Therefore, the implementation of sustainable smart city with the integration of blockchain technology has become an effective antidote to solve and improve overwhelming urban issues. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the potential of integrating blockchain technology into smart sustainable city development in Malaysia by construction practitioners.
Introduction
Background of Study
Smart city is defined as a high-density urban area with the adoption of information and communication technologies (ICT) to connect and manage the essential infrastructures and services with the aim of improving efficiency and operational sustainability in environmental, economic and social aspects ( Treiblmaier, Rejeb and Strebinger, 2020). The features of blockchain technology, which include immutability, encryption, transparency, programmability, consensus and data distribution, make it possible to complement the formation of smart cities (PWC, 2018).
Problem Statement
However, limited past research has thoroughly examined the application of blockchain technology in SSC development in Malaysia. This makes it possible to assess the future development possibilities of SSC in Malaysia through the integration of blockchain technology.
Research Aim
In addition, these existing studies lack a proper review of the integration of blockchain technology in SSC that fully covers the smart and sustainable elements (Wong et al., 2020). Therefore, this research aims to fill this gap by exploring the potential of integrating blockchain technology into SSC development in Malaysia.
Research Objectives
Some studies only presented the adoption of blockchain technology in one particular component instead of including all major components in SSC. Therefore, there is a lack of explanation about the potential of integrating blockchain technology into SSC development in Malaysia, incorporating both smart and sustainable elements.
Research Methodology
Research Scope
Chapter Outlines
As for chapter four, it covers the detailed interpretation of collected data and the results of analysis. Finally, chapter five summarizes the achievement of research objectives and the contributions of this study.
Summary of Chapter
Introduction
Smart Sustainable City
Definition of Smart Sustainable City
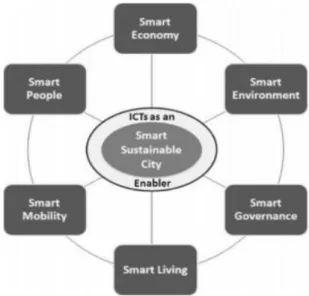
Concept of a Smart Sustainable City
The fusion of "smart" and "sustainable" functions in SSC can bring many desirable results in the six dimensions mentioned above. The quality of living of current residents and their future generations in SSK is emphasized.
Blockchain Technology
Definition of Blockchain Technology
By accessing the latest information regarding the streets' congestion level, the residents in SSC can choose the best route and transport medium from the alternatives provided (Silva, Khan and Han, 2018). The improvement on the last dimension which focuses on the social and human capital can be achieved by providing an environment that promotes continuous learning and investment in human capital (Yigitcanlar, et al., 2019; United Nations, 2014; Hollands, 2008).
Types of Blockchain Technology
As for the consortium blockchain, it is a blockchain formed by the consolidation of the public and private blockchains (Bhushan, et al claimed that the formation of the consortium blockchain is related to a multi-signature scheme, therefore , the responsibilities of consensus and block validation are shared among a set of individuals. The immutability and irreversibility of the consortium blockchain are vulnerable to tampering attacks as approvals and signatures from all controlling nodes are required for block validation (Bhushan, et al ., 2020).
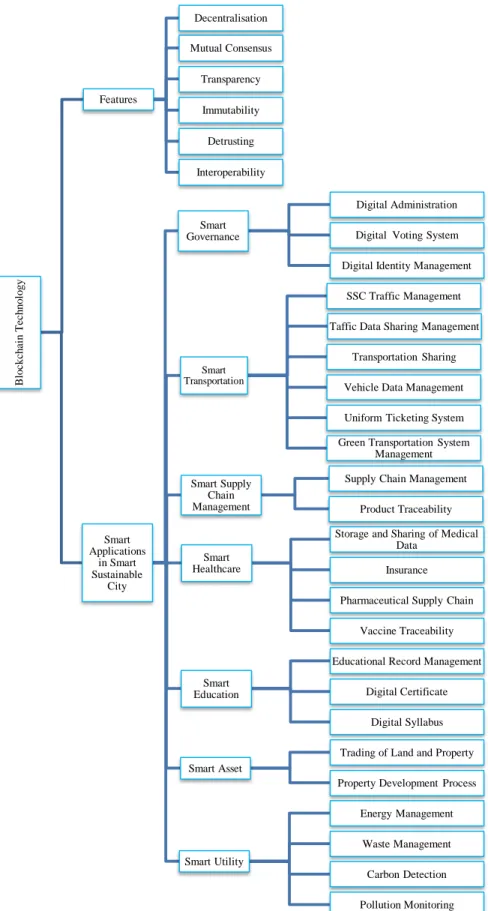
Features of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralisation
- Mutual Consensus
- Transparency
- Immutability
- Detrusting
- Interoperability
The dominant monopoly over information does not exist in blockchain technology as data is recorded, maintained and updated collectively in the distributed network (Wong, et al., 2020; PWC, 2018). The immutability of blockchain technology is an advantageous feature enabled through the use of cryptography (Bhushan, et al., 2020).
Potential Applications of Blockchain Technology in Smart Sustainable City
- Smart Governance
- Smart Transportation
- Smart Supply Chain Management
- Smart Healthcare
- Smart Education
- Smart Asset
- Smart Utility
A democratic e-voting system that is secure and transparent can be achieved by integrating blockchain technology (Wong, et al., 2020). The agricultural and food traceability is another potential application of blockchain technology (Xie, et al., 2019).
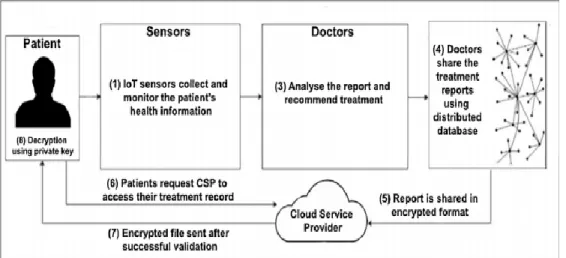
Summary of Blockchain Application in Smart Sustainable City Figure 2.4 summarises the findings obtained from literature review. The
This in turn leads to fuel consumption by waste collection trucks, as waste collection schedules can be properly planned in advance (Wong et al., 2020). Monitoring pollution levels is essential for authorities and communities in the South South to implement immediate and effective strategies to combat pollution and address problems caused by pollution (ITU-T, 2020; Wong et al., 2020).
The Influence of Social Demographic on Technology Adoption This study intends to explore the relationship between the social demographics
Additionally, a number of previous studies have discovered that individuals with higher education levels tend to accept and adopt new technology faster than less educated individuals (Lleras-Muney and Lichtenberg, 2002; Krueger, 1993; Wozniak, 1987; Wozniak, 1984; Welch, 1970). With insufficient confidence to adopt the latest technology, less educated individuals tend to perform poorly on tasks related to the new technology.
Summary of Chapter
Introduction
Research Method
Quantitative Research Approach
Creswell and Creswell (2018) defined the quantitative research approach as a method where the relationship between variables is examined to test objective theories. In addition to being able to test theory and explanation, the quantitative research method is suitable for use in three types of research problems.
Qualitative Research Approach
However, the qualitative research approach lacks replicability as there is no means of verifying the statements produced due to the elimination of scientific methods and inquiry processes (Daniel, 2016; Cohen, Manion and Morrison, 2011). Therefore, the results of the qualitative research approach are not consistent and reliable as the explanations are given based on the interpretations of the researchers (Leed and Ormrod, 2014; De Vaus, 2014).
Justification of Selection
It is considered less appropriate to follow a qualitative research approach in this study due to the involvement of a large number of participants. Apart from that, qualitative research approach is less preferable as qualitative method generally focuses on interpretations of data based on personal views, feelings and understanding.
Literature Review
This will lead to lower reliability and consistency of interpretation results compared to the use of measurable numbers and figures in the quantitative research approach. At the end of the process, the literature review was written referring to the selected existing studies in discussing the concept and benefits of SSC and the types, features and potential applications of blockchain technology in SSC.
Quantitative Data Collection
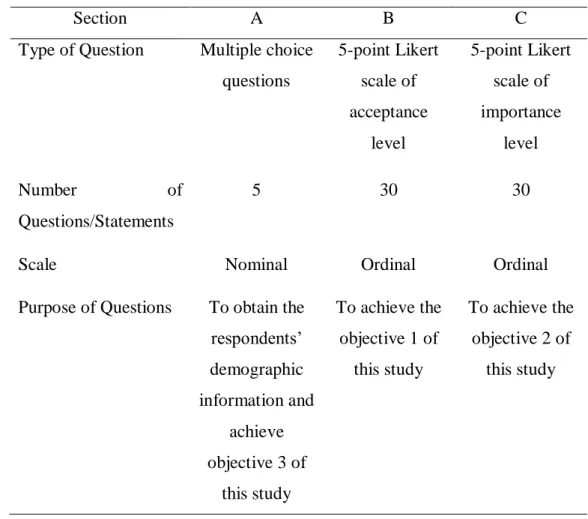
Questionnaire Design
In Section A, questions were designed to obtain the demographic profiles of the respondents and to achieve the third objective of this study. The five-point Likert scale was used in the questions where respondents were asked to rate their acceptance of the application of blockchain technology in SSC in Malaysia.
Sampling Determination
Questionnaire Distribution
CIDB), Board of Quantity Surveyors Malaysia (BQSM), Board of Architects Malaysia and Board of Engineers Malaysia.
Data Analysis
- Cronbach’s Alpha Reliability Test
- Arithmetic Mean
- Mann-Whitney U Test
- Kruskal-Wallis Test
H0 (null hypothesis): There is no significant difference in accepting the blockchain technology between the genders. H1 (alternative hypothesis): There is a significant difference in accepting the blockchain technology between the different age groups/levels of education.

Summary of Chapter
The Kruskal-Wallis test was applied to analyze the differences in acceptance level in the application of the blockchain technology in SSC between the groups of age and highest education level. Two types of hypotheses namely H0 and H1 are formulated below to identify the difference in the acceptance level of the application of blockchain due to different age groups and education levels of construction workers, - H0 (null hypothesis): there is no significant difference in the acceptance of the blockchain technology between the different age groups/educational levels.
Introduction
Demographic Background of Respondents
Regarding years of work experience, most of the 93 respondents have less than 6 years of work experience, while only 1 respondent has 11 to 15 years of work experience. The number of respondents with 6 to 10 years of work experience and 16 to 20 years of work experience is 19 and 6, respectively.
Cronbach’s Alpha Reliability Test
In terms of education level, there are 3 HAVO certificate holders, 6 SPM certificate holders and 1 STPM certificate holder. In addition, there are 23 Diploma graduates, 86 Bachelor's Degree graduates, 28 Master's Degree graduates and 6 Doctoral Degree graduates.
Arithmetic Mean
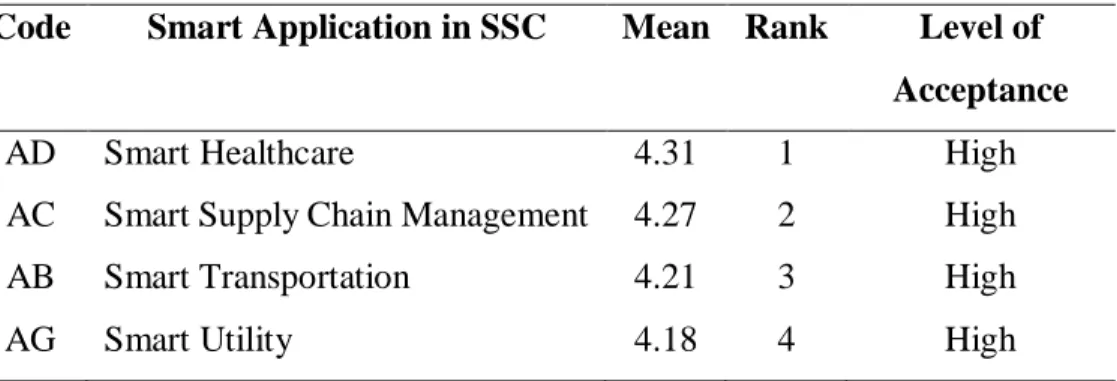
- Mean Ranking of Acceptance Towards the Main Smart Application of Blockchain Technology
- Mean Ranking of the Acceptance Towards the Sub-Smart Application of Blockchain Technology
- Mean Ranking of the Importance of the Main Smart Application of Blockchain Technology
- Mean Ranking of the Importance of the Sub-Smart Application of Blockchain Technology
BF2 An asset's data should be stored on a digital platform that is more transparent and systematic to maintain data accuracy throughout the asset's lifetime. BC2 Real-time shipment tracking information must be stored on a digital platform where product verification and traceability can be performed at any time.
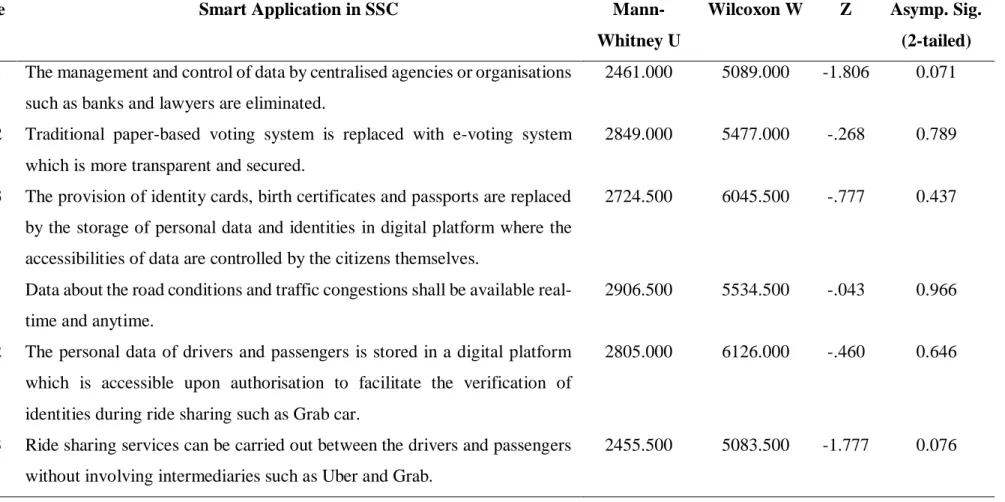
Mann-Whitney U Test
AC2 The shipment's tracking information is reliably synchronized in real time in a digital platform, which facilitates traceability. AF2 The construction drawings, specifications, approvals, reports and documents involved in the real estate development process are stored on a digital platform that is more secure as the data is immutable.
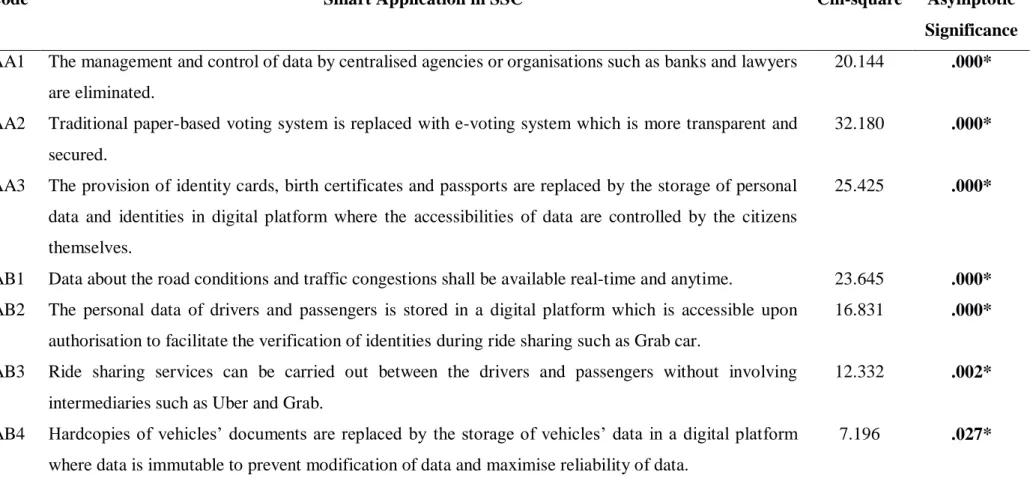
Kruskal-Wallis Test
Kruskal-Wallis Test on Age Group The two hypotheses formulated are as follows
AD1 Hard copies of medical reports are replaced by storing the complete medical history on a digital platform, which can be accessed by doctors with patients' authorization. Order AB2 The personal data of drivers and passengers is stored on a digital platform which is.
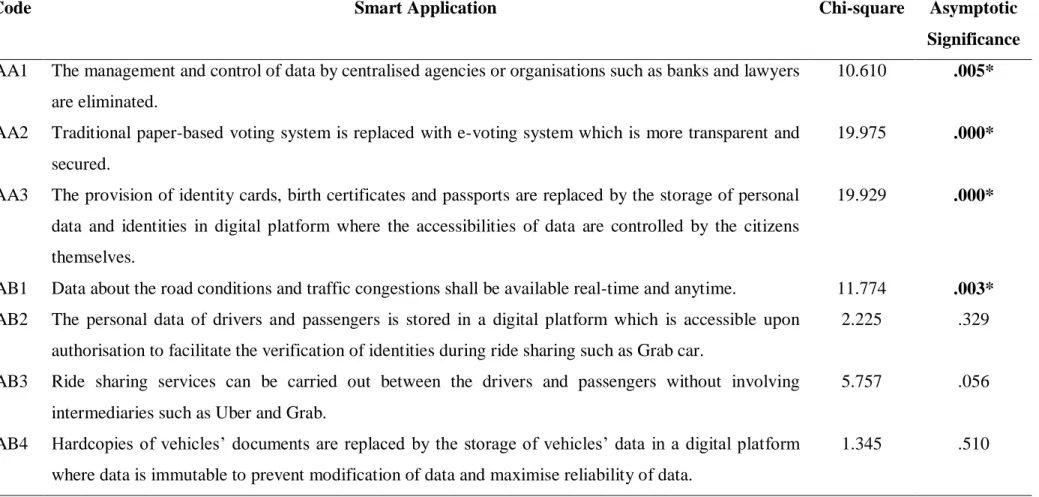
Kruskal-Wallis Test on Educational Level The two hypotheses formulated are as follows
AD4 The records of pharmaceutical supply chains such as medicines are stored in a digital platform which. AD5 Official medical licenses of medical practitioners are stored in a digital platform where data is.
Summary of Chapter
Introduction
Accomplishment of Research Objectives
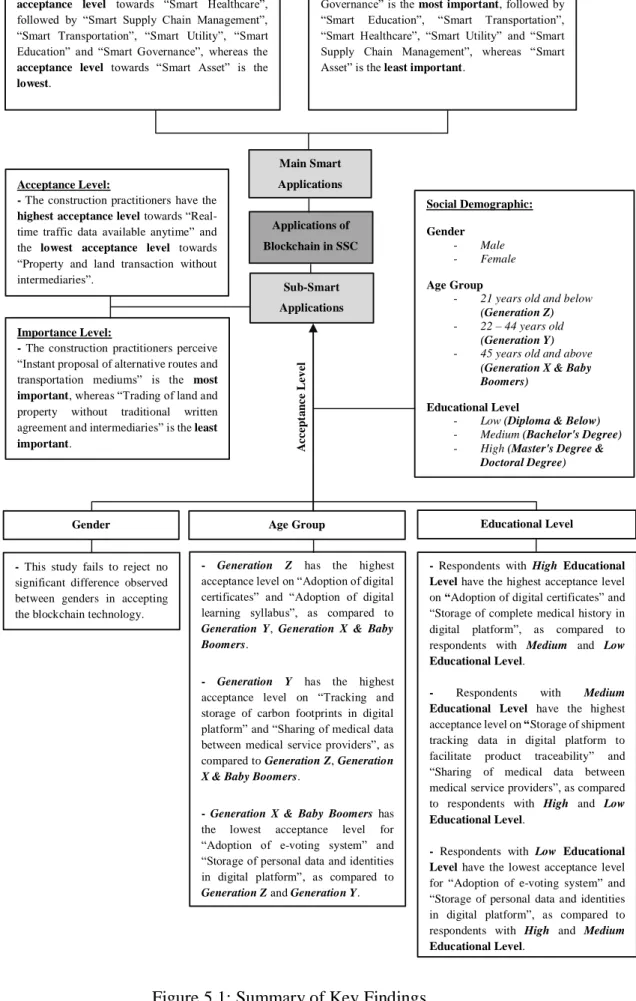
Then, by applying the arithmetic mean analysis on the data collected through the distribution of questionnaire surveys, the acceptance level of the 7 main intelligent applications and 30 sub-intelligent applications of blockchain technology were ranked and listed in Table 4.3 and Table 4.4, respectively. In addition, in the context of Malaysia, the sub-intelligent application with the highest level of acceptance is AB1 = "Data on road conditions and traffic jams will be available in real time and at all times", while AF1.
Transactions of land, real estate and housing can be carried out between buyers and sellers without intermediaries such as lawyers to prepare paper documents for verification and agreements as property, buyer and seller data stored on a digital platform can be exchanged and verified. the least acceptable sub-smart application from the perspective of the respondents. On the other hand, it was noted that BB1 = "Alternative routes and transport media can be immediately proposed to the drivers and public transport users during traffic congestion or accidents thanks to the sharing of the real-time data on road conditions and traffic congestion" is of the paramount importance, while BF1 = “Land and real estate trading should be simplified as the involvement of traditional written agreements and multi-layered authorized intermediaries is eliminated” is seen as the least important sub-smart application of all sub-smart applications.
Respondents with a High Level of Education have the highest acceptance level on “Adoption of Digital Certificates” and. Respondents with a low level of education have the lowest acceptance level for "Adoption of e-voting system" and.
Research Contributions
Research Limitation
45 years and older”, due to the inadequacy of the respondents to meet the CLT requirement. Fourth, of all social demographics, this study only examined the diverse attitudes of respondents of different genders, age groups, and education levels in adopting the blockchain technology.
Research Recommendation
This minimizes discoveries about the impact of other types of social demographics on technology adoption that can help stakeholders develop a SSC framework by integrating blockchain technology in Malaysia. This could fully explore the impact of these social demographics on the adoption of blockchain technology and allow relevant parties to make better decisions based on more comprehensive findings.
Summary of Chapter
3 Personal data and identities should be stored on a digital platform instead of providing identity cards to prevent loss, theft and fraud. 11 Real-time shipment tracking information should be stored on a digital platform where product verification and traceability can be performed at any time.