Debt Investment at Amortized Cost
Debt investments held-for-collection and selling
However, at each reporting date, companies
Debt Investments—Held-for-Collection and Selling (HFCS)
Held-for-Collection and Selling (HFCS)
Illustration (single security): To apply the fair value method to these debt investments, it is assumed that at 31 December 2019 the fair value of the bonds is £105,000. The following illustration identifies the amortized cost, the fair value and the amount of unrealized gain or loss.
Sale of HFCS Securities
Illustration: Webb reports this realized loss in the “Other Income and Expense” section of the income statement.
Financial Statement Presentation ILLUSTRATION 17.10Reporting of HFCS
Debt Investments—Trading
A capital gain or loss is the net change in the fair value of a security from one period to another, excluding. On the acquisition date, Western Publishing recorded these trading securities at cost in the account titled Debt Investments. Companies have the option of reporting most financial assets at fair value, where all gains and losses related to changes in fair value are reported in the income statement.
The company must measure this instrument at fair value until the company no longer owns it.
Fair Value Option
If Hardy chooses the fair value option to account for this investment, it makes the following entry per December 31, 2019. Hardy uses the debt investment account to record the change in fair value as of 31th December. The unrealized gain or loss is recorded as part of net income even if it manages the investment on a hold-for-collection basis.
Hardy must continue to use the fair value method to record this investment until it is no longer owned.
Equity Investments
Equity investment represents
Holdings of Less Than 20%
IFRS allows companies to classify some equity investments as non-trading
Equity Investments—Trading (Income)
Equity
Investments
Trading
On December 31, 2019, Republic prepares an adjusting entry to record the decrease in fair value and record the loss as follows.
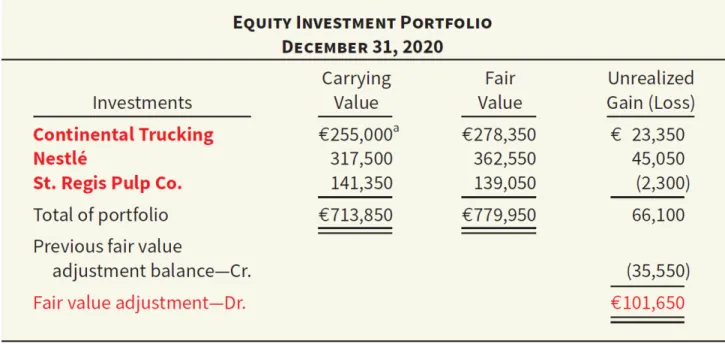
Companies report the unrealized holding gain or loss as other comprehensive income
Equity Investments—Non-Trading (OCI)
On December 20, 2020, Republika sold all of its common shares of Hawthorne Company and received net proceeds of EUR 22,500. An investment (direct or indirect) of 20 percent or more of the investee's voting shares should lead to the assumption that the investor has the ability to exercise significant influence over the investee in the absence of evidence to the contrary. In cases of "significant influence", the investor must account for the investment using the equity method.
Holdings Between 20% and 50%
Equity Method
Controlling Interest - When one company acquires a voting interest of more than 50 percent in another company
Holdings of More Than 50%
A company must evaluate each debt investment carried at amortized cost at each reporting date to determine whether it has suffered impairment - a loss in value such that the fair value of the investment is below its carrying value. The company accounts for the write-off as a realized loss, and it includes the amount in net income.
Impairment of Value
Other Reporting Issues LEARNING OBJECTIVE 4 Evaluate other major issues
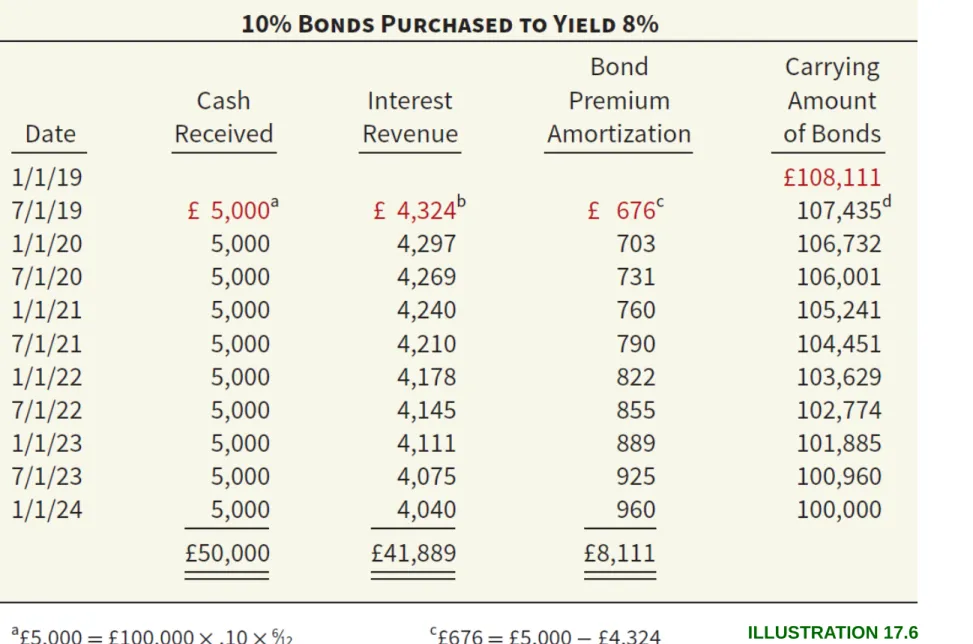
The investment has a term of four years, with annual interest payments of 10 percent, paid at the end of each year (the historical effective interest rate is 10 percent).
Impairment—Investment Measured at Amortized Cost
Investment Measured at Amortized Cost
If the impairment loss subsequently decreases, some or all of the previously recognized impairment loss will be reversed by a.
Recovery of Impairment Loss
Impairment—Debt Investments (HFCS)
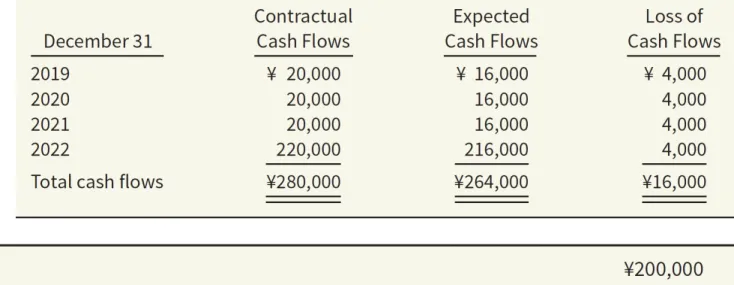
In this case, the third entry in Illustration 17.24 changes because the impairment loss of €30,000 is reported in the income statement, not in other comprehensive income. Assuming Alexander sells his debt investments on 1 January 2020 for €960,000 (its fair value at that time), the entries are as follows. What happens if Alexander decides to keep his debt investment and later finds that his credit risk on this investment has decreased by €15,000.
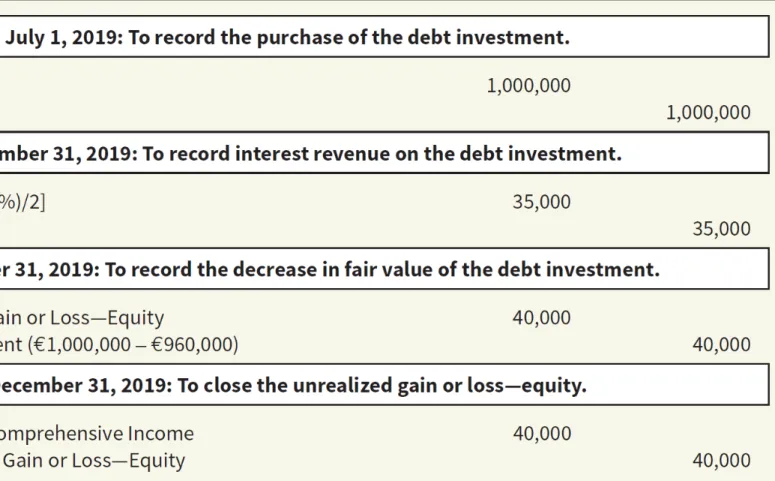
Recycling Adjustments
Reporting Issues
On June 30, Hinges sold a portion of the HFCS collateralized debt portfolio and realized a gain as shown. When a company sells securities during the year, double counting the realized gains or losses in. This double counting results when a company reports unrealized gains or losses in other comprehensive income in a prior period and reports those gains or losses as part of net income in current period.
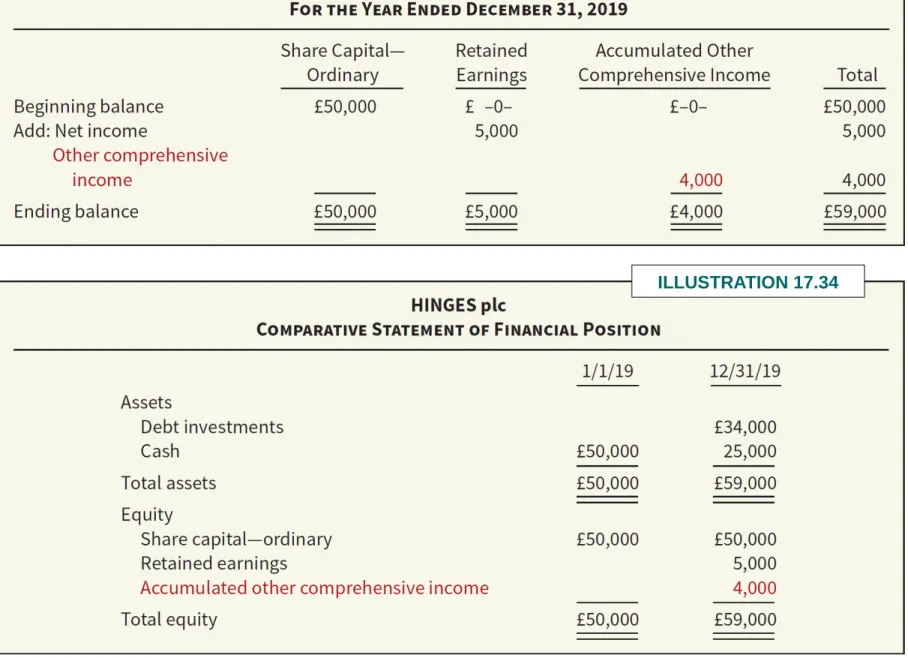
Reporting Issues Multi-Period Example
If Open reports net income in 2018 of €350,000, it presents a statement of comprehensive income as shown. The entry to transfer the unrealized holding gain—equity to accumulated other comprehensive income is as follows. This illustration shows the calculation of the change in the fair value adjustment account (Woods Co. investment only).
The accounting for the transfer of the unrealized holding loss – equity to the accumulated other comprehensive income is as follows. This reclassification adjustment can be made in the income statement, in the accumulated other comprehensive income or in a note to the financial statements. The IASB prefers to disclose the reclassification amount in accumulated other comprehensive income in the notes to the financial statements.
Transferring an investment from one classification to another
Transfers Between Categories
Illustration: British Sky Broadcasting Group plc (GBR) has a portfolio of debt investments that are classified as commercial; that is, debt investments are not held for collection, but are managed to benefit from changes in interest rates. Illustration: As part of the strategic planning process, completed in the fourth quarter of 2018, British Sky's management decided to move away from its previous strategy – which required active management. British Sky makes the following entry to transfer these securities to the classification held for collection.
Three types of derivatives
Defining Derivatives
APPENDIX 17A Accounting for Derivative Instruments
Who Uses Derivatives, and Why?
Basic Principles in Accounting for Derivatives
Derivative Financial Instrument (Speculation)
Intrinsic value is the difference between the market price and the predetermined strike price at any point in time. On January 2, 2019, the intrinsic value is zero because the market price is equal to the predetermined strike price.
Accounting for Derivative Instruments
Because there is some expectation that the price of Laredo stock will rise above the strike price over the life of the option. That is, the company can exercise the call option and purchase 1,000 shares of Baird Investment for $100 per share. On March 31, 2019, she records the increase in the intrinsic value of the option as follows.
In addition, it reports the call option at fair value and reports any gains or losses in income.
Differences between Traditional and Derivative Financial Instruments
Derivatives Used for Hedging
Fair Value Hedge
Illustration: As of December 1, 2019, Hayward Tire Fabricators has an inventory of 1,000 tractor tires, with a cost of €200 per tire. Hayward has built up an inventory of tractor tires, anticipating the demand for these tires in the near future. Until Hayward sells the tires, the company faces the risk that the value of its tire inventory will decline.
Hayward wants to hedge its exposure to declines in the fair value of its tire inventory (the inventory is pledged as collateral for one of its bank loans). Illustration: To protect against this risk, on January 2, 2020, Hayward locks in the value of its tire inventory by purchasing a put option to sell the tire at a fixed price. This put option (which . expires in nine months) gives Hayward the option to sell 4,000 pounds of rubber at $50 per pound, which is the current spot price of rubber in the market.
The following journal entry records the increase in the value of the put option to sell rubber, assuming the spot price for.
Cash Flow Hedge
The aluminum futures contract gives Allied the right and obligation to purchase 1,000 tons of aluminum at ¥1,550 per tonnes (amount in thousands). Assume that the price to be paid today for inventory to be delivered in January—the spot price—is equal to the contract price.
Instruments
Allied makes the following entry to record the increase in the value of the futures contract. Allied reports the futures contract in the statement of financial position as a current asset and the gain as part of other comprehensive income. Illustration: In January 2020, Allied purchases 1,000 metric tons of aluminum for ¥1,575 and makes the following entry.
Allied accumulates the gain on the futures contract in equity as part of other comprehensive income until the period in which it sells the inventory. Illustration: Because the effect of the expected transaction has now impacted earnings, Allied makes the following comment regarding the hedging transaction.
July 2020
Other Reporting Issues
Embedded Derivatives
Qualifying Hedge Criteria
Summary of Derivative Accounting
Comprehensive Hedge Accounting Example
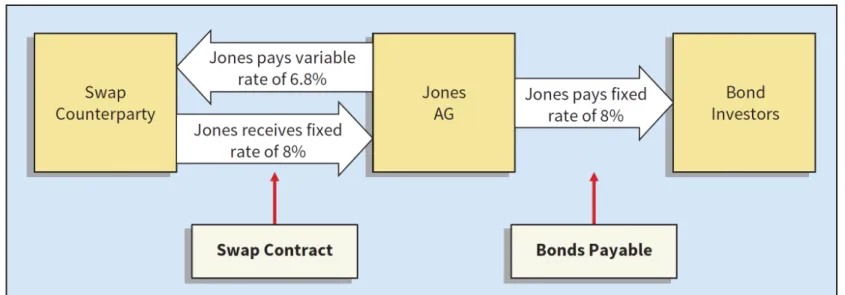
To protect against the risk of loss, Jones hedges the risk of falling interest rates by entering into a five-year interest rate swap contract. Assuming Jones enters into the swap on January 2, 2019 (the same date as the debt issuance), the swap at this time has no value. In addition, a market estimate shows that the value of the interest rate swap has increased by €40,000.
Because interest rates have fallen, the company records a loss and an increase related to its liability as follows.
Disclosure of Fair Value Information
Financial Instruments
APPENDIX 17B Fair Value Disclosures
Information on non-financial assets measured at fair value at amounts that differ from the assets' highest and best use. The correct hierarchy classification for items not recognized in the balance sheet but disclosed in the notes to the financial statements. GAAP has increased situations where investments are recorded at fair value, with gains and losses recorded in income.
GLOBAL ACCOUNTING INSIGHTS
GAAP and IFRS use similar classifications for financial assets: cash, loans and receivables, investments and derivatives. Held-to-maturity investments (US GAAP) and investments held for collection (IFRS) are accounted for at amortized cost. Amortized cost or fair value is used depending on the classification of the financial instrument.
GAAP and IFRS use the same test to determine whether to use the equity method of accounting, that is, significant influence with a general guideline of greater than 20 percent ownership. That is, the option to use the fair value method must be made upon initial recognition, the selection is irrevocable, and gains and losses are reported as part of income. GAAP classifies debt investments as trading investments, available for sale and held to maturity, IFRS classifies debt investments as held for collection, held for collection and sale (debt investments) and trading.
GAAP requires that all changes in fair value for all equity securities be reported as a component of income. IFRS requires changes in the fair value of non-trading equity securities to be reported as part of other comprehensive income. GAAP allows the option of fair value for all financial assets; IFRS allows the option of fair value if it reduces the accounting discrepancy.
At one time, both the FASB and IASB indicated that they believed that all financial instruments should be reported at fair value and that changes in fair value should be reported as part of net income. GAAP and IFRS are substantially converged, except for non-trading equity investments and the measurement of credit losses.
Copyright