It means, when translating a text, to consider the writer's intention in the source text, to find the most equivalent words that can well express that message in the target text. Based on the above definition, translation is the process of transferring meaning in one source language to the target language. The translation of multi-word verbs, which is a phrasal verb expression that does not follow the normal pattern of the language or does not have a complete meaning.
What is the most common strategy for translating transitive phrasal verbs in Indonesian in PS. The scope of the research is on the translation of transitive phrasal verbs found in Roman PS. But the narrower translation is the transfer of the message of a text from one source language (SL) through equivalent text material in another target.
This was found to be the case because a frivolous translation process will lead to a misunderstanding of the message in the source language (SL) into the target language (TL). This means that the translator must translate the text in such a way as to transfer the meaning of the source text to the target text. Although the form of the source text changes, the meaning of the text remains the same.
And in a good translation, the meaning or message is central, because the most important thing is that the result of the translation has the same meaning and purpose as the source.
Translation Strategy
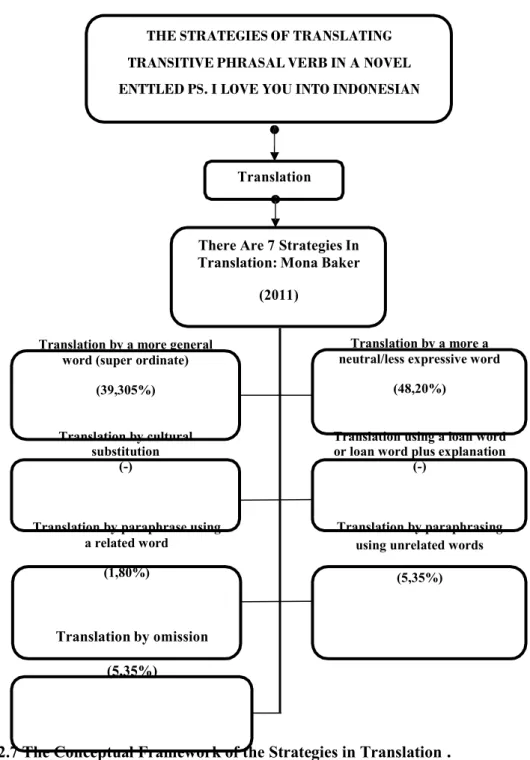
- Translation by a more general word (super ordinate)
- Translation by a more a neutral/less expressive word
- Translation by cultural substitution
- Translation using a loan word or loan word plus explanation Using loan word is particularly common in dealing with culture-
- Translation by paraphrase using a related word
- Translation by paraphrasing using unrelated words
- Translation by omission
Translation is the process of representing, replacing, rewriting or transferring the meaning (message) in the source text to the most equivalent, comparable meaning (message) in the target language. She has identified seven strategies that can be applied when translating the source text into the target text, such as translation with a more general word, translation with more neutral/less. The use of a general word (superordinate) to overcome a relative lack of specificity in the target language relative to the source language.
This strategy is one of the most common strategies for dealing with many types of non-equivalence, especially in the domain of propositional understanding. Using a word that may be close to the meaning of the source word even though the meaning is not exactly the same. Source Text (English) : We would go out into the yard and feed up to five hundred feet of string through a mixture of ground glass and glue.
From the example above, the translator uses a translation strategy which is translation through a more neutral word. Because the word "ground" in the source language which actually means "tanah" which is replaced by the translator, becomes "bubuk". This strategy is used when the target language does not have the same proportional meaning, but is likely to have similar impact on the target readers.
In the example above, the translator uses a loanword and an explanation to translate the word blangkon into English, making it blangkon (Javanese hat), which has no direct equivalent, without giving any explanation in the target language. When the concept expressed by the source item is lexicalized in the target language, but in a different form, and when the frequency with which a certain form is used in the source text is significantly greater than it would naturally be in the target language. This strategy is usually used when the concept expressed by the source item is lexicalized in the target language, but in a different form, and when the frequency with which a.
Change the parent ordinate or simply unpack the meaning of the source item, especially if the item in question is semantically complex. So it is used when the source item is not lexicalized in the target language at all, but the translator wants to paraphrase, so the paraphrase can be based on changing the superordinate or simply unpacking the meaning of the source item, especially if the item in question is semantically complex. From the example above, the translator dropped the word Raden Ayu from the source language to the target language because it is not the central part of the sentences.
Phrasal Verb
Definition of Phrasal Verb
The word Raden Ayu has already been clarified with the word his mother followed by it, so the translator leaves the word Raden Ayu and translates it to her mother. Based on the definitions of phrasal verbs above, it can be concluded that phrasal verbs are combinations, which consist of a verb followed by an adverb particle, and repeated constructions in English, which are used in phrasal verbs will sound more natural. This phrase can be split if the object is a noun, but must be split if the object is a pronoun.
However, because the intransitive phrase is not followed by a direct object, it cannot be separated. With a separable phrasal verb, a noun can come either between the verb and the preposition or after the preposition. In this sentence there is no object followed by the phrasal verb, therefore the words fall into the category of intransitive verbs, as it does not require an object.
The equivalents are also categorized as intransitive verb because they are not followed by objects after the verbs. The meaning of words comes out above: visit, and the closest equivalents of the words given above are mampir and berkunjung, as these also have the meaning of meaning, visit casually. Mastering verbs is important because it is commonly used in both verbal communication and written text, such as textbooks, novels, magazines, newspapers, and other types of books.
This phrase is important because it is often used in everyday conversation and written language. Various verbs can be derived from the verb and the particle, where the particle emphasizes the meaning. The various verbs whose meaning can be guessed by the element (verb and particle) are idioms.
Kind of phrasal verbs
Word Order in Phrasal Verb
Take a look at these transitive and intransitive examples: Table 2.5.3.2 Examples of transitive and intransitive phrasal verbs. When this type of phrasal verb has a direct object, we can usually separate the two parts. Direct Object Run out of Use up, exhaust We have out out of Eggs Pot up with Tolerate I won't up up with Your approach Look forward to anticipation with.

The Previous Research
An analysis of the translation of phrasal verbs in the novel "The Undomestic Goddess" Written by Sophie Kinsella. This study attempts to find out how the phrasal verbs are translated from the source language (English) to the target language (Indonesian), the appropriateness of the translated version of the novel and the benefits of the phrasal verbs' use in English classroom communication for EFL teaching on high school level grade X. From the research it was found that paraphrase translation strategy of Baker (1992, p.85-92) has the highest frequency of all 81.67%.
From the results of the research, the translation version of the novel meets the criteria of a good translation proposed by Massoud (1988) as cited in Barus (2010); This research also made a positive contribution to EFL teaching, especially in the use of transitive, inseparable phrasal verbs in teacher-student informal learning communication in class X, and it could improve students' vocabulary of phrasal verbs. This research aims to investigate the most used strategies used by six EFL students when translating English Phrasal verbs into Indonesian.
The research tries to serve its purpose by using several basic strategies suggested by Mona Baker namely similar meaning and form, different meaning and form, paraphrase and omission. It was found that the most frequently used strategy was similar in meaning and form, with paraphrasing in second place. The absence of other strategies showed that the students could not achieve greater creativity in creating natural meanings.
The findings showed that the existence of strategies in translating idiomatic expressions could help students to translate the text and, therefore, these strategies should be further emphasized to expand students.
Conceptual framework
Research Design
Source of Data and Data
Technique Of Collecting Data
Data Analysis