Fears of a global recession, coupled with high levels of youth unemployment, have brought apprenticeships back on the policy agenda. It is recognized that countries with well-established apprenticeship systems tend to be better at managing youth school-to-work transitions and have lower youth unemployment rates. In this context, the Korean government has paid much attention to the apprenticeship system as a way of revitalizing youth employment and effectively linking skill development with skill application.
The Korean Ministry of Employment and Labor (KMOEL) established the apprenticeship system in 2013 and has expanded it with a goal of accommodating 120,000 apprentices by 2022. As a public research institute on vocational training policies, the Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education and Training (KRIVET) publishes this book with the support of the Korean Ministry of Employment and Manpower and Human Resource Development Korea (HRD Korea), with a view to. The first and second chapters provide an overview and current state of the Korean apprenticeship system.
The development and operation of the apprenticeship program are described in more detail in the third chapter. It is hoped that this book will help international readers get a bigger picture of our apprenticeship system and provide practical implications for improving their apprenticeships.
Background of Korean Apprenticeship
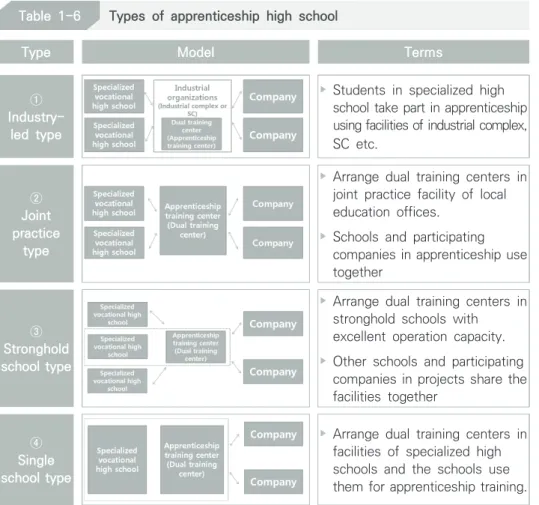
Types of Korean Apprenticeship
Governance and Finance of Korean Apprenticeship
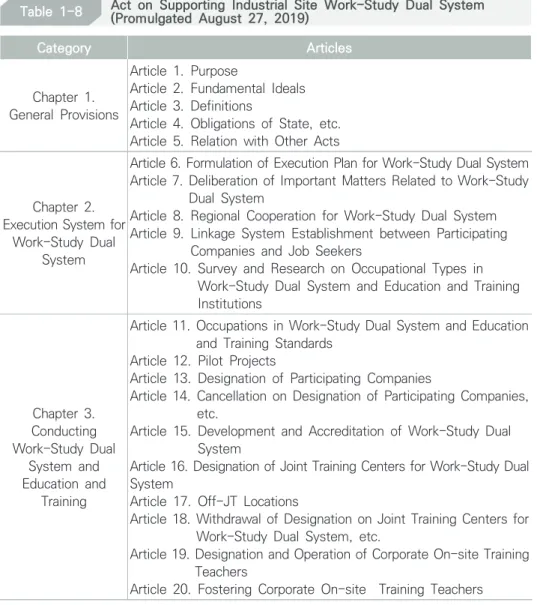
Since the pilot operation of nine schools in 2015, the work-study dual system of industry-academy has. The number of schools participating in IPP-type work-study dual system continued to increase from 13 schools in 2015 to 38 schools in 2019. Later in March 2019, the "Act on Support of Industrial Site Work-Study Dual System" the subcommittee of the standing committee as well as the general meeting.
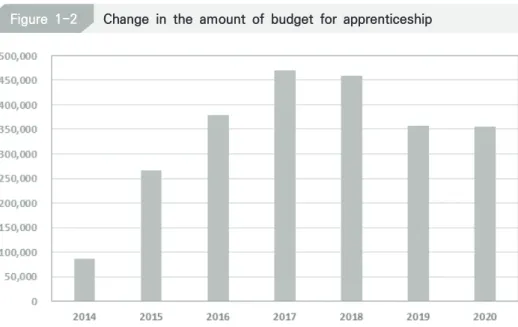
The implementation of the law is expected to greatly contribute to the development of the work-study dual system and stability of the system. Survey and research on occupational types in work-study dual system and education and training institutions. From 2018, when the system began to stabilize, the budget for work-study dual system projects began to decrease somewhat, with records of KRW 459.841 million.
Support is provided for the cost of developing Dual Work-Study System training programs and learning tools and pays for up to three occupations per training course for each. Subsidies are provided for the cost of activities provided by corporate teachers in the field conducting Dual Work-Study Training, administrative management and counseling of training employees, etc.

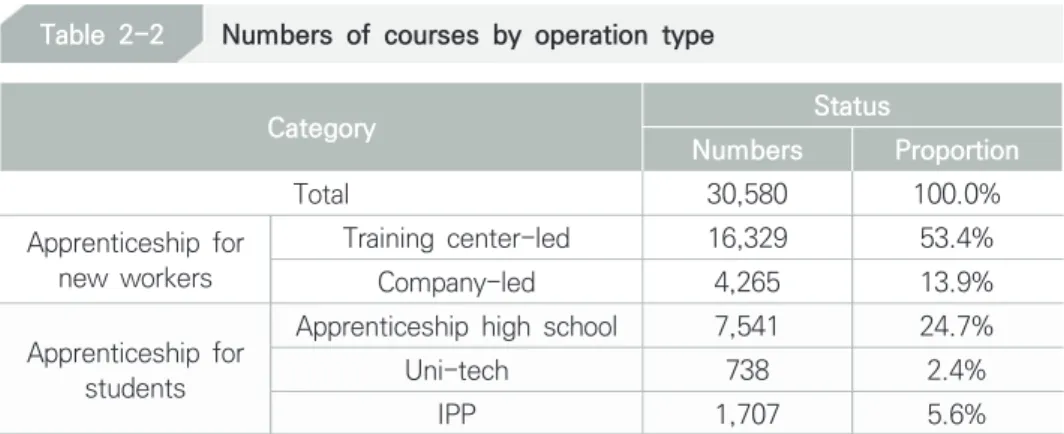
Current Status of courses
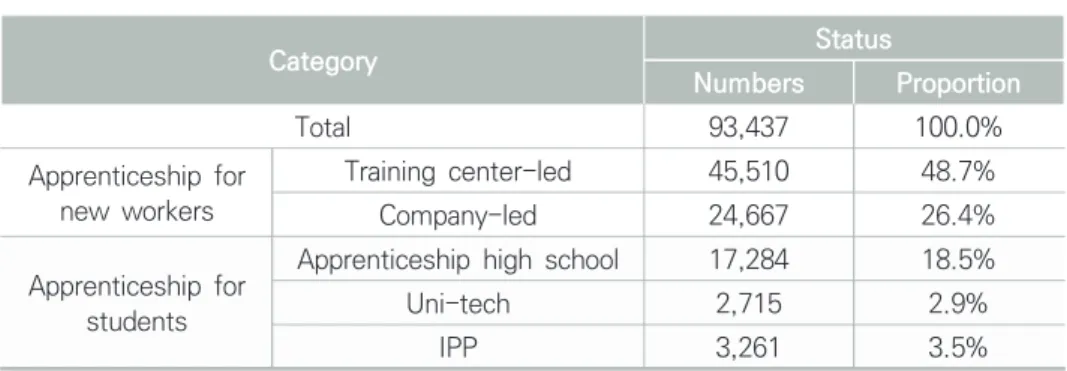
Current Status of Apprentices
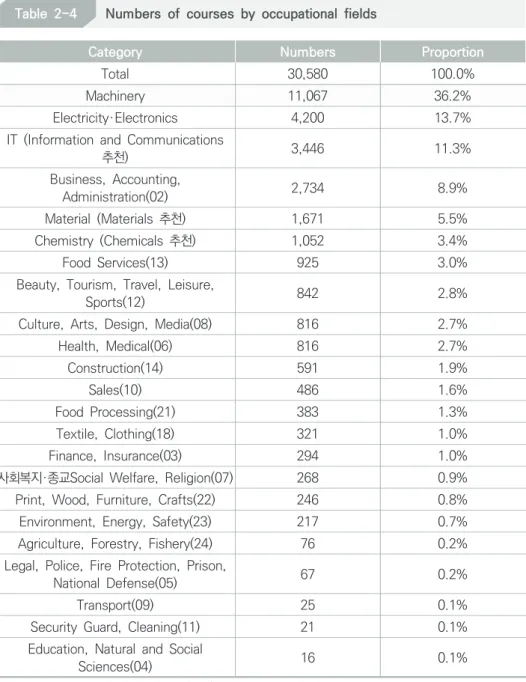
training courses are provided in SMEs with less than 300 employees, and specifically 18,586 training courses are offered at small companies with less than 50 employees, which accounts for 60.8% of the total. On the other hand, there are only 526 training courses (1.7%) offered in large companies with more than 1,000 employees. The occupational types with the most training are in the machinery sector, of which 11,067 of the total 30,580 training courses are in the machinery sector, accounting for 36.2%.
After the machinery sector follow electricity and electronics (13.7%), information and communication (11.3%), business, accounting and administration. Professional areas are classified according to the NCS classification. Apprenticeships for new employees involve apprentices in the training center-led type of apprenticeship programs, while apprenticeships involve apprentices as the company-led type. In terms of the demographic distribution of the apprenticeships, the participants are male and only female apprentices participate in such programs, indicating that men are more involved in the apprenticeships than women.
A large proportion of apprenticeship participants are either specialized vocational high school graduates or master's high school graduates, which represents apprentices. In addition, individuals with university and higher education have joined apprenticeship programs.

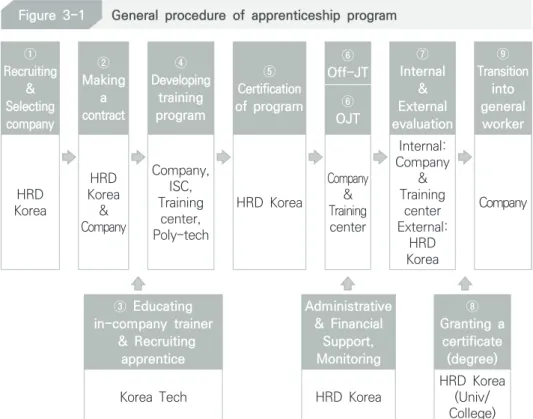
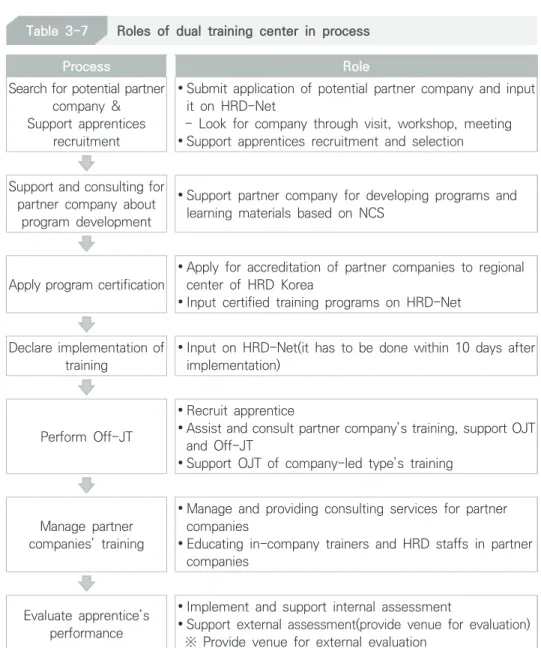
General Procedure
Selecting Company and Training Center
Development and Verification of Apprenticeship Program
In-company Trainer & HRD Staff
Selection and Treatment of Apprentices
Operation of OJT & Off-JT
Internal & External Evaluation
Monitoring & Consulting
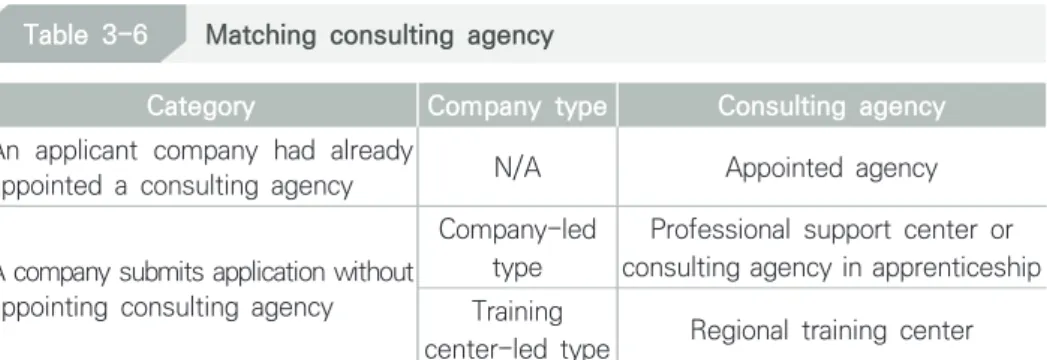
Second, in the "finalization of the agreement" stage, the selected companies enter into an apprenticeship training contract with the regional branch of HRD Korea. Currently, most of the dual training centers are College, Polytechnic and Industrial Skills (ISC) Apprenticeships. The selection standards for the dual training center are as follows; a) have the will to do business, b) have the business ability, c) meet the conditions regarding the qualifications for application, d) have the organizational ability, e) be suitable for training, f) have the training infrastructure. Source: Ministry of Employment and Labor (MOEL) & Korea Human Resource Development Service (HRD Korea) (2017). The main factors that will be checked include a) the quality of the program, b) the standardization of the program according to the type of job and level, c) the state of competence of the company, d) the applicability of the NCS.
⑥ The company must assign appropriate duties and tasks, after taking into account the student's physical ability. ② The reason, type and process of the disciplinary measure is applied according to the company's employment rules. Apprentices under the age must not work in harmful .. amp; hazardous areas in accordance with Article 40 Section 4 of the Labor Standards Act. ① Sections not included in a contract follow the Labor Standards Act, the Workforce Development and Training Act, the Vocational Training Act.
The scope of the external evaluation includes all required competence units of NCS-based qualification. The largest part of the total benefits of apprenticeship is apprentice's productivity, which is one of the items at the company level, and it represents 50.6%. ② "Training company" is defined as a company that conducts dual training as part of the apprenticeship system pursuant to Article 13.
② The Minister of Employment and Labor could entrust part of the investigative work under paragraph 1 to a relevant investigative agency designated by presidential decree. Fields in which the Minister of Employment and Labor recognizes through the apprenticeship system that the operation of the qualification system at national or industrial level is appropriate. ② The methodology and process of the pilot project according to paragraph 1 are defined in the regulation of the Ministry of Employment and Labor.
② The detailed criteria for the administrative measure should be laid down in a regulation of the Ministry of Employment and Labor, taking into account the type of violation and the degree of violation. ⑤ The necessary items under paragraph 4 are determined by the regulation of the Ministry of Labor. ④ The necessary procedure for issuing a certificate of completion, in accordance with paragraphs 1 and 3, shall be determined by the regulation of the Ministry of Labor and Labor.
① The Minister of Employment and Labor and the employer of the training company should evaluate the apprentices according to whether they have achieved their goals according to the vocational training standards in Article 11 on the apprenticeship training program. ③ The Minister of Employment and Labor should manage the digital system needed to facilitate administrative work such as apprenticing and issuing qualifications. ① The Minister of Employment and Labor shall revoke the apprenticeship qualification if the person with this qualification falls under any of the following subparagraphs.
① The Minister of Employment and Labor may delegate authority to the Executive Director of the Regional Employment and Labor Administration and/or the head of the local government.