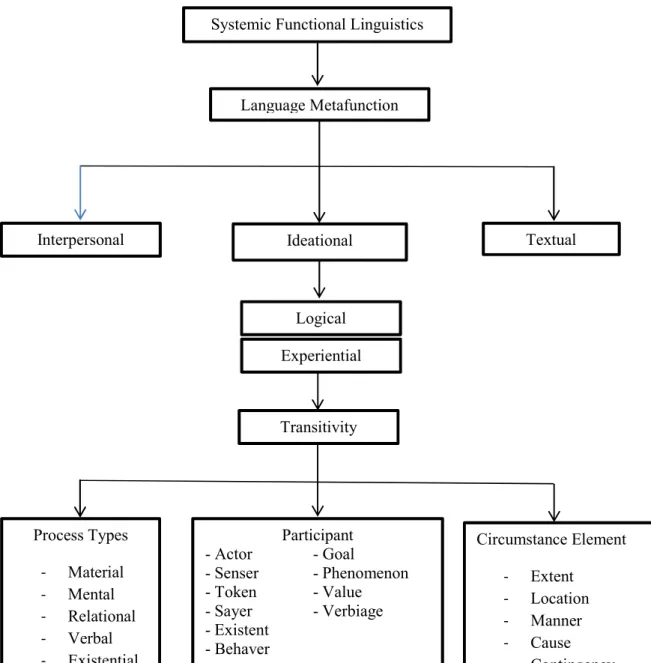
Based on the background of the study, the author formulates the problem of this research as follows. Systemic functional linguistics studies the relationship between language and its functions in the social environment. Based on the above explanations, the author concludes that the interpersonal function is one of the three metafunctions, the others being the ideational function and the textual function.
The ideational function is the expression of how language involves experience, thought and feeling. The clause in this sense functions as a representation. According to Eggins in functional systemic linguistics, the ideational string of meaning that includes two components: that of experiential meaning in the sentence and that of logical meaning between. According to Eggins in functional systemic linguistics, the ideational string of meaning that includes two components: that of experiential meaning in sentences and that of logical meaning between sentence complexes in sentences.
Transitivity System
Process Types
- Material Process
- Mental Process
- Relational Process
- Behavioral process
- Verbal Process
- Existential Process
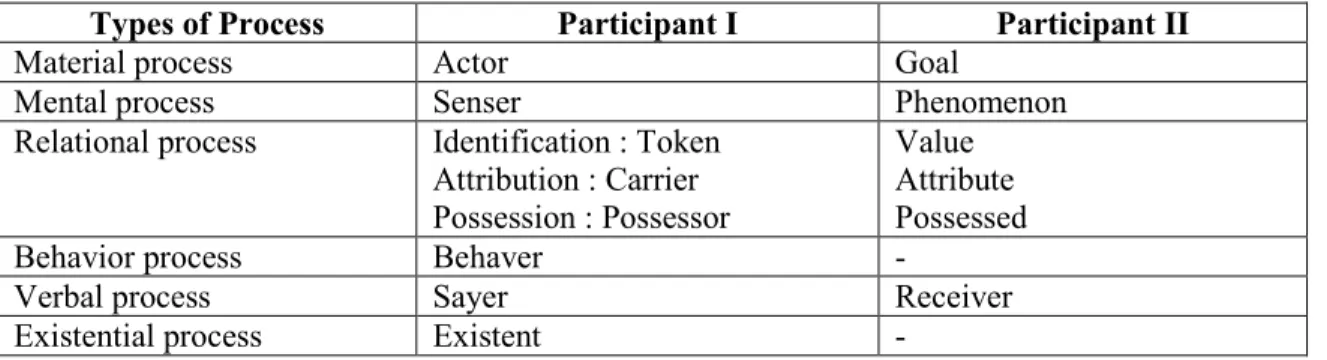
It is central to transitivity and consists of the different types of processes together with the structures that realize these processes. Actor is the one who does the action, and the target is the one who undergoes the process. According to Eggins that a clause of mental process, there is always one participant who is a conscious person; it is the one who senses, feels or perceives and names the participant as observer.
The participants in a mental process are an observer and a phenomenon: the observer is the conscious being involved in a mental process and the phenomenon felt, thought, or seen by the conscious observer. According to Halliday, verbs can be divided into three classes: cognition (verbs of thinking, knowing, and understanding), affection (verbs of sympathy, fear), and verbs of perception (verbs of seeing, hearing). The writer concluded that mental processes mental processes can also be described as sensory verbs that encode the meaning of thinking or feeling.
The form of the above explanation, the writer ended up in the behavioral process described semantically as a "halfway house" between the mental process and the material process. This is the sense that they realized that they were in the middle of the road between the material on the one hand and the mental on the other. The process of behavior related to something physical or mental, which is the roles of the participants as behavior.
The sayer is the participant who is responsible for the verbal process, the receiver is the one to whom the verbal process is intended, and the verbiage is the nominalized statement of the verbal process. The only mandatory participant in this process is the so-called existing one.
Participant
These cover all kinds of speech categories, not only in terms of ways of saying (saying, asking, stating, arguing), but also semiotic processes that are not verbal (showing and indicating). When used in existential processes, it has no representational meaning: it does not refer to a location. There' has no representational function, no representational meaning: it does not refer to a location.
Participle expresses person or thing as subject or object and is realized by a noun or a nominal group. The participant is categorized into two, that is participant I (one who does the activity), and participant II (one for whom the process is done, says that a participant can be a person, a place or an object, and in the grammar of a clause the Participant is realized by a nominal group, typically a noun or pronoun From the explanations above, the author concluded that participants are the doer who does an action in a clause .
Different types of participants should also be distinguished from each other with different labels.
Circumstances Elements
According to Derewianka (2013:5), one important function of language is to enable us to represent what is going on in the world; to talk about our experience, to reflect on our observations, to share knowledge and ideas. From explanations above, the author concluded that circumstances specify when, where, why and how of the process, and processes are what kind of event/condition is described.
Writing
Writing Process
The writing process as a classroom activity involves four basic stages of writing, planning, preparation, editing, and final version. It is very important because when we talk about planning what we will write in the newspaper. Although planning is the first activity you undertake, generating ideas is an activity that runs throughout the writing process.
Planning is freely exploring topics, choosing a topic, and beginning to gather and organize details before writing. These are steps where you start putting the ideas and everything in line with the topic. At this stage, don't pay attention to such things as spelling at this stage.
So it is important to know whether the text is clear or not, and the way it is ambiguous or confusing. Final version is a process of reviewing and editing the draft, making the change deemed necessary. This may look significantly different from both the original plan and the initial draft as things have changed during the editing process.
Based on the explanations above, in the writing process, the writer finds some steps that should be done, such as planning, drafting, editing and final version. It aims to help the writer easily in writing a text to get the good product because it is completed by making a process.
The Purpose of Writing
Informative purpose is to explain possible answers to the question, to give the readers new information about the topic, share knowledge and develop the idea. Persuasive writing is in many ways the most difficult to do well because it requires knowledge of the subject, strong convictions, logical thinking and technical skill. From the explanations above, the writing purpose will give students a rhetorical sense to their writing.
This will also help students to be aware of the mistakes they are writing for. However, there are many more, including expressing feelings, exploring an idea, evaluating, mediating, problem-solving, or arguing for or against an idea.
Genre of Writing
They are narrative, narrative, descriptive, report, explanation, analytic exposition, hortatory exposition, procedure, discussion, review, anecdote, news item and parody. There are thirteen text genres: Narrative, Narrative, Descriptive, Report, Explanation, Analytical Exposition, Hortatory Exposition, Procedure, Discussion, Review, Anecdote, News Item, and Parody. Recount text is a text that recalls and reconstructs past events, experiences, and achievements in a logical sequence.
Narrative text is a text that narrates a series of logically and chronologically related events caused or experienced by factors. Explanation is a text that tells processes related to the formation of natural, social, scientific and cultural phenomena. The generic structure of the statement is: general statement (listing the phenomenon issues to be explained), sequential statements (listing a series of steps that explain the phenomena).
The generic structure of discussion, they are: statement of issue (indicating the issue to be discussed), list of supporting points (presentation of the point in support of the presented issue), list of counterpoints (presentation of other points disagreeing with the supporting point), recommendation (indicating the author's recommendation of the discourse). The generic structure of news item, that is: main events (they tell the event in summary form), elaboration (they elaborate on what happened, with whom, in what circumstances), source of information (it contains comments by participants to, witnesses to and authorities expert on the event). Spoof is a text that tells the events of the past with an unexpected and funny ending.
A description is a text that contains two generic structures, namely: identification (identifies the phenomenon, person, place or thing to be described, description (describes parts, properties, properties). A generic structure of a text with a stimulating explanation, these are: thesis ( problem statement), arguments (a reason for concern that leads to a recommendation), a recommendation (a statement of what should or should happen).
Paragraph
- Parts of Paragraph
- Characteristics of a Good Paragraph
- Descriptive Paragraph
- Generic Structures of Descriptive Paragraph
- The Language Features as Follows
Supporting sentences are developed to explain and give details about the idea of the topic sentence. The main idea is the central thought of the paragraph which is usually expressed in a topic sentence. The position of the topic sentence can be at the beginning or end or in the middle of the paragraph.
Unity is important for a paragraph to have unity, meaning all sentences in it discussed only one main idea. Descriptive paragraph is an activity that the students perform to express their ideas to entertain or amuse the reader. It is a kind of paragraph that talks about something, describes things, someone and the other.
According to Sumarsih and Sanjaya (2016: 6) the paragraph of description is a type of paragraph of the written text, in which it has the specific function of describing an object (living or non-living beings) and aims to give the description of clearly contradict the reader. They can be concluded in the descriptive paragraph is one that describes a person, place or object. It means you can do this by observing and recoding specific details of the person, place, or object that appeal to your reader's senses.
When writing a descriptive paragraph, the writer must know the concept of writing a descriptive paragraph. A writer summarizes by knowing both concepts in writing a descriptive paragraph, students as a writer can adapt the concept to their writing.
Previous Research
Conceptual Framework
Research Design
The Subject of the Study
The Instrument of Collecting Data
The Technique of Collecting Data
Asking students to write a descriptive paragraph students will be given 25 minutes to write a descriptive paragraph with a free topic on a piece of paper the paragraph should be a maximum of 100 words.
The Technique of Analyzing Data