It is hereby certified that the work included in the thesis entitled “Effectiveness of Central Bank intervention in the foreign exchange market: evidence from India” submitted by Topunuru Kaldhar (LA12M1006) in partial fulfillment of the degree of Master of Philosophy in the Department of Liberal Arts. , Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, is a record of genuine research work done by him under my supervision and guidance. The first objective is about analyzing the effectiveness of the RBI's intervention on the exchange rate level and volatility.

INTRODUCTION
- INTRODUCTION: Historical perspective of central bank intervention and its relevance
- CENTRAL BANK INTERVENTION: Definition
- Objectives of central bank intervention
- Kinds of intervention
- CENTRAL BANK INTERVENTION IN INDIA
- Objectives of central bank intervention in India (RBI)
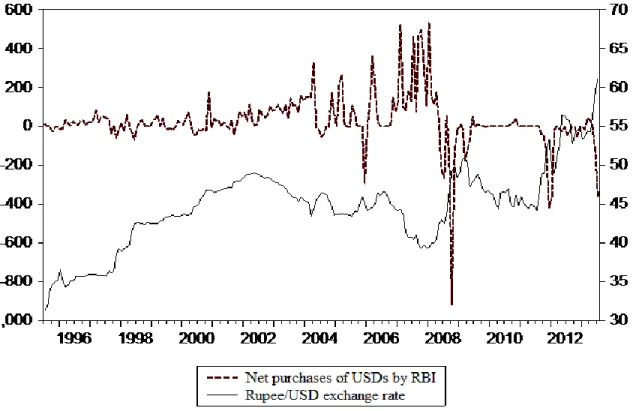
- Reserve bank of India intervention trends
- Research Issues
- Organization of thesis
Central banks pursue intervention with specific goals and objectives to influence the exchange rate in the foreign exchange market. This allows the basic condition of supply and demand to determine exchange rate movements in the foreign exchange market.
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
INTRODUCTION
THE MECHANICS OF CENTRAL BANK INTERVENTION
- Channels of influences
Central bank intervention is said to be sterilized, when a change in the NFA does not lead to a change in the monetary base. Central bank intervention affects the exchange rate and this can be explained through different channels.
EMPIRICAL LITERATURE
- Central bank intervention, exchange rate level and volatility: Empirical literature
- Asymmetric impact of central bank intervention on the exchange rate level and volatility
- Central bank intervention in the Indian context
In the analysis of the sub-sample period, the intervention turns out to have a mixed impact on the exchange rate level and volatility. The empirical results show that there is no effect of the simultaneous intervention on the exchange rate. Also, this study finds that there is no long-term effect of intervention in exchange rate movements.
Furthermore, it also finds that intervention leads to an increase in exchange rate volatility in the foreign exchange market. Some of the recent and notable studies analyze the asymmetric impact of central bank intervention on the exchange rate level and volatility of the foreign exchange market. Asymmetric effect implies that buying and selling have different influence on the exchange rate level and volatility.
Thus, the study finds that RBI intervention is not effective in affecting the exchange rate level. The study also found that higher exchange rate volatility leads to aggressive RBI intervention. Using GARCH, this study finds that RBI intervention is ineffective in affecting the level of the Rupee/USD exchange rate.
However, the net purchases of US dollars lead to a decrease in exchange rate volatility in the foreign exchange market. This study suggests that RBI intervention is not an effective instrument to cushion the exchange rate.
RESEARCH GAP
By applying OLS and Granger causality tests, the study finds that RBI intervention is not effective in stabilizing the exchange rate level and concludes that intervention is insufficient to move the exchange rate in a desired direction. In addition, the causality test result indicates that RBI intervention has no causal relationship with monetary variables and exchange rate. Similarly, intervention causes changes in the level of foreign exchange reserves. 2003) makes an attempt to estimate the impact of RBI intervention on the exchange rate for the period January 1993 - March 2002.
However, these studies did not address issues related to the asymmetric effect of the intervention on the exchange rate. However, it is established from the literature that there can be asymmetric effects related to purchases and sales on the level and volatility of the exchange rate (see Frenkel et al, 2004; Guimaraiesa and Karacadag, 2004; Lahura and Vega, 2013; and Domac and Mendoza, 2004). Therefore, it can be argued that the available studies in the Indian context have not attempted to address the asymmetric effect of RBI intervention on the level and volatility of the exchange rate by disentangling the effects of sales and purchases.
In the Indian context, there is a possibility of asymmetric impact of intervention in the adjustment process of the Rupee/USD exchange rate and in the limitation of exchange rate volatility. Further, this argument is supported by Prabheesh et al. 2009) that the RBI follows undervalued exchange rate policies against the US dollar to maintain export competitiveness. This study thus examines the asymmetric effect of intervention on the exchange rate level and volatility.
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
Changes in exchange rate (forward) changes, intervention, Monday effect, macroeconomic announcement, interest rate changes. 10 Fatum (2008) Event analysis Change in exchange rate, intervention, Co-movements of USD coordinated intervention 11 Chang and Taylor GARCH Exchange return, intervention and. Exchange rate returns, net purchase and sale intervention dummies, small and large intervention variable 15 Laura et al.
EGARCH Intervention, selling and buying intervention , Signal dummy (signal on exchange rate policy, ON (intervention impact on the money market) BRADY (Brady bond yield).

EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
INTRODUCTION
EMPIRICAL MODEL
Similarly, ht stands for exchange rate volatility and is the parameters to be estimated and is intercepted. The measurement of the variables and the expected theoretical relationship between the exchange rate and its determinants are discussed below. An increase in exchange rate returns indicates depreciation and a decrease indicates appreciation of rupee against the US dollar.
Similarly, net purchase intervention is expected to reduce exchange rate volatility. According to the theory of relative purchasing power parity, a change in the inflation rate compared to trading partner countries will cause a change in the exchange rate, i.e. a higher difference in the inflation rate causes the domestic currency to depreciate, and a lower difference in the inflation rate causes the foreign currency to appreciate. exchange market. This means that higher net FII inflows lead to an appreciation of the foreign exchange rate and lower net FII inflows lead to a depreciation of the exchange rate in the foreign exchange market.
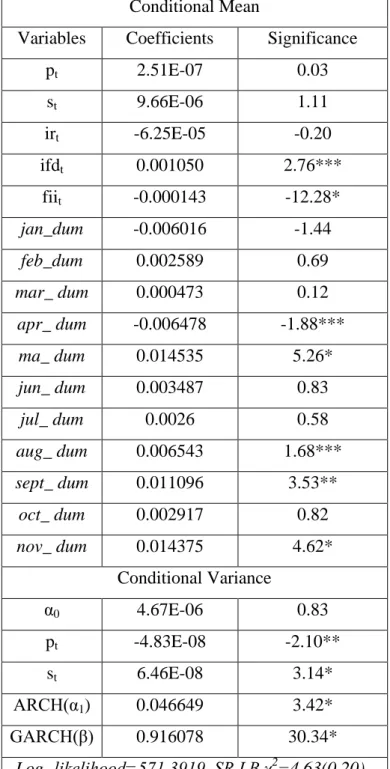
In the second model, our main focus is to analyze the asymmetric impact of RBI intervention on the Rupee/USDs exchange rate level and volatility. Therefore, purchases (pt) are positively and sales (st) are negatively related to exchange rate returns in the level equation. In the case of volatility, both purchases and sales are expected to moderate the volatility of the exchange rate in the foreign exchange market and thus a negative relationship between ht and st, and ht and pt is expected.
ECONOMETRIC METHODOLOGY
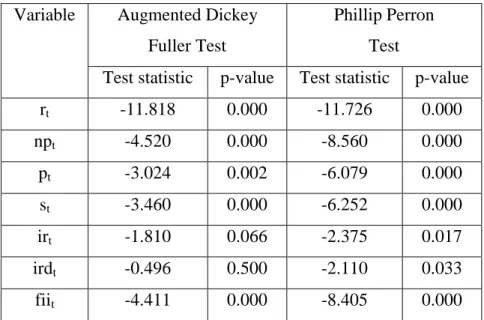
- Unit root test or test of stationarity
In the case of Philips and Perron unit root tests, this test is similar to ADF tests. Equation (3.9) is the variance equation, which shows that the conditional variance ht depends on the mean value ω and the information about the volatility from previous periods. The magnitude and significance of αt-1 indicates the presence of the ARCH process or volatility clustering in the series.
The important aspect of ARCH effect is that ARCH effect presence in the time series results from the dependence caused by its second movement not from the serial correlation of the error term (linear relationship). To ensure that >0, parameters in Equation (3.10) must also be bound by the following constraints: >0, >0 and >0, Conditional Variance Equation, is the conditional variance because it is one that is one period ahead . estimate for the deviation based on any previous information. This conditional variance depends on a weighted function of a long-term mean value and one lagged value of squared residuals, i.e. information about volatility observed in the previous period and one period lagged value of the conditional variance.
This means that the conditional variance cannot be influenced only by the size of innovations and by past values of the conditional variance. For the GARCH process to be stationary, it is necessary that αi+βi < 1wich. Furthermore, there is one more point worth mentioning: if there is a larger value for the GARCH (βi) parameter, there is a higher degree of autoregressive persistence in the conditional volatility or long memory and a larger impact of errors on the conditional volatility. In the conditional volatility equation (3.12), the conditional volatility is a function of lagged squared residuals and lagged squared conditional variance under additional interventions.
EMPIRICAL RESULTS
- Descriptive Statistics
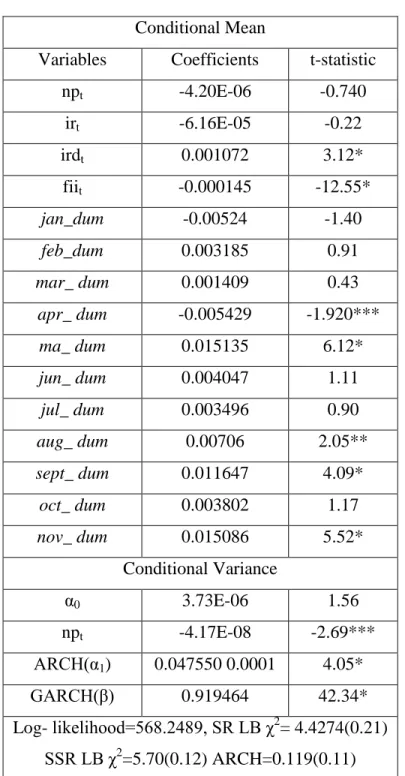
- GARCH Results
This means that the level of the exchange rate is not explained by intervention in the foreign exchange market. Similarly, the interest rate (irt) is also found to be statistically insignificant in explaining the level of the exchange rate. This means that higher FII results in lower exchange rate returns ie. causes the rupee to appreciate against the US dollar.
The second part of Table 3.3, the conditional variance, shows the effect of the intervention on exchange rate volatility. This provides support for the effectiveness of the intervention in reducing the volatility of the rupee/USD exchange rate. The results show that purchases (pt) and sales (st) are not statistically significant in the exchange rate level equation.
This indicates that neither purchases nor sales of US dollars by the RBI determine the Rupee/USD exchange rate in the Indian foreign exchange market. However, in the case of exchange rate volatility, we found that the RBI intervention is effective in reducing the volatility. This indicates that RBI effectively reduces the volatility of the exchange rate during the period of exchange rate appreciation of rupee against the US dollar in the foreign exchange market.

SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
The results based on model I show that the RBI intervention is not effective in influencing the level of the rupee/USD exchange rate. However, in the case of exchange rate volatility, the study found that RBI intervention is effective in reducing volatility. Further, the empirical findings show that buying intervention significantly reduces volatility while selling intervention significantly increases exchange rate volatility.
This means that the existing size of the intervention is not sufficient for the target level of the exchange rate. Behera, H.K., Narasimhan, V., and Murty, K.N., (2006), “The Relationship Between Exchange Rate Volatility and Central Bank Intervention: An Empirical Analysis for India.” Paper presented at the Sixth Annual IGIDR Conference on Money and Finance in the Indian Economy . Consequences of publicly announced and covert interventions for the euro exchange rate and its volatility”, Journal of Policy Modeling, vol.26, pp.661–.
Frenkel, M., Pierdzioch, C., and Stadtmann, G., (2005), "The Foreign Exchange Intervention of the ECB", Journal of International Money and Finance, (17), pp. Goyal.A., and Arora .S.,(2012), “The Indian exchange rate and the action of the central bank: an analysis of EGARCH”, Journal of Asian Economics, vol. Kappler M., Reisen, H., Schularick, M., and Turkisch,.E., (2011), "The Macroeconomic Effects of Large Exchange Rate Appreciations", OECD Development Center Working Papers, 296.