Investors will try to mask feelings of anxiety about the conditions that have occurred by looking for news related to the COVID-19 pandemic. H4: The number of positive cases and death rate of COVID-19 has a negative impact on stock returns. This is reinforced by (Rizvi et al., 2021) who from the results of his research showed the results that the presence of Fiscal Policy by the government during the COVID-19 pandemic definitely brought an economic stability which ultimately led to a had an impact on the stock. market that increased.
Regarding the COVID-19 pandemic, (Haykir & Ozturk Cetenak, 2021) In a study conducted in Turkey, it was said that the reduction of interest rates as the monetary policy of Turkey during the COVID-19 pandemic had an impact on stock returns. liquidity and. H10: The number of positive cases and death rate from COVID-19 has a positive impact on stock volatility. In the process of finding out how the COVID-19 pandemic affects the Indonesian stock market, this study first uses individual stock price index data from companies that are listed on the Indonesian stock exchange.
In testing the impact of aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic on individual company stock returns, this study estimated a model similar to the previous research model once used by (Kaplanski & Levy, 2010). ). , that is. 𝐺𝑉𝑆𝐼 𝐶𝑜𝑣𝑖𝑑 ) is a search volume index for keywords related to the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia at the time of t (GsviCovid). 𝑀2) is the growth of the broad money supply in Indonesia at that time as a form of monetary policy enacted in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic (M2).
𝐸𝑋𝑃𝐸𝑁𝑆𝐸) is the increase in government spending at time t as a form of fiscal policy issued in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic (Government Spending).
RESULTS
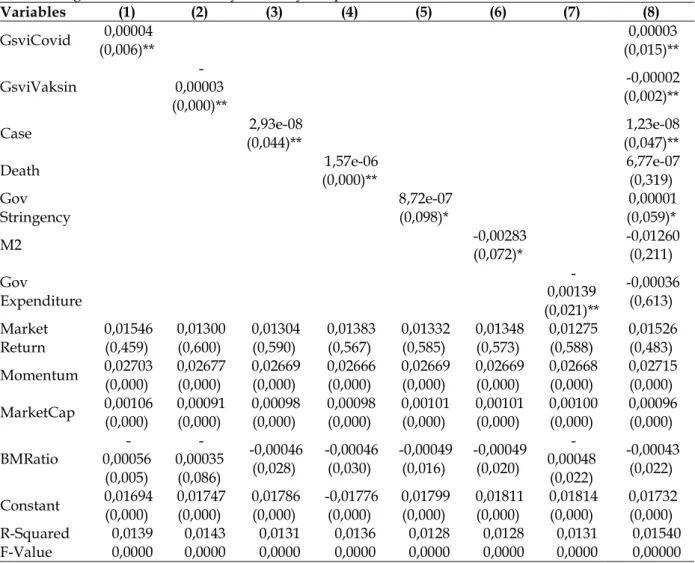
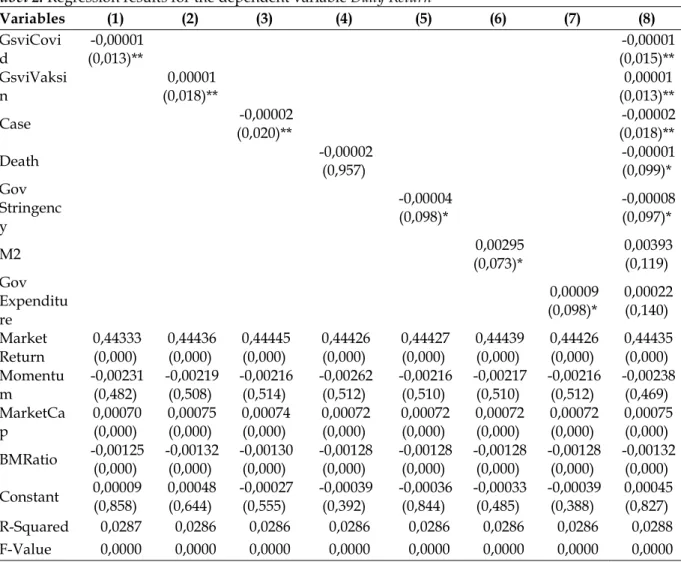
This finding shows that the information about the outbreak of COVID-19 really affects the stock market performance in Indonesia, where the given impact is negative, so the greater the level of public concern about the information about the outbreak of COVID-19. able to cause the rate of return on the stock market to decrease. Therefore, as hypothesized in the previous hypothesis, it is proven that the information of the outbreak of COVID-19 has generated negative feelings in the market and as a result the performance in the stock market has decreased. In the same direction as (Chundakkadan & Nedumparambil, 2021) which shows that in 59 countries, including one of them in Indonesia, it can be seen that attention to the COVID-19 pandemic that is sweeping the world has created a negative feeling for market participants . ultimately results in pressure on the stock market.
So this confirms that the information about the COVID-19 vaccine can make the Indonesian people more calm and influence the investors will be even more optimistic in stock trading so that in the end it will have a positive impact on the stock return rate . exchange, in accordance with the second hypothesis formed. So this result is consistent with what is hypothesized in the third hypothesis, namely it is proved that the number of positive cases of COVID-19 causes excessive concern to the public, especially investors, and causes a decrease in the daily rate of return of stocks in Indonesia. Then in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, (Rizvi et al., 2021) and (Haldar & . Sethi, 2022) mentioned that the existence of fiscal policy during the COVID-19 pandemic can bring economic stability and with the help of the distribution of data on the provision of health facilities, manpower, and so on creates a good feeling because it is considered capable.
Because it is described with investors reacting positively to a rate cut that happens, which can ultimately bring stability to the stock market. Then (Prabheesh et al., 2021) also revealed that monetary policy generally proved to be effective in stabilizing the economy, especially in the stock market. In addition to the impact of the aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the rate of return, Table 3 also shows the results of the estimations of each independent variable on the volatility of the market to determine whether the unrest, fears and improvements of the COVID-19 pandemic can affect the stability or movement of activity in the Indonesian stock market .
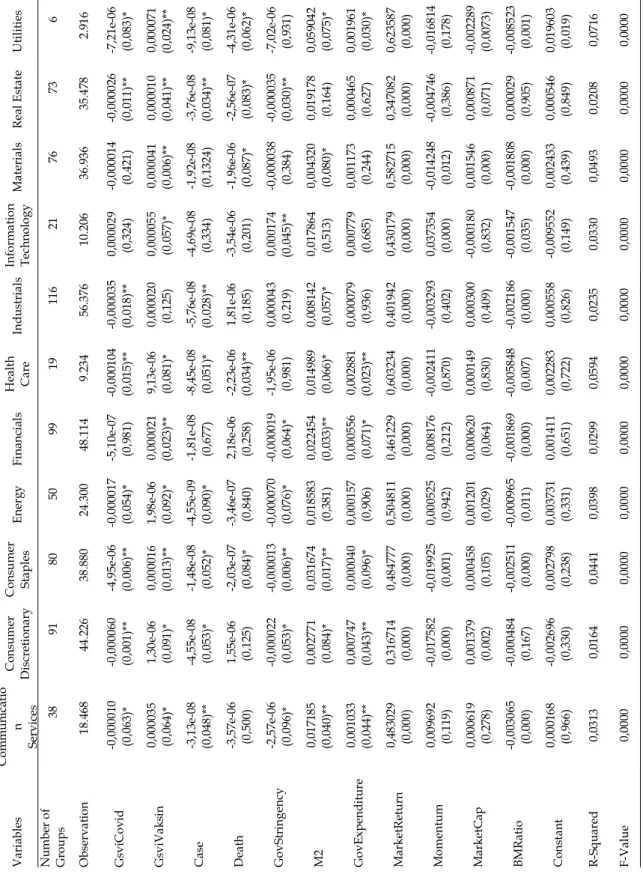
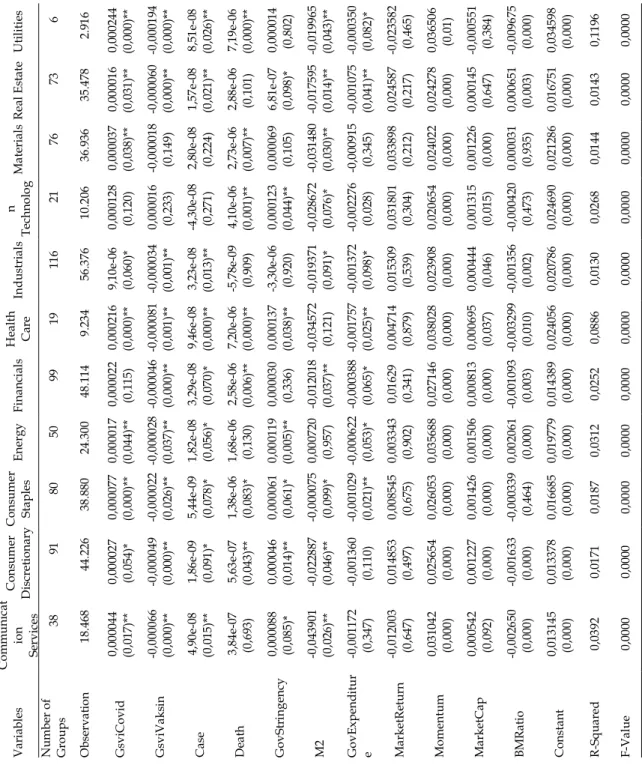
These results are similar to those of previous studies (Chundakkadan & Nedumparambil, 2021) suggesting that negative sentiment caused by the existence of information related to the COVID-19 pandemic caused excessive volatility in the stock market. This result is consistent with the literature that argues that investor sentiment during the COVID-19 pandemic can explain stock market volatility (Baek et al., 2020). This suggests that with the large amount of information related to the COVID-19 vaccine, it reduces the public's sense of fear and anxiety, which can make people more optimistic and cautious when trading stocks, which in turn reduces volatility. stock market.
The results are reinforced by the same findings from the study conducted by (Hong et al., 2021) and (Rouatbi et al., 2021) earlier, which said that the existence of a COVID-19 vaccine provided stability in the stock market. This answers what has been elaborated in hypothesis 10 that it is proven that the government tightening index has an influence that can increase the volatility of the Indonesian stock market. In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic (Haldar & Sethi, 2022) and (Rizvi et al., 2021) provide an explanation of where the state of the stock market has become more stable since the government's issuance of fiscal policy.
Thus, the 12th hypothesis in this study is proven, which states that monetary policy can reduce excessive volatility in the stock market by increasing the money supply. It is highlighted that apart from the financial industry and information technology groups, most industries support the finding that the sentiment created by the information about the COVID-19 pandemic is correct to cause excessive volatility in the stock market.
CONCLUSION
Based on the results obtained in this study, it can be said that it is good for the public, especially investors, to always be careful in following the development of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic in carrying out an investment activity. Because when the volume of information searches related to the COVID-19 pandemic is high, as well as the number of cases and the death rate, it can lead to reduced stability and performance in the stock market. Next, in addition to information related to the development of the COVID-19 pandemic and the bans carried out by the government, investors should also pay attention to how the assistance or policies provided by the government and vaccines are a response to the health pandemic problem. .
Due to the vaccine and assistance from the government in terms of policies, it will be able to create good sentiment and improve the performance and stability of the stock market, therefore, after delaying investment activities due to the COVID-19 pandemic, when the level of vaccine distribution is even distributed, as well as the decrease in the impact of the pandemic that society feels due to government policies, the public, especially investors, can carry out reinvestment activities. Keywords related to the COVID-19 pandemic used as Google's search index in this study may indicate that the resulting search volume index represents negative sentiments generated by the rise of the pandemic, but it does not represent all existing parties because there are actually certain parties that purely actually benefit from this pandemic, as well as for keywords related to covid-19 vaccines. Additionally, this research in the process also only uses one variable each that is used as a proxy for fiscal and monetary policy during the COVID-19 pandemic, namely government spending growth and money supply growth (M2), which are actually many other things that actually are related and can be used to represent these policies.
The Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic on Global Stock Markets: Return, Volatility and Bad State Probability Dynamics. The effect of COVID-19 pandemic on the Philippine stock market, peso-dollar rate and retail price of diesel. Impact of the West African Ebola Epidemic on Agricultural Production and Rural Welfare: Evidence from Liberia.
Stock market responses to the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak: Quantitative evidence from ARDL bounds tests and granger causality analysis. Testing the relationship between stock market returns and inflation in Nigeria: Significance of the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic. The Heterogeneous Effects of the COVID-19 Outbreak on Stock Market Returns and Volatility: Evidence from Panel Quantile Regression Model.
The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Stock Markets: An Empirical Analysis of the World's Major Stock Indices. Measuring leverage effect of covid-19 on share price volatility of energy companies using high frequency data. Response of Stock Market Returns to COVID-19 Pandemic and Containment Policy: Evidence from Stock Returns of Nigerian Firms.
The impact of COVID-19 and the severity of government policy responses on stock market returns worldwide. The spread of COVID-19 and stock market responses: An event study and panel data analysis for G-20 countries.