1
REPORT
THE INTERNATIONAL JOINT SEMINAR & VISIT TO CLEAN AUTHORITY OF TOKYO
(Shin-Koto Incineration Plant) TOKYO METROPOLITAN GOVERNMENT
(Humanizing Collaboration between Indonesia and Japan)
“PROCESSING WASTE”
(A MODEL FOR GREEN PROJECT OF WASTE IN INDONESIA)
Arranged by
REPHY EKAWATIE
Student ID:
120820160027
Occupation:
Staff at Central Bureau of Statistic of Kapuas District
in Central Kalimantan Province
Held by
Graduate School of International
Cooperation Studies
Master of Management Program
Faculty of Economics and Business Universitas Padjadjaran
2
INTRODUCTION
Green Economy Phenomenon
The attentions to green economy moved from developed to developing and less developing countries in last decade. Three pillars of green economy such as social, economy and environment become important as element to fulfill sustainable development. Japan is one of developed country that has been implement consistency preserve environment to support economy and social. It is proved by result of Global Green Economy Index in 2016. Japan has been ranked nine on the top ten by respondents of GGEIs survey in perception, even though based on result of performance in green economy, Japan was not enter the top ten. The achievement that achieved by Japan in green economy makes Japan become a suitable benchmarks as a model of green economy for the developing country such as Indonesia1.
Green Innovation Strategy is a respond of result from second conference at Rio de Jeneiro in 2012 which is general known as Rio+20. Naoya Tsukamoto (2011) stated that Japan was transitioning to a green economy. The vision manifested as a strategy which are concerned to technology innovation. It fosters “a win-win” solution for issues related to environment, energy and economic growth. Japan Government emphasizes the need to stimulate the economy through green innovation of the environment and utilization energy technology. In effort to fill it, Japan carries out various measures including promoting renewable energy; the facilitation of low-carbon finance and investment; the application of information and communication technology; the usage of nuclear power; the acceleration of resources and development of innovative technology; the promotion of modal shift; the dissemination of energy-saving electrical appliances; the enabling of efficient electricity demand; and the recycling of domestic resources2.
Indonesia as the developing country stills in efforts to change old paradigm to the Green Economy. Indonesia pursues added values that can reach from green such as the better quality of life, environment, society, economy and welfare. Steps that Indonesia has done as far as are gradually changes fossil fuels into renewable energy sources. Indonesia also, establishes policy adjustments that do support sustainable economic, social and environmental development based on green principles. The policies like mix energy policy which has a positive impact on reduced subsidies on fossil fuels from 3.4 percent to 1.8 percent of national gross domestic product in 2009. In 2012, Indonesia government has begun an effort to replace kerosene for household cooking which using of lot of subsidies, to substitute with liquefied petroleum gas. Programs of reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation plus (REDD+) are result of proof of sincerity Indonesia government to solve the problems of gap between needs to product bio fuels and deforestation which impact ecosystem changes issues3.
Indonesia still struggle on its transition. The changes of paradigms are not easy. Government must struggles towards hindrance from internal and external factors. As olds say “learn from others experiences are a wisely things". Indonesia can learn many things from Japan as the developed country which has done green transition in its country. Models of green implementation on Japan can be adopted in Indonesia by adjusting contextually.
1 Tamanini, Jeremy, Valenciano, Julieth. 2016. The Global Green Economy Index: Measuring National
Performance in Green Economy. Dual Citizen LLC.
2
Tsukamoto, Naoya. 2011. A Green Economy in the contex of sustainable development and poverty
eradication. Text of Statement Delegation of Japan 2nd Preparatory Committee UN Conference on Sustainable Development.
3
3
MARKETING ANALYSIS AND CULTURAL ANALYSIS
Economy
In last five years, similar to the economy condition of the others countries in the world, Japan faced economy deceleration. Even though obtain stimulus for four years, Japan's economy grew only about 2.2 percent in real terms. Japan's Government pushed companies to boost an investment at home and increase wages to support demand, stimulate Japan's economy and drift away from deflation, and maintained the rate of improvement. The government has been pushing companies to encourage pay, supporting to assist to increase consumption, inflation and demand4. How Japan can survive pass this conditions indicate as a Nation, Japan has been growing on step of maturity. The maturity of Japan as a country is felt and seen through its manner to manage elements to support economy inside its country. Even though global economy condition is not supported, Japan can maintain economy condition inside its country and preserve National economy condition to protect its society.
Japan maintains its economy stability collaborates with government and business owner. Japan preserves its economy through keep balance supply and demand of goods needs of society. The Government seriously protects supply and way to distribute goods to the society. The supply of goods from outside Japan is strictly prohibited. The Government policy purpose is to protect suppliers and small and medium entrepreneurs inside the country. Protected supply and distribution lane make small and medium business are growth. It supports to stimulate economy movement in Japan by increase purchasing power.
The Japanese government provides support to economic development by building traditional and non-traditional shopping centers to encourage national consumption. Low tax policies for small businesses and retailers make the prices affordable for consumers. This policy supports the increase of public consumption to support the economic movement in Japan nationally. Outlets and shops are always present at strategic points where tourists will visit such as Asakusa temple, Harajuku, Sky tree, Odaiba, and Ginza. The existence of stores and outlets at these points are to encourage tourists to spend their money in Japan. This will indirectly affect the economic movement in Japan.
In the implementation of green economy, Japan is concerned with maintaining resources and energy efficiency. Based on report International Energy Efficiency Scorecard in 2016 released by the nonprofit American Council for an Energy Efficient Economy (ACEEE), Japan stays at 2nd place with Italy after Germany in the 1st place5. Japan stays at the second place in the category of the national effort. Japan has done significant energy reduction in 2000-2013 and showed hard energy efficiency efforts. Japan has strong energy saving goal then become one of most efficient thermo electric power systems6. Indonesia stays at 18th place. As far as, Indonesia has shown it progress to commit in energy efficiency by stay at 18th passed Mexico, Thailand, South Africa, Brazil and Saudi Arabia7. How Japan is reaching success in National Energy Efficiency as reference for Indonesia to adopt its model to implement.
4 Cadman, Emily, Harding, Robin, Bernard, Steve. 2016. The Japanese economy at glance. Source:
https://ig.ft.com/sites/numbers/economies/japan [June, 10, 2017; 11PM].
5
Kiker, Patrick. 2016. Germany, Italy and Japan Top World Energy Efficiency Rankings. American Council for Energy Efficiency Economy.
6
http://aceee.org/sites/default/files/pdf/country/2016/japan.pdf
7
4
The Interesting things are known from Japan is a smart options that Japan have elected to protect National economy and its society. Japan has done and still does energy efficiency to face the impact of global economy, especially, slowdown of economy in recent times. But, beside it, Japan has become intensify integrated in global value chains, primarily in Asia. Japan gets advantages from international trades through large firms which are owned by its country. The parallel impacts are increasing export of few small and medium enterprises (SMEs) gradually. Japan policies on SMEs to enter international markets will support an inclusive growth. The policies also open an opportunity of more SMEs to join international markets by improving quality and quantity of their products. The domino's effects will be happened are lots of SMEs and micro entrepreneur which appearing and boost Japan’s economy. Despite, it is policies will reduce subsidies to the farmers as like coin with two sides8.
Indonesia now had been decreased dependency on raw commodity exports and promotes the manufacturing industry to growth. The Indonesian government in recent times place high priority on infrastructure development and on investment with focus on long term not short term. SMEs in Indonesia grow consistently and become a micro power of economy in Indonesia. Benchmarks to Japan, how do Japan’s effort to involve its SMEs in value of international chains of trades can be a good input for Indonesian government as consideration to support SMEs to gain values in international trades9.
Social, Technology, Legal and Environment
Japan Government has main focus to protect the economy situation through its society. Depend on the three pillars of Green Economy, specific on social factor, Japan maintain employment and focus to solve the problem of inadequate funds for enterprises. The stimulus package provided by Japan Government is cheap invests in the environment and employment. It includes goal to decrease gas emissions of greenhouse by 50 percent by 2050 to produce low carbon society. Its influence is softening negative effects of owning an aging population by regenerating social security infrastructure10.
5
Technology is supporting efficiency and effectiveness. Most transaction of micro activities in Japan use technology. Technology is used generally and becomes a part of society. At the corners of the city even in traditional markets, market like Tsukiji, makes market area to be clean and tidy. Government of Japan is strict about environment, especially about waste. Hard to find garbage dumped carelessly in Japan. All looks clean, even in the traditional market like Tsukiji. The real phenomenon in Japan drive us to think how Japan could maintain its waste so perfectly?. The answer yet is waste management and environment law. Japan Government made a legal system for form a recycling oriented society. Basic environment law promotes the creation of recycling oriented society. Maintain the recycling materials used by society, reduce the consumption of native resources, and degrade environmental impact.Japan government have been formed the waste management and public cleansing act regulations. It is formed with purposes to reduce of waste generation, appropriate treatment of waste include recycling, regulation on the establishment of waste treatment facilities, set a regulations regarding waste treatment business, formation of waste handling standards. It is espoused step in encourages potent utilization of resources. This act includes recycling of reusable resources, innovations such as easily recyclable structures and materials, labeling for sorting recyclable resources, and increment the efficient use of product.
Basic law then is breakdown to specific regulations targeted at the characteristics of specific product groups. The specific laws for the product groups are packaging recycling law, household devices recycling law, meal waste recycling law, building materials recycling law, end life of vehicle's recycling law, and minor household tool's recycling law. Each law has a role to manage kinds of waste under its rules which has been set.
Recommendation Business Owner
Economic, social and environmental stability in Japan is inseparable from the role of business owners. Benchmarks to the existing business owners in Japan, business owners in Indonesia can adopt the way business owners in Japan in support of the national economy of the country. Business owners which have been involved in economy cycles can attract the others chain of business inside the country to stimulate economy movement. This can be done by substituting foreign goods suppliers into existing domestic suppliers. By doing so, new domestic efforts will grow due to market demand. The growth will affect the increase in domestic consumption and improvement of people's welfare through its purchasing power of society.
Government
Japan Government braves to take a position to protect society and business owner inside the country. Japan strict prohibits goods distribution and supply from outside to protect its peoples and domestic business chain. Japan Government also protects business chain by imposing low taxes for domestic business owners. Indonesia can adopt Japan way to little bit strictly regulate distributor and supplier chain from outside. Reduce import and increase production domestic goods to accommodate domestic demand is a wisely way to boost productivity of society that have impact to National economy in the end. The important point that Indonesia must learn from Japan are how Japan Government and National elements can manage country with mature ways, even in politic, economy, social, cultural and environment.
Differences in Value, Beliefs, Policy and Acculturation
6
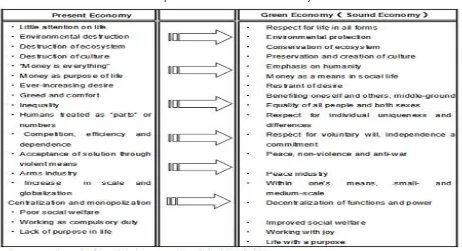
Table 1Comparison Present and Green Economy
Most of Japanese people felt that green economy has a significant impact to make a better quality of life, respect on society and environment, and maintain values of traditional cultures and beliefs14. Green economy drive Japanese society to new pages of economy reforms based on concerns to environment which is correlates with society and welfare. As a developed country, Japan has adjusted Green principles in its country covered all aspects of society. Green economy paradigm as a driving forces to transform Japan as a Nation to do a reform in all aspects.
Japanese culture is tightly correlates with values. The values based on cultures have a substantial role in every-days life of Japanese peoples. Basic elements of essential Japanese values, such as: age, silence, traditions, history, religion, family, government, nature, and education15. Japanese cultures plant value to the young people how to respect elders and appreciate them as important community fellows. The elders are respected as persons who will bequeath a verbal custom of across generation. Contras with Indonesia, on Japanese cultures, the credibility of a persons are measured by more little words are spoken. Their non oral communications are more powerful than verbal communication. Manner how Japanese peoples communicate is another interesting point from Japanese culture. The Japanese are accustomed to bowing about 45 degrees when meeting with others who
are known as a way to greet with respect and courtesy. It is slightly different from the existing culture in Indonesia. In Indonesia when meets with others people who are known people generally will reach out to shake hands or hugs if the people is old friends. Habits shake hands when meeting people who are known also performed by some Japanese people that has been acculturated with western culture. However, until now the majority of Japanese people still preserve the original culture and values that have been rooted from generation to generation.
Value and beliefs that mixed with Japanese culture become inseparable parts of Japanese society life. It rooted until the highest level of formal organization include elements of society, government, institutions, company, ministry etc. Regularity, obedience, and discipline is a value that
14
http://www.kanbun.org/2006/060601greenkeizai/060601greenkeizai_report_english.pdf
15
7
built by belief to the gods. As far as we know, Shinto is majority belief in Japan. Based on Bureau of Democracy, Human Right and Labor report 51 percent of citizen in Japan were Shinto, Buddhist were 44 percent and Christian were 1 percent. Then, about 5 percent of Japanese were belonged to other religious groups. In Japan, most of Shinto believer also follow Buddhist faiths, and opposite16. Value and beliefs that manifest in act through habit (regularity, obedience and discipline) are transmitted to all aspect of life, like working, studying, to play a role in society, socialize, run the organization, etc.Nature is an important element for Japan society. As previous mention, nature is one of basic element of Japan essential value. Histories and beliefs are driver for Japanese people to protect and take care of nature. Water, mountains, soil, air, trees, earth, seas and whole nature element are having means for Japanese peoples so they protect it carefully. The protection forms are shown not only through regulation but through local wisdoms. This is a most reasonable cause why green economy can be implemented well in Japan. Basically, the three pillars of green economy, specifically environment, in principle have been implemented by Japanese society since thousands years ago. Transformation of periods and inventions of technology makes pollution increases. The pollution transforms in many interfere and dangerous forms. Example: noise of operating machines, dust from construction of buildings and roads, harmful chemicals from industrial waste, carbon dioxide from incomplete combustion, etc. Pollutions in this recent period are more complex from thousands years ago. Pollutions came from goods and tools that are peoples in this time dependent with it.
The same principles drive into ways of thinking to give solution for recent conditions. Japan as benchmarks, how to solve and manage waste as a real example, can be inspired Indonesian Government to adopt Japan processing waste models as reference to manage waste in Indonesia. Learns and analysis ways of waste processing in Japan can be a good steps for Indonesia to develop and implement the models of processing waste.
Recommendation Business Owner
Understand the culture, value and belief held by the surrounding community becomes an important key in building and developing a business. Indonesian business owner can adopt Japan's value and ways to operate business. Respect times, discipline, loyal, integrity, always try to do the best, innovative and consistence. All of that value can improve business performance.
Government
The Positive values from Japan (discipline, respect times, obedience, loyal, always try to do the best, innovative and consistence) can be adopted on Indonesia Government to improve civil servant performance. Indonesia uses the phenomenon of moving attentions of Green Economy from the developed to the developing and less developing countries, as a power to reform all aspect on Indonesia systems to reach a better quality of life and society.
16
8
COMPANY VISIT
BACKGROUND
Trash is a crucial problem in almost of all developing countries. Indonesia is a one of country with numerous of waste. Nationally, waste in Indonesia is about 200 thousand ton a day or similar 73 million ton a year 17. The high number of waste in Indonesia can be seen as a big potential of resources in positive perspective. The spread wide of green economy paradigm changed the way of society views today in seeing waste.
Technological and scientific developments made waste as a resource that has benefit and economic value. The developing countries can use opportunity in technology development to probe potential of waste in support economic. The potential waste and advantages of technology existence can be managed properly through waste management. Waste management involves role of society, government, private, and all parties in implementation. Assets management of house hold becoming an important to support it is triumph.
Japan is one of the developed countries in Asia that are successful in managing waste. Japan has proven that collaboration of technology development and consistency of waste management till the lowest level (household) give a positive impact to support economic and environment. The significant impact of waste management successful is the ways of Japanese people to manage their household assets. The ways of Japanese people to manage household assets are supported by the Government. The Government made rules to guarantee every steps of waste management were obtained by the society. The result of it is Japan success to recycle plastics waste 77% in 201018.
Waste management is applied in Japan by classified waste into each group of waste and be managed. Application of waste management is such as combustible waste, incombustible waste and large size waste. It is arranged from the micro levels of society. Here, the assets management of household plays important roles to make an asset decisions. Unused household assets can be replaced with the new one. The old assets can be dumped into group of large size waste and be managed. Throughout this process, management of assets in micro sector is moving and gives positive impact on economic and consumption.
Japan’s experiences and waste technology development made Japan is suitable to be a model to learn. Indonesia as a developing country which facing complicated problems caused by waste can adopt experiences and technology that Japan’s has to develop waste systems in Indonesia. As known, Indonesia is a big country that has 34 provinces. Each provinces run it’s governance under control of central government which is lead by President. Each province has classical problems with waste. Indonesia population is about 255,461,700 peoples19.
The great number of population made number of consumption and consumerism increase. The result of this phenomenon is increasing waste from consumerism follows the rising number of population. Situations that are commonly in developing countries, where the numbers of population are big and implementation of management, basically, are weak. Learning how Japan’s successes implement its waste management and impact to household’s assets management, can be a good way to adopted in Indonesia.
WASTE PROCESS ANALYSIS
Japan has seriousness to implement innovation in technology to support Green Economy. Correlate with economy, social, technology, and environment supported with values, beliefs, and policies that Japan has in its society, waste management become an one of implementation of all it. The technologies impacts on Waste’s processing become interesting to observe. Waste which do relate with pollutions, dirty and disturbers if well managed will give added values for environment, economy, and society. Japan has prove that waste can be alternative source to support energy through technology waste can be managed in order becomes environment’s friendly. How does Japan manage processes on waste will be described as bellow:
Waste processing location
9
construction. Chubo Incombustible Waste Processing Centers there are 2 at 23 Cities. Large sized Waste Pulverization Processing Facility there is 1 at 23 City.Processing waste
The wastes that has been sorted according to its type, is processed on each one intermediate processing of waste. The process being done as bellow:
Process combustible waste
The process of combustible waste is starting from measure the weight of waste then waste collection vehicles dump waste into the bunker. Waste is temporary stored in the bunker until incineration. Waste is mixed and then crane. The waste is leveled and sent to the incinerator. Air is sent from the waste bunker to the incinerator by forced draft fan. Incinerator burns waste at a high temperature of over 800oC (1,472oF). The previous process produces steam from heat generated when waste is burned. The steam used for heat supply and electric power generation. Cooling tower is a place where freezes upper heat exhaust exuded from the incinerator about 150oC (302oF) for avoiding the re-composition of dioxins. Bag filter is used to remove smoke black and dust, dioxin, mercury, hydrogen chlorides, and sulfur oxides from exhaust. The exhaust is pure by water and chemicals to remove mercury, hydrogen, chlorides and sulfur oxides. The tower of catalyst reaction is used as a place to decompose dioxins and nitrogen oxides in exhaust using catalysts. An exhaust is sent to the stack by induced draft fan.
A stack of exhaust that is exempted of harmful substances or smell is released into the air. A solid and heavy metal in wastewater produced from incineration plant are removed to the limit or below before waste water is released into the sewer. The process to free wastewater from harmful substances is called wastewater treatment facilities. All activities are controlled at central control room. The central control room as a central to control and monitor facilities including the waste bunker and
the incinerator. Each facility continuously sends information to the control computer system and operation across the entire incineration plant. Then, all process can be observed on the monitors.
Combustible waste are carried into incineration plants sometimes contain waste unsuitable for incineration. The unsuitable wastes are such as metals, glass or oversized waste that exceeds the disposal capacity of the plant. Such improper waste may cause the halt or failure of incinerators, costing a great deal of money and time before recovery. Once the facilities become incapable of accepting waste, waste
collection and transfer operation will be interrupted, seriously affecting waste management in all 23 cities. Every year, some incineration plants are forced to stop operation due to improper waste. To prevent carry in of improper waste and to ensure safe and stable plant operation, inspection of incoming waste is reinforced, and awareness raising activities are undertaken. Special weeks are also set to enhance the above inspection and to perform close observation of platforms in each incineration plant. Overall regular inspection on incoming waste is also conducted at all incineration plants in collaboration with the 23 cities.
Process incombustible waste
10
Process large size waste
Large sized waste is separated into combustible large sized waste, such as wooden furniture, and into incombustible large sized waste such as bicycles. The separation work is performed manually at large sized waste transfer stations in each city or at the receiving yard of the large sized waste pulverization processing facility. Combustible residue after pulverization is incinerated at incineration plant, while incombustible residue is sent to landfill disposal sites.
Results of waste processing
Waste processing in intermediate processing of waste result, such as: the heat energy. The heat energy generated from incineration is used to beneficial purpose, such as power generation and supplier energy. Electricity and hot water produced at plants are used within facilities to operate the plant, thereby reducing electricity purchases and fuel costs. Surplus electricity is sold to power companies. All of the plants sell electricity and four plants sell heat as hot water to other facilities. The bottom ash as result of burned process is recycled as cement materials. Bottom ash after removing ash to be melted into slag, as well as after processed with chemicals are sent to landfill disposal on the New Sea Surface Disposal Site, which has been established and is managed by Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Because it is really difficult to find new landfill disposal sites in Tokyo Port, a full scale initiative has been undertaken to recycle bottom ash into cement materials for the purpose of reducing the amount of landfill disposal and achieving more efficient use of resources.
11
temperature of over 1,200oC (2,192oF) and then rapidly cooled, it turns into sandy slag. As slag, the volume is almost half that of ash and approximately one fortieth of its original state as waste. The process of making slag decomposes dioxins within the ash and traps heavy metals inside, thereby making it safe and efficient for use as construction materials and so on.Residue from a process of Chubo Incombustible Waste Processing Center and Large sized Waste Pulverization Processing Facility which are not be recycled, will bring to landfill disposal to manage by Tokyo Metropolitan Government. At the outer Central Break Water Landfill Disposal Site and New Sea Surface Disposal Site established and managed by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government, residue after treating general waste in 23 Cities, waste from municipal facilities such as sewage sludge, and industrial waste from small and medium sized companies in Tokyo are put in landfill disposal.
Combustible waste and combustible past of large sized waste after pulverization are incinerated. A part of the bottom ash is recycled into cement materials or melted into slag while the remainder of bottom ash and chemically treated fly ash goes to landfill. Incombustible waste is pulverized, while ferrous metals and aluminum are recovered as resources, before the residue is buried into landfill. Large sized waste is pulverized, while ferrous metals are recovered as resources before the incombustible residue is buried into landfill. In addition to waste, materials from dredging the sea and the rivers as well as generated by construction (dirt and sand) are buried in landfills but are placed separately from waste because their treatment method differs.
On landfill disposal site, furrows are made with waste. When a furrow reaches the height of approx. 3 meters, it covered with approx. 50 centimeters of soil. Subsequently, waste is buried in the resulting ridge. When the ridge is filled, it is also covered with approx. 50 centimeters of soil. Landfill disposal is performed by repeating these steps (sandwich pattern). The soil covering prevents the scattering of waste, spread of odor, vermin and fire. Bottom ash is disposed of using a framing method where a trench is created into which as is dumped, so that it will not be dispersed by wind.
Environment protection
Incineration plants have done protection to environment. Environment measure is used to prevent exhaust and wastewater emissions. Soot and dust are removed by bag filters. Generation of dioxins is restricted through control of waste incineration process and their re composition is prevented by rapid cooling of exhaust in the cooling tower. Dioxins are also removed by bag filters and decomposed in the catalyst reaction tower using catalysts. Mercury are removed by adsorption into activated carbon in bag filters and by liquid chelate in the gas scrubber. Hydrogen chlorides and sulfur oxides decomposed in the catalyst reaction tower through a reaction with ammonia.
12
Recommendation
Government in Indonesia can use the models of processing waste to implement in each province in Indonesia. The intermediate processing of waste at each province in Indonesia become important because of Indonesia demographic structure separated by seas and strait. Each province can make a region income from processing waste in its territory. Income can be used to develop and construct its own territory or invest on further development of waste technology. Management of waste models can be adopted and implement in Indonesia, specially, in provinces which almost all that have classical problem with rubbish.
Benchmark to Japan as a country that is succeed to implement waste management in all of its territory, about 23 city, Indonesia can develop the same way of Japan to manage waste in each territory in Indonesia which is called as provinces. It is not easy to manage people with large and huge number of population to concern and focus to reach the goal of green economy in Indonesia. Different character of society is aware as the other problem to implement it. It is going possible because human resources development in Indonesia going better every single years. Based on Central Bureau of Statistic data, human development index in Indonesia since 2010 till 2016 are increase20. It is shown by Table 2 as bellow.
Table 2
Human Development Index of Indonesia (2010-2016)
Implication of this statistic is a slowly change of mind set and point of view most of Indonesian society in responses global switch of environment, social, economy, culture, and value to a better ways. How is society view phenomena can impact acts and build the new culture with higher aware. The importance of reducing waste and cares the environment become a basic reason why processing waste are important to apply in developing countries, such as, Indonesia. The previous data about how is human resource in Indonesia are going better is contrast with the data of waste in Indonesia.
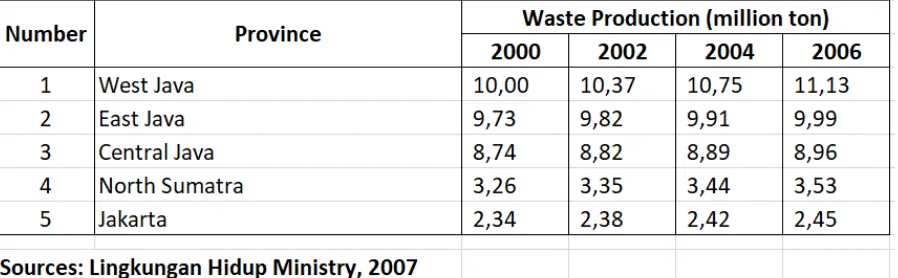
The condition of waste that producing in each province in Indonesia in period 2000 – 200621 can be described in Table 3, as bellow:
Table 3
Waste Production in a few provinces in Indonesia (2000-2006)
Based on Table 3, number of waste since 2000 till 2006 has a pattern increases. The number of waste is estimated will increase continuously until 2019. The production of waste, nationally in 2019 will touch number of 67,1 million ton a year22. Mostly waste are produced by the household. The serious condition of waste in
20
https://www.bps.go.id/linkTableDinamis/view/id/1211
21
http://sampahmasyarakat.com/2016/03/21/statistik-sampah/
22
13
Indonesia attracts attention to solve it. Learning and going deep into central of the problems as soon as possible in effort to make a correct solution can reduce the worse impact in the future. First steps that can be started is learn from the country which has face the same problems in the past and succeed to fix it.GENERAL CONCLUSION
Based on previous descriptions, consistency on implementation the vision is an important thing to drive transformation. Green Economy paradigm is possible to implement, even though in Indonesia which is known as the developing country. Indonesia has many potential things to develop by managing in suitable ways. It not only an optimist words or ambitious will, but it is real facts. Indonesia has 34 divisions which are called as provinces23. Each province has the authority to manage its regional resources to support the local economy under control of central government which are lead by the President. Central of Statistics of Indonesia reports in last six years human resources development (HDI) of Indonesian society are increase24. Human Development Index configuration involves longevity and healthy living, knowledge, and decent living standards25. Indonesia focuses on resources which can be renewable and preserve for long term. Policy to explore marine to support economy26 is a one choice followed unstable extractive industries impacts, such as coal mining, on Indonesian's economy27. In renewable energy, Indonesia is the great bio fuels producer in the world28. It supports to develop potential of oil palm plantation to support national economy in Indonesia.
Indonesia geography consists of islands which are separated by seas and straits. The significant of topography differences between urban and rural areas in Indonesia made government under recent president, Joko Widodo, do priorities to develop and built infrastructure primarily on the rural areas29. If compared with Japan as a stable country, Indonesia still lack on infrastructure and technology to support its economy. Benchmarks to Japan, as a country which are strictly develop technology and infrastructure on its country, will give an added values for Indonesia to develop its country. Waste management is one of models that can be adopted from Japan technology. How is Japan processing its waste and managing it would be a good input for Indonesia to develop next on each province that in Indonesia.
23
http://www.statoids.com/uid.html
24
https://www.bps.go.id/linkTableDinamis/view/id/1211
25
https://www.bps.go.id/Subjek/view/id/26#subjekViewTab1|accordion-daftar-subjek1
26
http://www.thepresidentpost.com/2014/08/04/time-to-focus-on-marine-economy/
27
http://www.greenpeace.org/seasia/id/PageFiles/595527/How%20Coal%20Mining%20Hurts%20the%20Indonesian%20Economy%20-%20English.pdf
https://www.iea.org/countries/non-membercountries/indonesia/
14
REFERENCE:
Tamanini, Jeremy, Valenciano, Julieth. 2016. The Global Green Economy Index: Measuring National Performance in Green Economy. Dual Citizen LLC.
Tsukamoto, Naoya. 2011. A Green Economy in the contex of sustainable development and poverty eradication. Text of Statement Delegation of Japan 2nd Preparatory Committee UN Conference on Sustainable Development.
https://ourworld.unu.edu/en/green-economy-transition-in-indonesia
Cadman, Emily, Harding, Robin, Bernard, Steve. 2016. The Japanese economy at glance. Source: https://ig.ft.com/sites/numbers/economies/japan [June, 10, 2017; 11PM].
Kiker, Patrick. 2016. Germany, Italy and Japan Top World Energy Efficiency Rankings. American Council for Energy Efficiency Economy.
http://aceee.org/sites/default/files/pdf/country/2016/japan.pdf http://aceee.org/sites/default/files/pdf/country/2016/indonesia.pdf http://www.oecd.org/economy/japan-economic-forecast-summary.htm https://www.indonesia-investments.com/culture/economy/item177
http://www.socialsecurityextension.org/gimi/gess/ShowTheme.action?th.themeId=1444 http://fortune.com/2013/09/23/japans-green-energy-evolution/
http://thediplomat.com/2012/09/japan-goes-green/
https://japantoday.com/category/tech/japan-announces-long-term-strategy-for-green-technology-innovations http://www.kanbun.org/2006/060601greenkeizai/060601greenkeizai_report_english.pdf
http://acad.depauw.edu/~mkfinney/teaching/Com227/culturalPortfolios/japan/values.htm https://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/irf/2006/71342.htm
http://health.liputan6.com/read/831503/sampah-di-indonesia-paling-banyak-berasal-dari-rumah-tangga https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2011/dec/29/japan-leads-field-plastic-recycling
https://www.bps.go.id/linkTabelStatis/view/id/1274 http://www.statoids.com/uid.html
https://www.bps.go.id/linkTableDinamis/view/id/1211
https://www.bps.go.id/Subjek/view/id/26#subjekViewTab1|accordion-daftar-subjek1 http://www.thepresidentpost.com/2014/08/04/time-to-focus-on-marine-economy/
http://www.greenpeace.org/seasia/id/PageFiles/595527/How%20Coal%20Mining%20Hurts%20the%20Indone sian%20Economy%20-%20English.pdf
https://www.iea.org/countries/non-membercountries/indonesia/
https://www.indonesia-investments.com/business/risks/infrastructure/item381 https://www.bps.go.id/linkTableDinamis/view/id/1211