The National Academy of Engineering was established in 1964 under the charter of the National Academy of Sciences as a parallel organization of outstanding engineers. The Institute of Medicine was established in 1970 by the National Academy of Sciences to provide the services of distinguished members of the relevant professions in the study of policy issues relating to public health.
Acknowledgment of Reviewers
Contents
Definition of the length scales and time scales of interest, 43 Evaluation of material behavior at high strain rates, 45 Investigating shock physics, 47. 4-13 Photographs taken by a high-speed camera (interframe times of 1 μs and exposure times of 100 ns) of the dynamic failure process in uncovered transparent AlON, 50.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
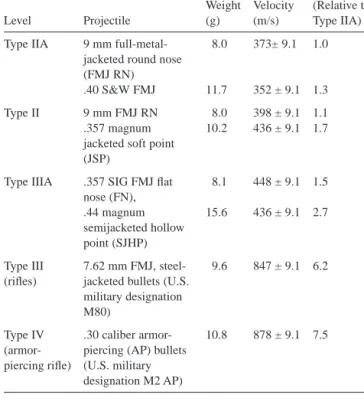
SAN poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) SAPI small arms protective insert SCS shear compression (test) SEM scanning electron microscope SiC silicon carbide.
Summary
The first element of the PMD initiative would be to develop a better fundamental understanding of the mechanisms of high-rate3 material deformation and failure in various protection materials, discussed in Chapter 3. The Department of Defense should develop a program of sustained investment in basic and applied research that will facilitate a fundamental understanding of the mechanisms of deformation and failure due to ballistic and blast events.
Overview
This accurately describes the problems encountered in the development of new protective materials, which are the focus of this study. A review and assessment of the current theoretical and experimental understanding of the main issues related to protective materials.

Fundamentals of Lightweight Armor Systems
Thus, the primary factor in jacket armor design is fiber selection. Army Research Laboratory, "A Review of Ceramic Armor Technology Development - Past, Present, and Future".
Mechanisms of Penetration in Protective Materials
Homogeneous plastic flow (4) is made clear by the deviation of the process roll lines from the horizontal. It is not understood how the material microstructure at this level (the nano-level) affects the deformation, localization and failure behavior of the material.

Integrated Computational and Experimental Methods for the Design of Protection Materials and Protection
Systems: Current Status and Future Opportunities
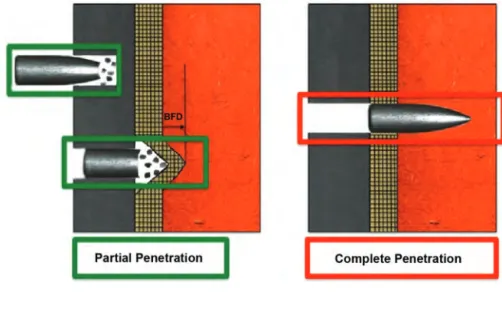
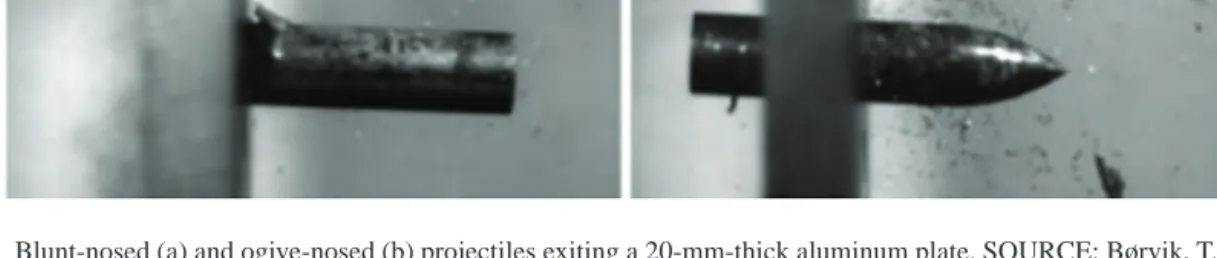
These simulations represent the state of the art in calculations for the ballistic performance of ceramic armor components. In the case of the cylindrical projectile, the full impact of the impact is felt immediately by the target. Most of the control phenomena operate on much smaller time scales (microseconds to nanoseconds).
In this section, state-of-the-art experimental methods capable of exploring various regimes in the length scale–. On the other hand, there are noticeable differences in the size of the fragments and the reaction of the tungsten projectile.
Lightweight Protective Materials
Ceramics, Polymers, and Metals
Because of the similarity of the tetrahedral bonding, SiC has a surprisingly wide variety of polytypes. By modifying the impact angle of the projectile, the ballistic performance of the ceramic can be improved. Modeling and experimental study of the influence of twist on the mechanical properties of high performance fiber yarns.
Fluctuations in the curve are an artifact of the experimental technique and do not represent material behavior. Controlling the mechanical impedance of the interlayer is therefore important in armor design.
The Path Forward
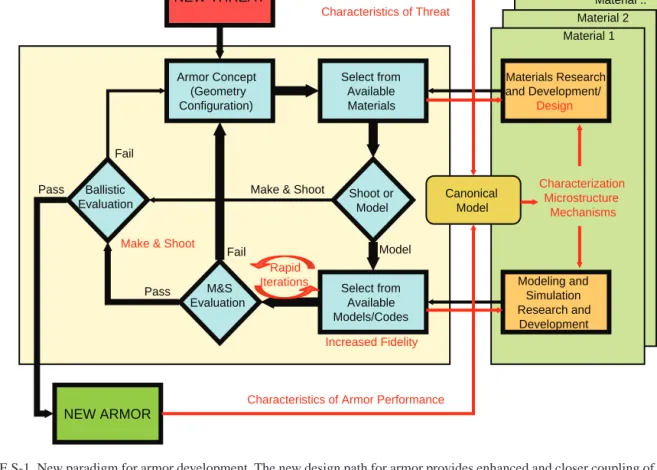
The design modeling and simulation of the material takes place before the longer iterations involving physical testing. The first element of the PMD initiative would be to develop a better fundamental understanding of the mechanisms of high-rate2 material deformation and failure in various protection materials, discussed in Chapter 3. The Department of Defense should develop a program of sustained investment in basic and applied research that provides a fundamental understanding of the mechanisms of deformation and failure resulting from.
The second element of the PMD initiative would be to advance and exploit the emerging computational and experimental methods capabilities discussed in Chapter 4. The third element of the PMD initiative is the development and production of new materials and material systems, characteristics and characteristics and performance can achieve the proven behavior in the modeling and simulation of the new armor system.
Appendixes
Appendix A
Background and Statement of Task
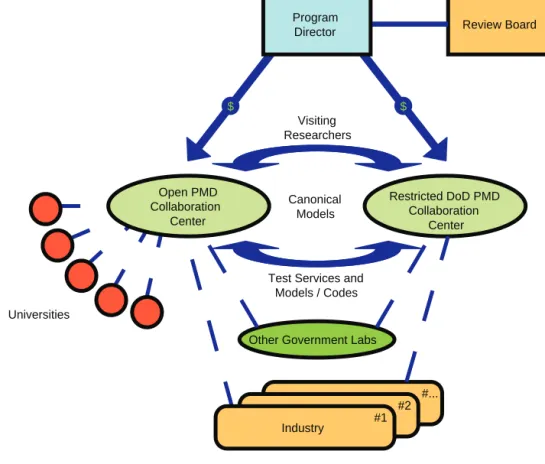
An ad hoc committee will conduct a study and report on military protective equipment to explore the possibility of a path forward for this equipment. Determine the key challenges and technical gaps for the development of the future generation of lightweight protective equipment for the military, aiming for valid multi-scale predictive simulation tools for performance and, conversely, protective equipment by design. Propose a way forward, including approach, organizational structure and team building, including processing, materials characterization (composition and microstructure), quasi-static and dynamic mechanical testing and model development and simulation and likely timescales for the military to deliver the next generation of protective materials.
Multi-scale modeling techniques to predict energy dissipative mechanisms (twinning, stacking faults, etc.) from atomic scales and bulk material response.
Appendix B
Biographical Sketches of Committee Members
He has served as a trustee of the American Ceramic Society and chairman of its Programs and Meetings Committee. He was an associate editor of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers Journal of Applied Mechanics and is currently the editor for the period 2002-2012. Association for Computational Mechanics, and an elected fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Ramesh is the director of the Center for Advanced Metallic and Ceramic Systems (CAMCS) in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Johns Hopkins University. Ramesh was the chair of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Johns Hopkins University in 1999-2002.
Appendix C
Committee Meetings
- 2010, WASHINGTON, D.C
- 2010, WASHINGTON, D.C
- 2010, ABERDEEN, MARYLAND
- 2010, WASHINGTON, D.C
- 2010, BECKMAN CENTER, IRVINE, CALIFORNIA
Chabalowski, Acting Director, Research and Laboratory Management, Office of the Deputy Assistant Secretary of the Army for Research and Technology/Chief Scientist. Barsoum, Manager, Blast Resistant Coating, Joint Enhanced Blast Resistance Coating Exploitation, Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration, Ships and Engineering Systems Division, Office of Naval Research. Goldwasser, Program Manager, Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency A National Lab Perspective on Protection Materials, Bruce Remington, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Army Applications of Magnesium Alloys: Past Lessons and Future Solutions Suveen Mathaudhu, Army Research Laboratory.
Objectives: Limited definitive information collection; reviewing the report writing process so far; go through the first full draft message; discussion of conclusions, recommendations and next steps.
Appendix D
Improving Powder Production
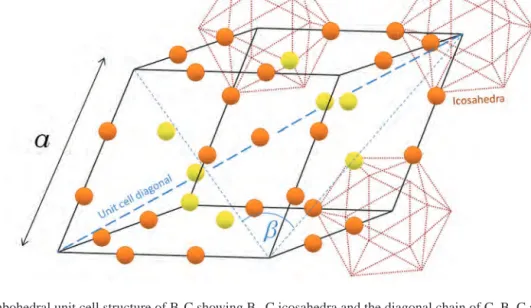
Armor ceramics make up less than 1 percent of the world market for high-purity SiC.7. Within the ceramic zone, both green SiC (>99 percent SiC) and black SiC (95–98 percent SiC) can be found, with metallurgical SiC (80–94 percent SiC) making up the rest of the reaction zone. Here, a water-cooled crucible is insulated with a packed wall of the mixed boron oxide and carbon precursors.
The carbothermal method is a very high temperature operation with large temperature variations across the crucible, and the stoichiometry of the boron carbide product is typically rich in carbon, usually B4-xC. The particle size of the calcined powder is reduced depending on specifications set by the end user.
Appendix E
Processing Techniques and Available Classes of Armor Ceramics
The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: A review of the spark plasma sintering method. The widespread use of SPS in the last decade was possible due to the availability of commercially built SPS systems. For example, the final shape of the armor product is created from a flat, hot-pressed part by grinding with diamond wheels.
A phonic crystal prevents the propagation of elastic waves if the frequencies of the waves fall within a band gap. The normalized bandgap width - the ratio of bandgap width to the central frequency of the gap - is a measure of the performance of the particular phonic crystal design.
Appendix F
High-Performance Fibers
After the successful commercial development of Kevlar in the 1970s, considerable research effort was devoted to the development of other rigid-rod polymers. The structuring mechanism of the rigid bar chains of Zylon and M5 fibers is very similar to the structuring mechanism of Kevlar and is quite different from that of the flexible chain-gelspun polyethylene (Dyneema and Spectra). Unlike liquid crystalline solution processing of rigid rod polymers and gel spinning of flexible chain polyethylene - both of which are processed from polymer solutions containing 85% to 95% solvent (which must be removed during fiber processing) - there is no solvent that must be removed when processing thermotropic liquid crystalline polymers.
The development of modern carbon fibers dates back to the 1960s with research carried out by Shindo in Japan, Watt in England and Bacon at Union Carbide in the US. Fiber tensile strength is limited by defects, residual stresses and structural inhomogeneities in the fibers.
Appendix G
Failure Mechanisms of Ballistic Fabrics and Concepts for Improvement
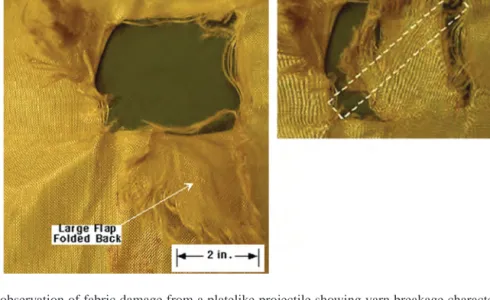
Yarn distance failure occurs in tests of both transverse load (perpendicular to the yarn direction) and cylindrical load (along the yarn direction). Remote yarn failure can be difficult to detect because broken fibers may be buried in the mesh of the fabric. Ranged yarn breakage does not affect the projectile load until the frictional force on the yarns decreases to a value that cannot tolerate additional ranged yarn breakage.
Since remote yarn failure involves yarns in a large area of the fabric target, it can significantly increase energy absorption. The wedge phenomenon occurs when the hole formed is smaller than the diameter of the projectile.
Appendix H
Metals as Lightweight Protection Materials
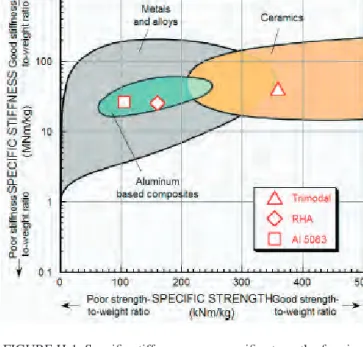
This material can be considered as an advanced alloy, a nanostructured material or a specific metal-matrix composite - its value lies in the use of all associated strengthening mechanisms. One of the more promising strengthening approaches appears to be the development of ultrafine-grained or nanostructured magnesium alloys through severe plastic deformation. Most commercially used MMCs are aluminum-based and ceramic-reinforced,7 and have been thoroughly researched.
The compressive viscoplastic response of an A359/SiCp metal-matrix composite and of the A359 aluminum alloy matrix. Thus, the stress-to-failure ratio increases as the depth of penetration increases.
Nondestructive Evaluation for Armor
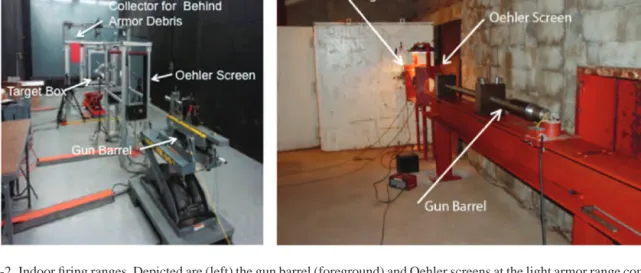
To date, XCT has proven to be the most effective at this task, as it can provide three-dimensional images of damaged areas. XCT can be performed on armor composed of multiple tiles and used to illustrate how this configuration reduces damage spread to surrounding areas. Because testing can be performed without changing the state of the sample, residual projectile particles can be visualized.
XCT provides excellent visualizations of material-induced damage and can map large compositional changes, but cannot provide the level of microstructural information possible through ultrasound spectroscopic analysis. There is clearly room for improvement: Damage and defect characterization can be made even faster and more robust, as many defects below a critical size are currently not detected.
Appendix J
Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites
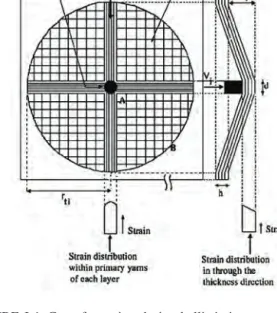
During cone formation, the stress is greatest along the middle primary threads in each layer of the composite. When the yarns and fabrics fail, the friction between the damaged laminates dissipates some of the kinetic energy from the projectile. They found that the resistance to friction depends on the shape of the projectile and that it increases with increasing thickness of the composite.
The properties of the fabrics, the surrounding matrix and the interfaces affect the overall performance of the laminates. Effects of glass fiber dimensions on the strength and energy absorption of the fiber/matrix interface under high loading rates.