Service recovery of online services is a contemporary issue that needs to be studied due to the changing shopping trends. There have been no previous surveys of customer satisfaction with online service recovery in Malaysia. This study examines the effect of the three dimensions of justice theory, namely distributive justice, procedural justice and interactive justice (DJ, PJ and IJ) on the customer satisfaction (CS) and emotion (E) evoked by the service remediation actions.
Results also show that customer emotions evoked by service recovery action mediate the effect of perceived justice on customer satisfaction.
INTRODUCTION
- Introduction
- Research Background
- Problems Statement
- Research Objectives
- General Objective
- Specific Objective
- Research Questions
- Hypotheses of the Study
- Research Significance
- Conclusion
A customer who has encountered a service failure often expects the service provider to take action to restore the service (Mirani, Hanzaee, & Moghadam, 2015). Customer emotions in response to a service recovery action mediate the effect of perceived justice elements on CS. Customer emotions in response to service recovery action mediate the effect of perceived justice dimensions on CS.
Customer emotions elicited by the service recovery action mediate the influence of perceived justice on CS.
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Introduction
This chapter involves the relevant theoretical theories and reviews the relevant literature on the effects of DJ, PJ and IJ on emotions and CS. An illustration of the proposed research framework and CS hypothesis is formed to investigate the factors that influence the perceived service recovery.
Review of the Literature
- Distributive Justice
- Procedural Justice
- Interactional Justice
- Emotion
This is supported by del Río-Lanza (2009) who claimed that DJ has the significant influence on overall CS of service recovery. & Wang define this dimension of fairness as the various processes, systems and policies put in place to address service failure. The customer often has a certain level of emotional association in perceiving the flexibility, efficiency, appropriateness and process attempted by the offending firms to address the service failure.
Negative emotions are often associated within the customer when they make complaints, the customer perceives fair behavior in the context of service redemption based on the service provider's way of expressing concern, honesty and courtesy; as well as the service contributor's way of rectifying service disappointment and making sincere efforts to address service failure (Kumar & Kumar, 2016).
Review of Theoretical Framework
- Theoretical Framework 1
- Theoretical Framework 2
This theoretical framework was proposed by Siu et al. 2013) to investigate the effect of justice and customer satisfaction in customer retention. This study indicates that different remedial actions and compensation provided by the company and different variables may impose different effects leading to unique outcome of customer satisfaction level. The result of the study further verified the significant relationship between perceived justice and satisfaction towards organization.
Customer evaluation in relation to perceived fairness through dimensions such as ethics, fairness and also appropriateness was also discussed in the research.
Proposed Research Framework
Research Hypothesis
In addition, the findings of Río-Lanza et al. 2009) shows that customer emotions triggered by service recovery actions have a significant effect on CS, while high perception of PJ will have a significant effect on both emotion and CS. IJ focuses on the attitude shown by the service provider from the customer's point of view, practically it is about handling complaints. According to Kumar & Kumar (2016), customers who have perceived fair behavior in the context of service recovery expect service providers to make appropriate efforts and take action to resolve problems.
There is an increasing number of studies that focus on customer emotions such as anger or happiness towards CS at the service provider company (Ozkan-Tektas & . Basgoze, 2017).
Conclusion
Consumers' evaluation of the perceived fairness of reimbursement is the main cause that leads to the generation of positive and negative emotions (Wen & Geng-qing, 2013). There are some research studies that focus on the significant relationship between customer emotions and their level of satisfaction (Bonnefoy-Claudet & Ghantous, 2013; Hosany & Prayag, 2013).
METHODOLOGY
- Introduction
- Research Design
- Data Collection Method
- Sampling Design
- Target Population
- Sampling Frame and Sampling Location
- Sampling Elements
- Sampling Techniques
- Sampling Size
- Research Instrument
- Pilot Test
- Questionnaire Design
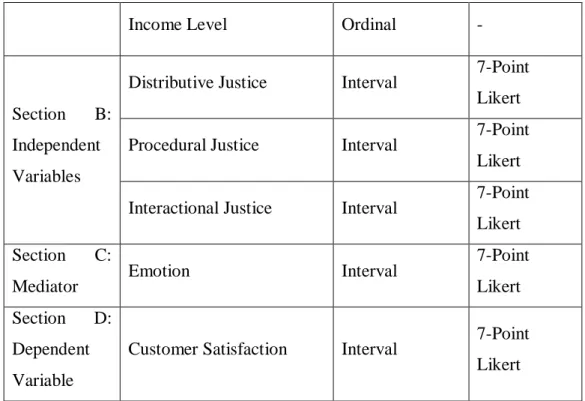
- Constructs Measurement
- Scale of Measurement
- Operational Definition of Construct
- Data Processing
- Data Checking
- Data editing
- Data Coding
- Data Transcribing
- Data Cleaning
- Data Analysis
- Demographic Analysis
- Inferential Statistic
- Representatives of Data to the Population
- Conclusion
Malhotra (2010) defines sample size as the number of elements needed in the study. When studying the research, closed, structured questions are used in the construction of the questionnaire. Section D focuses on customer satisfaction related to service recovery and the questions are designed similarly to section B.
The subsequent results of the analyzed data will be further discussed in the next chapter.
DATA ANALYSIS
- Introduction
- Survey Response Analysis
- Demographic Profile of Research Respondents
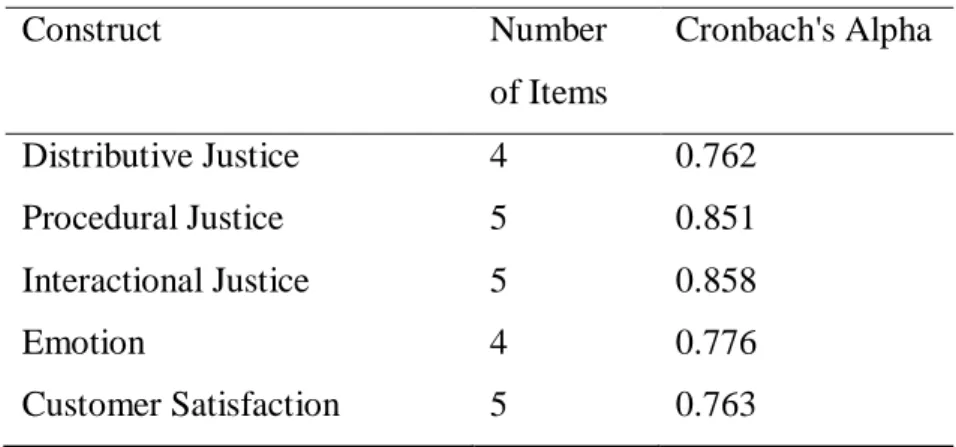
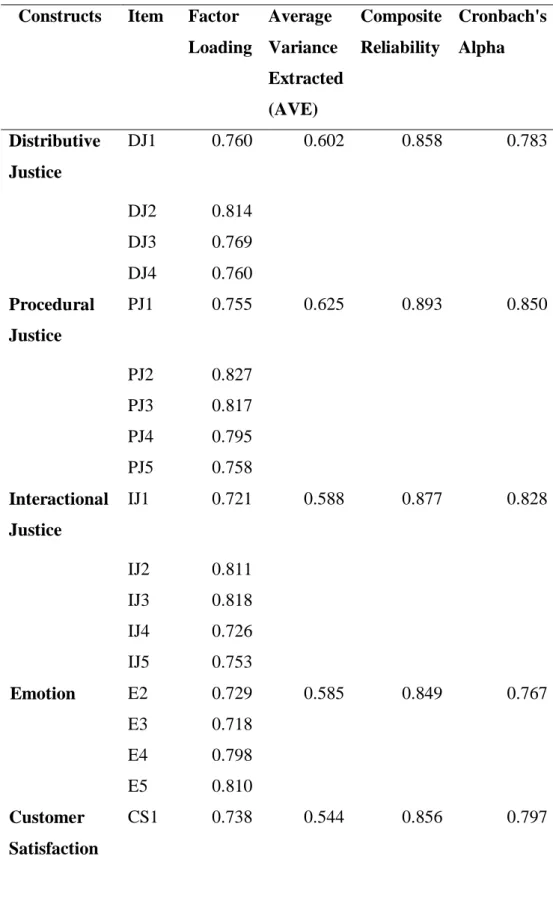
- Validity, Reliability, Multicollinearity Analyses
- Convergent Validity
- Discriminant Validity
- Conclusion
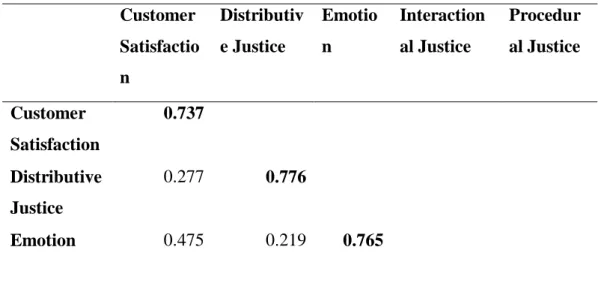
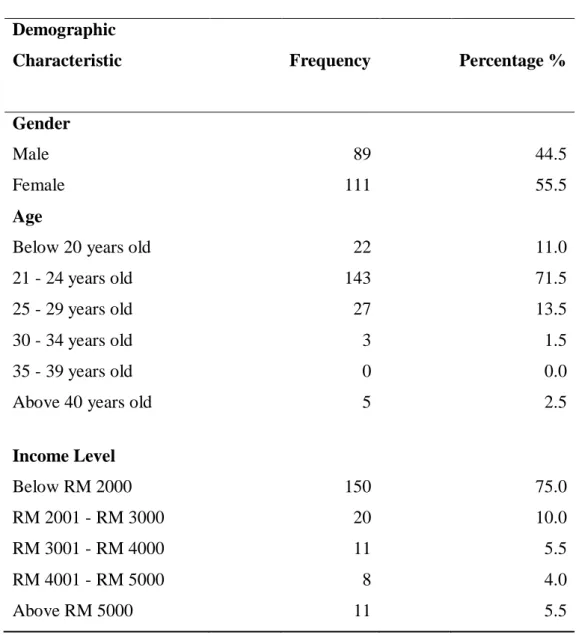
The majority of respondents have an income of less than RM 2000 with 150 respondents representing 75% of the study. Results in Table 4.3 show that all the constructs in this study achieved a larger square root of AVE than other constructs' coefficient. According to the results of Table 4.3 and 4.4, it was proved that the model achieved fair discriminant validity as both tests produced a satisfactory fair result.
Therefore, this research successfully got rid of multicollinearity problems as all VIF values are lower than 2.5.
DISCUSSION, CONCLUSION AND IMPLICATIONS
Introduction
Summary of Statistical Analyses
- Descriptive Analysis
- Demographic Profile of Research Respondents
- Scale Measurement of Research
- Convergent Validity
- Discriminant Validity
- Inferential Analysis
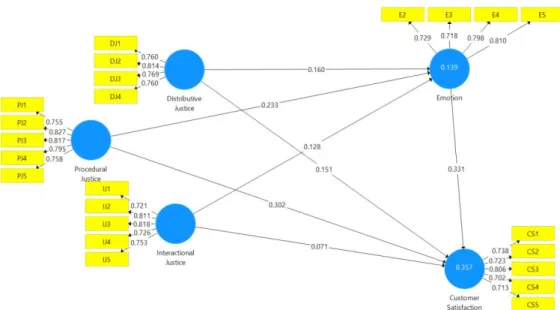
- Path Analysis
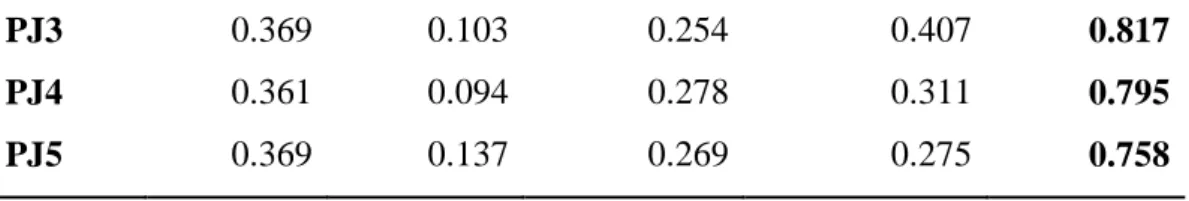
In general, all the constructs in the research are accepted as they all achieved a composite reliability value of more than 0.7, which ranges from 0.849 to 0.893. The square root of AVE together with all other constructs in our research is higher than the coefficient of other constructs. Because of loadings and cross-loadings, each loading value of our indicator is higher on the corresponding construct compared to other constructs.
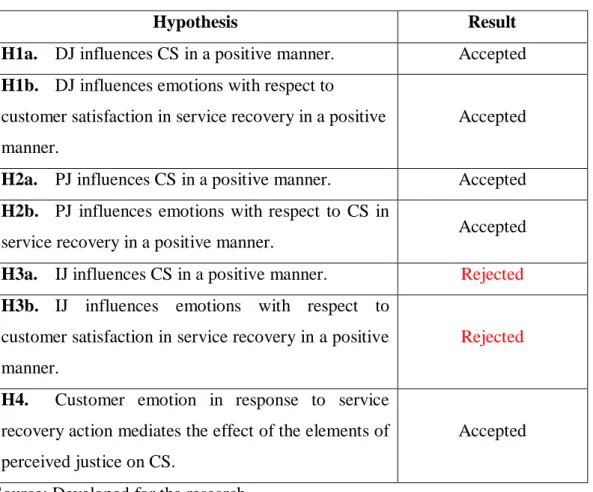
All IVs are positively associated with both E and CS as their T-statistic values exceed 1.96 except for the interactional justice.
Discussion of Major Findings
Process control, scheduling, flexibility, accessibility, and design control, which contribute to procedural justice, can significantly influence the customer's level of satisfaction with service recovery. Research by Del Río-Lanza et al. 2013) supports that PJ will have a significant impact on customer E triggered by service recovery actions. Furthermore, Wen & Chi (2013) also argue that the effect of PJ on CS on service recovery is partially mediated by positive emotions.
Customers are more specific about the outcomes and procedures for service recovery rather than their interaction with the service provider.
Implication of study
- Managerial Implication
- Distributive Justice
- Procedural Justice
- Emotions
- Customer Satisfaction
- Academic Implication
Emotions have been proven to have a significant effect in mediating perceived justice and CS for service recovery. Service providers should be more attentive during the service recovery process to observe customer reactions and the responses to the recovery offered by service providers. Customer satisfaction with service recovery is driven by distributive and procedural fairness, in addition to the mediating effect of emotions.
In order to manage recovery of services in an efficient manner, service providers are advised to focus on distributive and procedural justice while carrying out recovery measures. Service providers should constantly note the changes in customer sentiments to ensure better customer satisfaction. In most of the previous research on customer satisfaction in relation to service recovery, such as research conducted by Nikbin et al. 2014), the theory of perceived justice is the only framework used in the research.
However, our research does not only apply the theory of perceived justice, but seeks to expand the affectors that can significantly influence customer satisfaction. Findings from the research demonstrated the significant effect of emotions as a mediator in influencing customer satisfaction. Emotions, which serve as mediators, are created when customers evaluate the perceived fairness of a recovery and can influence customer satisfaction with a service recovery.
This finding could serve as a basis for researchers conducting related studies on customer satisfaction in the service recovery process. Unlike previous studies that argued that all available variables in justice theory significantly influence customer satisfaction, the finding shows that interactional justice could not influence both customer emotions and satisfaction towards service recovery.
Limitation of study
In addition, the research has revealed a number of conflicting views compared to previous research on the same topic. This finding could help the researcher to reinterpret the application of the theory of perceived justice in the market segment in Malaysia. The former may have lost just a few minutes or hours to get an appropriate service recovery, but the latter may have to cancel a booked hotel because he or she is unable to reach the vacation destination as planned.
Without prior mention in the survey, respondents can make up their own imaginations about the type of service failure in order to answer the service recovery questions. There is another limitation of the research in which the quantitative research method is used within the study. Compared to qualitative research, quantitative research does not include an in-depth description of experiences (Choy, 2014), whereby respondents could not provide more detailed and personal answers during the data collection process.
Recommendation
This would cause inconsistency in the data due to variation in the respondent's imagination. In addition, prospective researchers are advised to use qualitative research or a mixed strategy of quantitative and qualitative research when dealing with a study that requires an in-depth personal opinion of the client. This implementation could allow respondents to better interpret, evaluate and respond during the survey process.
Conclusion
Customers' perceived justice, emotions, direct and indirect reactions to service recovery: moderating effects of recovery efforts. The Effects of Perceived Service Recovery Justice on Customer Devotion, Loyalty, and Word-of-Mouth. Post-purchase satisfaction and intentions with service recovery of online shopping websites: Perceived fairness and emotion perspectives.
Impact of service recovery quality on consumers' repurchase intention: The moderating effect of customer relationship quality. The effect of service recovery on customer post behavior in the banking industry using the theory of perceived justice. The relationship of service failure attributions, service recovery justice and recovery satisfaction in the context of airlines, Scandinavian Journal of Hospitality and Tourism, 12 (3), pp.
Emotions and pre-recovery satisfaction: a moderated mediation model for service and reputation recovery in the banking industry. The effects of service recovery justice and perceived switching costs on customer loyalty in e-tailing. This study is an attempt to determine the influence of perceived service recovery on customer satisfaction.
Your kind cooperation will help us get more information related to customer satisfaction. detected service recovery after a service outage. This section consists of three dimensions of perceived fairness that would influence your satisfaction with service recovery in response to a service failure. PJ5 Responsive action to restore the service could alleviate my inconvenience, frustration, disruption and anxiety caused by the service failure.
IJ5 I would be more satisfied with service recovery if the service provider treated me in a. This section contains some of the emotional responses that are likely to be triggered during service recovery. Indicate to what extent you agree with the following statements after receiving the service renewal.
Outer Loadings (without withdrawal of item E1)
Outer Loadings (with withdrawal of item E1)
Construct Reliability and Validity
Fornell and Larcker’s Criterion
Cross Loadings
Inner VIF Values
Path Coefficients