Assessing the quality of a comprehensive plan for storm and flood damage reduction in Korea. A Comprehensive Plan for Storm and Flood Damage Reduction (CPSFDR), which is required by section 16 of the Natural Disaster Countermeasures Act, aims to reduce human and property damage and to promote community safety. The purpose of this study is to develop the plan quality index to assess the quality of CPSFDRs in Korea.
Similar mitigation measures exist in most municipalities, although there are different regional characteristics and options for dealing with natural disasters.
INTRODUCTION
LITERATURE REVIEW
Plan assessment and plan quality indicator
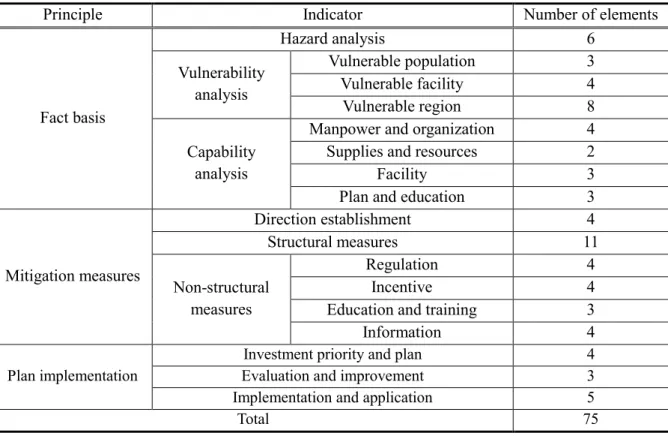
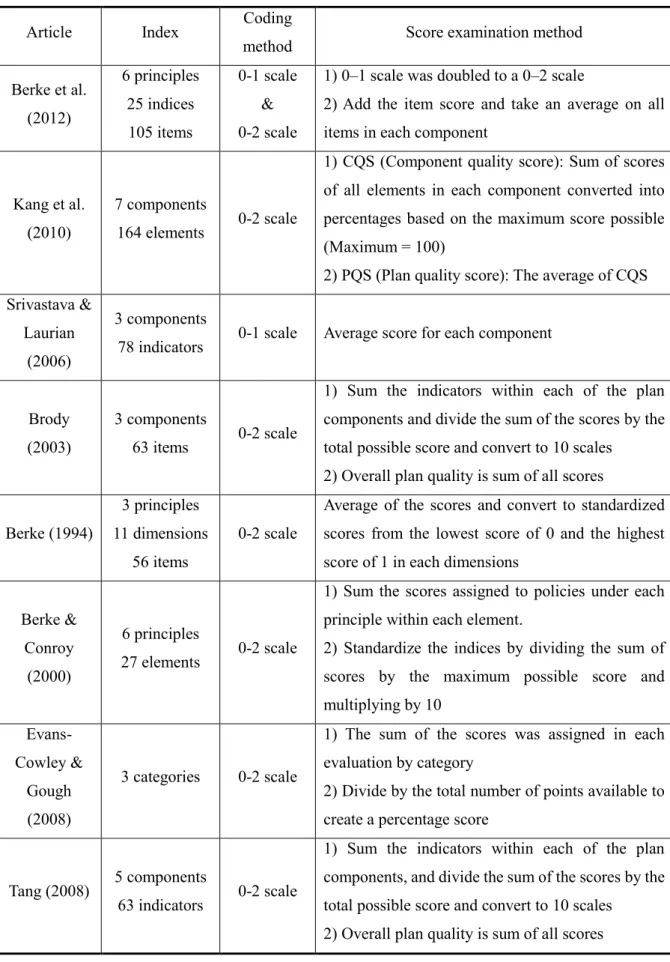
However, there are two measures to calculate the overall plan quality, such as average or sum of scores. Plan quality indicators are divided into three principles: 'Factual basis', 'Averting measures' and 'Plan implementation'. In this indicator there are some elements to assess the plan quality of various structural mitigation measures.
Moreover, the maximum score (46.53) is less than half of full score, so the plan quality of 'Non-structural measures' is relatively lower than structural measures.
Plan quality assessment method
COMPREHENSIVE PLAN FOR STORM AND FLOOD DAMAGE REDUCTION (CPSFDR)
In January 2012, the National Planning and Land Use Act was modified to make the mandatory reflection of the urban plan in the creation of the KPSFDR. There are two levels of CPSFDR as province level (Do) and city level (Si, Gun, Gu). The 158 municipalities (cities and counties) in Korea must establish this plan, and the target year of the CPSFDR is 10 years from establishment to review the completion of mitigation measures.
Other plans are also composed of similar content, because all the plans are prepared on the basis of the detailed guideline of CPSFDR.

METHODS
Data
Plan quality index
In the case of 'Vulnerable facility', 4 elements are included in this indicator, and most of them are used to assess the definition and analysis result of the current state of each facility type. In 'Vulnerable Region' there are 8 elements to assess qualities of content about explanation of vulnerable region of each disaster type. Facility' contains the elements about disaster related facilities such as disaster mitigation facilities and shelters.
EHPs (Emergency Action Plan) prepared for damage prevention facilities such as dams and reservoirs are also included. The second principle is 'Mitigation measures', and it is composed of 3 indicators: 'Direction establishment', 'Structural measures', and 'Non-structural measures', and 30 elements. Direction establishment', there are 4 elements to determine which factors or how to consider in direction establishment process of mitigation measures such as regional characteristics, environmental change, connectivity, resilience and sustainability.
In the case of “Structural measures”, the detailed guidelines of the CPSFDR explained only about the extent of mitigation measures. However, all structural measures mentioned in CPSFDRs are included, so the plan quality index was developed based on their content and some literature that explained structural mitigation measures (Godschalk & Brower, 1985; Phillips et al., 2011). Non-Structural Measures' is similar to 'Structural Measures' because its content was explained roughly in the detailing guide.
Therefore, all non-structural measures mentioned in the plans were used to develop the plan quality index and more measures were added to refer to the literature on disaster mitigation measures (Godschalk & Brower, 1985; Phillips et al., 2011). Since, the content of non-structural measures in local risk plans is smaller than structural measures.
Assessment
It can be used to easily compare the quality of the plan with other plans because all plans include these contents. Most of the mitigation measures were related to flood prevention, such as dam, line, rainwater storage facility and drainage lines. The number of indicators for another disaster such as slope disaster and wind hazard is relatively small due to its importance.
In particular, this indicator is composed of 4 detailed indicators according to the characteristics of measures which follow as regulatory measures such as land use regulation, incentive measures such as tax benefit, education and plan, and information such as forecast and warning facility. The third principle is 'Plan implementation' and it is composed of 3 indicators: 'Investment priority and plan', 'Evaluation and improvement' and 'Implementation and application' and 12 elements. In addition, financing measures, which are the important part of the implementation of plans, are also included in this indicator.
The left is Yeongwol's plan, and the right is Gangneung's plan. In the case of Yeongwol, the content of related organizations was defined with detailed responsibilities, so it was marked '2'. After assigning points to each of the indicators, this study compared different measures to calculate the overall quality of the plan and followed the calculation measures used by Brody (2003).
Ij is the plan quality for the jth indicator, and nj is the number of elements within the jth indicator. It is also calculated by averaging the scores of each of the three principles, and we used this score for overall plan quality (maximum score = 100).
RESULTS
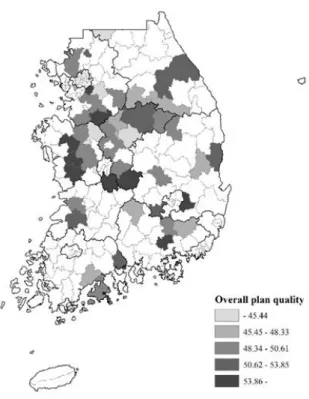
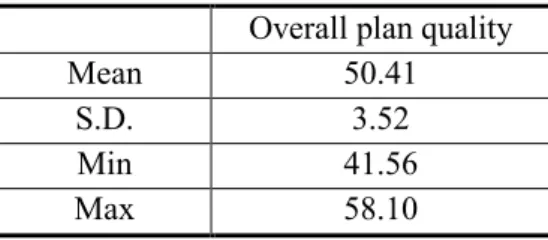
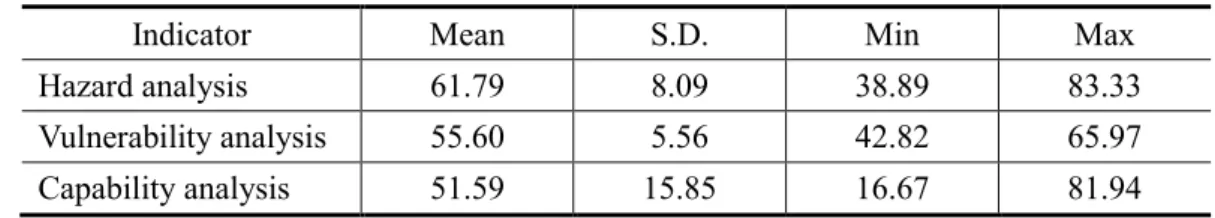
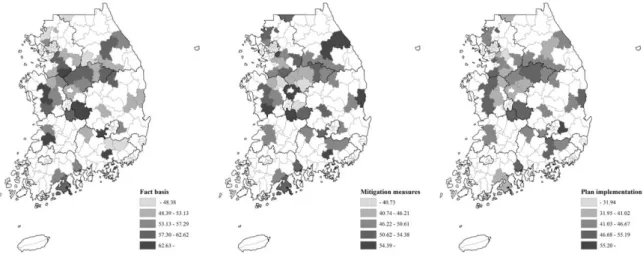
The spatial distribution and the range of overall plan quality scores are displayed on Figure 3. The half score means that the plan includes all content simply in plan quality indicators, but there is an insufficient part in the plan that plan quality score is below half score. The spatial distribution of overall plan quality score is displayed on maps and graphs (Figure 4).
The establishment of mitigation measures is necessary due to the increase in rainfall intensity from the abnormal climate and the increase in imperviousness from urbanization…” in the plan of Anseong (Score = 72.22). The third detailed indicator is 'Education and training', and contains 3 elements to assess the quality of the disaster education and training plan, such as training program for PAA and education program for common people or experts. For example, educational measures are described as "Production and supply of educational and publicity materials for disasters that reflect regional characteristics, considerations for regular education and educational measures for persons responsible for disaster prevention are proposed." in Wonju's plan.
Factual basis Mitigation measures Plan implementation Overall plan quality Gyeonggi-do Gangwon-do Chungcheongbuk-do Chungchoengnam-do Jeollabuk-do Jeollanam-do Gyeongsangbuk-do Gyeongsangnam-do. To compare the difference in plan qualities between provinces (Do), the scores for each principle and the overall plan quality were taken as an average for municipalities in each province. However, there isn't much of a difference, so it's hard to compare the plan quality just using the overall plan quality.
Among the indicators for mitigation measures, the scores for structural measures are the highest in all provinces, and non-structural measures have the lowest joint plan quality. During plan implementation, most indicators scored higher plan quality than 50.00, except for the indicator on evaluation and improvement. In addition to implementation and application, the average plan quality scores are higher in municipalities with an average population density.
The result showed that the overall quality of the plan is negatively related to property damage due to the accident and is statistically significant.
DISCUSSION
In the case of fact base, most indicators have a negative relationship with disaster property damage except the vulnerable area, but all the indicators are not statistically significant. In the case of mitigation measures, most indicators have a positive relationship except directionality and regulation in non-structural measures, but there is no coefficient that is statistically significant. All the indicators in plan implementation have a negative relationship with disaster property damage, and two indicators are statistically significant except evaluation and improvement.
Detailed CPSFDR guidelines should include detailed content to guide the selection of mitigation measures by presenting detailed measures. In particular, non-structural measures need direction, as most consulting companies do not develop new measures and repeat similar content in each plan. Connectivity is described in the current status section with an explanation of the associated plans and is included as an indicator for deciding on a priority investment.
Maps showing planning areas and facilities should be included in the CPSFDR to compare content in different related plans and to analyze the relationship between plans. This map can increase the connectivity between the plans and it is also possible to prevent the duplication of plans. As indicated in this study, the connectivity between the CPSFDR and the urban plan is important to promote non-structural measures and to produce effective measures.
Continuous evaluation and monitoring should be enforced before renewal, but detailed plans of it are not proposed in plans. The detailed guideline should include the content on continuous evaluation and monitoring to draw up detailed plans for it.
CONCLUSION
It is essential to expand the scope of the study area for regional comparison, and it will also be used to develop the plan quality index due to the plan diversity. Second, the plan quality index was developed based on an article on research on risk reduction plans in the US. To assess the relationship between risk reduction plan quality and rural status in a cohort of 57 counties from 3 states in the southeastern US.
Definition of vulnerable population Current state of vulnerable population Analysis of future vulnerable population Vulnerable facility. Current condition of vulnerable area of river disaster Current condition of vulnerable area of flooding Current condition of vulnerable area of mud flow disaster Current condition of vulnerable area of wind disaster. Current state of vulnerable area from other disasters (facility and ocean) Explanation about disaster risk districts.
The current state of voluntary organizations. Persons responsible for the task of disaster management. Resources and supplies. Current state of disaster-related resources. Current status of existing disaster plans Connectivity between disaster plans and CPSFDR Current status of disaster education or training Mitigation measures. Content of dam construction or improvement Content of embankment construction or improvement Content of river improvement.
Contents of rainwater storage facilities Contents of rainwater penetration facilities Contents of drainage pumping facilities Contents of retarding reservoirs Contents of drainage lines. Content of slope stability measures Content of height of a ground level Content of structural reinforcement.