Solid medications can be administered orally as powders, pills, capsules, capsules, or tablets. These dosage forms contain an amount of drug that is administered as a single unit and are collectively known as solid unit dosage forms, even in the case of prolonged action. preparations that technically contain the equivalent of several normal doses of the drug. The stringent formulation requirements of modern drugs, the many advantages of tablet and capsule drugs, together with expanded health services and the need to engage in large-scale economic production have led to a steady decline in the prescription of powders and pills. Tablets and capsules currently account for a good two-thirds of the total number and cost of medicines produced worldwide. It is the most popular pharmaceutical form and 70% of all medicines are dispensed in tablet form. Repeat-acting tablet: Sugar-coated tablets or multi-compressed tablets are used for this purpose. The core of the tablet is usually coated with shellac or a gastro-resistant polymer, so that it does not release its active ingredient in the stomach, but in the intestines.
Diluent: Diluents are fillers used to make the required bulk of the tablet when the drug dose itself is insufficient to produce the bulk.
Surface area: Dissolution of a drug depends on surface area of powder materials or granules. The most common method for determination of surface
Strength & Friability: After formation of granules these are used for tableting
It is the maximum angle between the surface of a pile of powder and the horizontal plane when powder is allowed to flow freely from a certain height. Powder or granulation is allowed to flow through the hopper until the top of the conical pile just touches the tip of the hopper. Uncovering and lamination: Total or partial loss of top and bottom crowns on a tablet from the main body is called uncovering.
Separating a tablet into two or a tablet from its main body is called capping. Picking & Sticking: Surface materials of a tablet that stick to the punch and are removed from the tablet surface are picking. When sticking occurs, additional force is required to overcome the friction between the tablet and the die wall during ejection.
Mottling: It is an uneven distribution of colors on a tablet with light and dark areas on the tablet surface.
Mottling: It is an unequal distribution of colors on a tablet with light and dark areas on tablet surface
The extent to which the material in the matrix has been compressed can be estimated from the relative volume (Vr), relative density (Pr) or porosity of the tablet. Multi-station presses are called rotary because the tablet machine head, which holds the upper punches, dies and lower punches, rotates. The part of the head that holds the upper and lower punches is called the upper and lower turrets, and the part that holds the dies is called the cutter table.
The tablets hit the sweeping blade attached to the front of the feed frame (A) and slide down the chute into the hopper. This will give the percentage of cavity volume that will be occupied by the active ingredient 4. The powders are compressed and occupy the size of the slot formed in the punch.
The part of the head that holds the upper and lower punches is called the upper and lower turrets, and the part that holds the dies is called the die table. After compression, the upper punches are retracted by a cam to raise the upper punch (H) and the lower punch by a cam (I) that raises the tablet above the surface of the dies. The tablet hits the sweep blade attached to the front of the feed frame and slides down to the receiver.
General Appearance: The general appearance of a tablet, its identity and general elegance is essential for consumer acceptance, for control of lot-to-lot uniformity and
These powders would be properly mixed and compressed into tablets using the same process as chewable tablets. Multi-station presses are called rotary because the machine head that holds the upper punches, dies and lower punches rotates. As the head rotates, the tablet granulation flows from the hopper through the feed frame into the dies.
At the start of a compression cycle, granulation is discharged from the hopper into the feed frame (A), which has several interconnected compartments. These spaces spread the granulation over a large area to give time to the dies (B). Pull the cam (C) down, bringing the lower pistons to the bottom of their vertical travel, allowing the die to the comb (E), which reduces the filling in the molds to the desired amount. A wiper blade (D) at the end of the feed frame removes excess granulation and backs it into the front of the feed frame.
Then the lower punch moves over the lower compression roller (F) and the upper punches ride under the upper compression roller (G). The upper punch enters the dies a fixed distance, while the lower punches are raised and compact the granulating material in the dies. To control the upward movement of the lower punches, the height of the pressure roller is changed. At the same time, the lower punch enters the lowering cam (C) again and the cycle is repeated.
Organoleptic properties: Color distribution must be uniform with no mottling
Hardness and Friability: Tablet requires a certain amount of strength or hardness and resistance to friability to withstand mechanical shakes of handling in
By breaking the tablet between the second and third fingers with the thumb acting as a fulcrum. In this test the tablet is placed between two anvils, force is applied to the anvils and the crushing force that just causes the tablet to break is recorded.
Drug Content and Release
The Tablet passes the test if 9 of the 10 tablets must contain no less than 85% and no more than 115% of the labeled drug content and the 10th tablet must contain no less than 75% and no more than 125% of the labeled content . If these conditions are not met, the remaining 20 tablets can be tested individually and none may fall outside the 85 to 115% range. To test for disintegration time, one tablet is placed in each tube and the basket rack is placed in a 1-L beaker of water, simulated gastric fluid, or simulated intestinal fluid at 37 ± 20 C so that the tablet remains 2.5 cm below the surface. liquid on their upward motion and no closer than 2.5 cm from the bottom of the cup on their downward motion.
Allowing the tablets to float can be prevented by placing perforated plastic discs on each tablet. According to the test, the tablet must disintegrate and all particles must pass through the 10 mesh screen within the specified time. Device-1: A single tablet is placed in a small wire mesh basket attached to the bottom of the shaft and connected to a variable speed motor.
The motor is adjusted to rotate at the specified speed and a sample of the fluid is taken at intervals to determine the amount of drug in the solutions. The dosage form is allowed to sink to the bottom of the flask before stirring. Test tolerance is expressed as a percentage of the labeled amount of drug dissolved within the time limit.

Stage 1: Six tablets are tested and are acceptable if all of the tablets are not less than the monograph tolerance limit (Q) plus 5% if fail
Stage 2: Another six tablets are tested. The tablets are acceptable
Small amounts of dust powder may be added to reduce stickiness and cohesion of the tablets during the drying stage. The cycle of alternating wetting and drying is continued to build up a layer of the required properties. This stage of the process is continued until the tablets have a rounded appearance and the edges are well coated.
Enteric coatings resist the acidic conditions of the stomach, but are readily dispersed in the nearly neutral fluids of the small intestine. The composition of fluids in the gastrointestinal tract is not constant, but varies over time and from person to person. Only one of the carboxyl groups of phthalic acid is attached to cellulose, the other is free for reaction.
In the case of gastro-resistant tablets, efficacy is determined by the thinnest part of the film, and for reproducible properties between and within batches, the coating must be of known uniform thickness. The coating time for an 85-kilogram batch of tablets (90 minutes) is half the time required by the corresponding manual process, and the coating weight is reduced and more uniform. Programmed control of coating composition, spray application and drying air flow is provided at each stage of the process.
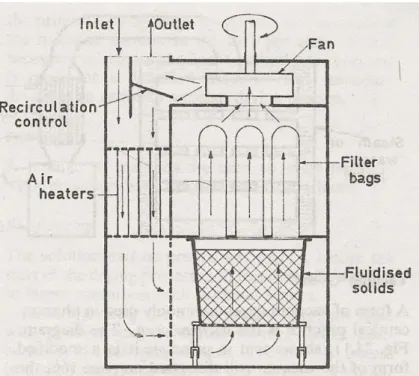
Fluid-Bed Coating
Compression Coating
The spring-loaded arms of the transfer unit engage with small collars on the upper turret to ensure accurate ejection of the core tablet into a cup equipped with a free-sliding weighted piston. Next, the cup passes over a 'bridge' where dust is removed to prevent contamination of the coating granules and then engages with the collar on the upper turret of the coating press. As the lower punch descends, the tablet is pushed out of the cup into the center of the lower fill of coating granules by the action of the weighted piston.
The cavity is then filled with granules for the sides and top of the coating, which are bonded to the core by compression. The surface of a soft tablet made of large granules is somewhat porous and provides a good 'key' for coating adhesion. The gap between the core and the cover wall should be at least 0.13 cm to facilitate the uniform deposition of coating grains around the edges of the core tablet and thus to ensure adequate coating strength.
Also for these reasons, the grain size should not exceed a quarter of the thickness of the skirting. Provided the edge thickness requirements are met, the coating weight is maintained with considerable accuracy and can vary over a wide range. With a smaller cylindrical insert, the core stream rises in the center of the device along with a spray mist applied in the middle of the bottom.