AAB BI OFLUX
Adva n ce s in Agr icu lt u r e & Bot a n ics-
I n t e r n a t ion a l Jou r n a l of t h e Biof lu x Socie t y
Br in e sh r im p le t h a lit y a ssa y of w h ole pla n t
e x t r a ct s of Ele u sin e in dica
1
Mae A. Respont e,
1Maria R. B. Dacar,
1Olga M. Nuñeza,
2Mylene M. Uy
1
Depar t m ent of Biological Sciences, College of Science and Mat hem at ics, Mindanao St at e Univ er sit y - I ligan I nst it ut e of Technology, I ligan Cit y , Philippines; 2 Depar t m ent of Chem ist ry , College of Science and Mat hem at ics, Mindanao St at e Univ er sit y - I ligan I nst it ut e of Technology, I ligan Cit y , Philippines. Cor r esponding aut hor: O. M. Nuñeza,
olgam nuneza@y ahoo. com
Abst r a ct . Br ine shr im p let halit y assay ( BSLA) is an im por t ant m et hod in t he ev aluat ion of plant
bioact iv it y for t he subsequent isolat ion of bioact iv e com pounds fr om t he plant ex t r act s which m ay lead t o t he dev elopm ent of new dr ugs. I n t his st udy, BSLA was em ploy ed t o ev aluat e t he pot ent ial cy t ot ox ic pr oper t ies of t he whole plant ext r act s of Eleusine indica. E. indica has been widely used for t he t r eat m ent of sev er al diseases lik e k idney pr oblem s, diabet es, gast r o- int est inal diseases and is used as diur et ic. The m ost com m on m et hods of ex t r act ion ( decoct ion, absolut e et hanol, 50% w at er - 50% et hanol) wer e t est ed t o det er m ine cy t ot ox ic effect s against t he br ine shrim p nauplii. Result s showed t hat t he best ex t r act ion m et hod for t he whole plant sam ples of E. indica is t hr ough t he use of 50: 50 et h anol- wat er m ix t ur e ex t r act . The acut e let hal concent r at ion ( LC5 0) of E. indica aft er 6 h ex posur e t o m ix t ur e ext r act
was 153. 99 ppm , while t he et hanolic ex t r act obt ained an LC5 0 of 40 9. 73 ppm . Aft er 24 h ex p osur e,
incr eased m or t alit ies of br ine shr im ps wer e r ecor ded in all pr epar ed ext r act s. Max im um m or t alit ies ( 100% ) wer e obser v ed in t he t hr ee concent r at ions of 1 00- 10 00 ppm in t he m ix t ur e ex t r act of E. indica. I n t his r espect , E. indica possesses cyt ot ox ic behav ior suggest ing t he pr esence of pot ent ial bioact iv e chem ical com ponent s in t he plant ’s ex t r act .
Ke y W or ds: Bioact iv it y, cy t ot ox ic, decoct ion, let hal concent r at ion, m edicinal.
I n t r odu ct ion. Many of t he essent ial needs of hum ans, including life- saving
phar m aceut ical agent s hav e been pr ov ided by plant s. Hist orically , plant s hav e for m ed t he basis of t r adit ional m edicine pr act ices t hat hav e been used for t housands of y ear s by m any count r ies led by China and I ndia ( Singh 20 06) . Plant s ar e st ill im por t ant sour ces of m edicines especially in dev eloping count r ies t hat st ill rely on plant - based t r adit ional m edicine for t heir healt hcar e ( Ram esh & Okigbo 200 8) . Ther e is a per cept ion t hat m or e t han t w o billion people all ov er t he w or ld m ay be heav ily r eliant on m edicinal plant s ( Sm it h- Hall et al 2012 ) . Accor ding t o Wor ld Healt h Or ganizat ion, t r adit ional m edicine has m aint ained it s popularit y w or ldwide since t he 1990s unt il it s use has sur ged in m any dev eloped count ries. As an im por t ant sour ce of nut r it ion and subst ances w hich pr oduce phy siological act ion on t he hum an body ( Olow a & Nuñeza 2013) , plant s are r ecom m ended for t heir t her apeut ic v alues w hich can be used in dr ug dev elopm ent and sy nt hesis ( Ram aw at & Merillon 2008) .
consum ed lar gely ( Melanie 1999) . Hence, t her e should be a pow er ful and pr oper deep assessm ent on t he phar m acological qualit ies of her bal- deriv ed r em edies ( Fir enzuoli & Gor i 2007) .
I n Philippine t r adit ional m edicine, E. indica is one of t he m edicinal plant s t hat has been widely used for t he t r eat m ent of sev er al diseases like kidney pr oblem s, diabet es, gast r o- int est inal diseases and is used as diur et ic ( Cast illo et al 2005) . This plant is com m only k now n as “ Bila- bila” , “ Bak is- bakisan” and “ Par ag- is” , w hich is nat ive in t he t r opics and subt r opical r egions ( Haber & Sem aan 200 7) . E. indica is an abundant w eed in w ast e places and along r iv er bank s, r oads, and set t led ar eas in t he Philippines ( St uar t 201 3) . I t has a br oad t oler ance t o a w ide r ange of env ir onm ent al condit ions, but it s v eget at iv e gr ow t h is significant ly r educed during dr y seasons ( Leach et al 1995) .
The w hole plant of E. indica, especially t he r oot has been r epor t ed in Malay sia as depur at iv e, diur et ic, febrifuge and lax at iv e, and hence is used for t he t r eat m ent of influenza, hy per t ension, oliguria and ur ine r et ent ion ( Al- Zubairi et al 2011) . I t is also used for kidney ailm ent s in Trinidad and Tobago ( Lans 200 6) . I n t he Philippines, a sur v ey on t he Resear ch I nfor m at ion Ser ies of Ecosy st em s ( RI SE) by Cast illo et al ( 2005) show ed t hat decoct ion of fr esh plant s of E. indica is used as a diur et ic and for dy sent er y . The ent ir e plant is also m ix ed wit h coconut ext r act t o be used as ant i- dandr uff and pr ev ent t he loss of hair . The ex t r act ed j uice fr om t he leav es is k now n t o be used aft er childbirt h for placent a elim inat ion ( Gbadam osi & Ot obo 2 014) . The w hole plant , par t icularly t he r oot , m ay be used for fev er , liv er com plaint s and for t r eat ing cough. Mor eov er , t his plant is used as poult ice in spr ains and is used as ant i- helm int ic ( Et t ebong et al 2012) .
At pr esent , t her apeut ic benefit s of t his m edicinal plant ar e oft en at t r ibut ed t o it s ant ioxidant ( Al- Zubairi et al 2011; I qbal & Gnanar aj 201 2) and ant iplasm odial and ant idiabet ic pr oper t ies ( Ok ok on et al 2010) . How ev er , et hnophar m acological and scient ific r epor t s on t his plant ar e st ill scar ce, especially on it s phy t ochem ical observ at ion and cy t ot ox ic pr oper t ies. Thus, fur t her inv est igat ion of t his m edicinal plant is needed in t he count r y t o uph old m or e of it s significance as her bal- deriv ed r em edies. To dat e, no scient ific inv est igat ion has been r epor t ed on ev aluat ing t he cy t ot oxicit y of E. indica using anim al m odels. Ther efor e, t his st udy w as conduct ed in or der t o ev aluat e t he t oxicit y of E.
indica w hole plant ex t r act s using Br ine Shr im p Let halit y Assay ( BSLA) . The m ost com m on
m et hods of ex t r act ion ( decoct ion, absolut e et hanol, 50% w at er - 50% et hanol) w er e t est ed in t he pr esent st udy for cyt ot oxic effect s of ex t r act s against t he brine shr im p nauplii and r elat ed t oxicit y r esult s wit h E. indica’s k now n t r adit ional uses. Specim ens of t he brine shrim p, Ar t em ia sp. , a m arine m icr ocr ust acean, ar e used as t ar get or ganism s t o det ect bioact iv e com pounds in plant ex t r act s in w hich t he t ox icit y t est against t hese anim als has show n t o hav e a good cor r elat ion w it h ant it um or act ivit y ( Ar canj o et al 201 2) . Ther eby , t his t y pe of bioassay m ay pr ov e adv ant ageous in t he ev aluat ion of plant bioact ivit y for t he subsequent isolat ion of bioact iv e com pounds fr om t he plant ext r act s, leading t o t he possible dev elopm ent of new dr ugs.
M a t e r ia l a n d M e t h od
Pla n t colle ct ion . Thr ee kilogr am s of w hole plant sam ples ( including r oot s) of E. indica
w er e collect ed in Bar angay Dit ucalan, I ligan Cit y in Januar y , 2014. Docum ent at ion and labeling pr ocedur e w er e done accor ding t o t he pr ot ocol of Guev ar a ( 200 5) . Plant ident ificat ion w as based on Cast illo et al ( 2005 ) .
Pr e pa r a t ion of t h e pla n t e x t r a ct . I n t his st udy , E. indica w hole plant ex t r act s w er e
using a st erile elect ric blender. The pow der w as w eighed, divided int o t w o equal par t s and st or ed in glass cont ainer s; one w as per colat ed wit h enough 95% et hanol and t he ot her one w as soak ed wit h 50: 50 pr opor t ion m ix t ur e of w at er and et hanol for t hr ee day s ( 72 h) . Each solut ion w as t hen filt er ed using What m an filt er paper and collect ed in a glass cont ainer . Enough am ount of t he filt er ed et hanol solut ion w as subj ect ed t o r ot ary ev apor at or t o obt ain t he cr ude plant et hanol ex t r act . The 50: 50 m ix t ur e ex t r act w as concent r at ed in v acuo and subsequent ly fr eeze- dried t o obt ain t he cr ude m ix t ur e ex t r act .
Br in e sh r im p le t h a lit y a ssa y ( BSLA) . Br ine shr im p eggs w er e pr ov ided by t he
Chem ist ry Depar t m ent of MSU- I I T. Filt er ed st er ile seaw at er w as put in a hat ching cham ber w it h a par t it ion for dar k ( cov er ed) and light ar eas. Shr im p eggs w er e added int o t he dar k side of t he cham ber w hile t he lam p abov e t he ot her side of t he cham ber at t r act ed t he hat ched shrim ps. The nauplii lar v a br ine shrim ps w er e used for t he bioassay aft er t w o day s.
Four concent r at ions of t he t hr ee ex t r act ( decoct ion, m ixt ur e and et hanol) of E.
indica w er e pr epared: 10 g/ m L, 100 g/ m L, 50 0 g/ m L and 1 00 0 g/ m L. To m ak e t he
st ock solut ion, w eighed am ount s of t he t h r ee ex t r act s ( decoct ion, m ixt ur e and et hanol) , 36. 5 m g, 25. 1 8 m g and 35. 4 m g w er e dissolved separ at ely wit h sufficient am ount of solv ent t o obt ain t heir r espect iv e 10,000- ppm st ock solut ion. Et hanol w as used as solvent for t he alcohol- based ex t r act s and allowing it t o ev apor at e for t w o day s. Aft er t he ev apor at ion of et hanol, DMSO, a sur fact ant w as added t o t he t w o ex t r act s, ex cept for t he decoct ion. Fr om t hese st ock solut ions, 10 ppm , 100 ppm , 500 ppm and 1 000 ppm concent r at ions w ere derived t hr ough serial dilut ion. Thr ee r eplicat es w er e prepar ed for each ex t r act and 5 m L of filt er ed st erile seaw at er ser v ed as cont r ol. Subsequent ly , five br ine shrim ps w ere int r oduced int o each t ube. Thus, t her e w er e a t ot al of 30 br ine shr im ps per dilut ion. Then, t he v olum e w as adj ust ed w it h st erile seaw at er and t he t ubes w er e left uncov er ed under t he lam p. Aft er 6 h and 24 h, t he n um ber of dead and sur v iving nauplii in each t ube w er e count ed and r ecor ded.
St a t ist ica l an a ly sis. The Reed- Muench m et hod ( Reed & Muench 1938) w as used t o
det er m ine t he r elat iv e t oxicit y of t he v ar ious concent r at ions of t he ex t r act s t o Ar t em ia
salina. LC5 0 r epr esent s t he dose let hal t o half of t he A. salina populat ion. This w as
det er m ined by plot t ing t he % m or t alit y ( y- axis) v er sus log dose ( x - axis) w it h t he dose w hich r ender ed 50% m or t alit y as t he LC5 0.
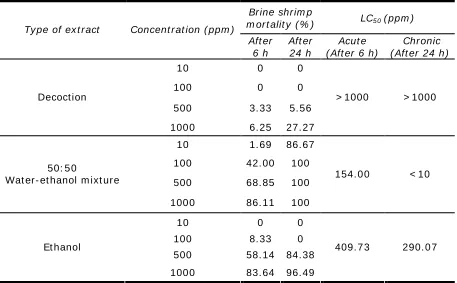
Re su lt s a n d D iscussion. Table 1 show s t he percent m or t alit ies and LC5 0 v alues aft er 6
h ( acut e) and 24 h ( chr onic) ex posur e t o v ar ious ex t r act s of E. indica. The least per cent m or t alit ies w er e r ecor ded for t he decoct ion ex t r act w hich r anged fr om 0- 27. 77% , w hile high per cent m or t alit ies w er e r ecor ded for t he alcohol- based ext r act s ( m ix t ur e and et hanol) . Result s also show ed t hat t he degr ee of m or t alit y w as dir ect ly pr opor t ional t o t he E. indica concent r at ion in all t y pes of ext r act s. Aft er 24 h ex posur e, incr eased m or t alit ies of brine shr im ps wer e r ecor ded in all pr epar ed ext r act s. Maxim um m or t alit ies ( 100 % ) w er e obser v ed in t he t hr ee concent r at ions of t he m ix t ur e ex t r act t est ed ( 100, 500, 1 000 ppm ) . Am ong t he t hr ee ex t r act s of E. indica, t he m ost cy t ot oxic t o t he brine shr im p aft er bot h 6 h and 24 h ex posur es w as t he w at er- et hanol m ixt ur e as indicat ed by it s low est LC5 0 v alue of 154 ppm and < 10 ppm , r espect iv ely . Thus, t he best ex t r act ion
m et hod for t he w hole plant sam ples of E. indica is t hr ough t he use of a m ix t ur e of et hanol and w at er as indicat ed by t he per cent m ort alit y and LC5 0 v alues.
Accor ding t o Mey er et al ( 1982) , LC5 0 low er t han 100 0 ppm is consider ed cy t ot oxic
( act iv e) on t he ev aluat ion of plant ex t r act s by BSLA, w hile non- t ox ic ( inact iv e) if it is gr eat er t han 1 000 ppm . The r esult s of t he decoct ion plant pr epar at ion exhibit ed inact ivit y w her ein v er y low m or t alit y am ong t he br ine shr im p nauplii w as obser v ed. This w ould m ean t hat usage of t his plant ex t r act as t her apeut ic agent poses no high risk of har m upon adm inist r at ion especially w hen pr epar ed as decoct ion w hich is t he t r adit ional w ay of pr epar at ion. How ev er, alcohol- based ex t r act s ( w at er- et hanol m ix t ur e and et hanol) of E.
indica, w er e pot ent or act iv e w hich caused high m or t alit ies against t he brine shr im ps.
Table 1 LC5 0 v alues of t he Eleusine indica plant ext r act s against t he brine shrim p, Ar t em ia salina
Br ine shr im p
m or t alit y ( % ) LC5 0 ( ppm )
Ty pe of ex t r act Concent r at ion ( ppm )
Aft er 6 h
Aft er 24 h
Acut e ( Aft er 6 h)
Chr onic ( Aft er 24 h )
10 0 0
100 0 0
500 3. 33 5. 56 Decoct ion
100 0 6. 25 27. 27
> 1000 > 1000
10 1. 69 86. 67 100 42. 00 100
500 68. 85 100 50: 5 0
Wat er- et hanol m ixt ur e
100 0 86. 11 100
154. 0 0 < 10
10 0 0
100 8. 33 0
500 58. 14 84. 38 Et hanol
100 0 83. 64 96. 49
409. 7 3 290. 0 7
Our st udy has dem onst r at ed t hat E. indica possess cy t ot oxic behaviour , suggest ing t he pr esence of pot ent ial bioact iv e chem ical com ponent s in t he plant ’s ext r act . As m ent ioned, plant s pr oduce a lar ge num ber of nat ur ally occur r ing secondar y m et abolit es w hich hav e m any unique phar m acologic act ivit ies ( Salim et al 2005) . A phy t ochem ical scr eening of t he ex t r act of E. indica show ed t hat t he ex t r act cont ains secondar y m et abolit es lik e alk aloids, t er penes, flav onoids, t annins, ant hr aquinones, saponins and car diac gly cosides ( Ok ok on et al 2010) . These phy t ochem icals hav e been im plicat ed on t he cyt ot oxicit y act ivit y dem onst r at ed by t he alcohol- based ex t r act s of E. indica.
E. indica pr oduced phy sical signs of t oxicit y in albino wist ar r at s depending on t he
dose giv en r anging fr om w r it hing, decr eased r espir at ion and deat h 2 4 h aft er adm inist r at ion of t he et hanolic leaf ex t r act of E. indica ( Ok ok on et al 201 0) . Mor eov er , Hansak ul et al ( 2009) had ex am ined t he ant iprolifer at ive and cy t ot oxic effect s of t he hex ane and but anolic ex t r act s of E. indica on hum an lung and cer vical cancer cells. Result s show ed t hat bot h hex ane and but anolic ex t r act s of E. indica dem onst r at ed cy t ot oxic effect s against lung and cer vical cancer cells via apopt osis. On t he ot her hand, a cy t ot oxicit y st udy by Al- Zubairi et al ( 201 1) r ev ealed t hat t he hex ane, dichlor om et hane, et hyl acet at e and m et hanol ex t ract s of E. indica w er e found t o be non-effect iv e in inducing cell deat h t ow ar ds t he MCF- 7 hum an br east cancer cells, HT- 29 hum an colon car cinom a cells and Hum an T4- ly m phoblast oid cell line, following guidelines of t he Am er ican Nat ional Cancer I nst it ut e.
under st ood. Thus, fur t her inv est igat ions ar e needed t o v erify t he cy t ot oxic effect and ot her biological pr oper t ies of t his plant .
Con clusion s. Alcohol based ex t r act s ( et hanol and w at er- et hanol) of E. indica hav e
caused high m or t alit ies against t he brine shr im ps, unlik e t he decoct ion plant pr epar at ion in w hich v er y low m or t alit y am ong t he br ine shr im p nauplii w as obser v ed. The best ex t r act ion m et hod for t he w hole plant sam ples of E. indica is t hr ough m ix t ur e of et hanol and w at er as it dem onst r at ed m axim um m or t alit ies ( 100% ) and high LC5 0 v alues against
t he br ine shrim ps.
Re fe r e n ce s
Al- Zubairi A. S. , Abdul A. B. , Abdelw ahab S. L. , Yuan P. C. , Mohan S. , Elhassa M. M. , 201 1 Eleucine indica possesses ant ioxidant , ant ibact erial and cy t ot oxic pr oper t ies. Ev id Based Com plem ent Alt er nat Med Ar t icle I D 9 65 370, pp. 1- 6. ht t p: / / dx . doi. or g/ 10. 109 3/ ecam / nep0 91
Ar canj o D. D. R. , Albuquer que A. C. M. , Melo- Net o B. , Sant ana L. C. L. R. , Medeir os M. G. F. , Cit ó A. M. G. L. , 2012 Bioact ivit y ev aluat ion against Ar t em ia salina Leach of m edicinal plant s used in Br azilian Nor t heast er n folk m edicine. Br az J Biol 72( 3) : 505-509.
Cast illo E. T., Siapno F. E. , Sam br ana D. G. , De Leon N. P. , Silv oza E. Q. , 2005 Gr assland species wit h m edicinal pot ent ials. Resear ch infor m at ion Series on Ecosy st em s 17( 1-3) : 1- 3.
Et t ebong E. O. , Nw afor P. A. , Ok ok on J. E. , 20 12 I n v iv o ant iplasm odial act ivit ies of et hanolic ex t r act and fr act ions of Eleucine indica. Asian Pac J Tr op Med 5: 673- 676. Fir enzuoli F. , Gor i L., 2007 Her bal m edicine t oday : clinical and r esear ch issues. Evid
Based Com plem ent Alt er nat Med 4( 1) : 3 7– 40.
Gbadam osi I . T. , Ot obo E. R., 2014 Assessm ent of nut r it ional qualit ies of t en bot anicals used in pr egnancy and child deliv er y in I badan, Niger ia. I nt er nat ional Jour nal of Phy t om edicine 6( 1) : 16- 22.
Guev ar a B. Q. , 2 00 5 A guidebook t o plant scr eening: phy t ochem ical and biological. Manila: Univ er sit y of Sant o Tom as Publishing House, Manila, pp. 1- 149.
Haber R. M. , Sem aan M. T., 2007 Tw o new r ecor ds fr on Lebanon: cham aesy cenut ans ( Lag. ) sm all ( Euphor biaceae) and Eleusine indica ( L. ) Gaer t ner ( Poaceae) . Tur k J Bot any 31 ( 4) : 34 1–3 43.
Hansak ul P., Ngam kit idechak ul C., I ngk aninan K., Sir eer at aw ong S. , Panunt o W., 2009 Apopt ot ic induct ion act ivit y of Dact y loct enium aegy pt ium ( L. ) P. B. and Eleusine
indica ( L. ) Gaer t h, ex t r act s on hum an lung and cer v ical cancer cell lines.
Songk lanak ar in J Sci Technol 31( 4) : 27 3- 2 79.
Hussain M. D. S., Sheeba F. , Ansari M. D., Ak hlaquer R. , Ahm ad I . Z. , Saeed M., 2012 Cur r ent appr oaches t ow ar d pr oduct ion of secondar y plant m et abolit es. J Phar m Bioallied Sci 4( 1) : 10 –2 0.
I qbal M. , Gnanar aj C., 2012 Eleusine indica L. possesses ant ioxidant act ivit y and pr ecludes car bon t et r achloride ( CCl4) - m ediat ed ox idat iv e hepat ic dam age in r at s. Env ir on Healt h Pr ev Med 17( 4) : 3 07 –3 15.
Lans C. A. , 2006 Et hn om edicines used in Trinidad and Tobago for ur inar y pr oblem s and diabet es m ellit us. J Et hnobiol Et hnom ed 2: 45. doi: 10. 11 86/ 17 46- 426 9- 2 - 4 5.
Leach G. E. , Dev ine M. D. , Kirk w ood R. C. , Mar shall G. , 1995 Tar get enzy m e- based r esist ance t o acet yl- coenzy m e a car box ylase inhibit or s in Eleucine indica. Pest ic Biochem Phy siol 51: 129–13 6.
Melanie J. C., 1999 Her bal r em edies: adv er se effect s and dr ug int er act ions. Am Fam Phy sician 59( 5) : 1 23 9- 1 24 4.
Mey er B. N., Fer rigni N. R. , Put nam J. E., Jacobsen L. B. , Nichols D. E. , McLaughlin J. L., 198 2 Br ine shr im p: a conv enient gener al bioassay for act iv e plant const it uent s. Plant a Med 45( 5) : 31 - 34.
Olow a L. F. , Nuñeza O. M., 2013 Br ine shr im p let halit y assay of t he et hanolic ex t r act s of t hr ee select ed species of m edicinal plant s fr om I ligan Cit y , Philippines. I nt Res J Biological Sci 2( 11) : 7 4- 7 7.
Ram aw at K. G. , Merillon J. M., 2008 Bioact iv e m olecules and m edicinal plant s. Spr inger, Ber lin, Heidelber g New Yor k, p. 323.
Ram esh P. , Okigbo R. N. , 2008 Effect s of plant s and m edicinal plant com binat ions as ant i-infect ives. African Jour nal of Phar m acy and Phar m acology 2( 7) : 1 30- 135.
Rasool Hassan B. A. , 2012 Medicinal plant s ( im port ance and uses) . Phar m aceut Anal Act a 3, e139. ht t p: / / dx . doi. or g/ 10. 4172 / 21 53- 24 35. 1 0 00e1 39
Reed L. J. , Muench H., 1938 A sim ple m et hod of est im at ing fift y per cent endpoint s. Am J Hy g 27: 4 93- 497
Salim A. A., Chin Y. W. , Kinghor n A. D., 2005 Dr ug discov er y fr om plant s. Spr inger, Ber lin, Heidelber g New Yor k, p. 379.
Singh H. , 2006 Pr ospect s and challenges for har nessing oppor t unit ies in m edicinal plant s sect or in I ndia. Law, Env ir onm ent and Dev elopm ent Jour nal 2( 2 ): 1 96- 211.
Sm it h- Hall C., Lar sen H. O. , Pouliot M. , 2012 People, plant s and healt h: a concept ual fr am ew or k for assessing changes in m edicinal plant consum pt ion. J Et hnobiol Et hnom ed 8: 43. doi: 10. 11 86/ 17 46- 42 69- 8- 4 3
St uar t G. , 2013 Philippines m edicinal plant . Ret r iev ed fr om ht t p: / / w ww . st uar t x change. com / Par agis. ht m l
Wor ld Healt h Or ganizat ion. Tr adit ional m edicine. Ret riev ed fr om ht t p: / / w w w. w ho.int / t opics/ t r adit ional_m edicine/ en/
Receiv ed: 17 June2 015.Accept ed: 17 July201 5.Published on line: 14 August 201 5. Aut hor s:
Mae Alia Respont e, Mindanao St at e Univ er sit y - I ligan I nst it ut e of Technology , College of Science and Mat hem at ics, Depart m ent of Biological Sciences, Philippines, I ligan Cit y , 920 0 Lan ao del Nor t e, Andr es Bonifacio Av e, e- m ail: r espont em ae@gm ail. com
Mar ia Rhot sy n Booc Dacar , Mindanao St at e Univ er sit y - I ligan I nst it ut e of Technology , College of Science and Mat hem at ics, Depart m ent of Biological Sciences, Philippines, I ligan Cit y , 920 0 Lan ao del Nor t e, Andr es Bonifacio Av e, e- m ail: r hot syndacar _m am am ia@y ahoo.com
Olga Macas Nuñeza Mindan ao St at e Univ er sit y - I ligan I n st it ut e of Technology , College of Science and Mat hem at ics, Depart m ent of Biological Sciences, Philippines, I ligan Cit y , 920 0 Lan ao del Nor t e, Andr es Bonifacio Av e, e- m ail: olgam nuneza@y ahoo. com
My lene Mondar t e Uy , Mindanao St at e Univ ersit y - I ligan I nst it ut e of Technology , College of Science and Mat hem at ics, Depar t m ent of Chem ist r y , Philippines, I ligan Cit y , 9200 Lanao del Nor t e, Andr es Bonifacio Av e, e- m ail: m y lene603@y ahoo. com
This is an open- access ar t icle dist r ibut ed under t he t er m s of t he Cr eat iv e Com m ons At t r ibut ion License, which per m it s unr est r ict ed use, dist r ibut ion and r epr oduct ion in any m edium , pr ov ided t he or iginal aut hor and sour ce ar e cr edit ed.
How t o cit e t his ar t icle: