This project is a research study on cyber hygiene during COVID-19 to avoid cyber attacks for academic purposes. Five hypotheses were developed in hopes of identifying the relationship between the factors and cyber hygiene behaviors.
Research Overview
- Introduction
- Research Background
- Problem Statement and Motivation
- Project Objectives
- General Objectives
- Specific Objectives
- Research Questions
- General Questions
- Specific Questions
- Research Hypothesis
- Research Significance
- Conclusion
Additionally, the purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between variables and cyber hygiene behaviors. GQ1: What elements influence cyber hygiene behavior during COVID-19 to avoid cyber attacks.
Literature Review
- Introduction
- Previous Findings on Cyber Hygiene Research
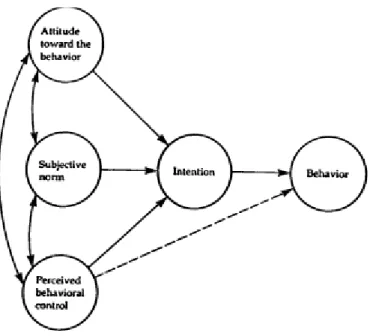
- Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB)
- Variables Review
- Dependent Variable - Cyber Hygiene Behavior (CHB)
- Independent Variable - Self-efficacy (SE)
- Independent Variable - Cyber Hygiene Knowledge (CHK)
- Independent Variable - Cyber Hygiene Awareness (CHA)
- Independent Variable - Cyber Hygiene Attitude (CHAtt)
- Independent Variable - Cyber Hygiene Intention (CHI)
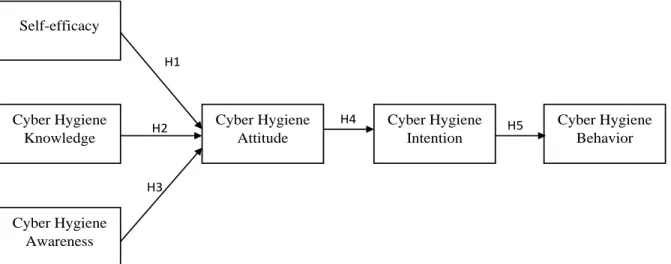
- Proposed Conceptual Framework
- Hypothesis Development
- Self-efficacy and Cyber Hygiene Attitude
- Cyber Hygiene Knowledge and Cyber Hygiene Attitude
- Cyber Hygiene Awareness and Cyber Hygiene Attitude
- Cyber Hygiene Attitude and Cyber Hygiene Intention
- Cyber Hygiene Intention and Cyber Hygiene Behavior
- Conclusion
According to [57], although people are more aware of security breaches, many people are not taking basic cyber hygiene to protect their data. Behavioral intention is a strong predictor of actual behavior, according to another systematic literature review of cyber hygiene habits [55].
Research Methodology
Introduction
Design for the Research
Data Collection Methods
Design of the Sampling .1 Target Population
- Sampling Technique
- Sample Size
Because no sampling frame was available for this study, a non-probability sampling approach was used. The total number of people to be surveyed from the study's target demographic is called the sample size.
Instruments .1 Survey Design
- Pilot Test
- Fieldwork
To ensure that the data collected is accurate, the structure of the questionnaire should be simple and comprehensive. Respondents can contact the researcher if they have any concerns because the researcher's contact information is included in the questionnaire.
Constructive Measurements .1 Scale Measurement
- Origin of Construct
- Operational Definition
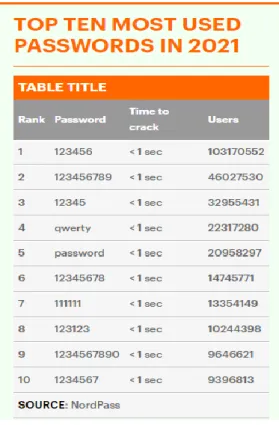
Alharbi & Tassaddiq (2021) Intention of cyber hygiene Alharbi & Tassaddiq (2021) Cyber hygiene behavior Cain, et al. Password with minimum 8 characters including upper and lower characters, numbers and special characters is considered strong and secure password. Using public Wi-Fi (such as in an airport or coffee shop) is generally not safe for sensitive activities such as online banking.
All my passwords include at least 8 characters, including uppercase and lowercase characters, numbers and special characters. I believe that only simple, easy-to-guess passwords are at risk of becoming victims of cybercrime. I will change my password from time to time and I will use different passwords for each account.
I set passwords with at least 8 characters, including uppercase and lowercase characters, numbers, and special characters.
Data Processing
- Questionnaire Check
- Editing of Data
- Encoding of Data
- Transcription of Data
- Cleansing of Data
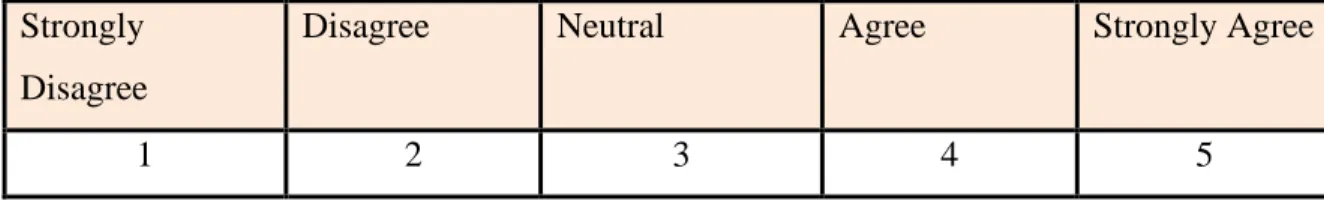
In this study, researchers assigned male respondents a score of 1 and female respondents a score of 2. In addition, for Sections B, C, D, E, and F, researchers assigned a score of 1 for Strongly Disagree, 2 for Strongly Disagree, 3 for Neutral, 4 for Agree and 5 for Strongly Agree. In section G, the researcher will never be 1, rarely 2, sometimes 3, very often 4 and always 5.
This can be achieved with software that delivers and transcribes the coded data in the opening sentence of the questionnaire into multiple results [89]. The researchers used a keyboard technique to transfer coded data directly from the questionnaire to the system. As a result, researchers must reverse the process and go back in time to find problems with survey editing and coding.
Because if there is no value, the researcher comes to an ambiguous or questionable conclusion.
Data Analysis Tool
- Structural Equation Modeling (SEM)
- SmartPLS Version 3.3
- Analysis for the Descriptive
- Indicator Validity .1 Outer Loadings
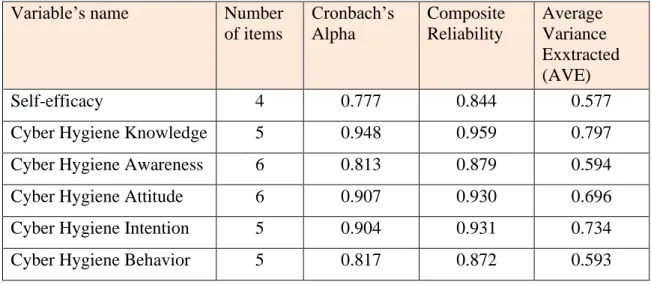
- Internal Consistency Reliability .1 Cronbach’s Alpha Reliability
- Composite Reliability
- Convergent Validity
- Average Variance Extracted (AVE)
- Discriminant Validity Test .1 Fornell-Larcker Criterion
- Structural Model Measurement
The significance of each item or variable in a PLS analysis is determined by applying an external loading in the reflection measurement model. Manifest variables with a loading value less than 0.5 should be eliminated, although a loading value of 0.5 is considered acceptable [95]. According to [88], the researcher stated that the AVE should be more than 0.5 in an acceptable model to reflect the convergent validity of a particular construct.
When the AVE is less than 0.5, it means that the error variance is greater than the explained variance [88]. Because if the AVE is less than 0.5 but the composite reliability is greater than 0.6, the convergent validity of the construct is still sufficient. 97] provided the standard metric and advocated comparing the AVE of each construct with the square interconstruct correlation of that same construct and all other reflectively assessed constructs in the structural model [98].
According to [88], the square root of the AVE of each construct must be greater than the construct's highest correlation with every other construct in the model.
Project Timeline
Conclusion
Data Analysis
- Introduction
- Descriptive Analysis .1 Demographic Analysis
- Gender
- Education Level
- Main Use of the Internet
- Cyber-Attacks Experience
- Measurement of Structure's Central Trend
- SEM Analysis
- Analysis of Reliability and Validity
- Analysis of Discriminant Validity
- Structural Model
- Conclusion
The item with the highest standard deviation (standard deviation = 1.066) is "It is difficult to remember different passwords for each different account." The item with the second highest standard deviation (standard deviation = 1.049) is "Having different complex passwords for different accounts is annoying." The item that has the highest standard deviation (standard deviation = 1.048) is "I will change my password periodically and use a different password for each account."
The item with the second highest standard deviation (standard deviation = 0.985) is “I intend to participate in the cyber hygiene training class in the future”. The item "I intend to set a long and strong password" has the lowest standard deviation (standard deviation = 0.934). The item "I regularly performed an anti-virus scan" has the highest standard deviation (standard deviation = 1.132).
The item "I have set my passwords with at least 8 characters, including uppercase and lowercase characters, numbers, and special characters" has the lowest standard deviation (standard deviation = 0.921).
Implications, Findings, And Conclusions
Introduction
Statistical Analysis Summary .1 Descriptive Analysis
- Respondent Demographics
- Central Trend Measurement of Structures
- SEM Analysis Summary
- Analysis of Reliability and Validity
- Analysis of Discriminant Validity
- Summary of Structural Model
The item with the smallest standard deviation is “I use two-factor authentication whenever possible”, which is 0.886. On the other hand, the item that has the highest standard deviation (standard deviation = 1.066) is “It is difficult to remember the different passwords for every other account”. The item has the lowest standard deviation (standard deviation = 0.836) was “Locking a device when I no longer use it is something I find useful and easy”.
In addition, the item with the largest standard deviation (standard deviation = 1.048) is “I will occasionally change my password and use different passwords. The item has the smallest standard deviation (the standard deviation was “I intend to set a long and strong password.” In addition, the statement with the largest standard deviation (standard deviation = 1.132) is “I regularly performed antivirus scanning.”
The statement that has the lowest standard deviation (standard deviation = 0.921) was “I set my passwords with a minimum of 8 characters including upper and lower characters, numbers and special characters”.
Discussion of Key Findings .1 Findings on General Question
- Relationship Between Self-efficacy and Cyber Hygiene Attitude
- Relationship Between Cyber Hygiene Knowledge and Cyber Hygiene Attitude
- Relationship Between Cyber Hygiene Awareness and Cyber Hygiene Attitude
- Relationship Between Cyber Hygiene Attitude and Cyber Hygiene Intention SQ4: Is cyber hygiene attitude significantly explaining Internet users’ cyber hygiene
- Relationship Between Cyber Hygiene Intention and Cyber Hygiene Behavior SQ5: Is cyber hygiene intention significantly explaining Internet users’ cyber hygiene
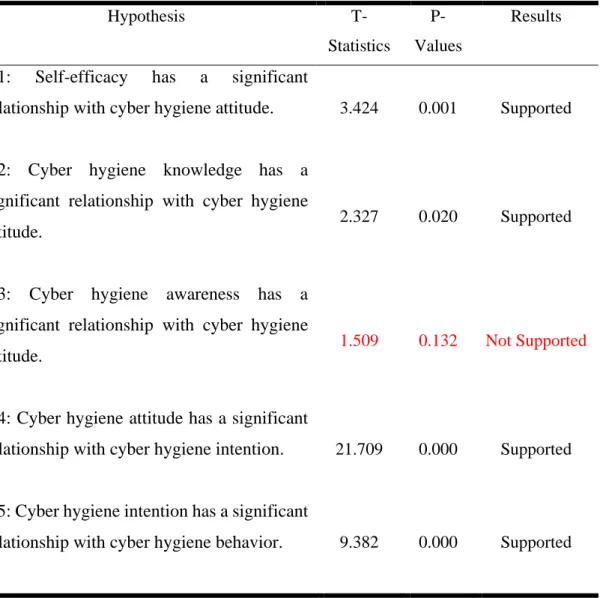
Meanwhile, cyber hygiene intentions, which mediate cyber hygiene behaviour, are influenced by cyber hygiene attitude. The results increase researchers' knowledge of the elements that influence Internet users' cyber hygiene behaviour. Self-efficacy and cyber hygiene attitude had a path coefficient of 0.388, which was between the recommended value of 0.1 and 1.
Finally, p-values and t-statistics indicate that there is a significant positive relationship between cyber hygiene attitudes and self-efficacy. Finally, this research suggests that there is a strong relationship between cyber hygiene knowledge and cyber hygiene attitudes. However, the results of this research show that there is no significant relationship between cyber hygiene awareness and cyber hygiene attitudes.
In conclusion, the hypothesis that cyber hygiene attitude has a significant relationship between cyber hygiene intention is accepted in this current research.
Implications of Study
As shown above, this study proves that cyber hygiene attitudes are positively related to cyber hygiene intentions. Finally, this study shows that cyber hygiene intention is also one of the most important factors influencing cyber hygiene behaviour. In this study, researchers have reached a result about cyber hygiene intention that has a significant relationship with cyber hygiene behavior.
Self-efficacy and knowledge of cyber hygiene were revealed in this study as influencing factors in cyber hygiene attitudes. At the same time, cyber hygiene intention is influenced by cyber hygiene attitude, which in turn influences cyber hygiene behaviour. Furthermore, this research discovered that cyber hygiene attitude and intention are essential elements in determining cyber hygiene behaviour.
In the field of research, most previous studies have focused on cybersecurity behaviors, but only a few studies have focused on cyber hygiene behaviors.
Limitations of Study and Recommendations for Future Research
As a result, respondents in a hurry who need to complete a task quickly may decide to answer questions randomly or based on their own interpretation of the question. This is a subjective activity that is not recognized and consequently affects the correctness of the overall results. To overcome this limitation, future researchers need to collect surveys using multiple methods such as face-to-face interviews.
A face-to-face interview can allow the respondents to answer and clarify more questions at the same time. This is due to the absence of physical confrontation, minimizing the amount of effort required to complete the questionnaire. As a result, the findings of research studies may not fully reflect cyber hygiene behaviors, intent and attitudes.
In my recommendation, future researchers should distribute the surveys through the Internet or through mortar tools, as this is a more genuine and accessible way to get responses from the general public.
Conclusion
Stadig, "An Exploratory Study of Cyber Hygiene Behavior and Knowledge," Journal of Information Security and Applications, vol. Mackie, "Encouraging Users to Improve Password Security and Friendliness," International Journal of Information Security (2019), vol. Samsudin, "Cyber Security Behavior among higher education students in Malaysia,” Journal of Information Assurance &.
Shukur, “Information Security Awareness Training, Transfer, and Development for the Healthcare Industry,” (IJACSA) International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, vol. Sumari, "Prevention of phishing attacks based on discriminatory key", International Journal of Computer Science and Security (IJCSS), vol. Kim, “Exploring Factors Influencing Student Information Security Behavior,” Journal of Information Systems Education, vol.
Larcker, "Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error," Journal of Marketing Research, p.
Questionnaire Sample
Eliminate item CHA7, CHB7)
Include all items)
FINAL YEAR PROJECT WEEKLY REPORT
WORK DONE
WORK TO BE DONE
PROBLEMS ENCOUNTERED
SELF EVALUATION OF THE PROGRESS Keep working up and seek help from supervisor
SELF EVALUATION OF THE PROGRESS
Develop the research design, data collection methods, sampling design and questionnaire design based on the pilot test done in FYP1. I found that some of the questions in my survey are not that good and not that related to the study. You have to wait for the help of the respondents to complete the survey only you can continue to the next chapter.
Define the implications of the study, limitations of the study, and recommendations for future research. Note Promoter/Candidate(s) is/are required to provide a soft copy of the full set of the Originality Report to the Faculty/Institute. Based on the above results, I hereby declare that I am satisfied with the originality of the.
Form Title: Supervisor Comments on Originality Report Generated by Turnitin for Final Year Project Report Submission (for Undergraduate Programs).
UNIVERSITI TUNKU ABDUL RAHMAN FACULTY OF INFORMATION & COMMUNICATION
TECHNOLOGY (KAMPAR CAMPUS)