hypothesis, but identify the problems that are going to be explored.
The design of spoken English materials is an Instructional Design based of
16
aim of instructional design is to make learning more efficient and effective and less difficult (Morrison, Ross, Kalman, & Kemp, 2011, p. 2).
There are fifteen parts in Morrison‟s, Ross‟s, Kalman‟s, and Kemp‟s
instructional design model, which are instructional problems, learner characteristics, task analysis, instructional objectives, content sequencing, instructional strategies, designing the message, development of instruction, evaluation instruments, planning and project management, support services, formative evaluation and revision, implementation, summative evaluation, and confirmative evaluation (Morrison, Ross, Kalman, & Kemp, 2011, p. 1).
Instructional problems are the first part in this instructional design model. The need of the students or the problems of the students is identified. Here, it will be decided if the problems can be solved by instructional design or not. If the problem can be solved by instructional design, then designer can choose which element from
Kemp‟s instructional design model we want to do next. We can choose learner
characteristics as the next part to do. In this part, the characteristics of the students should be analyzed and defined. Another element is task analysis. It is to determine the knowledge and procedure needed to be included in the instruction in order to help the students accomplish the objectives.
17
order the information given to the students in a logical sequence so that the students can grasp the ideas more efficiently and effectively. Instructional strategies is important to design the way to present information that help the students integrate the new information with ideas they already understand. The message is the pattern of words and pictures created to communicate with the students. Designing the message is the process to arrange the words and pictures.
Development of instruction is to produce the instructional materials such as print materials, web pages, or video recordings. Evaluation instruments are used to
assess the student‟s mastery of the objectives. The following processes are ongoing throughout the instructional design project. Planning and project management are important to develop and manage the schedule and budget for a project support services. The project needs the support or resources from the others such as evaluator. Formative evaluation and revision evaluates all the process from the first step, instructional problems, till the last step. After that, the revision can take place. Implementation is to apply the instruction that has been made. Summative evaluation is used to evaluate the effectiveness of the final materials when they are used as planned. Confirmative evaluation is a process that instructional designer uses to determine whether a course or instruction remains appropriate over time.
The paper conducts the Elizabeth Hurlock‟s theory of Child Growth and Development; Jean Brewster and Gail Ellis with Denis Girard‟s theory of the Primary
18
children; also Anderson Curriculum to support this final paper. It‟s really helpful to find the properly teaching techniques information for the children.
This paper uses the Gardner‟s theory of Multiple Intelligences as the achievement goals of the design, spoken English materials. Howard Gardner is a psychologist professor at Harvard, who identified eight different types of human intelligences. The theory has emerged from recent cognitive research and documents the extent to which students possess different kinds of minds and therefore learn, remember, perform, and understand in different ways (Gardner, 1991). Gardner stated that, we are all able to know the world through language, logical-mathematical analysis, spatial representation, musical thinking, and the use of the body to solve problems or to make things, an understanding of other individuals, and an understanding of ourselves.
The paper conducts the children language acquisition of Piaget and David
19
Meanwhile, Professor Crystal, who is best known for his two Encyclopaedia of the English Language, states that the children learn language in five stages. These stages are:
1. Stage one: the children usually say things to get something they want, get
someone‟s attention and draw attention to something.
2. Stage two: the children usually ask questions, become concerned with naming and classifying things by frequently asking, also begin to talk about the characteristics of things for example: big/ small, hot/cool, and up/ down aim to learn things in opposite pairs.
3. Stage three: The children would ask lots of different questions but often signalling that they are questions with intonation alone and begin to express more complex wants by using more grammatically correct language.
4. Stage four: the children use increasingly complex sentence structures and begin to explain things, ask for explanation the word “why”, and making a wide range of requests “shall I do it?”
5. Stage five: the children regularly use language to do all the things that they need it for, such us giving information, asking and answering questions, requesting directly and indirectly, suggesting, offering, stating and expressing. The paper considers the children development toward multiple intelligences of
Elizabeth Hurlock‟s Theory. Hurlock‟s theory stated that giving the children play
time emphasizes learning in play to the child‟s ability and the health needed to enjoy
20
of a progressive or continuous series/ levels of changes of an orderly. According to Gesell (1952), “Development is more than a concept, but it can be observed,
appraised and measured.”
21
CHAPTER II
DISCUSSION
In this chapter, the writer presents and evaluates what is already known about the topic which contains the review of related literature and the findings as well as the interpretation of the findings. The writer provides relevant theories from some sources in discussing the issue followed by interpretation of the results. There are two sections in this chapter in order to answer the question. The first part is the units of the book. This part deals with the process of designing the spoken English materials for young learners. The second part discusses how the use of the book improves multiple intelligences.
A. Spoken English
In order to answer the question about how are spoken English materials are
used to improve young learners‟ MI, the writer conducted an instructional design model using Kemp model. The stages are:
1.Examine the learners‟ characteristics that should attract or receive attention during planning.
2.Identify subject content and analyze task components related to the stated goals and purposes.
3.State the instructional objectives for the learners.
22
5.Design instructional strategies to be mastered by each learner. 6.Plan the instructional strategies and delivery.
7.Develop the evaluation instruments to assess objectives. Therefore, the descriptions above were drawn as follows.
1. Examine the learners’ characteristics that should attract or receive attention
during planning.
The writer uses the summary of Josephine Sri Murwani Pudji Lestari, S.Pd., M.Hum., the EYL (English for Young Learners) lecture, 2015 Presentation of the English for Young Learners Class of Sanata Dharma University, about the general characteristics of the children as the young learner. They are curios, imaginative, enthusiastic, musical, love to play, egocentric, short span of concentration, physically active, great capacity of learning and excellent mimic.
2. Identify subject content and analyze the task components related to the
stated goals, topics and purposes.
The writer stated the goals, topics and purposes for kindergarten.
a. Goal
The writer made the goals of spoken English materials to improve young
learners‟ multiple intelligences according to their language levels found in 1969
Stern by Brewster, Ellis and Girard (2005: p.25-26), which aim to:
23
and practicing the language in a very controlled. So, the spoken English is an appropriate authentic language for them.
2) Build the kindergarten students‟ pronunciation and present their own knowledge or comprehension. They should start with separate sounds, and then build these into words then simple sentences without formal grammar and complex or brief instructions and explanations.
3) Help the kindergarten students to follow or obey the rules in the learning center. They should spend a lot of time to just listen without speaking. After listening and speaking for some time reading and writing skills are then added.
4) Help the kindergarten students to be confident and free in using or making the language used. They should not translate from L1 to L2 and vice versa. TPR and CLT method have been found to be very successful with beginners. This approach is good to encourage them to use L1 occasionally. So, the teacher can see how the language is learned from material designer, syllabus designers
or teacher‟s point of view.
b. Topics
After stating the goal, the writer made the list of topics based on the young
learners‟ characteristics. There were two general topics developed by the writer.
24
c. Purposes
Based on Brewster, Ellis and Girard (2005), the classroom procedures should involve the use of three stages which aim to provide the sort of scaffolding which helps children to think and learn with motivation, success and confidence. The three stages are meeting new language, manipulating it and making the language your own (MMM).
From those stages, the writer presented the general purposes of each unit.
UNIT 1: GOOD MORNING!
The learning objectives are:
a. The students are familiar with the new simple English language which is authentic, named spoken English.
b. The students know how to greet others in the morning time.
UNIT 2: I AM …
The learning objectives are:
c. The students are familiar with the new simple English language which is authentic, named spoken English.
d. The students know how to introduce themselves to others.
25
Warm Up, Lesson, Games and Review. The lists of subject content could be clarified as follows:
1) Warm Up
This section presented the opening or beginning activities which attract the students and build their confidence before starting the lesson. This section includes pronunciation goals which develop good language set of young learners that may have some advantages to emphasize their pronunciation as good as the models.
2) Lesson
This section presented the learning of the new language and learning the English vocabulary. In this section, the kindergarten students learn the meaning of words or sentences through listening to the instructions and pay attention to the teaching-learning process. It sets the students to obey the rules so the classroom will become more organized. The teacher can use TPR and CLT method to introduce new vocabulary and convey meaning by demonstration. For example as stated by Brewster, Ellis and Girard by:
using objects or things brought to the classroom.
using drawings on boards or cards covered with plastics.
using illustrations, pictures, flashcards from book, magazines, internet, and so on.
26
using technology such as video, computers, internet (web safety).
Those techniques will often help the students to memorize the words through visualization, body movement and doing then by themselves.
3) Physical Exercises
This section is a kind of refreshing time for the students. In this section, the students will stretch their body and relax their mind from the lesson. However, this subject content is still connected to the previous lesson. The kindergarten students can enjoy, express and show the language based on their cognitive freely, but still guided by the teacher.
4) Review
This section aims to practice the knowledge. This section involves students in activities that require them to do things with the words, in order to build and to make the language by themselves from their memory. It can be done in groups or individually.
5) Homework
27
3. State the instructional objectives for the learners.
From the subject content above, the writer states the instructional objectives for the learners.
UNIT 1: GOOD MORNING
Students are able to identify the morning time.
Students are able to identify how to greet in the morning.
Students are able to identify the things related to the morning time.
Students are able to give a simple sentence of greetings in the morning verbally.
UNIT 2: I AM …
Students are able to identify herself or himself.
Students are able to identify how to introduce herself or himself.
Students are able to identify the things related to the introducing one self. Students are able to say a simple sentence of introducing one self verbally.
4. Sequence content within each instructional unit for logical learning.
The sequence contents within each instructional unit for logical learning are: a. Warm Up:
28 b. Lesson:
This section is about the learning time process which presents a rule for the kindergarten students. The learning activities include Pictures or Flashcards or Handicrafts or Arts.
c. Physical Exercises:
This section shows the interesting learning time for the students‟ to enjoy. There is Sport or Body Movement or Games such as playing with blocks or sticks or moving things in emulation.
d. Review:
This section provides the Sharing time and Reinforcement as the quality moment for the children to be united and cooperative.
e. Homework:
This section is about the Task or Assignment related to the whole values of the lesson in the classroom that are going to be brought outside the learning center.
5. Design instructional strategies to be mastered by each learner.
The instructional strategies to be mastered by each learner based on four skills are:
UNIT 1 : GOOD MORNING
a. Activities 1 :
29
Speaking: Singing together of Good Morning Song. b. Activities 2 :
In the listening section, the learners listen to the teacher instructions while showing the flashcards or pictures related to the morning time. Then for the next listening and speaking section, the learners follow the teacher‟s instruction and repeat what the teacher said. After that, move to the speaking and reading section. The learners guess the flashcards or pictures. Through reading and writing section, the learners do the activities in the book, such as making a handicraft or learn how to write or identify by reading the letters; numbers; words; organizing the pictures which are related to the topics of morning time; and so on.
c. Activities 3 :
For the listening and speaking section, the learners listen to the teacher and look at what the teacher is doing while putting and moving the things related to the lesson or activity that has been learned. Then reading section, the learners do as the teacher has done individually. In listening and speaking section, the learners listen to the teacher and look at what the teacher is doing while putting and moving the things related to the lesson or activities that have been learned. After that, in reading section, the learners do as the teacher has done in groups or in pairs.
d. Activities 4 :
Listening: the learners listen to the teacher‟s instructions. Speaking, reading,
30
while the learners respond to and answer it. For the speaking, reading, and writing section, the teacher leads the sharing time which is enjoyable but organized with all the students in order to evaluate and solve the problems found in the classroom together for the quality moment together.
e. Activities 5 :
In the listening section, the learners listen to the teacher‟s instruction for the homework assignment, such as what they have to do dealing with the task of the book
and what to get after it, like asking the parents‟ signature when the learners are done with the homework. For speaking section, the learners may ask the teacher if they do not understand, then the teacher discuss it all the students. Then reading and writing section, the learners do the homework at their own houses. The teacher fills the space about the lesson today and explains the task that will be brought and done by the students at home.
UNIT 2 : I AM …
a. Activities 1 :
Listening: The learners listen to the Hello Hello How Are You Song (by MUFFIN SONGS).
Speaking: Singing together of Hello Hello How Are You Song. b. Activities 2 :
31
speaking section, the learners follow the teacher‟s instruction and repeat what the teacher said. In speaking and reading section, the learners guess the flashcards or pictures. For the reading and writing section, the learners do the activities in the book, such as making a handicraft or learning how to write or identify by reading the letters; numbers; words; organizing the pictures which are related to the topics of introducing oneself; and so on.
c. Activities 3 :
In the listening and speaking section, the learners listen to the teacher and look at what the teacher is doing while putting and moving the things related to the lesson or activities that have been learned. Then reading section, the learners do as the teacher has done individually. After that, move to the listening and speaking section, the learners listen to the teacher and look at what the teacher is doing while putting and moving the things related to the lesson or activities that have been learned. Then in reading section, the learners do as the teacher has done in groups or in pairs.
d. Activities 4 :
32 e. Activities 5 :
In listening section, the learners listen to the teacher‟s instruction for the homework assignment, such as what they have to do dealing with the task of the book
and what to get after it, like asking the parents‟ signature when the learners are done with the homework. For the speaking section, the learners may ask the teacher if they do not understand, then the teacher discuss it with all the students. Then in reading and writing section, the learners do the homework at their own houses. The teacher fills the space about the lesson today and explains the task that will be brought and done by the students at home.
6. Plan the instructional strategies and delivery.
The writer provides the instructional strategies for the teacher as the instructional menus, based on Campbell and Dickinson (2004: p.253) in order to
improve young learners‟ multiple intelligences. They are:
a. Musical Menu by writing song lyrics for singing that indicates the rhythmical patterns; using background music to enhance learning; collecting and presenting songs about the topic; making an instrument and using it to demonstrate; and also using musical technology.
33
c. Naturalist Menu by collecting and categorizing data; describing or cycling the patterns; comparing phenomena for explaining how the nature run; and using technology to explore it.
d. Kinesthetic Menu by making a choreograph or dance; building or constructing body movement through singing; attending a mini trip or field trip; and devising scavenger hunt, role play or simulate.
e. Interpersonal Menu by participating in a group; conducting a meeting; with a partner, trying to solve problem; acting out diverse perspectives; using social skills to learn; couching others; and doing a service project or collaboratively planing rules/ procedures.
f. Intrapersonal Menu by describing feelings, qualities; loving to write; explaining the reason of the study; self-assessing of own work; doing a project; receiving feedback; and using technology to reflect it.
g. Linguistics Menu by retelling story; conducting a simple form of debate when different perspectives exist; relating a short story; giving a presentation; leading the discussion; and using technology to write or to make it.
h. Logical Menu by designing and conduct an experiments; categorizing facts, design a code; creating a timeline or a detailed personality; using thinking skills to learn or solve problem; creating problems to be translated into a formula; and using technology to calculate.
34
Let’s sing along!
2) Lesson:
It’s art time! / Look and talk. / Look and Draw line in order! / Color and write! / Draw!
3) Physical Exercises:
Follow and Do it with your friends! / It’s play time! 4) Review:
Look and color it! / Look and Draw! / It’s sharing time! 5) Homework:
Put in order! / Homework!
[image:48.612.101.521.134.732.2]Meanwhile, the instructional deliveries that the teacher may will be beneficial when followed by TPR and CLT method. The procedures are elaborated Table 2.1.:
Table 2.1 The Procedures Table
Steps Teacher’s words Students’ words
1. T greets the class or does the opening activities as usual.
Good morning. How are you today?
Students greet and may respond variably. 2. T calls the students‟
name based on the attendance list or absences by singing.
Where is …? Where is …?
Here you are. (After the students respond.)
Students may follow the song when they familiar with the notes by singing Here I am. Here I am. or only raising their hands up.
35 music video,
or T introduces the song by singing and gives the gestures, or T demonstrate the chants or rhymes.
Hey class. I have a song. Listen.
Look at me and listen.
variably but have to obey the teacher‟s instructions to listen to the song or watch the music video.
4. T repeats the song and invites the students to sing along together slowly.
or T may repeat the song in the CD.
Let’s sing together!
Come on. Follow me. Ready?One, two, three. Do you want to sing again? Ok. Let’s sing.
Students may respond variably.
Students sing together and follow the gesture of the teacher slowly till fluently (if necessary). 5. T shows the
flashcards or pictures (choose one by one of the card)
Look. It is… Students have to obey and pay attention to the teacher.
6. T may repeat all the flashcards or pictures
Once again. Look and listen.
Students are able to pronounce the correct pronunciation.
7. T reviews the
material. T shows the flashcards or pictures (choose one by one of the card) followed by students
Look. What is it? Repeat after me. … What is it?
Come on. Repeat after me. …
Students have to obey and pay attention to the teacher.
Students are able to pronounce the correct pronunciation.
8. T may repeat it by showing all of the flashcards and pictures one by one followed by the students.
Once again. Repeat after me. …
Students are able to pronounce the correct pronunciation.
9. T introduces the materials. T shows all of the flashcards or pictures.
Now, listen and look carefully.
36 10.T reviews and asks
the students about the topics.
Now, look carefully. What is it?
Yes, it is …
Students are able to recognize the topics based on flashcards or pictures given with a complete
sentence “It is …”
11.T mentions the next activities and invite the student to open the materials.
It’s time to English Live Book.
Let’s open our English Live Book.
Students may respond variably.
Students have to obey and pay attention to the teacher.
12.T tells or reads and mentions the activities to do base on the
English Live Book.
Look on your book. What is it?
It’s coloring time. / It’s
art time. / Let’s study.
Students may respond variably.
Students are able to recognize the topic given and are able to work or do the assignments
mentioned at English
Live book correctly.
13.T asks the students to work in pairs or groups.
T chooses the group or the partner and let the students find and sit closed to their partners or groups. T demonstrates the games or physical exercises slowly and clearly to the students. T may repeat or give the example by finding the model or do it by yourself once again and has to make
Well, Look at me. I have a game.
So, work with your group or partner next to you and sit together.
Now, look at me. What am I doing?
Yes, I am …
So, you have to do like what I did before. For example.
Ready?/ Can we start now?
Ok. Let’s go!
Students may respond variably.
Students have to obey and pay attention to the teacher.
37 sure that the students
get the clear instruction.
14.T does the review or reinforcement and leads the sharing time,
don‟t forget to give
praises to all of the students by clapring hands together.
So, what we have learned today class? Yes!
(REVIEWING THE LESSON TOGETHER) Excellent!
Give yourself big applause!
Students may respond variably.
Students have to obey the teacher and are able to identify and describe the difficulties through the learning process today. 15.T gives the homework
as the follow up activity.
T has to make sure that all of the students get the clear
instruction.
Well, before we go home,
I’ll give you homework.
What you have to do is Next meeting I will ask the
You may but remember to
Understand? Any questions?
Students may respond variably.
Students have to obey and pay attention to the teacher.
Students are able to identify and recognize the assignment given based on the book.
16.T does the closing activity as usual, or T may stand beside the door to give the students handshakes or hugs while singing the Good Bye song instead.
That’s all for today.
Good bye kids. See you tomorrow.
Don’t forget to say good
bye to your friends. I love you and God bless you.
Students are able to greet others and say thanks politely or respectfully to the teacher.
7. Develop the evaluation instruments to assess objectives.
38
the writer made the evaluation instruments to assess objectives which will distribute
to the designed materials for the teacher of kindergarten students in teacher‟s book.
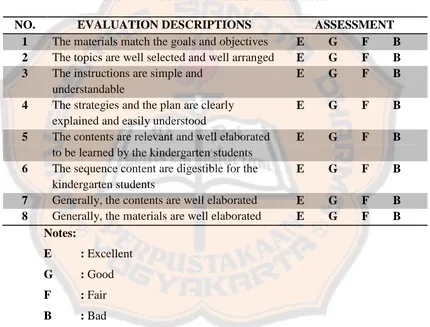
[image:52.612.105.535.235.562.2]However, in this paper, the writer is not going to discuss these deeper. The evaluation sheet was arranged in the form of Table 2.2.
Table 2.2 The Evaluation Instruments Table
NO. EVALUATION DESCRIPTIONS ASSESSMENT 1 The materials match the goals and objectives E G F B 2 The topics are well selected and well arranged E G F B
3 The instructions are simple and understandable
E G F B
4 The strategies and the plan are clearly explained and easily understood
E G F B
5 The contents are relevant and well elaborated to be learned by the kindergarten students
E G F B
6 The sequence content are digestible for the kindergarten students
E G F B
7 Generally, the contents are well elaborated E G F B 8 Generally, the materials are well elaborated E G F B
Notes:
E : Excellent
G : Good
F : Fair
B : Bad
B.
The Spoken English Designed Materials Improves Young
39
The writer designed materials in two books: Teacher Book and Student Book
named “English Live” book. The designed materials consisted of two units: 1. Good Morning
2. I am …
In general, the subject content of the designed materials consisted of five types of activities as mentioned below:
a.Activities 1 : Warm Up
This activity presents Song or Music Video or Phonics Chant or Rhymes. b.Activities 2 : Lesson
This activity presents Pictures or Flashcards or Handicrafts or Arts. c.Activities 3 : Physical Exercises
This activity presents Sport or Games: Play with blocks or sticks. d.Activities 4 : Review
This activity presents Sharing time and Reinforcement. e.Activities 5 : Homework
This activity presents Task or Assignment.
The contents can improve the kindergarten students‟ multiple intelligences.
The writer provided the instructional strategies for the teacher as the instructional menus, based on Campbell and Dickinson (2004, p. 253) to improve young learners‟ multiple intelligences, they are:
40 3) Naturalist Menu
4) Kinesthetic Menu 5) Interpersonal Menu 6) Intrapersonal Menu 7) Linguistics Menu 8) Logical Menu
The writer is going to explain and elaborate how these designed materials
improve the young learners‟ multiple intelligences based on the activities followed to
the instructional menus below:
1. Activities 1 : WARM UP
Through this activity, the intelligences that will be improved are Musical Intelligence. The students demonstrate the activities by listening to music then singing followed by music.
2. Activities 2 : LESSON
In this activity, the Visual-Spatial, Linguistic and Naturalist intelligences will be improved. The students meet the visual tools; deal with the learning process by coloring or making something with shapes; listening to learn; memorizing the words in the classroom; writing; collecting tools and organizing the equipment.
3. Activities 3 : PHYSICAL EXERCISES
41
perfect physical performance. The students will show the eye, walk or calming down exercises towards games or sports.
4. Activities 4 : REVIEW
Through this activity, the Interpersonal and Intrapersonal Intelligence will be improved. The students determine the class values and rules that have been ran in a class meetings; may try to understand the diverse perspectives; identifying and expressing feelings or emotions; establishing feelings in the classroom or the environment; gaining to know oneself through others or self-directed learning; and finding purpose in school and life.
5. Activities 5 : HOMEWORK
In this activity, the students will build their enthusiasm, engagement and achievement as well as the enhancement of their intellectual capacities which means, the Logical Intelligences will be improved through this part of activities.
In truth, all the activities in the designed materials can improve all of the
young learners‟ MI. It is not only one part of intelligences capacities but it can be two or more in each activity on the goals. For example in activities 2, there are four
intelligences that would improve the student‟s MI. It can be more than four
42
them. It is the same as in activity 5, which not only could improve the Logical Intelligences but it can be more, such as Visual-Spatial, Linguistic, Naturalist and Interpersonal Intelligences. Thus, in activity 4 it can improve Bodily-Kinesthetic too.
Therefore, after making the designed materials into a book named “English
Live”, the writer finally presented the final version of the spoken English materials to
improve young learners‟ Multiple Intelligences. The writer places the designed
43
CHAPTER III
CONCLUSION
In this chapter, the writer has showed at a variety of techniques that can be used to help students develop their language using spoken English materials through multiple intelligences. This chapter is the writer‟s summary of the major findings and the solution to the problems. The discussions are the issues and followed by interpretations of the results. The paper provided the deep information and procedures as the lesson plan that would improve kindergarten students‟ MI in the use of book in classroom to increase their language and mastery skill. Thus, the writer has discussed the research method based on some expert theories in library research to support this paper.
The writer has shown the reason why teacher should use spoken English and consider the multiple intelligences as the great shortcut improvement for the pupils‟ achievement. The design has been developed well including appropriate activities techniques up to their level of the children and how the teacher will use these techniques of the materials to develop the children‟s multiple intelligences. There were several activities which are used in this paper: they are songs, handicrafts, drawing and coloring activities, and so on. Practice in these areas can help to increase
44
REFERENCES
Beasley, R. O. (2008). The effects of listening repetition, Retrieved on September 25, 2015 from http://www.tesl-ej.org/wordpress/issues/.html
Brewsters, J., Ellis, G., Girard, D. (2004). The primary english teacher’s guide. Penguin English.
Campbell, L. B., & Dickinson, D. (1948). Teaching and learning through multiple intelligences, 3rd edition. Pearson Education.
Children Language Acquisition of Piaget‟s theory. (2011).
Crystal, D. (1979). British journal of educational studies: Child language, learning and linguistics. Taylor & Fracis, Ltd.
Deiner, P. (2010). Inclusive early childhood education:Development, resources, and practice (2nd edition). Delmar Learning.
Dukes, C. & Smith, M. (2007). Developing pre-school communication and language. London: Paul Chapman Publishing.
Erickson, E. H. (1997). The life cycle completed: A review. New York: W. W. Norton.
Froebel, F. (2003). Pedagogics of the kindergarten. Honolulu: University Press of the Pacific.
Gagne, R.M., & Briggs, L.J. (1974). Principles of instructional design (2nd edition). New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Gardner, H. (1993). Multiple intelligences: The theory in practice. Basic Books. George, M.W. (2008). The elements of library research. Princeton: Princeton
University Press.
Gustafson, K. L., & Branch, R. M. (2002). What is instructional design? In R.A. Reiser & J. A. Dempsey (Eds.), Trends and issues in instructional design and technology (pp.16-25).
Liliard, A. S. (2005). Montessori ‘the science behind the genius’. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
45
Morrison, G.R., Ross, S.M., Kalman, H.K., Kemp, J.E. (2011). Designing effective instruction (6th edition). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Murphey, T. (1992). Music and song. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press. Nasab, A., F. (2014). Medical Science Studies. Retrieved on September 25, 2015
from http://otec.uoregon.edutr
Petrie. G., O. (1997). Understanding children’s development. Taylor & Fracis, Ltd.
Profesional‟s Guide: Teaching with Multiple Intelligences. (2001).
Sunardi, Z. A., & Rosnija, E. (2013). Teaching speaking ability through role play. Pontianak: PBS, FKIP Tanjungpura University.
Temerová, L. (2007). How to improve students’ communicative skills. Brno: Masaryk University.
York, R.O. (1