Management
Management
Information Systems,
Information Systems,
10/e
10/e
Raymond McLeod and George
Raymond McLeod and George
Chapter 10
Chapter 10
Ethical Implications of Information
Ethical Implications of Information
Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
►
Understand how morals, ethics, & laws differ.
Understand how morals, ethics, & laws differ.
►
Be familiar with computer legislation that has been
Be familiar with computer legislation that has been
passed in the United States & know how legislation in
passed in the United States & know how legislation in
one country can influence computer use in others as
one country can influence computer use in others as
well.
well.
►
Know how a firm creates an ethical culture by first
Know how a firm creates an ethical culture by first
establishing a corporate credo, then establishing
establishing a corporate credo, then establishing
ethics programs, & then lastly establishing a corporate
ethics programs, & then lastly establishing a corporate
ethics code.
ethics code.
►
Know why society demands that computers be used
Know why society demands that computers be used
ethically.
ethically.
Learning Objectives (Cont’d)
Learning Objectives (Cont’d)
►
Know how the firm’s internal auditors can play a
Know how the firm’s internal auditors can play a
positive role in achieving information systems that
positive role in achieving information systems that
are designed to meet ethical performance criteria.
are designed to meet ethical performance criteria.
►
Be aware of computer industry codes of ethics, &
Be aware of computer industry codes of ethics, &
the wide variety of educational programs that can
the wide variety of educational programs that can
help firms & employees use computers ethically.
help firms & employees use computers ethically.
►
Know what the chief information officer (CIO) can
Know what the chief information officer (CIO) can
do to be a power center as the firm follows ethical
do to be a power center as the firm follows ethical
practices.
practices.
►
Be acquainted with the most produced piece of
Be acquainted with the most produced piece of
legislation to be levied on business in recent
legislation to be levied on business in recent
Prescriptive vs. Descriptive
Prescriptive vs. Descriptive
Coverage
Coverage
►
Prescriptive coverage
Prescriptive coverage
is when we
is when we
prescribe how the MIS
prescribe how the MIS
ought to be
ought to be
developed
developed
& used in a business firm.
& used in a business firm.
►
Descriptive coverage
Descriptive coverage
explains how things
explains how things
are being
are being
done.
done.
►
Our mission is to recognize that
Our mission is to recognize that
businesspeople in general & information
businesspeople in general & information
people in particular have definite
people in particular have definite
responsibilities in terms of performing within
Morals, Ethics, & Laws
Morals, Ethics, & Laws
►
Morals
Morals
are traditions of belief about
are traditions of belief about
right & wrong conduct; a social
right & wrong conduct; a social
institution with a history & a list of rules.
institution with a history & a list of rules.
►
Ethics
Ethics
is a collection of guiding beliefs,
is a collection of guiding beliefs,
standards, or ideals that pervades an
standards, or ideals that pervades an
individual or a group or community of
individual or a group or community of
people.
people.
►
Pirated software
Pirated software
– software that is
– software that is
Morals, Ethics, & Laws
Morals, Ethics, & Laws
(Cont’d)
(Cont’d)
►
Laws
Laws
are formal rules of conduct that a
are formal rules of conduct that a
sovereign authority, such as a
sovereign authority, such as a
government, imposes on its subjects or
government, imposes on its subjects or
citizens.
citizens.
►
In 1966, first case of computer crime
In 1966, first case of computer crime
Programmer for a bank altered a program
Programmer for a bank altered a program
not to flag his account for being overdrawn.
not to flag his account for being overdrawn.
Programmer not charged because no laws
Programmer not charged because no laws
existed.
Computer Legislation in
Computer Legislation in
U.S.A.
U.S.A.
►
U.S. computer legislation has focused on rights and restrictions
U.S. computer legislation has focused on rights and restrictions
related to data access, information privacy, computer crime,
related to data access, information privacy, computer crime,
and, most recently, software patents.
and, most recently, software patents.
►
The 1966 Freedom of Information Act
The 1966 Freedom of Information Act
gave U.S. citizens
gave U.S. citizens
and organizations the right to access data held by the federal
and organizations the right to access data held by the federal
government.
government.
►
The 1970 Fair Credit Reporting Act
The 1970 Fair Credit Reporting Act
dealt with the handling
dealt with the handling
of credit data.
of credit data.
►
The 1978 Right to Federal Privacy Act
The 1978 Right to Federal Privacy Act
limited the federal
limited the federal
government’s ability to conduct searches of bank records.
government’s ability to conduct searches of bank records.
►
The 1988 Computer Matching and Privacy Act
The 1988 Computer Matching and Privacy Act
restricted
restricted
the federal government’s right to match computer files for the
the federal government’s right to match computer files for the
purpose of determining eligibility for government programs or
purpose of determining eligibility for government programs or
identifying debtors.
identifying debtors.
►
The 1968 Electronics Communications Privacy Act
The 1968 Electronics Communications Privacy Act
covered only voice communications; rewritten in 1986 to
covered only voice communications; rewritten in 1986 to
Computer Legislation in U.S.A.
Computer Legislation in U.S.A.
(Cont’d)
(Cont’d)
►
In 1984, U.S. Congress passed federal
In 1984, U.S. Congress passed federal
statutes that applied to computer crime.
statutes that applied to computer crime.
►
The Small Business Computer Security
The Small Business Computer Security
& Education Advisory Council
& Education Advisory Council
.
.
Advises Congress of matters relating to
Advises Congress of matters relating to
computer crime against small businesses.
computer crime against small businesses.
Evaluate the effectiveness of federal & state
Evaluate the effectiveness of federal & state
crime laws in deterring & prosecuting computer
crime laws in deterring & prosecuting computer
Computer Legislation in U.S.A.
Computer Legislation in U.S.A.
(Cont’d)
(Cont’d)
►
The Counterfeit Access Device &
The Counterfeit Access Device &
Computer Fraud & Abuse Act made it a
Computer Fraud & Abuse Act made it a
federal felony for someone to gain
federal felony for someone to gain
unauthorized access to information
unauthorized access to information
pertaining to national defense or foreign
pertaining to national defense or foreign
relations.
relations.
Misdemeanor to gain unauthorized access to a
Misdemeanor to gain unauthorized access to a
computer protected by the Right to Financial
computer protected by the Right to Financial
Privacy Act or the Fair Credit Reporting Act &
Privacy Act or the Fair Credit Reporting Act &
to misuse information in a computer owned by
to misuse information in a computer owned by
Software Patents
Software Patents
►
In July 1998, in the
In July 1998, in the
State Street Decision,
State Street Decision,
the
the
US Court of Appeals affirmed that a business
US Court of Appeals affirmed that a business
process could be patented.
process could be patented.
►
In April 2001, the U.S. Congress introduced a
In April 2001, the U.S. Congress introduced a
bill requiring a determination of the significance
bill requiring a determination of the significance
of the patent & whether it is appropriate for use
of the patent & whether it is appropriate for use
with computer technology.
with computer technology.
►
In this fashion, the U.S. federal government has
In this fashion, the U.S. federal government has
gradually established a legal framework for
gradually established a legal framework for
computer use.
computer use.
►
As with ethics, however, the computer laws can
As with ethics, however, the computer laws can
vary considerably from one country to the next.
Ethics Culture Concept
Ethics Culture Concept
►
Ethics culture
Ethics culture
states that if a firm is to be
states that if a firm is to be
ethical, then top-management must be
ethical, then top-management must be
ethical in everything that it does & says, i.e.
ethical in everything that it does & says, i.e.
lead by example.
lead by example.
►
Corporate credo
Corporate credo
is a succinct statement of
is a succinct statement of
values that the firm seeks to uphold.
values that the firm seeks to uphold.
►
Ethics program
Ethics program
is an effort consisting of
is an effort consisting of
multiple activities designed to provide
multiple activities designed to provide
employees with direction in carrying out the
employees with direction in carrying out the
corporate credo.
Figure 10.1 Top-level
Figure 10.1 Top-level
Management Imposes Ethics
Management Imposes Ethics
Figure 10.2 Corporate Credo
Figure 10.2 Corporate Credo
Ethics Culture Concept
Ethics Culture Concept
(Cont’d)
(Cont’d)
►
Ethics audit
Ethics audit
is when an internal
is when an internal
auditor meets with a manager in a
auditor meets with a manager in a
several-hour session for the purpose of
several-hour session for the purpose of
learning how the manager’s unit is
learning how the manager’s unit is
carrying out the corporate credo.
carrying out the corporate credo.
►
Tailored corporate credo
Tailored corporate credo
are usually
are usually
adaptations of codes for a particular
adaptations of codes for a particular
industry or profession that a firm has
industry or profession that a firm has
Computer Ethics
Computer Ethics
►
Computer ethics
Computer ethics
consists of two main activities:
consists of two main activities:
Analysis of the nature & social impact of
Analysis of the nature & social impact of
computer technology; and
computer technology; and
Formulation & justification of policies for the
Formulation & justification of policies for the
ethical use of such technology.
ethical use of such technology.
►The CIO must:
The CIO must:
1.
1.
Be alert to the effects that the computer is
Be alert to the effects that the computer is
having on society; and
having on society; and
2.
2.
Formulate policies to ensure that the technology
Formulate policies to ensure that the technology
is used throughout the firm in the right way.
Reasons for the Importance of
Reasons for the Importance of
Computer Ethics
Computer Ethics
►
James H. Moor believes there are 3 main reasons for
James H. Moor believes there are 3 main reasons for
the high level of interest in computer ethics:
the high level of interest in computer ethics:
Logical Malleability:
Logical Malleability:
The computer performs
The computer performs
exactly as instructed, so if it’s used for an
exactly as instructed, so if it’s used for an
unethical activity the computer is not the culprit.
unethical activity the computer is not the culprit.
The Transformation Factor: C
The Transformation Factor: C
omputers can
omputers can
drastically change the way we do things.
drastically change the way we do things.
The Invisibility Factor
The Invisibility Factor
:
:
I
I
nternal operations
nternal operations
provides the opportunity for invisible
provides the opportunity for invisible
programming values, invisible complex
programming values, invisible complex
calculations, & invisible abuse.
Social Rights & the Computer
Social Rights & the Computer
►
Mason coined the acronym
Mason coined the acronym
PAPA
PAPA
(privacy,
(privacy,
accuracy, property, and accessibility) to
accuracy, property, and accessibility) to
represent society’s four basic rights in terms of
represent society’s four basic rights in terms of
information.
information.
►
Mason felt that “the right to be left alone” is
Mason felt that “the right to be left alone” is
being threatened by two forces:
being threatened by two forces:
1.
1.
the increasing ability of the computer to be used
the increasing ability of the computer to be used
for surveillance.
for surveillance.
2.
2.
the increasing value of information in decision
the increasing value of information in decision
making.
making.
►
For example, decision makers place such a high
For example, decision makers place such a high
value on information that they will often be
value on information that they will often be
willing to invade someone’s privacy to get it.
More Rights …
More Rights …
►
Right to Accuracy:
Right to Accuracy:
the potential for a level
the potential for a level
of accuracy that is unachievable in
of accuracy that is unachievable in
non-computer systems;
computer systems;
some computer-based
some computer-based
systems contain more errors than would be
systems contain more errors than would be
tolerated in manual systems.
tolerated in manual systems.
►
Right to Property
Right to Property
: c
: c
opyright & patent laws
opyright & patent laws
provide some degree of protection.
provide some degree of protection.
►
Right to Access
Right to Access
: much information has
: much information has
been converted to commercial databases,
been converted to commercial databases,
Information Auditing
Information Auditing
►
External auditors from outside the
External auditors from outside the
organization verify the accuracy of
organization verify the accuracy of
accounting records of firms of all sizes.
accounting records of firms of all sizes.
►
Internal auditors perform the same analyses
Internal auditors perform the same analyses
as external auditors but have a broader
as external auditors but have a broader
range of responsibilities.
range of responsibilities.
►
Audit committee defines the responsibilities
Audit committee defines the responsibilities
of the internal auditing department &
of the internal auditing department &
receives many of the audit reports.
receives many of the audit reports.
►
Director of internal auditing manages the
Director of internal auditing manages the
internal auditing department & reports to the
internal auditing department & reports to the
CEO or the CFO.
Figure 10.3 Position of Internal
Figure 10.3 Position of Internal
Types of Auditing Activity
Types of Auditing Activity
►
Internal auditors offer more objectivity since their
Internal auditors offer more objectivity since their
only allegiance is to the board, the CEO, and the CFO
only allegiance is to the board, the CEO, and the CFO
►
Four basic types of internal auditing activity:
Four basic types of internal auditing activity:
A financial audit:A financial audit: verifies the accuracy of the firm’s records verifies the accuracy of the firm’s records
& is the type of activity performed by external auditors.
& is the type of activity performed by external auditors.
An An operational audit:operational audit: aimed to validate the effectiveness of aimed to validate the effectiveness of
procedures including adequacy of controls, efficiency, &
procedures including adequacy of controls, efficiency, &
compliance with company policy. Systems analyst does in
compliance with company policy. Systems analyst does in
SDLC analysis stage.
SDLC analysis stage.
A concurrent audit:A concurrent audit: is the same as an operational audit is the same as an operational audit
except that the concurrent audit is ongoing.
except that the concurrent audit is ongoing.
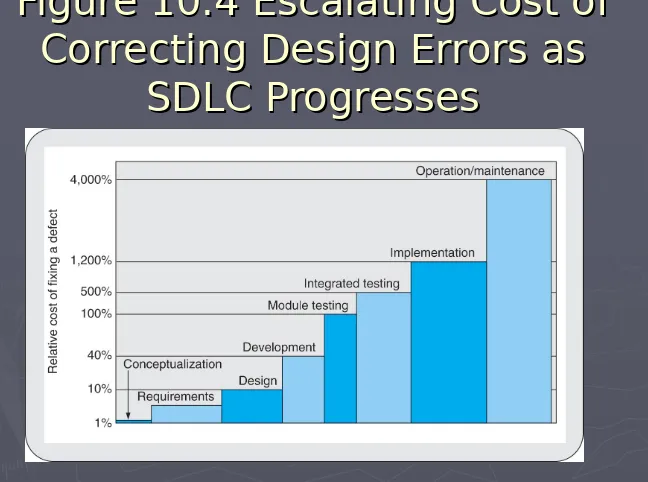
Internal Control Systems Design:Internal Control Systems Design: the cost of correcting a the cost of correcting a
system flaw increases dramatically as the system life cycle
system flaw increases dramatically as the system life cycle
progresses (Figure 10.4).
Figure 10.4 Escalating Cost of
Figure 10.4 Escalating Cost of
Correcting Design Errors as
Correcting Design Errors as
Internal Audit Subsystem
Internal Audit Subsystem
►
In the financial information system, the
In the financial information system, the
internal audit subsystem is one of the
internal audit subsystem is one of the
input subsystems.
input subsystems.
►
Including internal auditors on systems
Including internal auditors on systems
development teams is:
development teams is:
A good step toward having well-controlled
A good step toward having well-controlled
systems, & the systems are:
systems, & the systems are:
A good step toward giving management
A good step toward giving management
the information it needs to achieve &
the information it needs to achieve &
maintain ethical business operations.
Achieving Ethics in Information
Achieving Ethics in Information
Technology
Technology
►
Ethic codes & ethics educational
Ethic codes & ethics educational
programs can provide the foundation
programs can provide the foundation
for the culture.
for the culture.
►
Educational programs can assist in
Educational programs can assist in
developing a corporate credo & in
developing a corporate credo & in
putting ethics programs in place.
putting ethics programs in place.
►
Ethic codes can be used as is or can
Ethic codes can be used as is or can
Codes of Ethics
Codes of Ethics
►
ACM Code of Ethics & Professional
ACM Code of Ethics & Professional
Conduct.
Conduct.
Adopted in 1992.
Adopted in 1992.
Consists of 24 “imperatives” i.e. statements
Consists of 24 “imperatives” i.e. statements
of personal responsibility.
of personal responsibility.
►
Code is subdivided into four parts.
Code is subdivided into four parts.
General moral imperatives.
General moral imperatives.
More specific professional responsibilities.
More specific professional responsibilities.
Organizational leadership imperatives.
Organizational leadership imperatives.
Figure 10.5 ACM Code of Ethics
Figure 10.5 ACM Code of Ethics
Table 10.1 ACM Code of Ethics &
Table 10.1 ACM Code of Ethics &
Table 10.2 ACM Software
Table 10.2 ACM Software
Engineering Code of Ethics …
Engineering Code of Ethics …
ACM Software Engineering Code
ACM Software Engineering Code
of Ethics & Professional Practice
of Ethics & Professional Practice
►
This code consists of expectations in eight
This code consists of expectations in eight
major areas:
major areas:
Public.
Public.
Client & employer.
Client & employer.
Product.
Product.
Judgment.
Judgment.
Management.
Management.
Profession.
Profession.
Computer Ethics Education
Computer Ethics Education
►
College courses
College courses
– ACM developed a model
– ACM developed a model
computing curriculum of courses that should
computing curriculum of courses that should
be offered.
be offered.
►
Professional programs
Professional programs
– AMA, Amer. Mgt.
– AMA, Amer. Mgt.
Assoc., offers special programs addressing
Assoc., offers special programs addressing
ethics & integrity.
ethics & integrity.
►
Private educational programs
Private educational programs
– LRN, the
– LRN, the
Legal Knowledge Co., offers Web-based
Legal Knowledge Co., offers Web-based
course modules that address a wide range of
Ethics & the CIO
Ethics & the CIO
►
As of August 11, 2002, CEOs and CFOs are
As of August 11, 2002, CEOs and CFOs are
required to sign off on the accuracy of their
required to sign off on the accuracy of their
financial statements.
financial statements.
►
This requirement puts responsibility on the
This requirement puts responsibility on the
executives but also on the corporate information
executives but also on the corporate information
services unit and the information services units of
services unit and the information services units of
the business areas to provide the executives with
the business areas to provide the executives with
information that is accurate, complete, and timely.
information that is accurate, complete, and timely.
►
IS only one unit in the organizational structure but
IS only one unit in the organizational structure but
it is in a key position to have the most influence on
it is in a key position to have the most influence on
satisfying the demands of both government and
satisfying the demands of both government and
Ethics & the CIO (Cont’d)
Ethics & the CIO (Cont’d)
The CIO can bring financial reporting up to expectations
The CIO can bring financial reporting up to expectations
by following a program that includes the following:
by following a program that includes the following:
Achieving a higher level of understanding of Achieving a higher level of understanding of
accounting principles. accounting principles.
Reviewing the information systems that accomplish Reviewing the information systems that accomplish
financial reporting and taking remedial action. financial reporting and taking remedial action.
Educating the firm's executives on financial systems.Educating the firm's executives on financial systems. Integrating alarms into information systems that alert Integrating alarms into information systems that alert
executives to activities that require attention. executives to activities that require attention.
Actively participating in the release of financial Actively participating in the release of financial
information to environmental elements. information to environmental elements.
Keeping tight control on money spent for information Keeping tight control on money spent for information
Life under Sarbanes-Oxley
Life under Sarbanes-Oxley
►
The objective of Sarbanes-Oxley, known as SOX, is
The objective of Sarbanes-Oxley, known as SOX, is
to protect investors by making the firm’s
to protect investors by making the firm’s
executives personally accountable for the financial
executives personally accountable for the financial
information that is provided to the firm’s
information that is provided to the firm’s
environment, primarily stockholders & the financial
environment, primarily stockholders & the financial
community.
community.
►
SOX consists of 10 major provisions, 2 directly
SOX consists of 10 major provisions, 2 directly
affect the firm’s information services unit.
affect the firm’s information services unit.
CEOs & CFOs must certify the financial reports.
CEOs & CFOs must certify the financial reports.
SOX Provisions Affecting
SOX Provisions Affecting
Information Services, Resources,
Information Services, Resources,
& IT
& IT
►
SOX 404 – CIO must ensure that SOX imposed
SOX 404 – CIO must ensure that SOX imposed
control requirements are built into systems during
control requirements are built into systems during
systems development & activities should include:
systems development & activities should include:
Identifying systems that play a role in financial
Identifying systems that play a role in financial
reporting.
reporting.
Identifying the risks faced by these systems.
Identifying the risks faced by these systems.
Developing controls that address the risks.
Developing controls that address the risks.
Documenting & testing the controls.
Documenting & testing the controls.
SOX Provisions … (Cont’d)
SOX Provisions … (Cont’d)
►
SOX 409 – firm must be able to report changes in its
SOX 409 – firm must be able to report changes in its
financial condition in
financial condition in
real time
real time
– as the changes
– as the changes
occur.
occur.
Should feature online inputs.
Should feature online inputs.
Output subsystems should be capable of immediately
Output subsystems should be capable of immediately
reporting changes in the firm’s financial condition.
reporting changes in the firm’s financial condition.
►
SOX & COBIT
SOX & COBIT
COBIT is an industry organization that provides security
COBIT is an industry organization that provides security
standards for the firm’s information resources.
standards for the firm’s information resources.
COBIT can assist the firm in addressing its SOX
COBIT can assist the firm in addressing its SOX
responsibilities because COBIT standards align very well
responsibilities because COBIT standards align very well
with the SOX expectations.
with the SOX expectations.
COBIT has 47,000 members worldwide, its financial
COBIT has 47,000 members worldwide, its financial