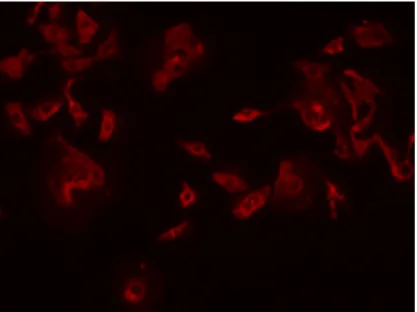
CM-DiI and MCF-7 breast cancer cell response to chemotherapeutic agents CM-DiI is a lipophilic, red fluorescent dye used for staining and tracking the migration of cells. CM-DiI allows cells to be visualized in histological areas and can therefore be very useful for tracking cancer cell proliferation and metastases in vivo. If CM-DiI-labeled cancer cells respond to chemotherapy agents similarly to unlabeled cancer cells, it facilitates screening of potential anti-cancer agents.
We hypothesized that CM-DiI would not affect cell viability and sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drug treatment. These results provided evidence to support future targets into which CM-DiI-stained breast cancer cells will be injected. Fluorescent human adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells labeled with CM-DiI under 10x magnification under a green excitation fluorescence filter at 570 nm………….4 Figure 3.
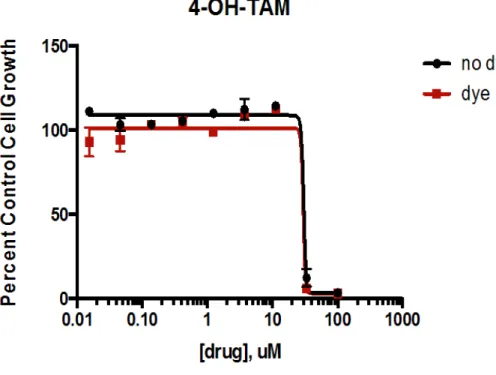
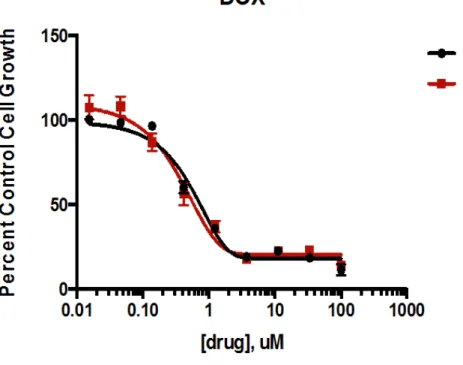
Doxorubicin concentration comparison for CM-DiI-labeled (dye) and unlabeled (no dye) MCF-7 adenocarcinoma cells……….16 Figure 7. 4-hydroxytamoxifen concentration comparison for CM-DiI-labeled (dye) and unlabeled (no dye) MCF - 7 adenocarcinoma cells……….17.
INTRODUCTION
- Breast Cancer
- Aims
- MCF-7 human adenocarcinoma cells
- CM-DiI
- Doxorubicin in cancer therapy
- Paclitaxel in cancer therapy
- MTS viability assay
- Hypothesis
An overall goal of the Willett lab is to use a combination of in vitro and in vivo breast cancer models to identify new, more effective breast cancer therapies. The aim of this study was therefore to determine whether the red fluorescent dye CM-DiI would affect the response of MCF-7 breast cancer cells to three common chemotherapeutic agents. Ultimately, the CM-DiI-labeled cancer cells are microinjected into the yolk sac of young zebrafish, potential cancer treatments are used and.
The MCF-7 cell line is a non-invasive breast cancer that has retained several features characteristic of the mammary epithelium, including the expression of estrogen receptor alpha (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR), meaning that these cells have receptors for both hormones , which could promote cancer growth (mcf7.com 2017). CM-DiI works by inserting itself into the cell's plasma membrane and then being retained in the daughter cells for generations. CM-DiI has also been reported to have increased water solubility, allowing the detection of labeled cells in histological regions (Andrade et al. 1996).
To date, there are no known effects of CM-DiI on cell viability or proliferation, but there are very few studies testing the effects of this dye on cell lines in combination with chemotherapy. If the cell viability and proliferation of CM-DiI-labeled breast cancer cells are not significantly different from those of unlabeled breast cancer cells after both CM-DiI-labeled and unlabeled cells are treated with chemotherapy, it should be possible to use CM-DiI-labeled examine cells. breast cancer cells in zebrafish using microscopy. It would then be possible to conduct further studies to treat these CM-DiI-labeled zebrafish breast cancers with new chemotherapeutic compounds and to investigate the effects of these chemotherapeutic agents by microscopy.
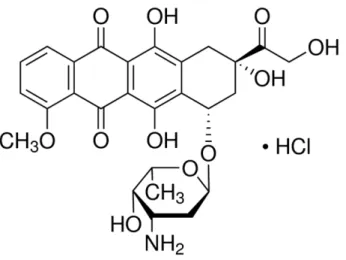
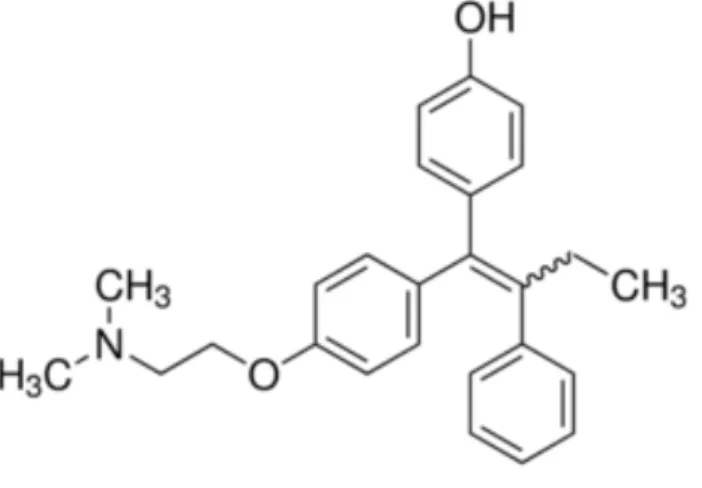
The xenotransplantation of CM-DiI-labeled MCF-7 cells in zebrafish was performed through microinjection of the CM-DiI-labeled cells into the yolk sacs of 2 dpf (2 days after fertilization) zebrafish and then keeping the fish at 35 degrees Celsius to promote cell proliferation (Roel, 2016). Doxorubicin (DOX) is a chemotherapeutic agent belonging to the drug class of anthracyclines, which is derived from bacteria of the genus Streptomyces (Patel et al. 2012). 4-Hydroxytamoxifen is one of the active metabolites of the prodrug tamoxifen and is not usually given to breast cancer patients as therapy unless they suffer from liver disease, other impaired liver function (where the drug is metabolized), or if a patient is a poor metabolizer. (PM) by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2D6 (Maximov et.
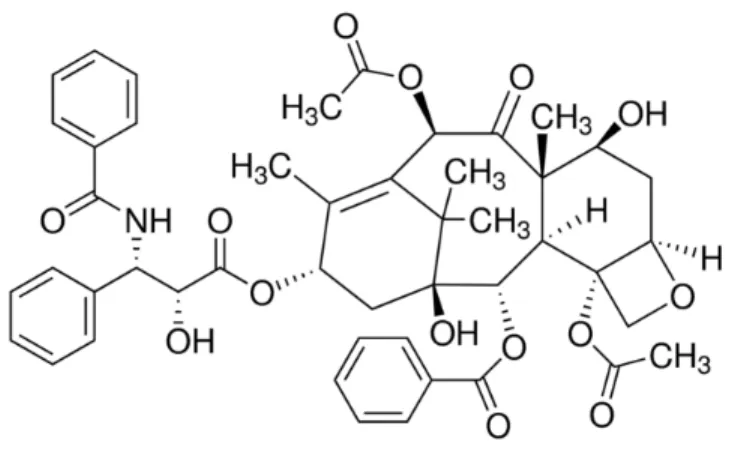
Paclitaxel is a commonly used chemotherapy agent for breast cancer, and patients experience many common side effects such as nausea, mouth sores, and hair loss. These drugs are taken to reduce the severity of hypersensitivity reactions to paclitaxel (Micromedex 2018; Quock et al. 2002). The assay involves the reduction of a tetrazolium compound to MTS [(3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-.
The hypothesis for this experiment was that the IC50 concentrations of reduced cell viability would not differ significantly between CM-DiI labeled and unlabeled MCF-7 cells after treatment with established chemotherapy drugs (doxorubicin, 4-hydroxytamoxifen and paclitaxel ). In other words, CM-DiI dye would have no effect on IC50 concentrations for doxorubicin, 4-hydroxytamoxifen, or paclitaxel.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- Cell culture
- Cell labeling and plating
- Drug treatment
- MTS assay
- Statistical analysis
CM-DiI stock solution was made by adding 25 µL of DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) to 50 µg of CM-DiI. Although only 3.4 x 105 cells per plate were needed for testing, more cells were needed to pass through the labeling protocol due to cell death during the labeling process. Cells in CM-DiI/PBS working solution were then placed in an incubator at 37 degrees Celsius for five minutes and then in a refrigerator at 4 degrees Celsius for 15 minutes.
After labeling, the cells were washed with PBS and resuspended in one milliliter of their appropriate media (DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin antibiotic (P/S)). Cells not labeled with CM-DiI were also plated in the same way, and both cell plates were then placed in an incubator at 37 degrees Celsius to allow the cells to attach overnight. If the plates were read too early, the cells did not have time to take up the PMS (electron carrier), and if the plates were read too late, the plates appeared dark brown and were too difficult to read.
Each drug experiment had triplicate internal biological replicates and, using GraphPad Prism Version 5.0, non-linear regression analysis was used to determine the IC50s for each compound. This was done using non-linear curve-fitting regression analysis and using the variable-slope dose-inhibition (log[inhibitor] versus response) equation.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
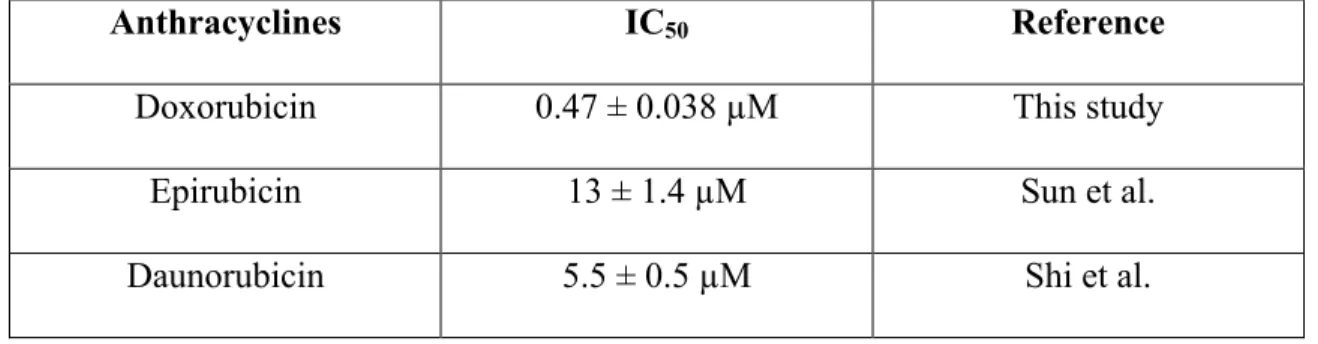
At the end of several experiments, we evaluated the cells in the wells of the plates using Three different classes of chemotherapy drugs were used in this study to test whether the use of a lipophilic dye, CM-DiI, would have any effect on the IC50 of the drugs when used to treat a breast cancer cell line, MCF -7, labeled with CM. - DiI. Epirubicin changes the orientation of a hydroxyl group on the sugar, and because of this change is less cardiotoxic than doxorubicin (Anthracyclines 2017).
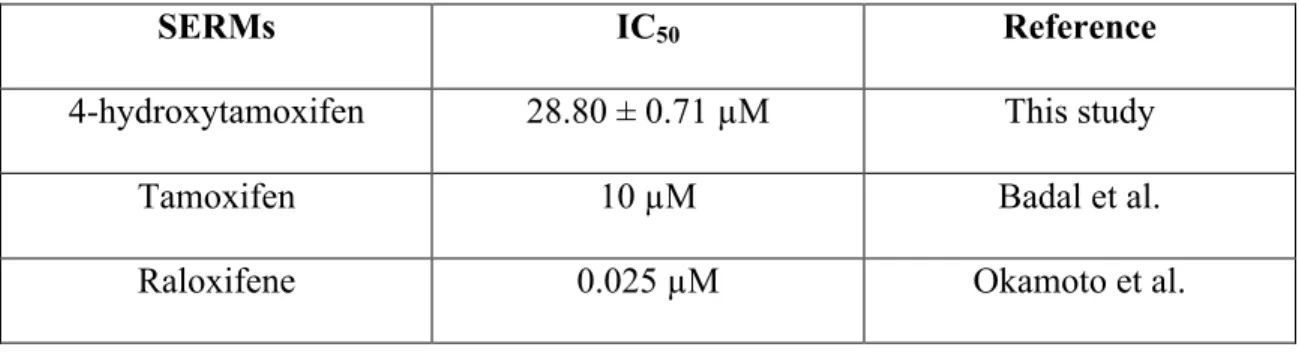
Therefore, DOX appears to be more cytotoxic in MCF-7 cells than daunorubicin or epirubicin. TAM is converted to 4-OHT by enzymes found in the liver, so in patients with liver problems who cannot or have a reduced ability to convert TAM to 4-OHT, administration of 4-OHT is often preferred (Whitfield et al. 2015 ). Therefore, it is effective in preventing osteoporosis and in preventing breast cancer without the side effect of developing uterine adenocarcinoma, which is a side effect of tamoxifen (Tu et al. 2012).
Studies disagree on whether raloxifene or tamoxifen is more effective in treating breast cancer. Tamoxifen is the most commonly prescribed therapy for the treatment of breast cancer and would be used in this study. Doxorubicin (DOX), 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) and paclitaxel (TAX) are not always used in the treatment of breast cancer.
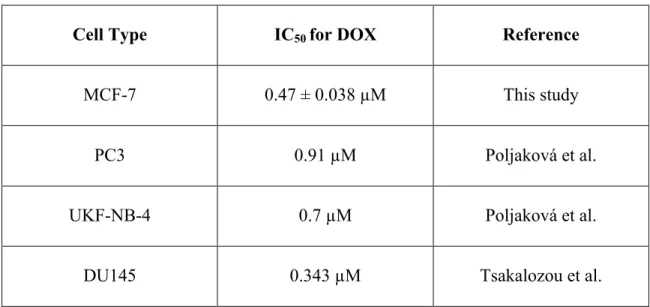
For example, DOX can be used in the treatment of prostate and neurofibroblastomas as well. Although these cell lines were not examined in this study, it is important to compare the efficacy of drugs in breast cancer with other types and lines of cancer. The IC50 value of DOX for the prostate cancer cell line DU145, however, is 0.343 μM suggesting that DOX is more effective in treating that specific type of prostate cancer (Tsakalozou et al. 2012).
T47D is a breast cancer cell line that is also estrogen receptor positive (ER+), but T47D cells are a ductal carcinoma cell line, while MCF-7 cells are an adenocarcinoma cell line (Mooney et al. 2002). However, according to the study conducted by researchers at the University of Gdańsk, the IC50 of 4-OHT when treating MCF-7 cells was 3.2 µM (Pawlik et al. 2015). The decision to use MCF-7 cells stemmed from the fact that MCF-7 cells are the most commonly used breast cancer cells in research.
In order to eventually establish a model system in the transparent zebrafish, it was important to test the most commonly used breast cancer cells. In conclusion, CM-DiI labeling did not significantly affect the viability of MCF-7 breast cancer cells treated with DOX or 4-OHT.
Available at: http://www.breastcancer.org/symptoms/understand_bc/statistics Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/statistics/state.htm Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. Sensitization of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell lines to 4-hydroxytamoxifen by isothiocyanates present in cruciferous plants.
Marine guanidine alkaloids crambescidines inhibit tumor growth and activate intrinsic apoptotic signaling that induces tumor regression in a colorectal carcinoma zebrafish xenograft model. Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake by MCF-7 breast tumor cells in vitro is modulated by treatment with tamoxifen, doxorubicin, and docetaxel: relationship to. PUMA gene transfection can increase the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
The enhanced antiproliferative response to combined treatment of trichostatin A with raloxifene in MCF-7 breast cancer cells and its relevance to estrogen receptor β expression.