However, sugar production is becoming an essential commodity for the world's population given its recognition and demand in the world market, regardless of the impact on the health of the world's population. Therefore, adding lime water to the sugar cane juice before heating could melt a large amount of lime. Both require a somewhat chemical substance; nevertheless, the research focuses on the chemical material used in the milling process.
It can also reduce the environmental burden by 95.4% and 95.8% for FWEP and MEP, and the eutrophication potential contribution attributed to the impacts associated with Mg (OH) 2, Triethylamine and ethanol (Gezae et al., 2016). Some of the wastewater with a large amount of sludge requires special techniques to implement the treatment process - the extensive constituents of wastewater require proper handling, treatment and disposal.
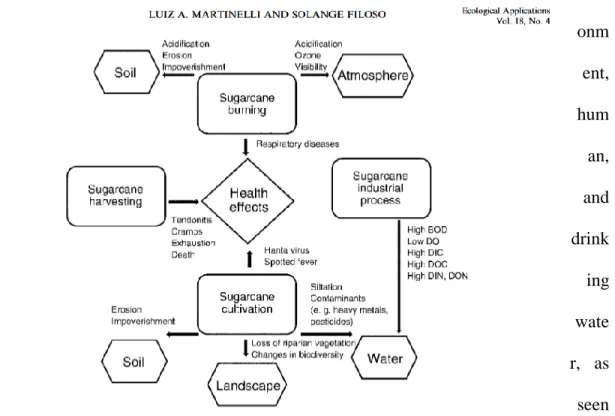
Wastewater Treatment of Sugarcane Factories
Sugarcane wastewater treatment is essential for the protection of environmental components, especially water quality. Furthermore, there are several approaches to reduce the concentration of wastewater; the concentration of sugarcane wastewater can be investigated through physicochemical and biological test. These processes have been studied with a particular focus on effluent decolorization and have been engaged and compliant with environmental regulations (Ghandour et al., 2017).
Before releasing sewage into the river, the effluent should be monitored through the bio-indicator process by rearing fish or other aquatic components in ponds. Sewage in ponds will be excellent if the concentrations are lower than the effluent standard before finally being discharged into the river (Qureshi et al., 2015).
Physiochemical characterization of the effluents wastewater on water .1 The physical influence
- Total Suspended solids (TSS)
- Turbidity
- Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
- Odors of the water
- Water Color
- The chemical influence
- Biological Oxygen demand (BOD)
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
- Total Alkalinity, pH and Hardness
- Ammonia NH3-N
- Calcium
- Phosphate (PO 4 )
- Chloride
- Nitrate (NO 3 )
- Nitrite (NO 2 )
- Sodium (Na)
It is also necessary to understand the values of the TSS to maintain and manage the characters of the effluent (Verma et al., 2013). The weight of the filter is the value of the TSS; the amount of the TSS is the difference between total dissolved solids and total solids. The calculation of the Turbidity is Turbidity A is NTU Turbidity in the diluted sample, fp is a dilution factor (Clesceri et al., 1998).
The TDS concentrations in drinking water can cause certain diseases such as cancer, coronary heart disease, arteriosclerotic heart disease, cardiovascular diseases, inflammation of the gallbladder and gallstones. A study conducted in Egypt on the TDS evaluation of the Nile River quality; the TDS was 183.5 mg/l, less than the permissible level determined by the Egyptian law mg/l). The water quality was acceptable in this area due to the proximity to the river.
This was possible due to the suspended minerals and dead organic matter (Mohsin & Sahib, 2013). This phenomenon happens due to the low quality water at El Nasria, mainly during June, July and August with a lot of organic pollution at the location during these months (Ali et al., 2014). It also measures the oxygen equivalent of the organic matter in a water sample that is susceptible to oxidation by a strong chemical oxidant, such as dichromate.
Where A is an absent sample and S is the slope of the calibration curve (ppm NH4/absorbance unit) (Lenore, 1998). The study carried out in Egypt on the assessment of the physicochemical properties of water and sediment in the Rosetta Branch recognized the sources of the pollutants of the industrial activities. Nitrate is one of the common parameters that affects water quality and causes several diseases such as Blue Baby Syndrome.
The results of a study in Bahawalpur city on the assessment of drinking water quality and its impact on the health of residents range between 4.5-6.4 mg/l in the Islamic colony, 3.4-3.5 mg/l in the satellite city and 3.2-3 .6 mg/l in Shahdrah. Sodium is one of the most accessible elements on the surface of the Earth and is a necessary component of living organisms.
Water quality index (WQI)
The water quality index is a mathematical tool used to transform large amounts of water quality data into a single number. In a drinking water quality assessment, decision making based on water quality data is considered to be a crucial issue. A combined result of nine chemical and physical tests (pH, nitrate, phosphate, DO, BOD, Turbidity, Faecal Coliform, TSS and Temperature) indicate the overall quality of a given body of water; the higher the score, the better the water quality (Dhany et al., 2018).
WQI methods combine many environmental parameters and efficiently convert them into a single value that can reflect the state of water quality. A study on the assessment of drinking water quality in terms of turbidity in the city of Rabak, White Nile State, Sudan, showed that the level of turbidity. Numerous researchers have developed numerous guidelines for irrigation water quality under various conditions.
The combined score of nine chemical and physical tests (pH, nitrate, phosphate, DO, BOD, turbidity, faecal coliform, TSS and temperature) indicates the overall quality of a particular body of water; the higher the score, the better the water quality (Dhany et al., 2018). Water quality index is defined as an assessment technique that gives the composite influence of individual water quality parameters on the overall quality of the water. It reduces a large amount of water quality data into a single numerical value (Vasanthavigar et al., 2010).
The final output of the study will categorize the water quality classes as seen in table 2.1. Another study was conducted in Iraq on water quality index of Al-Gharraf River, southern Iraq. The study evaluated the water quality of the Al-Gharraf River, the main branch of the Tigris River in southern Iraq.
The consequences of wastewater on human health
Human Health
A study conducted in Japan on Phosphate, a poison to humans and is the main chemical ingredient used in the purification of sugar syrup. Also, an increasing number of kidney diseases or injuries in society highlights the potential importance of this issue. Phosphate has negative effects on human health and natural ecosystems in both the short and long term.
A study was conducted in Iraq on the environmental and health risks associated with the reuse of wastewater, confirmed that wastewater poses risks to human health due to the existence of pathogens and toxic chemical compounds in wastewater. The following is some explanation of the potential risks of wastewater used in irrigation which poses several potential hazards to human health through consumption or exposure to pathogenic microorganisms, viruses, heavy metals and harmful organic chemicals. The result through laboratory analysis was used in the assessment of different parameters to classify wastewater pollution.
It is also used to evaluate OPI and to classify organic pollution due to organic compounds in treated wastewater. There is another study that claims that wastewater with pathogenic microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria and parasites can cause diseases and affect human health. They are often linked to several infectious and digestive diseases in developing countries and research on the public health effects of wastewater in the Middle East.
Most studies confirm that the wastewater has an adverse effect on human health and other types of environmental components. A study conducted in China related to the impact of urban sewage confirms that pathogenic microbes characterize the urban sewage; the majority of them belong to the bacterial kingdom, which pose a direct threat to human health in various diseases such as dermatitis, skin infections, diarrhea and respiratory infections (Wang et al., 2017). Many tools have been used to recognize the adverse effects of contaminated water on human health; nevertheless, this study limited itself to health risk assessment because it is one of the most critical tools to evaluate the risk to human health.
Health risk assessment
Human AdVs and another type of virus have been detected in sewage around the world (Libera & Rosa, 2017). Most of the environmental material comes from the polluted surface water, especially the water that has been used directly. The main reason for that is the absence of the regulations and policies that have the power to organize the water use and protect against the consequences.
The waste surface should be used according to regulations to avoid impact on human health.
The regulation of surface water in Sudan
This database will involve the strengthening of existing water resource units through training and motivation of personnel, ensuring the availability of necessary equipment and tools, and rehabilitation of hydro-met stations. To ensure continuity of services, water users (for irrigation, industry, domestic supply) should pay for the actual costs of the service, including operation, maintenance and replacement costs. Economical use of water and use of appropriate technology will increase the ability to pay.
Optimal and fair use of surface water should be promoted through cooperation between the national water users. The government has a regulatory function to ensure that water suppliers and users meet the relevant standards for service quality, sustainability and environmental friendliness. In the policies of the Nile Basin countries, there is no specific clause related to water pollutants mentioned in the agreement.
The Nile Basin Initiative (NBI) aims to strengthen cooperation on the use of the "common Nile Basin water resources." Under the auspices of the NBI, the riparian states began working on what they believed to be a permanent legal and institutional framework for governance of the Nile River Basin.
The spatial analysis
Spatial analysis interpolation
Interpolation can predict values for cells in a raster from a limited number of sample data points, unknown values for data on any geographic point (elevation, precipitation, chemical concentrations, and noise levels). For example, if you want to make a precipitation (precipitation) map for any country, you will not find enough weather stations evenly spaced to cover the entire region. Therefore, spatial interpolation can estimate temperatures at locations using the recorded temperature at nearby weather stations.
Functions of the spatial analysis
Definition of GIS