There is a greater need to find out expression profiles of the genes involved in desaturation of fatty acid biosynthesis, nuclear genome content and chromosome number. There is a greater need to find out functional and structural profiles of the genes involved in desaturation of fatty acid biosynthesis, DNA content and chromosome number. Fatty acid (FA) biosynthesis in oilseeds is catalyzed by a set of condensing and desaturating enzymes located in plastids and endoplasmic reticulum (ER).

LITERATURE REVIEW
This complex converts the single C-C bond into a double C=C bond in the carbon chain of the fatty acid substrate. Structural and functional characterizations of the above-mentioned genes were determined by Davydove et al (2005) and Lindquvist et al (1996). Knowledge of haploid nuclear DNA content (C-value) is important for basic and applied studies related to genome organization, species relationships, gene expression analysis, and germplasm improvement (Bennett 1995).
The obtained colonies were counted and the number of total colonies was considered to check the efficiency of the transformation. Controls were provided by plating the negative control reaction on selective (D), and non-selective medium (E).

INTRODUCTION
SAD catalyzes the desaturation of stearoyl-ACP to oleoyl-ACP and plays a key role in determining the ratio of saturated fatty acids to unsaturated fatty acids in plants (Lindqvist et al 1996) and this ratio is closely related to many plant functions , especially. in relation to low temperature acclimation (Kodama et al 1995). Although there are other fatty acid desaturases in plants, the SAD-catalyzed insertion of the first double bond at position nine in the FA carbon chain is the most important desaturation for the transformation of the gel state to the liquid crystalline state of membranes (Los & Murata 1998). Many genes encoding SADs have been cloned from different plants (Carthamus tinctorius, Thunbergia alata, Ricinus communis, Solanum tuberosum) and the structure and functions of some SADs have been studied (Davydov et al 2005; . Lindqvist et al 1996).
Antisense expression of the Brassica rapa SAD gene in Brassica napus led to dramatically increased stearate levels (up to 40%) in the seeds of transgenic B. Conversely, when the SAD gene from Lupinus luteus was overexpressed in tobacco, the transgenic tobacco contained very high of oleic acid (up to 60%) compared to control plants (Zaborowska et al. 2002). These imply that SAD promises to alter the composition of plant fatty acids by introducing/manipulating the SAD gene.
Pongamia pinnata (L.) Pierre, an arboreal legume, is a member of the subfamily Papilionoideae and family Leguminasae, native to tropical and temperate Asia, including parts of India, China, Japan, Malaysia and Australia. Pongamia has received much attention due to the high content of its seed oil (Kesari et al 2012), which contains high amounts of C18 fatty acids, of which oleic acid and linoleic acid represent about 46 and 27.1 %, respectively. As a first step towards understanding the feedback mechanism and regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic gene expression in Pongamia, we isolated and characterized a cDNA containing the complete coding region of the fatty acid gene (PpSAD) and analyzed its expression in species different tissues. .
In this study, based on the crystal structure of Ricinus communis (PDB code 1AFR), which was reported in 1996 by Lindqvist, the 3D structure of Pongamia steroyl ACP desaturase (PpSAD) is therefore constructed theoretically, and then the binding site is also evaluated by homology modeling.
MATERIAL AND METHODS .1 Plant material and growth
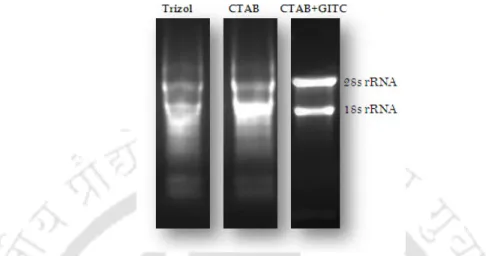
Equal intensity of rRNA bands was taken as a criterion for equal quantity and uniform quality of the samples. Physicochemical properties of the deduced protein were predicted by Protparam (http://www.expasy.ch/tools/protparam). Protein subcellular location was predicted by TargetP Server 1.1 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/).
For second strand synthesis corresponding to the fatty acid gene, namely SAD, gene specific primer was used and GAPDH primer as housekeeping gene was kept as standard to confirm the efficiency of the reaction. After real-time PCR, the absence of unwanted by-products was confirmed by automated melting curve analysis and agarose gel electrophoresis of the PCR product. Probes for DNA blot were generated through PCR amplification of the cDNA inserts using primers SAD-1F and 1R (described in Chapter-3 and Section 3.2.16).
Homology modeling combines the tools of computational chemistry and bioinformatics to calculate the atomic-resolution model of the target protein from its amino acid sequence and one or more experimental three-dimensional structures of related homologous proteins, i.e. In the present study, homology modeling studies were performed to derive the structure of the PpSAD protein; basically it consists of the following four steps: (i) template selection from database search, (ii) sequence alignment between target proteins and the model, (iii) model construction and refinement, and (iv) a final validation of the model (Liu et al. 2011). Secondary and 3D structures of the inferred protein were predicted by PredictProtein (http://www.predictprotein.org/) and Swiss Model, respectively.
The accuracy of the predicted model was examined by Ramchandran Plot obtained from the PROCHECK (Laskowski et al. 1993) and structural features were validated using various online server programs (PDBsum, VADAR, ModFold server, QMEAN server, SAVER and PDB2PQR Server ).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Domain-2 (63-391 amino acids), which is fatty acid desaturase involved in the end of the desaturation process, converting saturated fatty acid to unsaturated fatty acids (Figure 4.3B). Hydrophobicity plot analysis of deduced amino acid sequences of PpSAD and other SADs showed that these enzymes are likely to be water-soluble proteins (Figure 4.4). Subcellular localization of the deduced PpSAD amino acid sequence using the PSORT tool revealed that it was located in the chloroplast.
Physicochemical property predictions from the deduced amino acid sequence indicated that the chemical formula of PpSAD is C2006H3139N549O597S17, its molecular weight is 45.04 kDa, and its theoretical PI is 5.88. The expression pattern of the PpSAD gene in different tissues can provide essential information regarding the key role in fatty acid biosynthesis. Thus, quantitative analysis showed that the expression levels of PpSAD did not differ markedly between tissues, but showed constitutive expression levels.
To know the gene copy number of the PpSAD gene in the Pongamia genome, Southern hybridization was performed. The overlay of PpSAD on the template (1AFR) structure showed an RMSD of 0.796 Å, indicating that the overall tertiary structure of the model is very similar to its template. Validation of the PpSAD model was performed using various structure validation tools as mentioned in Section 4.2.8.
Expressed as the percentage of protein for which the calculated error value falls below the 95% rejection limit.
CONCLUSION
According to Heppard et al (1996), the gene showing a seed-specific expression pattern plays a predominant role in determining the polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) content of the seed storage oil. The expression pattern of the two genes was also examined in different tissues and during different stages of seed development. Probes for DNA/RNA blots were generated by PCR amplification of the cDNA inserts using primers PpFAD2-2F and 2R (Table 5.1), the amplification of PCR product with PCR reaction conditions described in Chapter 3, section 1.2 .16.
Alignment of the two deduced amino acid sequences revealed that PpFAD2-1 and PpFAD2-2 shared 83% identity (Figure 5.3). In particular, retrotransposons play a dominant role in nuclear DNA content differences, and most of the variation in plant nuclear DNA content can be attributed to their differential accumulation (Bennetzen 2007). Recent studies have shown that polyploidization resulted in better yields of biodiesel crops (Kanellos 2009).
An attempt was also made to see if there is any correlation between nuclear DNA content and chromosome number in five individuals of P. Nuclear DNA content was estimated by comparing the mean fluorescence intensity of the nuclei of the sample material with that of the reference standard and is obtained by multiplying the nuclear DNA content of the standard species by the ratio of their fluorescence intensities. Taking into consideration the minimum MFI shift of the standard (Z. mays), the nuclear DNA content estimated for internal pseudo-standardization, internal standardization was 2.58 pg and 2.29 pg, respectively (Table 6.5).
Combined processing of target and standard species can minimize but not completely eliminate the effect of inhibitors on the estimated nuclear DNA content. In the present research, a test for the presence of staining inhibitors clearly showed that Pongamia leaves contain compounds that bias the fluorescence of standard internal nuclei. Although the nuclear DNA content estimated in the antioxidant-supplemented buffer was higher compared to the unsupplemented one, we emphasized the best-fit curve factor in the internal standardization of P.
Drosophila (~175 Mb) using flow cytometry shows that the genome size in arabidopsis is ~157 Mb and thus ~25 % larger than the Arabidopsis Genome Initiative of ~125 Mb. Clarindo WR, Carvalho CR (2009) Flow cytometric analysis using SYBR Green I for genome size estimation in coffee. Dolezel J, Greilhuber J, Lucretti S, Meister A, Lysak MA, Nardi L, Obermayer R (1998 ) Plant genome size estimation by flow cytometry: Inter-laboratory comparison.
The effects of nuclear DNA content (C-value) on the quality and utility of AFLP fingerprints. Flavell RB, Bennett MD, Smith JB, Smith DB (1974 ) Genome size and the proportion of repeated nucleotide sequence DNA in plants. Galbraith DW, Lambert GM, Macas J, Dolezel J (1998) Analysis of nuclear DNA content and plody in higher plants.
Jedrzejczyk I, Sliwinska E (2010) Leaves and seeds as materials for flow cytometric genome size estimation of 11 Rosaceae woody species containing DNA staining inhibitors. O'Brien IE, Smith DR, Gardner RC, Murray BG (1996) Flow cytometric determination of genome size in Pinus. Pingzhi Wu et al (2013) Functional characterization of two microsomal fatty acid desaturases from Jatropha curcas L.
Thiem B, Sliwinska E (2003) Flow cytometric analysis of nuclear DNA content in cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus L.) in vitro cultures.
PUBLICATIONS
13th Indo-US Workshop on "Applications of Flow Cytometry in Plant Genomics and Nanotechnology" at IIT Guwahati, from 8 to 10 October, 2012. Characterization of a stearoyl-acyl carrier protein desaturase gene from potential biofuel plant, Pongamia pinnata, National conference on SCIENCE OF OMICS FOR AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTIVITY: FUTURE PERSPECTIVES. Under the auspices of Society for Plant Biochemistry & Biotechnology, New Delhi, pp 181 (Awarded as Young Scientist).
కోట సతీష్, బి మోహన సుబ్రమణియన్, ఆది మూలం రమేష్, నీరుజోగి హనుమంత రావు, రాజన్ శ్రీరామన్ మరియు VA శ్రీనివాసన్ (2009). పొంగమియా పిన్నాట (ఎల్.) పియర్ యొక్క అభ్యర్థి ప్లస్ ట్రీస్ (CPT)లో క్యారెక్టరైజేషన్, ఉత్తర గౌహతి నుండి బహుముఖ పప్పుదినుసు.



![Table 3.2: CTAB-GITC buffer composition [Modified buffere (Cheng et al 1993)].](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/azpdfnet/10495952.0/56.918.153.735.759.1026/table-ctab-gitc-buffer-composition-modified-buffere-cheng.webp)