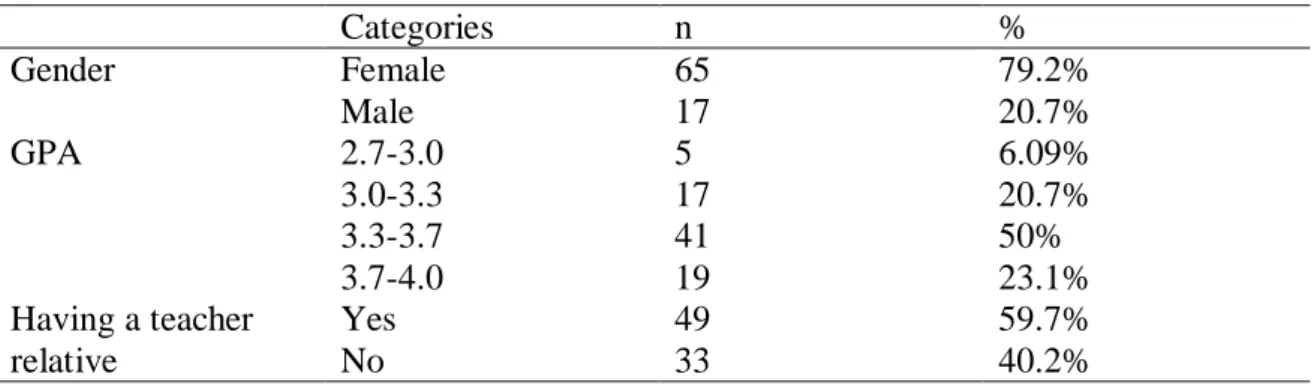
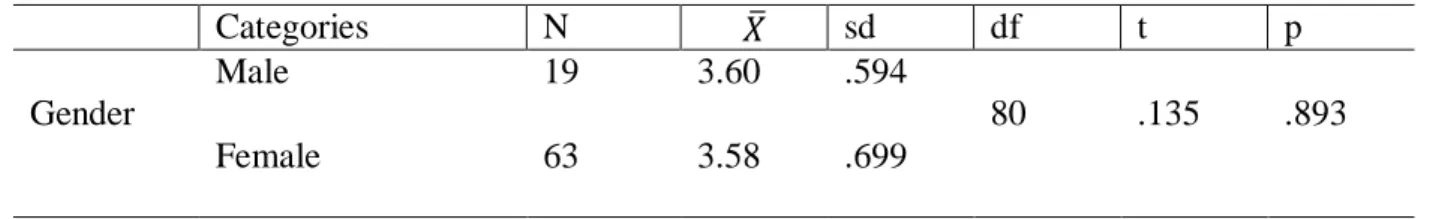
Furthermore, it tends to determine whether teacher candidates' attitudes toward and readiness for the teaching profession change in terms of their GPA, gender, and having a teacher relative. The findings of the study indicated a positive relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes toward and readiness for the teaching profession. Independent t-test: Results of teacher candidates' attitudes toward the teaching profession mean mean scores based on gender.
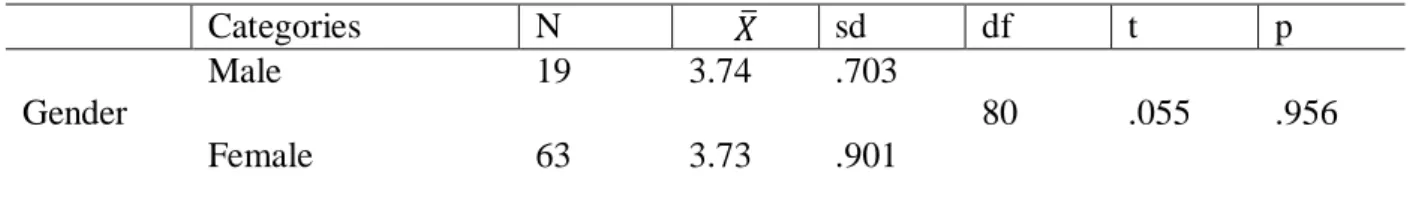
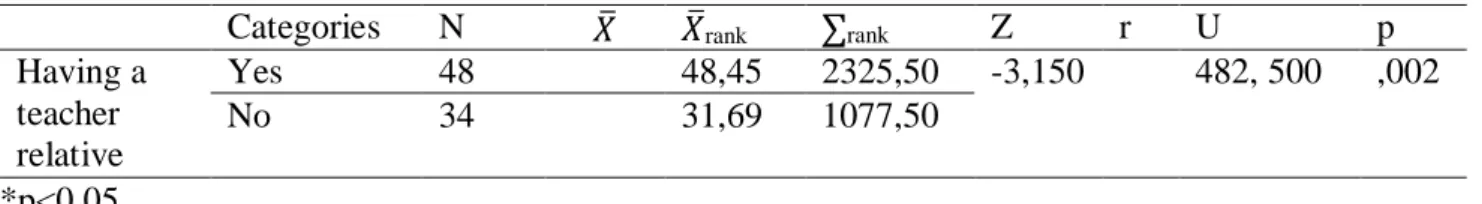
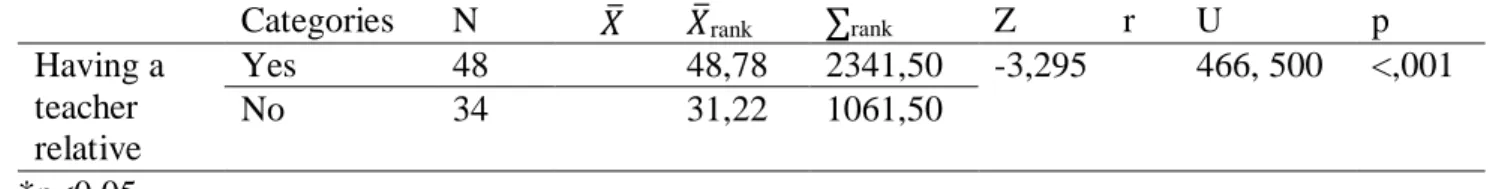
Independent t-test: results of teacher candidates' readiness levels for the teaching profession mean scores by gender. Mann-Whitney U: results of teacher candidates' attitudes toward the teaching profession mean scores according to the fact that a teacher has relative variable. Mann-Whitney U: results of teacher candidates' readiness levels for the teaching profession mean scores according to the fact that a teacher has relative variable.
The purpose of this study is to investigate teacher candidates' attitudes towards and levels of readiness for the teaching profession. What is the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes towards and levels of readiness for the teaching profession. If teacher candidates have positive attitudes towards and better levels of readiness for the teaching profession, they can understand the vitality of this profession.
Therefore, the meaning of this research is to find. a positive relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes towards and levels of readiness for the teaching profession. Additionally, no work has been done to examine the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes toward and levels of readiness for the teaching profession in a Kazakhstani context. To summarize, this chapter has discussed the reasons why teacher candidates' attitudes and readiness levels towards the teaching profession are examined while they are admitted to the teaching programs.
There are various factors that influence the attitude and level of preparation of teacher candidates for the teaching profession. Another important characteristic to consider when studying the attitude and level of preparation of teacher candidates for the teaching profession is gender. However, other studies indicate that the attitude or level of preparation of prospective teachers for the teaching profession does not differ by gender.
Finally, having a teacher family member can be considered another form of factor that may influence teacher candidates' attitudes and readiness levels towards the teaching profession. According to Ozcan's (2020) study, there is a significant difference between teacher candidates' attitudes and readiness levels towards the teaching profession. This means that prospective teachers' attitudes and levels of readiness towards the teaching profession differ with regard to the fact that a teacher is a family member.
Furthermore, quantitative research designed as a correlational model is supported by Ozcan (2020), who also investigated the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession. Since this study aims to examine the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession based on numerical data, the quantitative research method is best suited to conduct the research. The quantitative approach provides an opportunity to illustrate the attitudes and readiness levels of the larger population (teacher candidates) for the teaching profession.
Furthermore, the quantitative research allows to examine the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and their readiness for the teaching profession, as well as factors such as GPA, gender, and having a teacher family member that may influence them. The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and their readiness for the teaching profession. What is the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and their readiness for the teaching profession?
To understand about teacher candidates' attitudes towards and levels of readiness for teaching. H0: There is no significant difference between teacher candidates' attitude towards and readiness for the teaching profession and their gender. H0: There is no significant difference between teacher candidates' attitude towards and readiness for teaching and having a teacher relative.
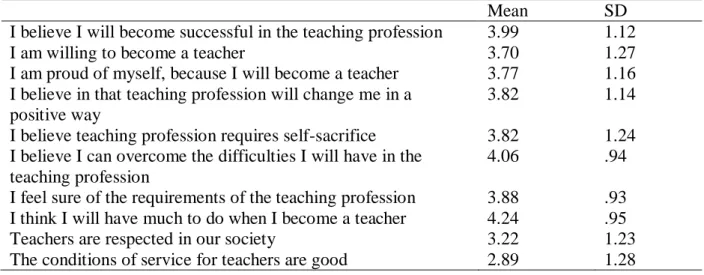
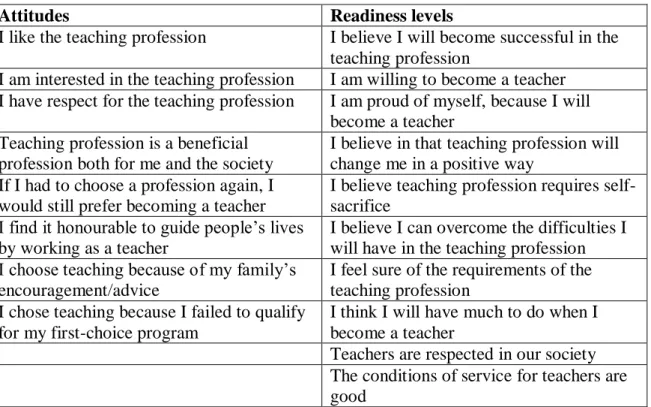
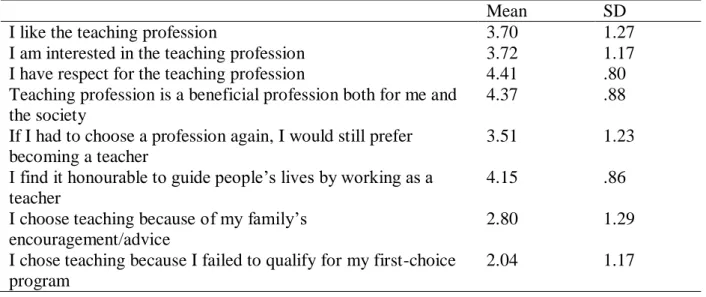
In order to identify the readiness levels and attitudes of teacher candidates towards the teaching profession, a survey design was used. To measure teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness towards the teaching profession, 16 items were developed based on the components of attitude and readiness (Table 1). Finally, to answer the main research question of the study - What is the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession.
Consequently, Spearman's rho was used when analyzing the relationships between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession.
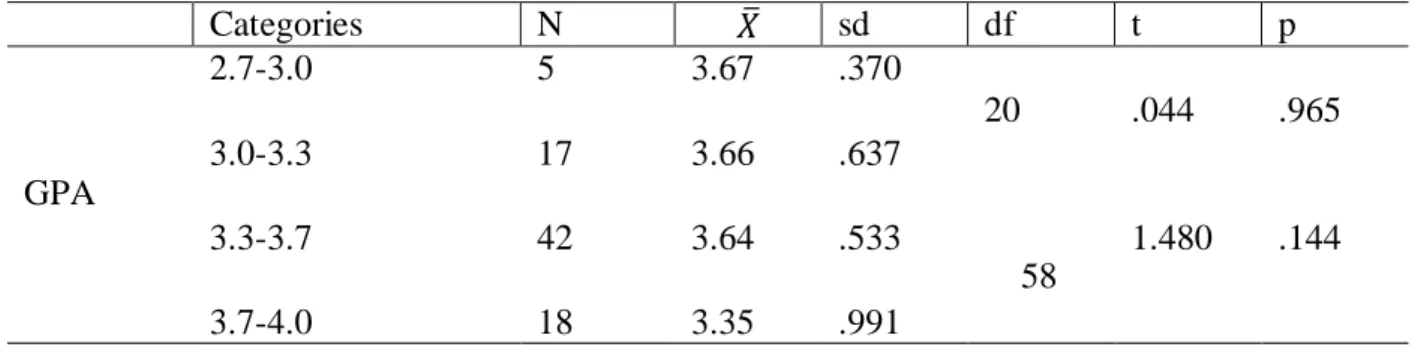
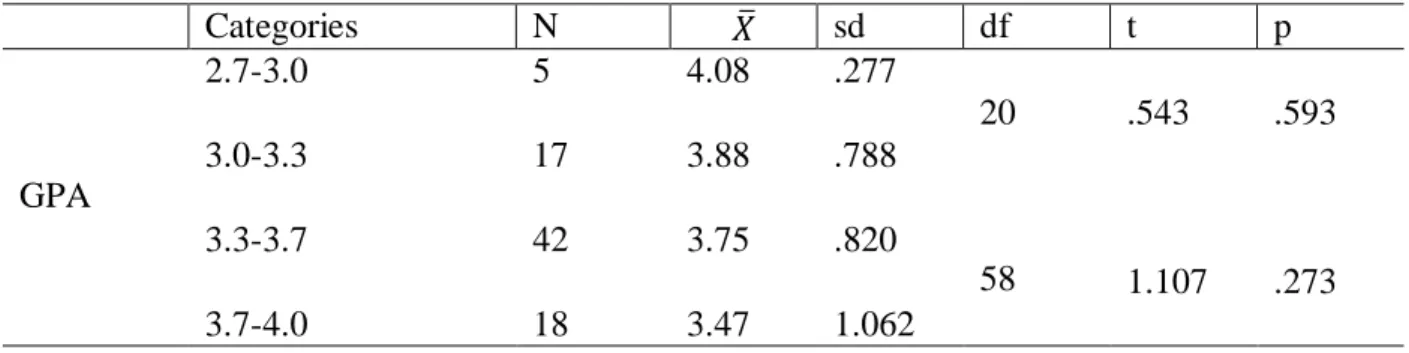
Eight different elements characterizing teacher candidates' attitudes towards the teaching profession were constructed according to the Likert scale questionnaire. To be precise, the p-value of the attitudes of teacher candidates is p>0.05 and the level of readiness of teacher candidates is p>0.05. Therefore, we fail to reject the null hypothesis, which means that there are no significant differences between teacher candidates' attitudes and readiness and GPA.
According to Table 8, the attitude of teacher candidates towards the teaching profession does not differ significantly by gender (p>.05). As a result, we can conclude that there is no significant difference between the attitude of teacher candidates and their gender. Similarly, the level of preparedness of teacher candidates for the teaching profession also does not differ significantly by gender (p>.05).
Consequently, we can claim that there is a significant difference between teacher candidates' attitudes and having a teacher family member. In order to see the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and readiness levels, Spearman's rho test was used. Therefore, it can be concluded that there is a high level of correlation between teacher candidates' attitudes and readiness levels in relation to
Therefore, we can conclude that there is a relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness. As the results show, there is a positive relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession. Another factor, such as the relative of the teacher, also affects the attitude and level of readiness of teacher candidates towards the teaching profession.
However, no associations were observed between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession and other variables such as GPA and gender.
The results suggest that teacher candidates' attitudes or level of preparedness for the teaching profession do not change according to their GPA level. This may lead to the conclusion that teacher candidates' academic performance as measured by GPA does not define their attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession. In order to draw conclusions about teacher candidates' attitudes and readiness levels for the teaching profession according to their GPA, it is therefore essential to study various factors that may influence them.
Thirdly, in this study, a significant difference has been observed between teacher candidates' attitudes and readiness and having a teacher relative. The final results of the current study explain that teacher candidates' attitudes towards and levels of readiness for the teaching profession are highly correlated. This finding is consistent with Ozcan's (2020) findings, who also observed a positive relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of preparedness towards the teaching profession in a Turkish university.
A positive attitude towards and better levels of readiness for the teaching profession can influence further career choices of teacher candidates. Consequently, preparing future teacher candidates who have positive attitudes towards and better levels of readiness for the teaching profession is crucial in educating the next generation of quality teachers within society. In conclusion, the interpretation of the research findings of the given study shows that there is a positive relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes towards and levels of readiness for the teaching profession.
Teacher candidates' attitudes towards the teaching profession tend to change in relation to their levels of readiness. The study also examined other factors such as GPA, gender, and having a teacher family member that may influence teacher candidates' attitudes toward and levels of readiness for the teaching profession. As a result, it was found that teacher candidates' attitudes and readiness levels did not differ with respect to their GPA and gender.
As a result, being aware of certain characteristics of the profession and understanding a clear career path before choosing it can lead teacher candidates to a more positive attitude towards the teaching profession and to a better level of preparation for it.
Additionally, this research has revealed a strong relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes toward and readiness for the teaching profession. This implies that teacher candidates' attitudes towards the teaching profession improve along with their level of readiness. A positive attitude towards and better preparedness for the teaching profession is likely to influence further career choices of teacher candidates.
The attitude of teacher candidates towards the teaching profession and their readiness for it do not differ according to their average achievement. A possible explanation for this could be that the GPA level or academic achievements of teacher candidates cannot define their attitude towards and readiness for the teaching profession. The attitude of teacher candidates towards the teaching profession and their readiness for it do not change depending on their gender.
However, the results of this study assumed that teacher candidates' attitudes towards and readiness for the teaching profession do not change with regard to their gender. Finally, the findings of this study observed that teacher candidates' attitudes toward and readiness for the teaching profession differ in relation to being a teacher family member. This probably means that teacher candidates' teaching family can influence their attitude towards and readiness for the teaching profession.
Therefore, a conscious choice of the future profession can lead to teacher candidates having positive attitudes towards and better levels of readiness for the teaching profession. In this way, it is expected that there will be more prospective teachers with positive attitudes and readiness levels towards the teaching profession. Examining the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes towards and readiness for the teaching profession was a valuable yet challenging experience for me.
You are invited to participate in a research study entitled "The relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession". The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession. Appendix B: Questionnaire for identifying teacher candidates' attitudes and levels of readiness for the teaching profession.