8 Article 5 of the Law on WDP provides as follows: (1) Every enterprise must be registered in the Register of Enterprises ('Daftar Perusahaan'). Change in the form of the enterprise in question; or b. Liquidation of the company in question; or. Based on the above, the definition/meaning of the enterprise register (daftar enterprise) is the enterprise register (daftar enterprise) as provided in the PPDP Law.
A Brief Overview of Regional Autonomy Viewed from the Perspective of Governance Principles in Indonesia
At the same time, regional governments lack qualified experts in the implementation of regional government functions. In such a case, the government distributes its functions to the regions, thereby creating representative offices of the central government in the regions with a hierarchical status based on the principle of expertise. They implement the functions of the central government in the relevant regions in accordance with the policy determined by the central government.
Civil servants assigned to the regions on the basis of the principle of devolution are employees of the central government, while their territory is referred to as administrative territory. In addition to creating autonomy, the delegation of central government functions to the regions also leads to co-government functions to the regional government concerned. On the other hand, according to the principle of devolution, the official territory/administrative territory fall within the organizational hierarchy of the central government.
Based on the concept of autonomy, each regional government is essentially free to make decisions, to take its own initiative, independent of the control of the central government. At the same time, under the aid function or medebewind such a right should be based on central government policy.
Indonesia Is a State Based on the Principle of Law
Manufacturing industries that are important to the country and affect the livelihood of the population are under the control of the state. Accordingly, the existence of the goal of a state is a prerequisite for the existence of such a state. The objectives of the country are defined in the constitution of the respective country, being the 1945 constitution.
In other words, as a logical consequence, the Republic of Indonesia is a state based on law (Rechtstaat) and not only on power (Machstaat). Based on the data presented in the diagram above, we can conclude that most of the mentioned economic entities are aware of the provisions on company registration. Based on the above information and the data obtained, it seems that there is a misunderstanding of the legislation, which in turn leads to an obstacle in the prosecution.
Such a situation exists and is happening in the country of the Republic of Indonesia, which is a rule of law based on law. Applicability of the WDP Act after the enactment of the Limited Liability Companies Act.
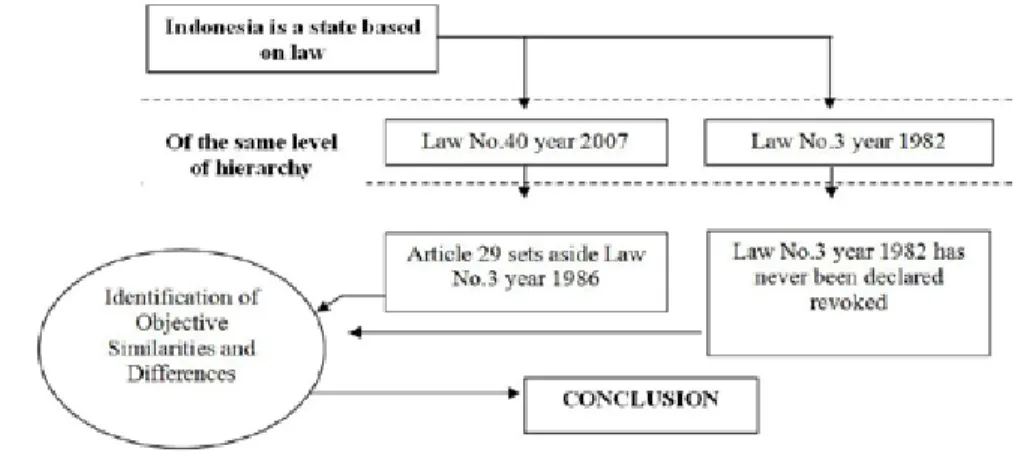
Applicability of the WDP Law Fo llowing the Effectiveness of the Law concerning Limited Liability Companies
The opinion of M. Yahya Harahap
The provisions on company registration according to the Act on limited companies are listed in chapter II, third part, subsection 1, which allows for company registration consisting of article 29, so there is only one article. At the same time, the business register ('daftar perseroan') had been administered by the registrar of the District Court (originally raad van justitie) during the KUHD era. Shareholders are obliged to register in the public register at the district court within the jurisdiction of the company's registered office.
Neither the registration system in Article 21 of Act number 1 of 1995 nor that in KUHD's Article 38 is adopted in Article 29 of the Act on limited companies. A person who is interested in knowing the identity of the amendment of a company's articles of association can check it with a single agency. One must remember the confirmation in the provision in Article 29, paragraph 5, namely that the "Daftar Perseroan" is open to the public.
The data to be entered in the company register ('daftar perseroan') provides information on the overall objective conditions of the company in question. According to the clarification to § 29, subsection 4, letter c), "changes in the company's data" includes, among other things, "transfer of rights" on shares, change of board and board members. , liquidation of the company.
In the opinion of Rudhi Prasetya 48 a. Registration and Announcement
The district court in the place where the limited company has its registered office as stipulated in its articles of association. The intention of registration with the Registrar of the District Court, in the Business Register ('Pendaftaran Perusahaan') or the Business Register ('Daftar Perseroan') as well as publication in the Supplement to the State Gazette are all forms of publication to the public.\. In the spirit of KUHD, the registration at the district court must be accompanied by a set of copies of the memorandum of association stating the articles of association approved by the Minister of Justice.
The purpose of such a request is to ensure that anyone can view the articles of association of the limited liability company (PT) concerned so that they are aware of the provisions applicable to the limited liability company (PT) concerned. While according to the KUHD and Act no. 1, year 1995, publication in an addendum to the Official Gazette by the company's board of directors, according to the Limited Liability Companies Act, the minister and not the board of directors is required for such publication (see Article 30 of the Limited Liability Companies Act). Pursuant to Article 5 of the WDP Act, every company shall be entered in the Register of Companies ('Daftar Perusahaan') (administered by the Ministry of Trade and Industry), including companies (Firma), limited partnerships (CV) or other forms of business entities.
Pendaftaran Perusahaan') under the aforementioned PDP Law, as an instrument for announcing the establishment of Limited Liability Companies. According to Article 29 of the Law on Limited Liability Companies, the Register of Companies ('Daftar Perseroan') is managed and maintained by the Minister.
Applicability of the WDP Law after regional autonomy
One of the causes that lead to such hindrance is due to business registration ('pendaftaran persahaan') administration patterns that do not fully apply the same guidelines. As his view clearly indicates, an attempt has been made to reposition the understanding of the differences between the objectives of enterprise registration ('pendaftaran persaharan') and company registration ('pendaftaran perseroan'). The authorization to implement enterprise registration ('pendaftaran persahaan') which is given to the Enterprise Registration Office (KPP) of the Regency/.
It is the duty of the Central Government to set the guidelines, develop human resources, coordinate, control, supervise the administration and submission of mandatory enterprise registration information ('wajib daftar pershakan') on a national scale. It is the duty of the Regional Government to coordinate, control, supervise, report and present the information resulting from the compulsory registration of enterprises ('wajib daftar pershakan') at the provincial level. In addition, each administrator of enterprise registration at the regency/city/municipality level must submit a report on the administration and implementation of compulsory enterprise registration ('wajib daftar ushangan') in the form of the report on the administration of enterprise registration and a copy. of the approval of the form for the KPP of the Province and the Central KPP.
In the implementation of the mandatory registration of enterprises ('wajib daftar pershakan'), the Regulation of the Minister of Trade No. 37/M-DAG/PER/9/2007 Regarding the Administration of Enterprise Registration is the implementation of the provisions of Law No. Consequently, since the Regulation of the Minister of Trade No. 37/M-DAG/PER/9/2007 Regarding the Administration of Enterprise Registration is the implementation of the Law on PPDH, the existence of the regulation of the Ministry of Trade in question is recognized and is mandatory . in nature.
Conclusion
At the same time, the context of the implementation of the WDP Act, regional regulations must implement and serve as an extension of arms in view of matters determined in the WDP Act, as well as other implementing regulations, including Regulation of the Minister of Trade Number 37/M-DAG/PER/9/2007 Regarding the Administration of Enterprise Registration. Regional governments must make policies that are not inconsistent with the WDP Act and the aforementioned Minister of Trade Regulation. In addition to the foregoing, province and city-region governments are also required to report on the implementation of registration activities by attaching copies of the approved business registration forms, as mandated in Regulation of the Minister of Trade Number 37/M-DAG/PER/ 9/2007 Concerning the Administration of Enterprise Registration.
In addition to the need to further provide for the technical aspects, the possibility of imposing stricter sanctions on enterprises as well as on public officials implementing the enterprise registration process in cases of non-compliance should also be considered. The implementation of the computerized network system and the WDP application program currently provided by the Ministry of Commerce is not able to automatically manage TDP issue numbers, is not integrated between WDP data managers at the organizational level, does not have the ability to validate the accuracy of the data automatically and does not possess the ability to integrate with the system created by PTSP. The EDP Law has suffered legal distortions compared to other laws and regulations, therefore it has changed the meaning of the law, especially regarding the obligation to perform EDP according to the Law on Limited Liability Companies (Law No. 40, year 2007).
Legal Bureau of the Ministry of Development Planning/Bappenas, Development and Implementation, Method of Regulatory Impact Analysis (RIA) For Policy Evaluation (Regulatory and Non-Regulatory) At the Ministry of Development Planning/Bappenas, Jakarta, 2011. Directorate of Trade Development Directorate General of Domestic Trade Ministry of Trade of the Republic of Indonesia, Academic Draft of the Draft Law Regarding Company Registration, Jakarta, 2012.