In order to determine whether there is a significant relationship between consumption and eating attitude, it was investigated as a result of binary correlation analysis and linear regression analysis. As a result of these regression and correlation analyzes examined, it was determined that there was a positive relationship between body image and eating attitude, a positive relationship between body image and Instagram use, and a weak positive relationship between eating attitude and Instagram use. People can produce content and interact with other users in social media (Carr & Hayes, 2015).
Social media platforms: Used by most adults in many parts of the world, especially Instagram, Facebook and Twitter (Tiggemann & Holland, 2016). Looking at social media usage data for 2021, Facebook is the number one platform with 2.74 billion users worldwide, while Instagram is in 5th place with 1.221 billion users (Kempt, 2020).
Instagram as a Social Media
Users can interact by sharing the content they produce with other people, and they can also create mutual appreciation and subsequent circulation (Ellison & Boyd, 2013).
Body
Real body
It contains objectively measurable data such as the person's height, weight and body mass index (Terzi, 2021).
Ideal body
Presented (revealed) body
Much of today's body image research focuses on the relationship between the real body and the ideal body. Especially in today's situation, the use of social networks and sharing of body image causes the ideal body to move away from the real body. Therefore, researchers began to question the possible effects of social media (Fardouly & Vartanian, 2016).
At the same time, the gap between one's real body and one's ideal body can bring some problems. The effort to achieve the ideal body can sometimes develop to extremes and lead to mental and physical illnesses (Özgenel, Canpolat & Ekşi, 2019).
Eating Attitude
Eating Attitudes
A person who exhibits emotional eating behavior prefers to deal with the emotions they feel when dealing with the situations and events they experience. External eating is defined as the tendency to eat independently of the feeling of hunger / satiety, as it is influenced by external stimuli related to food, such as taste, smell and. It is assumed that the difference between a person's hunger and satiety is wrongly evaluated when eating outside.
The media is considered one of the causes or triggers of eating disorders (Önal Sönmez, 2017). In the DSM-V (APB, 2013), the name of the diagnostic group related to IC was changed to "Feeding and eating disorders" and its range was expanded.
Hypothesis
Eating disorders have been evaluated in different categories such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge eating disorder, pica, rumination, avoidance-restricted food intake disorder, other defined feeding and eating disorders, and undefined feeding and eating disorders (APB, 2013).
Purpose and Contribution
This segment presents the approaches used, personnel involved, questionnaires used in data collection, along with strategies for data collection and verification. The purpose of this research is to determine the potential relationship between body perception and eating habits among women aged 18-30 who actively use Instagram. The relational screening model was used for this study, as it is an effective tool in determining the extent and direction of associations between research variables.
Participants
Procedure
Data Collection Tools Used in
- Personal Information
- Eating Attitude Test-26
- Ben-Tovim Walker Body Attitude
- Instagram Addiction Scale
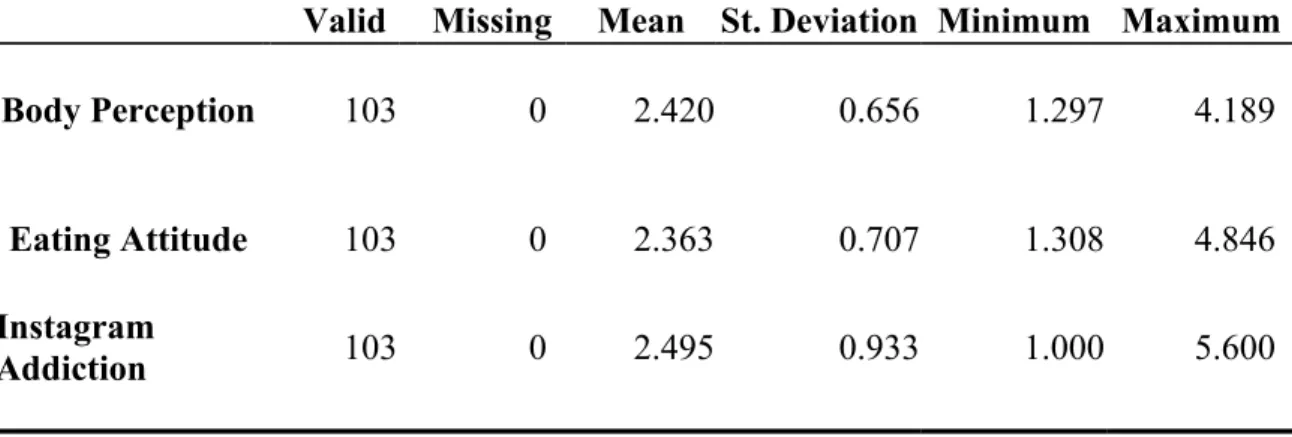
When examining the model's item distributions, which were subjected to four factors using Direct Oblimin as an oblique rotation method, it was observed that the 9., 13., and 41. In this part of the research there are analyzes and evaluations of the data entered on social platforms on the relationship between Instagram use and eating attitude and body perception. Regarding Eating Attitude, there are also 103 valid values in the table with an average value of 2.363 and a standard deviation of 0.707; along with a minimum score of 1,308 and a maximum score of 4,846 indicating moderate eating attitudes among participants.
According to this data, it can be said that the participants generally have a moderate level of Instagram addiction. Furthermore, the study found a moderate positive correlation between body image and Instagram addiction (r=0.266; p<0.01), implying that negative body perception may be linked to increased use of Instagram. In addition, there was a positive relationship between eating attitudes and Instagram addiction (r=0.257; p<0.01), suggesting that negative eating attitudes may lead to increased use of this social media platform.
Statistical data show an R value of 0.605, R² value of 0.366 and a corrected R² value of 0.353, pointing towards the limited explanatory power of the model for eating attitudes. Furthermore, an RMSE (Root Mean Square Error) value is calculated as 0.569, which represents that the model's estimates of eating attitudes have an average error of 0.569 units. Model H yielded an intercept coefficient of 2.363, with a p-value less than <.001, implying a constant significant coefficient ₀.
Statistical analysis reveals that the coefficient of the Instagram Addiction variable is calculated as 0.080, with a standard error value of 0.063, a standardized coefficient value of 0.106, a t-value of 1.284 and a p-value of 0.202. Findings show that Instagram addiction had no statistically significant impact on eating attitudes. This suggests that body perception significantly influences eating attitudes; as the perception of the body increases, so does the attitude towards eating.
DISCUSSION
First, the study's first hypothesis suggested that there was a significant and positive relationship between Instagram use and body image for women aged 18 to 30. In this case, it can be said that there is a positive relationship between the Instagram usage level of women between the ages of 18 and 30 and their body image. This finding supports the positive relationship between Instagram use and body image in our current study.
On the other hand, it has been thought in different studies that the Instagram platform, which is focused on in this study, can have strong effects on women's body image because it is a more image-based platform and its users focus only on images ( Fardouly et al., 2015). Several studies on the Facebook platform found that there is a negative relationship between the amount of time young women spend on Facebook and their body image (Eckler et al., 2017; Fardouly & Vartanian 2015; Mabe et al. 2014). On the other hand, one study claimed that exposure to Facebook in an experimental setting had an effect on women's body dissatisfaction and desire to change their physical characteristics (Fardouly et al., . 2015).
Second, the study's second hypothesis suggested that there would be a significant and positive relationship between body image and eating attitudes in women aged 18-30. In many studies on the subject; A positive relationship has been found between body image concerns, body comparison tendencies and acceptance of thinness norms (Jones, . 2001; Myers, 2012; van den Berg, 2002). In addition, another study found that eating disorders were more common in individuals with body image disorders (Shroff & Thompson, 2006).
A meta-analysis study found that body image had an effect on eating attitudes and that individuals with a negative body image had more problems with dieting, feelings of hunger, weight control, and eating regulation (Stice, 2002). . In summary, looking at our current research findings and other research findings on this topic, it is seen that there is a positive relationship between body image and attitude towards eating. Research by Holland and Tiggemann (2016) reveals that anxiety eating and body image are associated with increased emotional engagement and a tendency to seek negative feedback, as an illustration.
RESULTS
It has been suggested that young women are at risk of experiencing negative thoughts about their own bodies and symptoms of eating disorders due to exposure to idealized body images and perfectionistic norms on social media platforms (Fardouly et al., 2015; Holland &. Tiggemann, 2016). However, the effects of social media platforms are complex, leading to diversity in studies conducted across different platforms and uses. Eating attitude disorders are observed in women who are negatively affected by body image on Instagram.
This suggests that Instagram use is associated with negative body image and comparative trends with eating attitude issues. Ethnicity and Cultural Factors: It is essential to examine the impact of cultural inequalities and ethnic background on the correlation between social media. Therefore, it is imperative for future investigations to prioritize comprehensive studies that consider diverse factors and employ different techniques to gain a better understanding of the correlation between social media use, body image, and eating outlook.
The current study specifically examined a single social media platform, limiting its potential for generalization. More extensive research is needed to assess the impact of various social media platforms (Qutteina ve diğerleri Ethnic and cultural differences: the current studies used only samples of white people and examined the effects of other ethnic groups on social media use, body image, and eating attitudes have been neglected. Therefore, studies are needed that focus on sample groups belonging to different ethnicities and cultures (Meier & Gray Sampling Focus: the current study used data exclusively from individuals of white ethnicity, and did not take into account with the influence of other ethnic groups on social media use, body image and eating habits.
Body image concerns among Australian adolescent girls: The role of body comparisons with models and peers. Negative comparisons about one's appearance mediate the relationship between Facebook use and body image concerns. Social comparisons on social media: The impact of Facebook on young women's body image concerns and mood.
The role of the media in body image concerns among women: A meta-analysis of experimental and correlational studies. Investigating the relationship between social media use, body image and eating attitude among university students (Master's thesis, Istanbul Gelisim University Graduate Education Institute).
