4 Characteristics of the Defense Industry at the Beginning of the Twenty-First Century 129 5 The Workforce: Industry, Government, and the University 235. Eisenhower's famous warning in 1961 to beware of the "military industrial complex" was followed by a statement that The United States could not have won World War II without the defense industry. A major transformation of the defense industrial base is essential to make it robust, responsive and fit for the national security needs of the twenty-first century.
The Challenge
The answer to this question lies in part in another important security consideration for the twenty-first century. In the multipolar, global environment of the twenty-first century, it is critical that other nations (whether allies or adversaries) respect America (which has been lost in many areas in the early days of the twenty-first century). This cry was echoed by many observers in the first decade of the twenty-first century.
The Defense Industry in Perspective
The Cyclical Nature of Defense Procurements
Even during the long period of the Cold War (1947 to 1991), when a sustained level of expenditure was maintained due to continued concerns about the Soviet Union, there were still large variations in the expenditure and the size of the defense industry maintained (Figure 2.1). After each conflict in the second half of the twentieth century—Korea, Vietnam, and the Cold War—the public expected (and received) a large peace dividend, and. Kosiak, "Historical and Projected Defense Funding: Presentation of the FY 2008 Request in Tables and Charts," Center for Strategic and Budgetary Assessments (CSBA), June 7, 2007.
The Lack of Industrial-Base Structural Planning
Notes: *Some of the largest defense contractors during World War II; ** top ten performers of 2006, ranked by dollar value of awards received. This can be seen by comparing the lists of the main military suppliers in the Second World War with those of 2006 (Table 2.2). Furthermore, one of the main planning levers the government has in this area is determining how much of the defense industrial base should be in the public sector and how much in the private sector.
A Lack of Preparedness for the Next Time
In any industrial-based structural planning, these public versus private sector facilities and the amount of government ownership (even in those facilities operated by the private sector) must be assessed. After World War II, planning envisioned major increases in the production of ships, aircraft, and tanks. In the case of the Patriot missiles mentioned above, ordering the long-lead parts in advance of the ramp-up would have made them available for a ramp-up requirement at very little added cost, since the parts could be used in production of later years. if there had been no increased demand.).
The Lack of Actual Industrial Responsiveness
But individual parts were needed to increase the production rate of the Patriot, and the parts were not included in the peak schedule. But in Iraq, when roadside bombs began destroying unarmored vehicles, there was an immediate demand for armor, which (because it was unplanned) took years to satisfy. The industries that build the ships, planes, and tanks may be reluctant to change their traditional end-item-oriented readiness model, and the military may be slow to change traditions built around these platforms.
The Lack of an Industrial Base to Match Changing Needs
Until World War I, the Minuteman model of mobilizing manpower in response to war was the nation's planning approach. The Importance of Science, Technology, and Research and Development After World War II, Vannevar Bush helped the nation recognize that science.
The Importance of Science, Technology, and Research and Development After World War II, Vannevar Bush helped the nation to recognize that science
Signifi cant Differences among Industries in the Defense Industrial Base
At the lower levels, a large number of small suppliers produce parts and materials (such as castings, forgings and semiconductors) (figure 2.2. The majority of defense equipment used to come from commercial industries that converted to war production and returned to commercial operations at the end of In the years immediately following World War II, however, a specialized defense industry grew to meet emerging DoD technological needs (such as jet propulsion for fighter aircraft, microwave radars, missiles, fire control computers, and other unique or predominantly military equipment).
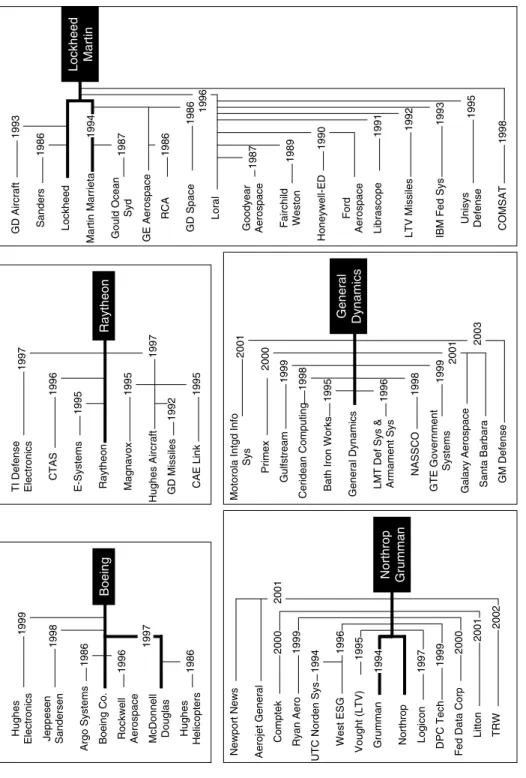
The Consolidation of Defense Firms
The False Perception of Autarchy
The total defense expenditures of the United States far exceed those of any other nation. Finally, not all of the costs of DoD health care appear in the DoD budget. A Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (at a four-star general officer level) will insert joint authority into the requirements process (through the chairman of a Joint Requirements Oversight Board who will review and approve all requirements) and will represent the users of the military equipment (the combatant commanders) in the requirements process (rather than that process being driven entirely by the military services).
Defense Budget Cuts
36 At the end of the Cold War, Russia and a number of other former Soviet Union states still had large arsenals (particularly strategic nuclear weapons) at their disposal. It was considered highly desirable to find ways (through negotiations known as cooperative threat reductions) for both the United States and the former Soviet Union to increase their strategic weapons stockpiles and the means of their transfer (1,846 Russian and 846 American ballistic weapons). rockets were literally sawn apart). This was a very stabilizing effort, but because of the financial instability of many of these former Soviet states, the costs of reduction had to come from the US.
Industrial Consolidation
39 Due to significant differences in the cultures of the defense and commercial environments (particularly in marketing, finance, and defense engineering's emphasis on maximum performance at all costs), diversification into the commercial world has proven difficult and largely. unsuccessful (although some firms have been successful in conversion). However, they allowed consolidations due to the shrinking of available business and the peculiarity of the defense market structure (a monopoly buyer and a small number of oligopolistic suppliers who fought fiercely for the few, rare and declining number of major procurements). 55 By the end of the decade, the financial condition of the defense industry was a growing concern.
Changes in Security Concerns
Globalization
The other more traditional argument for greater multinational considerations in the defense industrial structure is economic. The most notable of these was the aggressive acquisition program undertaken by BAE Systems (the dominant defense firm in the United Kingdom) in the United States. The firms were looking for markets that could help them maintain their existing production lines of the modern weapons built up for the cold war.
Outsourcing of Government Work
Early contractors in the Middle East combat zone numbered 65 (more than military and government personnel in the region), and nearly all of these contractors provided services (including food, housing, equipment maintenance, and logistical support). Since the United States is by far the largest of the world's defense markets, foreign defense companies want to have a presence in the US. $204 billion).
A final issue in this area is the citizenship of workers, even if the work is performed in the United States. In 2007, Business Week ranked the world's information technology companies, and only one of the top ten was based in the United States. In 2005, for example, the United States announced the sale of the GBU-12 (Paveway II) laser-guided bomb (with inertial navigation systems supported by the Global Positioning System) as the first US commercial sale of the bomb.
To achieve maximum joint effectiveness, their forces must be interoperable with those of the United States. There is no guarantee that a country that is currently an ally of the United States will not become an adversary in the future. Thus, state-of-the-art equipment supplied by the United States could end up being used against the United States.
The United States Government Accountability Office summarizes the need for change in US policies and practices.
National Security in the Twenty-First Century
This was the case with the anthrax attacks in the post office of the United States Congress. In the event of a chemical attack, people must get out of the area as quickly as possible so that they do not become infected. They believe that the country is guilty of the worst heresy imaginable - the separation of church and state and the maintenance of a secular society.
And with many of the world's poor countries (the vast majority of nations around the world), scarce resources (such as dwindling food supplies and water reserves during a period of drought) are even more pressing. In the commercial arena, the United States has an entire industry (advertising) that leads the world in getting people to buy things through a variety of advertising techniques (thus influencing their hearts and minds). The United States will engage in irregular warfare - in terms of the type of equipment used and the adversaries themselves (often small groups of non-nation actors, but organizationally globalized through information networks).
For hardware, continuous upgrading of the systems (via spiral development) using the best available technology (as proven) is the preferred alternative. First, the training function involves cooperation with the police and military of the countries where the United States is involved. Generally, having contractors in the combat zone supports the combatant's mission.
For example, is the military responsible, in any way, for the protection of non-military personnel. The agency and half of the general officers and senior positions in the navy and air force - were eliminated. However, they are responsible for almost all violent incidents that are reported in the media.
Characteristics of the Defense Industry in the Early Twenty-First Century
Even in the production of advanced fighter aircraft, only about 20 percent of the cost goes directly to the aircraft manufacturer. However, there are a limited number of sources of raw material (the main source is Russia). Another major concern at the lower levels of the defense industry is increased vertical integration.
For almost exclusively political and historical reasons (rather than military or economic reasons), much of the defense industrial base has been maintained in the public sector. Despite the politically attractive protectionist perspectives of many elected officials in the US 58. The advantage of a foreign option is also seen in the case of the United States' recent under-investment in helicopters.
In the defense world, most contracts are negotiated directly between a single buyer and a single supplier for an individual program. There is still disagreement about which part of the military should run the claims process. To do this, extensive system engineering and system architecture work must be done early in the development of the requirements process.
Then, the selection of the various elements within the system of the system is the responsibility of the government (with advice from the independent firm). To determine the realism of the offer, the government must conduct an independent cost analysis (ICA). The defense industry's relatively low profits depend on the government often assuming most of the risk (in essence, becoming a self-insurer).