John D'Angelo, my independent research advisor, for taking me under his wing to conduct conducting polymer research as an independent study. You have created the basis for me to realize one of my dreams of researching conductive polymers and their applications in medicine and biomaterials engineering. The reason that polypyrrole and some other conducting polymers can be conductive at all is the delocalization and.
Conductive polymers open a new research avenue into medical materials and devices. There are numerous different applications for which conductive polymers can be used, including wound dressings. I had a barebones structure of what my end goal was, which was to determine whether iron atoms were present in the structure of conducting polymers.
Conductive polymers are again unique because they can provide stimulation with an electrical charge to the cells they are in contact with. I hope that my passion for this field of conducting polymer research can be continued at some point by me or someone else who aspires to work with conducting polymers. This opportunity was a unique experience that I am extremely grateful for and opened the door for me to explore my dreams and interests with conductive polymers.
Introduction
Moreover, he was supportive and provided me with the ideas or tools necessary for me to progress with my research. Anthony Wren for being a supportive point of reference for me in my research and he helped guide me in the right direction with some of the earlier aspects of my independent study research. CPs are quite versatile in the fields of bioengineering and regenerative medicine and they can be synthesized with relatively simple methodologies that can then be adapted to serve different purposes.
With the ability to have their chemical, electrical and physical properties tailored with antibodies, enzymes or other biological molecules, CPs are poised to pave the way for new achievements in the field of biomaterials. In addition, it can have appendages attached to it at the location of each repeating pair of hydrogen atoms, increasing its versatility as a molecule. PT is a stable conductor of electricity with a relatively high electrical conductivity of up to 103 S/cm.
With this study, the construction of neural channels and never regeneration have become topics of great interest among CP researchers in the field of biomaterials3.
Experimental Procedure A. Synthesis of Polypyrrole
Notably, it has been observed that PPy can modulate cellular activities such as migration and cell proliferation in biological environments. Furthermore, a study examining the growth of PC-12 cells on PPy found that PPy sheets subjected to electrical stimulation had approximately twice as much cell growth as the PPy sheets that had no electrical stimulation. Three major studies on PPy will be presented, including investigations into its synthesis, characterization and experiments related to the material response to bacteria and its conductivity under different conditions.
In the third trial, methods were adapted to include a separatory funnel to slowly drip the 60ml of 0.2M Fe(III)Cl3 into the solution over the course of 15 minutes. In the fourth trial of PPy synthesis, major changes were made to the procedure. The beaker was replaced by a wide and shallow Pyrex dish, and the magnetic stir bar was replaced with a rocking device that could move the dish back and forth, thus simulating a mixing motion, and this device was set at a speed of 1.
In addition, the dripping time for Fe(III)Cl3 was extended to about 25 minutes and the vessel was covered. In the final attempt to synthesize PPy, the Pyrex vessel was replaced with a smaller, more rectangular Pyrex vessel and an amount of 0.2 M Fe(III)Cl3. After each PPy synthesis attempt, the product was analyzed using an SSM-7800F field emission line electron microscope (SSM, USA), which captured secondary electron (SE) images along with electron dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) scanning.
Characterization of Polypyrrole
Each plastic tube contains 20 ml of phosphate buffer solution (PBS) and approximately 0.0175 g of synthesized PPy. All samples were kept in a Fisher Scientific isothermal incubator for the duration of their digestion. Three samples were kept for one day in the incubator while the other three samples were kept in the incubator for one week and checked daily.
As part of the characterization test, the synthesized PPy was tested against hydrofluoric acid (HF) as an ultimate test of its corrosion resistance. PPy was placed in a plastic container resistant to HF and allowed to infuse for three days, after which it was observed. To ensure that the PPy would not damage the TA SDT Q600 instrument, the PPy was mixed with 13–14 mg of dried alumina powder until it was thoroughly mixed and resembled a gray powder.
One alumina crucible was designated as the control and was placed on the farthest weighing bar after opening the test chamber of the instrument. Once tared, the test chamber was opened again and the experiment alumina crucible holding the 13-14mg mixture of dried alumina power and PPy was placed on the closer weighing bar. When properly placed, the test chamber is closed, and settings are configured on the computer according to the needs of the experiment.
In the second trial of DTA, the same loading procedure and sample preparation procedure were followed except that nitrogen was used instead of room air, which involved closing the valve for room air and opening the valve on the nitrogen tank.
Bacterial and Conductivity Evaluation
Results
Polypyrrole Synthesis
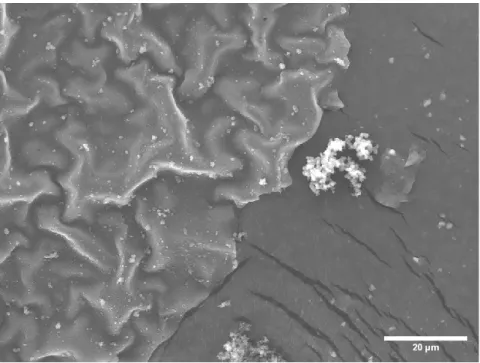
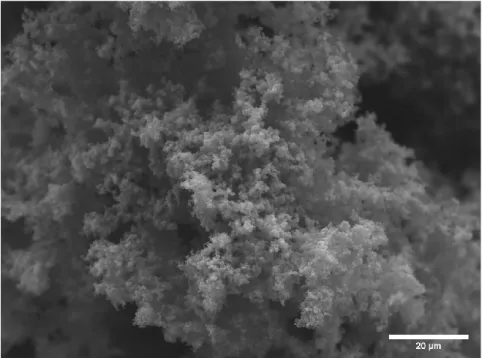
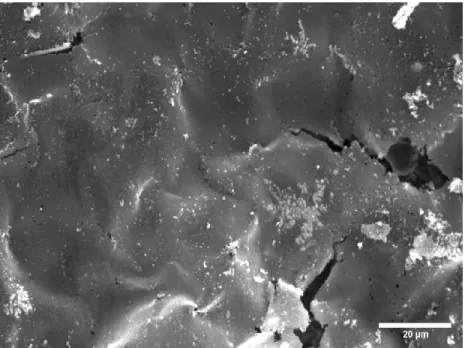
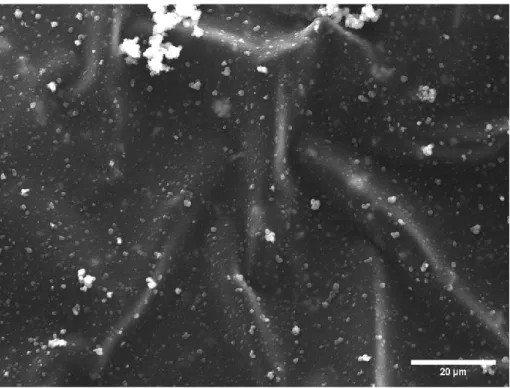
Very few conglomerated bits of PPy can be seen still attached to the PPy sheets that were formed. This form of PPy has smooth leaves with occasional PPy conglomerates appearing on the leaf. Solubility testing of PPy in PBS showed that PPy is insoluble, as can be seen from the one-day solubility test in Figure 8 and from the seven-day solubility test in Figure 9.
Furthermore, PPy did not break down into smaller pieces than what was present during the initial deposition in HF. By performing the analysis with air, a gradual increase in weight was observed, as well as a peak in temperature change and heat flow occurring around 100°C. There is a peak in heat flow and temperature change around 100°C as in DTA with room air.

Bacterial and Conductivity Observations
Discussion
In the first iteration of synthesis, as the material was mixed in a beaker with a magnetic stir bar, there were very few sheets of PPy present in the material. Since the second iteration involved an extremely rapid formation of the polymer by the addition of the pyrrole after the addition of the Fe(III)Cl3. There was an overload of Fe(III)Cl3 with which the polymer could react, thus leading to a highly conglomerated formation of PPy.
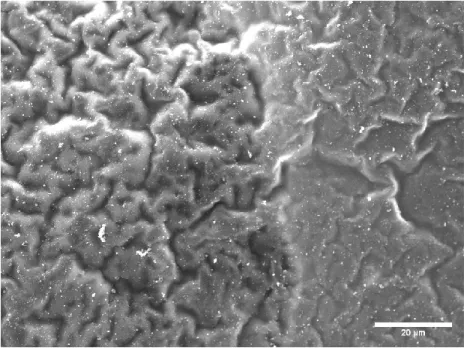
The changes that were made for the third iteration of the PPy synthesis were more PPy sheets were present, but many folds were in the material. There were two different levels of completion of the synthesis each with more or less folding. Within the fourth iteration of the PPy synthesis, since the method had switched to using a rectangular Pyrex container instead of a glass one, there was a large increase in the ability of the sheets to be formed.
The rocking table that mixed the Fe(III)Cl3 with the pyrrole throughout the day provided enough stimulation and mixing to promote sufficient reaction between the pyrrole and Fe(III)Cl3 while not being too rapid to cause skin formation of Not to disrupt PPy. Iteration four of PPy synthesis was a highly successful transition from iteration three of PPy. Iteration five confirmed this as the synthesized PPy, like the PPy from iteration four, had a continuous sheet-like nature with little appearance of decoupled PPy on the surface.
In addition, all iterations of synthesized PPy were found to have no Fe present in their structure or present in the surrounding area. This confirms that the conductivity found in PPy is caused by a delocalization of rearrangement of electrons due to oxidation. To achieve a relatively stable and repeatable process of chemical synthesis of PPy was attributed to a strict and stable adherence to protocols made during research.
If future synthesis of PPy were to be attempted, electrochemical synthesis would be recommended as it enables the deposition of a thin film of the polymer.
Polypyrrole Characterization
Conclusion
The chemical synthesis of PPy was generally improved with each iteration, and a stable and reliable synthesis method was established. Characterization of the synthesized PPy indicated that the material could potentially be a viable biomaterial in its current state, although it has already been proven to be a viable biomaterial1,2,6,7,8. The conductivity of the synthesized PPy was largely unsuccessful with the dry material, but when placed in water, the material showed promising conductivities of around 200-280 mV.
Bacterial testing of the synthesized PPy showed that the material is potentially antibacterial as several inhibition zones were observed around the PPy moieties when tested against E. These studies were promising in confirming PPy as a viable biomaterial, but will require more much research before being able to reiterate that PPy is viable. The synthesis of PPy can be further manipulated by the fifth iteration used in this research.
Cell culture viability assays will be useful to confirm whether PPy is toxic to cells and Schwann cells can be used to later test the conductivity of the PPy while interacting with the cells.
Appendix