The significant contribution of the manufacturing sector to the economy makes the dynamics of the manufacturing sector an inseparable factor in economic cycles. Several studies provide empirical evidence of the influence of business cycles in the dynamics of the manufacturing industry. The amount of ATC (Average Total Cost) varies depending on the characteristics of the market.
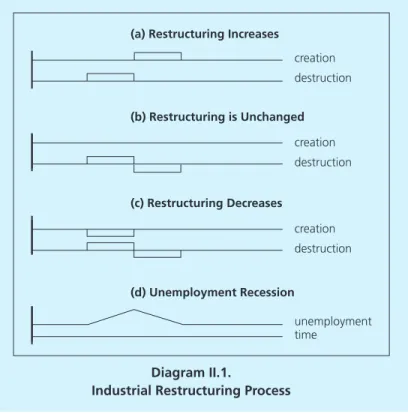
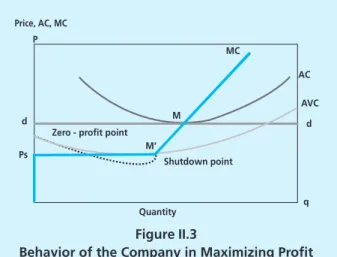
Based on the above explanation, the company will act rationally to produce at the level of the maximum profit. Joseph Schumpeter (1942) said that the dynamics of the enterprise is a «creative destruction process which is later considered the main cause of economic fluctuations. Shapiro (1997) found that the relationship between the level of entry and exit from the company is positively related to productivity.
The implications of increased manufacturing productivity are consistent with the higher level of input/output experienced by manufacturing industry countries (Marcos and Jaumandreu, 2004). Some other studies on the determinants of entry and exit of a company within the industry were brought by Audretsch (1995). It is analogous to specifying the probability of each event to be selected, as shown in the previous equation, but this time, the probability for each individual (cross-section) can be obtained.
Fixed effect model estimation will generate an unstable and biased estimator (Bernard and Jensen, 2004).
Data, Conceptualization and Measurement of Data Variable
Related to the selection of fixed and random effects models, within STATA itself, there is no command for fixed effect multinomial logit, as there is insufficient statistical evidence that the fixed effect can be adjusted with maximum likelihood. The value of α and β will vary between sub-industry, depending on the characteristics of the industry, whether they have a production function with increasing returns to scale, decreasing returns to scale or constant returns to scale. Calculating technology using the Solow residual does not account for the impact of technology improvements caused by other sectors.
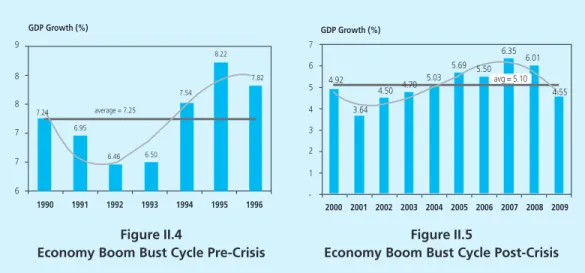
Concentration ratio (CR) = the degree of market concentration used to determine whether a particular industry is a group with a perfectly competitive market or a monopoly. The value of the concentration ratio ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 indicates the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market and 1 indicates a monopoly market. A boom period is a period when economic growth is above average, and vice versa a period of decline.
4 The economic downturn cycle can also be calculated using the real wage variable (appendix) and periodization of the economic downturn, without significant differences compared to the calculation using PPP. Other variables used are the amount of production work, which shows the size of the firm.
RESULT AND ANALYSIS
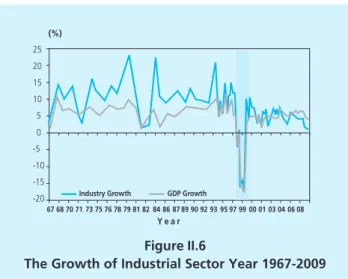
The Growth Of Industrial Sector
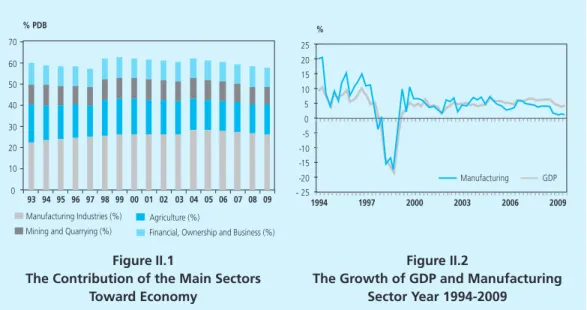
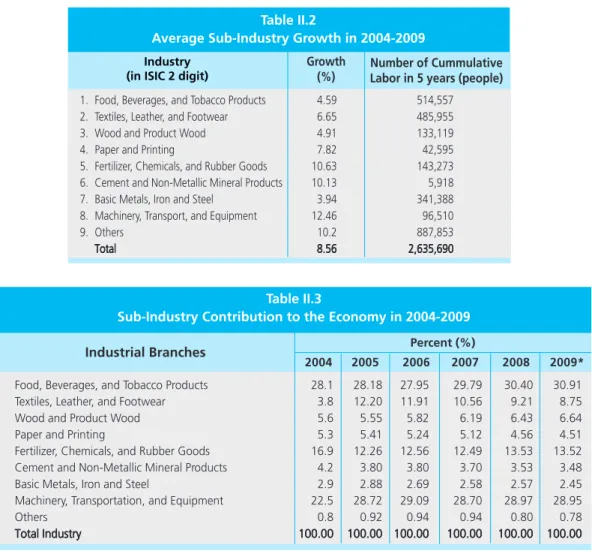
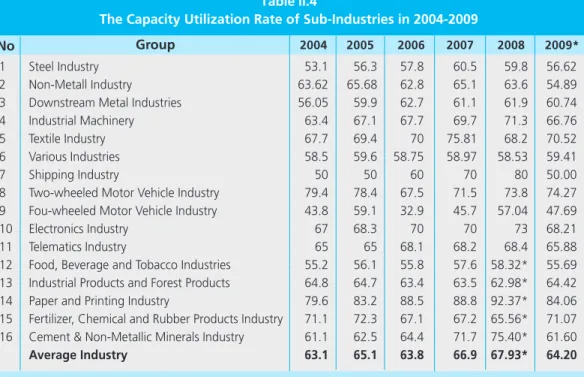
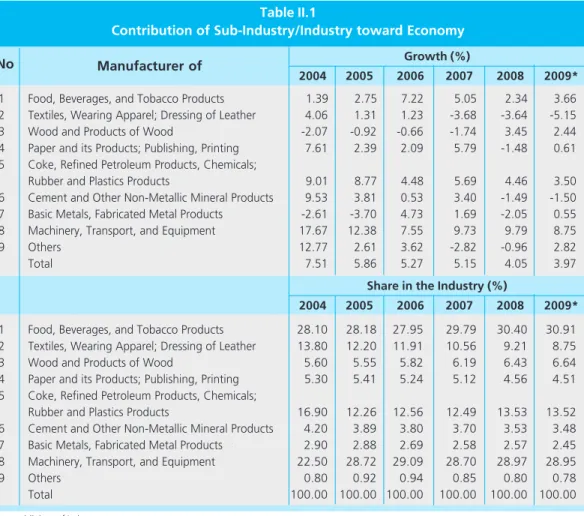
Table 1 shows that the industry of food, wood and forest products has recorded positive growth. On the other hand, a great contribution to the economy will also be made by the sub-industry, which will reach 28.95% in 2009. The highest level of employment is in the sub-industry of food, beverages and tobacco.
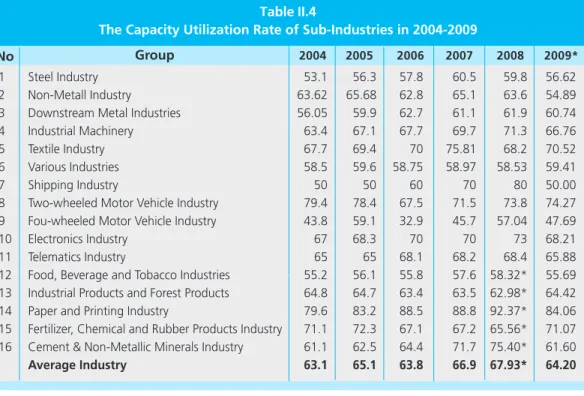
The sub-paper and printing industries have the highest capacity utilization, while the industry is experiencing. On the contrary, the fertilizer, chemical and rubber products industry shows a fall in capacity utilization, especially in 2008. This is due to the lack of supply of natural gas, which serves as a raw material and energy.
In terms of exports, the industries of palm/palm oil processing, iron steel, machinery and automobiles, textiles, rubber processing, and electronics are the major contributors to non-oil exports. In general, the non-oil-producing industries tend to have a higher export value during the first four years, except in 2009 due to declining demand from abroad due to the global crisis. While the iron, electronics, base chemical, textile and food and beverage industries are the major contributors to non-oil imports.
Generally, non-oil manufacturing industries have the trend of increased value of imports during the last five years.
The Model Estimation Result: Panel Multinomial Logit
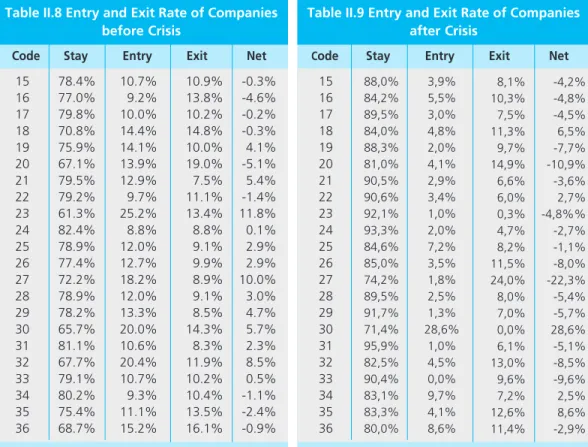
The estimation results (attached) show that there are differences in the sensitivity of capital growth to the company's opportunities to enter the industry during the downturn and the boom. Conversely, during a boom, a positive capital coefficient indicates that an increase in capital will increase the probability of firms entering the industry. In addition, firms that enter the industry during boom times also have more capital than firms that remain in the industry.
The opposite happened during the bust, the amount of capital in the companies does not significantly affect the chances of entering the industry. The behavior of the companies leaving the market showed very little difference during the boom. During the bust, capital changes do not affect the firm's decision to exit or remain in the industry.
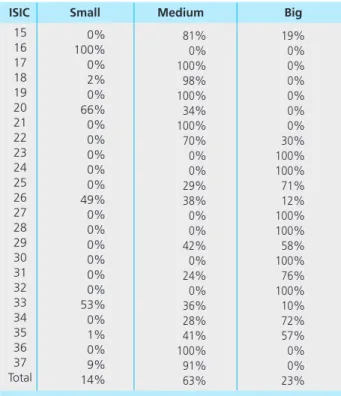
While during the breast, the increase of company size in tobacco sub-industry (16) will increase the chances of companies to be in the industry. In addition, the companies that exit during the boom are relatively smaller than the bust. During the boom, the larger the size of the company will reduce the probability of company to leave larger than during the bust.
During a collapse, the greatest sensitivity of firm size in relation to the probability of exit of firms from the industry is within the tobacco sub-industry (16). Meanwhile, during the boom, the sensitivity of firm size to the likelihood of firms exiting the industry is greatest in the furniture subindustry (36). Higher labor costs will increase the company's chances of exiting during an economic downturn.
Meanwhile, production costs during the boom period do not influence the company's decision to exit the industry. While the reduction in production costs during the boom will only reduce the number of firms entering the industry. Estimation results from the Logit panel show that the company entering the industry in the crisis period has less technology than during the boom period.
During the breast, the technology of the exciting company is more sophisticated than the boom. The companies leave the industry that led to the monopoly more easily, especially during the economy.
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDED POLICIES
Meanwhile, during the boom, market characteristics are not a factor influencing the company's decision to stay or leave the industry. In boom/bust periods, the probability of firms exiting the industry will be greater if the cost of production labor increases, if the size of the company decreases, and if there is a decrease in capital. It gives the consequence; capital raising policies would be more effective in improving the probabilities that companies enter the industry during booms.
While the growth of the company's capital during the bust will prevent the exit of companies from the industry. Therefore, to strengthen the manufacturing industry during the bust, greater incentives are needed to improve the company's capital. The data results also show that large-sized companies have a high chance of surviving in the industry due to economies of scale, while small companies are more likely to enter and exit during boom/boom.
During an economic downturn, manufacturing labor costs must be reduced because they will affect the firm's decision to enter or exit the industry. Whereas a reduction in production costs during a boom will only reduce the number of firms entering the industry. During the boom period, the company's chance to enter the industry is greater for companies with excellent technology.
While in the economy, the probability of entering the industry is higher for companies with low technology, small size and low levels of market concentration. Therefore, small-scale industries and low technology play an important role in anti-cycling the economy during the bust period. 34; Firm Dynamics and Productivity Growth: A Review of Micro Evidence From OECD Countries", OECD Economic Department, Working Paper No.
34; Determinants of Entry and Exit Rates in US Manufacturing Industries", Review of Industrial Organization, Vol. 5 No. 34; Entry and Exit Dynamics in Austrian Manufacturing Industries." Vienna University of Economics and Business Administration, Working Paper No. 34; Entry, Exit and the Dynamics of Productivity Growth in the Chinese Manufacturing Industry", ESRC Center for Business Research, University of Cambridge, Working Paper No.
APPENDIX
MANUFACTURE OF GARMENTS; DRESSING AND COLORING LEATHER TANNING AND DRESSING; MANUFACTURING OF WOOD AND WOOD PRODUCTS AND MANUFACTURING OF PAPER AND HARD PRODUCTS. PUBLISHING, PRINTING AND REPRODUCTION RECORDED PRODUCTION OF COKE, REFINED PETROLEUM PRODUCTS MANUFACTURING OF CHEMICALS AND CHEMICAL PRODUCTS MANUFACTURER OF RUBBER AND OTHER RUBBER PRODUCTS AND REFINED PLASTIC PRODUCTS AL PRODUCTS MANUFACTURING OF BASE METALS. OFFICE, ACCOUNTING AND INFORMATION MANUFACTURING ELECTRICAL MACHINERY AND APPLIANCE MANUFACTURING RADIO, TELEVISION AND COMMUNICATION MANUFACTURING MEDICINE MANUFACTURING PRECISION, DEMAND MOTORS AND OTHER TRANSPORTATION EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURING FURNITURE MANUFACTURING; PRODUCTION N.E.C.