Finally, this study presented the effect of burnout and informal learning on employees' job performance. The results of this research showed that the job demand control-support model could explain burnout and informal learning.
GENERAL INTRODUCTION
- Background of the Study
- Statement of the Research Problem
- Objectives of the Study
- Research Questions
- Scope of the Study
- Significance of the Study
This study attempts to make our understanding of the phenomenon of informal learning in the Thai context somewhat insufficient. Second, commercial bank managers in Thailand, human resources and managers can develop an appropriate strategy to deal with the problem of burnout and casual learning.
LITERATURE REVIEW: CONCEPTS
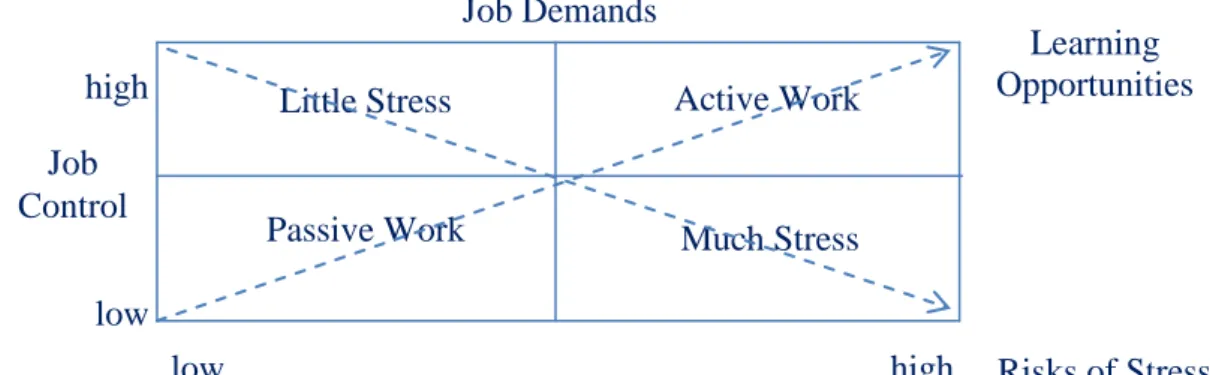
Job-Demand-Control Model
Active job The employee has been given the opportunity to decide, organize and carry out his work and is able to meet the demands effectively by being given the opportunity to control his work. Stressful job The employee is given very little control over his work, but is faced with high demands.
Job-Demand-Control-Support Model
- Job Demand-Control-Support and Burnout
- Job Demand-Control-Support and Informal Learning
Previous studies show that job characteristics and social support are the main effects of job stress and workplace learning behavior (Schaufeli and Bakker, 2004; Taris, 2006a; Taris and Kompier, 2005). Most studies tested the main effects of job demands, job control and social support on active learning (Taris and Kompier, 2005; Van Ruysseveldt et al., 2011).
Self-Efficacy
- Self-Efficacy and Burnout
- Self-Efficacy and Informal Learning
Consiglio, Borgogni, Alessandri and Schaufeli (2013) found that self-efficacy is associated with positive perception of work environment and social aspects. Judge, Locke, and Durham (1997) suggested that self-efficacy is also an antecedent or influence of job demands and resources.
Burnout
- Burnout and Job Performance
In-role performance refers to activities performed by employees that contribute (directly or indirectly) to In-role behaviors (IRBs) are responsibilities assumed by employees (for example, work a full 8 hours a day, complete assigned tasks on time, follow rules and regulations)”.
Informal Learning
- Informal Learning and Job Performance
Informal learning reflects on processes for assessing the outcomes of learning experiences and making choices about where to focus attention.”. However, a relatively large amount of research has been conducted on the empirical research on the effect of informal learning on job performance (Park and Choi, 2016).
Theoretical Frameworks
- Conservation of Resource (COR) Theory
- Self-Determination Theory
- Perceived Organization Support
Levinson (1965) stated that the actions taken by the organization's agents are indicative of the organization's purpose rather than attributable to the agents alone. When employees are favorable to supervision and HR practices, they are more satisfied with their work, feel more connected to the organization, and are more committed to the organization (Eisenberger et al., 2016).
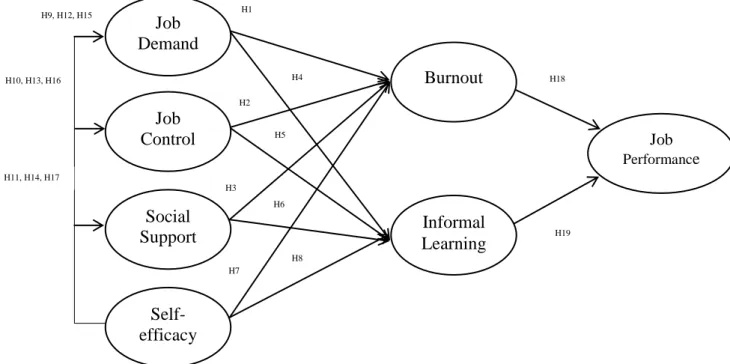
Conceptual Framework for the Study of the Relationship between Job Demand-Control-Support Model, Self-efficacy, Burnout, Informal
Job Demand-Control-Support Model and Burnout
Sometimes organization can provide employees with too much job control, this can be harmful for employee due to many reasons including role ambiguity, and having high responsibility with more difficult decision making (Warr, 1987; De Jonge and Schaufeli, 1998; Warr suggested that burnout in an employee arises from pressure demands, and little control, and less social support in the workplace This is called isolated work situation, which affects burnout in employee (de Jonge et al., 2003; Raemdonck et al., 2014).
Job Demand-Control-Support Model and Informal Learning
H1: There is a correlation between Job Demand and Burn Out H2: There is a correlation between Job Control and Burn Out H3: There is a correlation between Social Support and Burn Out. H4: There is a correlation between Job demand and informal learning H5: There is a correlation between job control and informal learning H6: There is a correlation between social support and informal learning.
Self-efficacy and Burnout as well as Informal Learning
Therefore, the level of social support can also affect an individual's learning by sharing knowledge about each other and providing support to each other when they face challenges. An employee can feel stress from work when he does not get any support from colleagues (de Jonge et al., 2003).
Self-efficacy and Job Demand-Control- Support Model
Burnout and Job Performance
Informal Learning and Job Performance
2007) The relationship between social support and self-. 2015) Self-efficacy - Burnout Does self-efficacy matter for burnout and. Positive Cho and Kim (2016) Self-Efficacy Job Demand Burnout Does self-efficacy matter for burnout and.

Research Design
Research Context
- The Role of Commercial Banks in Thailand
- Bank A
- Bank B
- Bank C
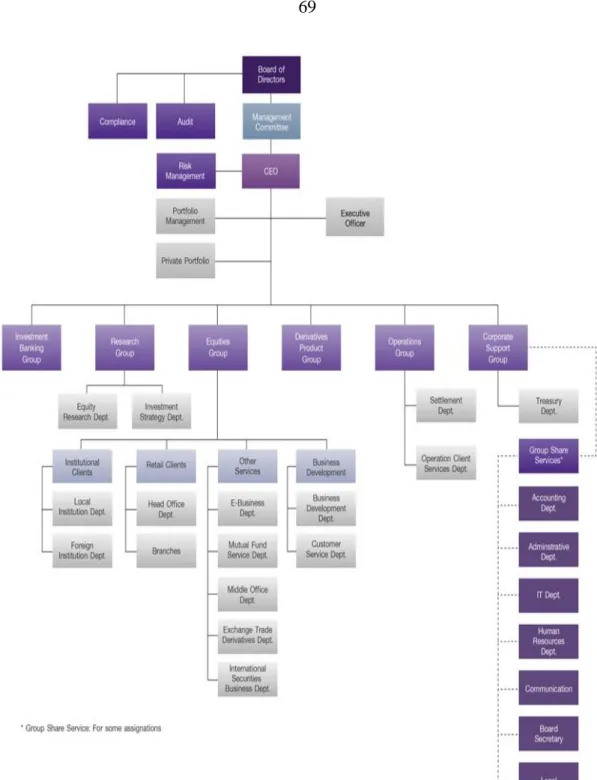
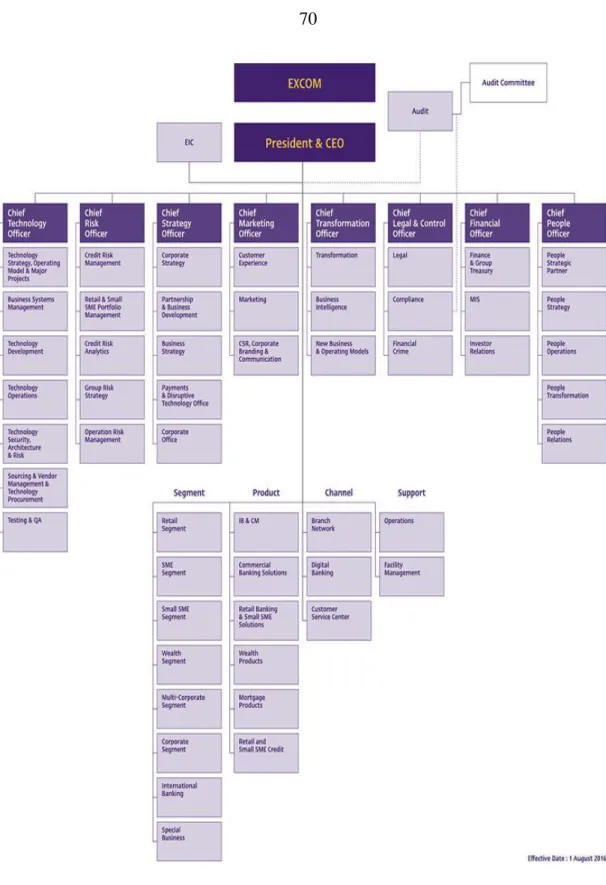
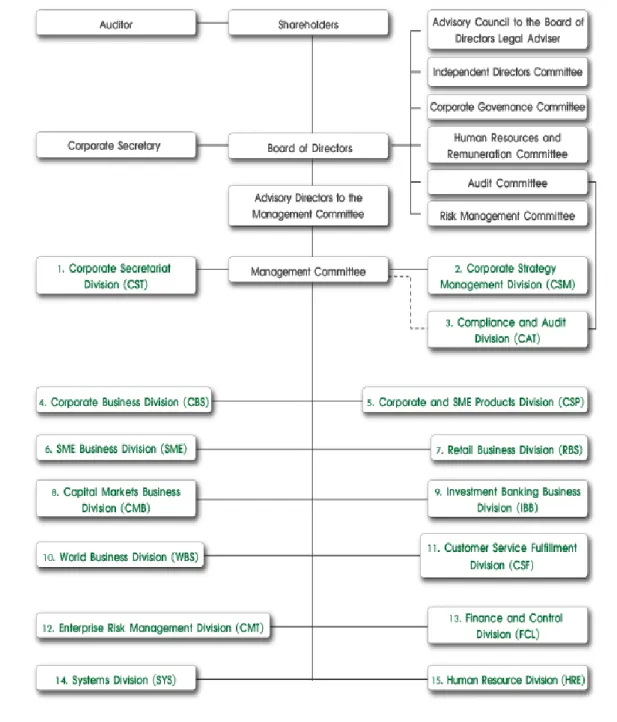
- Organizational Structure: Commercial Banks in Thailand
The bank treats its customers as one of the most important contributors to the bank's success and growth. A wide range of attractive benefits to promote the health and well-being of the bank's staff and their families.
Target Population
Sample Frame
Sampling Technique
Second, simple random sampling is used as probability sampling method to give everyone from the list an equal chance of being selected (Creswell, 2014). The people in the list are arranged in a table using a computer program, which is automatically selected.
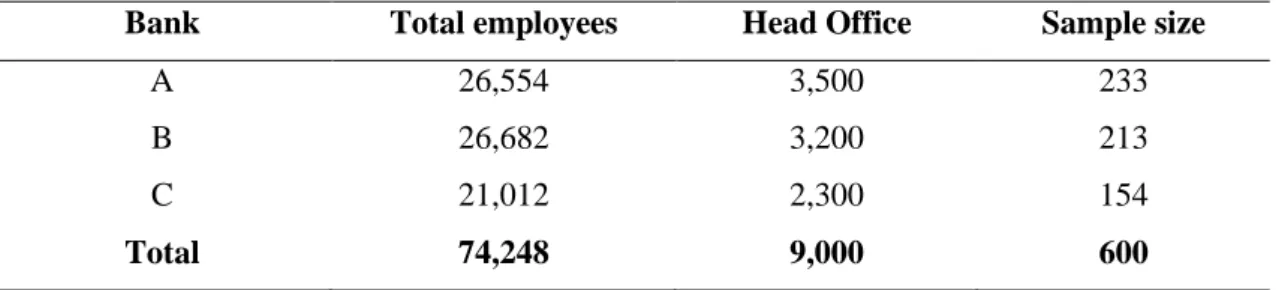
Sample Size
The sample frame or the list of the elements in the target group is created by HR from the individual bank. Researcher chooses larger sample size which is significant to get representative from the population in terms of SEM.
Research Instrument
II Work control Work autonomy, variety of tasks (1) strongly disagree with (6) strongly agree Social Support Supervisor Support,.
Measures
- Job Control
- Social Support
- Job Performance
- Burnout
- Job Demands
- Self-efficacy
- Informal Learning
The two dimensions were measured using a six-point Likert scale ranging from (1) = “do not agree at all” to (6) = “completely agree”. A six-point Likert scale ranging from (1) = “strongly disagree” to (6) = “strongly agree” was used in this study.
Data Collection
Data Analysis Strategy
- Measurement Model
- Structural Model
The basic events of SEM testing are to measure construct validity and to test the validity of the structural model and hypothesized theoretical relationships (Hair et al., 2010). After the structural model is developed, the modification is done to better improve the fitness of the model and the comparison is done.
Validity and Reliability
AVE is the average amount of variance in indicator variables that a construct is managed to explain, an AVE of 0.50 or higher indicates adequate convergent validity. On the other hand, standardized loading to examine statistically significant factor loadings on each construct, values of 0.50 or more indicate convergent validity (Hair et al., 2010).
Data Screening and Preparation
- Outliers
- Normality
- Multicollinearity, Linearity, and Homoscedasticity
Divergent validity is evident when the AVE of a construct is higher than the square of the correlation between the construct and other constructs (Hair et al., 2010). In a positively skewed distribution, the long tail of the distribution is on the right while a negatively skewed distribution has the ling tail on the left side.
RESULT AND ANALYSIS
Demographic Characteristics of the Respondents
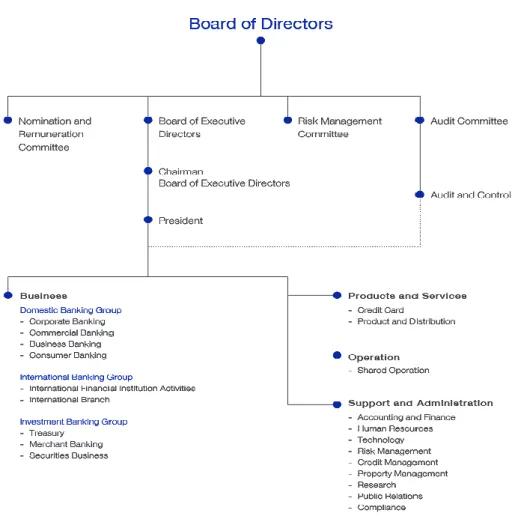
Descriptive Analysis of Measurement Scales
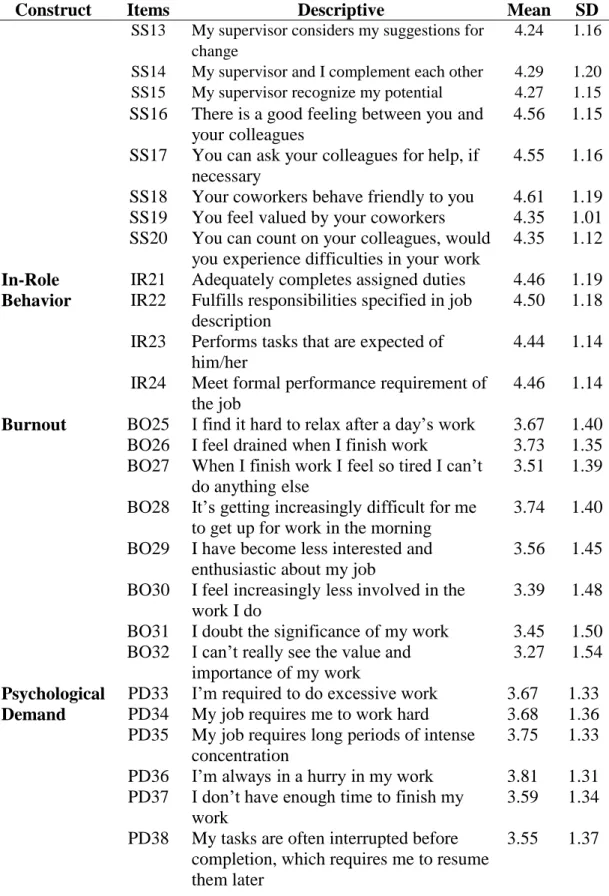
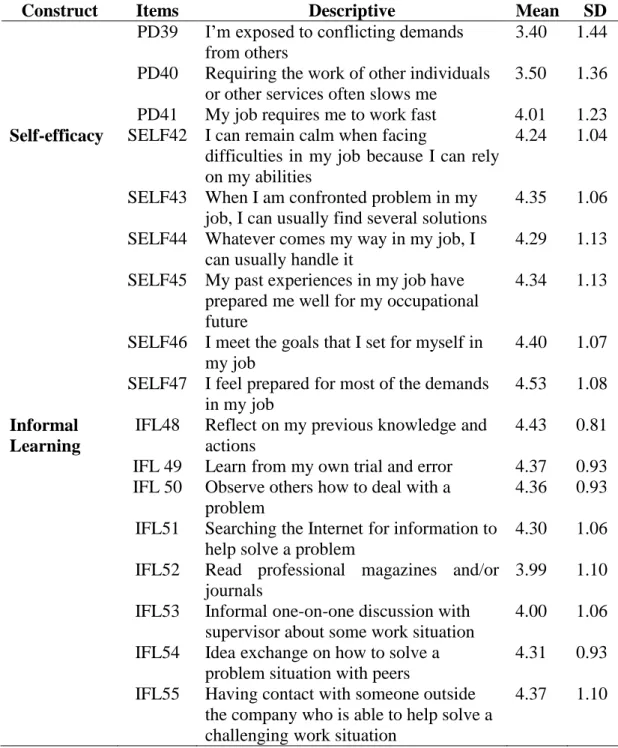
Regarding job performance (In-Role Behavior), mean scores were above average (4.44 to 4.50) and SD varied widely among respondents. Also, the mean of all items for Self-Efficacy was quite high (4.24 to 4.53), but the SD was highly variable.
Outliers
Testing for Multivariate Assumptions
- Normality
- Multicollinearity, Linearity, and Homoscedasticity
It means that there is no violation of the multicollinearity assumption because the correlation between the variables does not exceed 0.80.
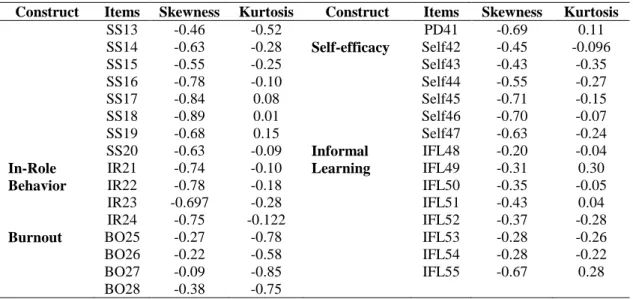
Measurement Model Evaluation
- CFA Results for Job Control
- CFA Results for Social Support
- CFA Results for Job Demand
- CFA Results for Burnout
- CFA Results for Self-efficacy
- CFA Results for Informal Learning
- CFA Results for Job Performance
Again, the path coefficient of each latent construct to the observed indicators was significant (p < 0.000) and the standardized regression. Again, the path coefficient of each latent construct to the observed indicators was significant (p < 0.000) and the standardized regression weight ranged from 0.76 to 0.91.
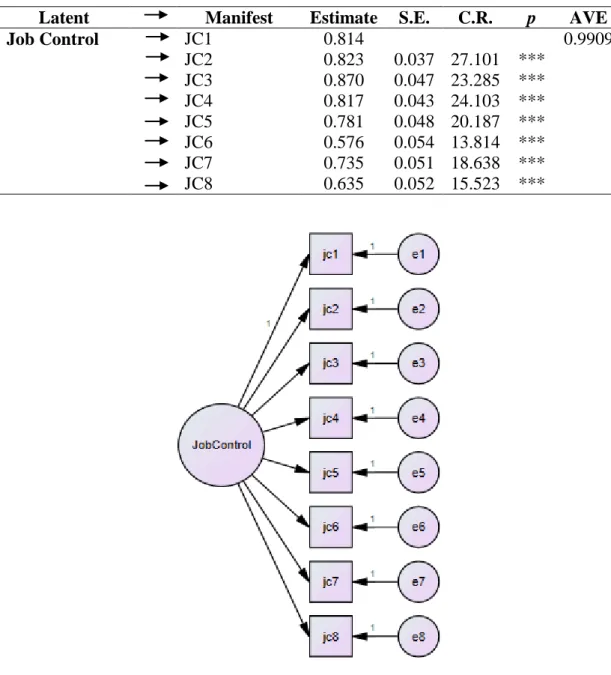
CFA Results for Measurement Model
- Overall
- Bank A
- Bank B
- Bank C
Measurement of Reliability and Validity
Convergent, Construct, Discriminant, and Criterion Validity
The square root of AVE should be higher than the correlation estimates between the construct and all other constructs shown in Table 4.13. The square root of the AVE for each construct was higher than the correlation between that construct and the other constructs.
Structural Equation Modelling
- Overall
- Bank A
- Bank B
- Bank C
Structural Model Modification
- Overall
- Bank A
- Bank B
- Bank C
The structural model fit and comparison of three models are shown in Figure 4.12 and Table 4.16, respectively. The structural model fit and comparison of three models are shown in Figure 4.13 and Table 4.17, respectively.
Hypotheses Testing: Direct Relationship: Overall
- Relationship between Self-efficacy and Job Demand-Control- Support
- Relationship between Burnout and Job Performance
- Relationship between Informal Learning and Job Performance This section showed that informal learning had a positive relationship with job
The researcher also investigated that the relationship between self-efficacy and informal learning is a positive and significant relationship (β = 0.557, p < 0.000). This part showed that there would be a negative and significant relationship between self-efficacy and job demand (β = -0.324, p < 0.000).
Hypotheses Testing: Direct Relationship : Bank A
- Relationship between Job Demand-Control-Support and Informal Learning
- Relationship between Self-efficacy and Job Demand-Control- Support
- Relationship between Burnout and Job Performance
- Relationship between Informal Learning and Job Performance This section showed that informal learning had a positive relationship with job
The researcher also investigated that the relationship between Self-Efficacy and informal learning was a positive and significant relationship (β = 0.549, p <. 0.000). This section showed that there would be a negative and significant relationship between self-efficacy and job demand (β = -0.327, p < 0.000).
Hypotheses Testing: Direct Relationship : Bank B
- Relationship between Job Demand-Control-Support and Informal Learning
- Relationship between Self-efficacy and Job Demand-Control- Support
- Relationship between Burnout and Job Performance
- Relationship between Informal Learning and Job Performance This section showed that informal learning had a positive relationship with job
The researcher also examined the relationship between self-efficacy and informal learning was positive and significant relationship (β = 0.573, p < 0.000). This section showed that there would be a negative and significant relationship between self-efficacy and job demand (β = -0.285, p < 0.000).
Hypotheses Testing: Direct Relationship : Bank C
- Relationship between Job Demand-Control-Support and Informal Learning
- Relationship between Self-efficacy and Job Demand-Control- Support
- Relationship between Burnout and Job Performance
- Relationship between Informal Learning and Job Performance This section showed that informal learning had a positive relationship with job
The researcher also investigated that the relationship between self-efficacy and informal learning was a positive and significant relationship (β = 0.610, p < 0.000). This section showed that there will be a negative and significant relationship between self-efficacy and job demand (β = -0.332, p < 0.000).
Hypothesis Testing: Mediating (Indirect) Relationship
- The Nested Models Approach
Supported In addition to Baron and Kenny's steps for examining the mediator in hypothesis testing, the researcher used the Sobel test. This calculation returns the Sobel test statistic and one- and two-tailed probability values.
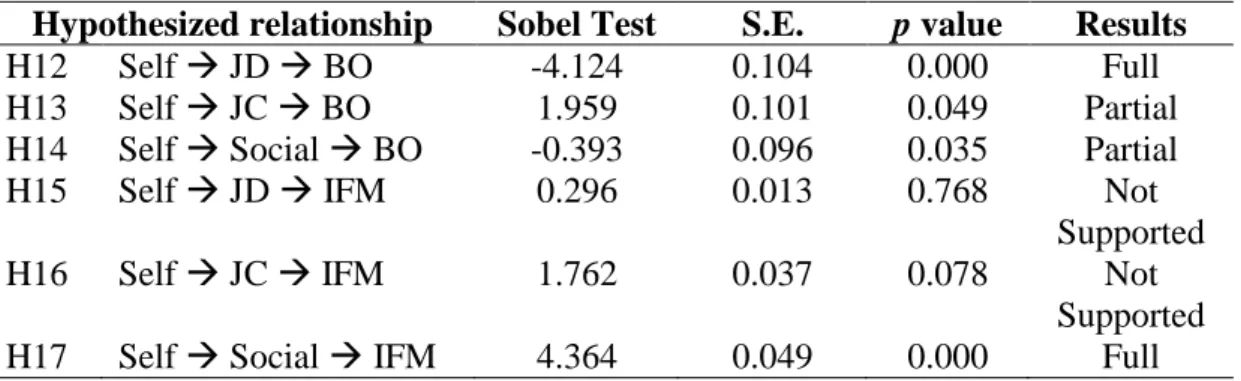
Mediation Role : Overall
- Self-efficacy and Informal Learning: Mediation Role of Job Demand-Control-Social Support
The result showed that task control had a mediating effect on the relationship between self-efficacy and informal learning (Sobel test = 3.665, p < 0.000). As a result, the researcher concluded that social support had a mediating effect between self-efficacy and informal learning (Sobel test = 5.602, p < 0.000).
Mediation Role : Bank A
- Self-efficacy and Burnout: Mediation Role of Job Demand- Control-Social Support
- Self-efficacy and Informal Learning: Mediation Role of Job Demand-Control-Social Support
As a result, the researcher concluded that social support has a full mediating effect between self-efficacy and informal learning (Sobel test = 4.364, p < 0.000).
Mediation Role : Bank B
- Self-efficacy and Burnout: Mediation Role of Job Demand- Control-Social Support
- Self-efficacy and Informal Learning: Mediation Role of Job Demand-Control-Social Support
The result showed that job control had no mediator effect on the relationship between self-efficacy and informal learning (Sobel test = 1.688, p < 0.091). As a result, the researcher concluded that social support had full mediation effect between self-efficacy and informal learning (Sobel test = 3.206, p < 0.001).
Mediation Role : Bank C
- Self-efficacy and Burnout : Mediation Role of Job Demand- Control-Social Support
- Self-efficacy and Informal Learning: Mediation Role of Job Demand-Control-Social Support
As a result, the researcher concluded that social support had no mediator effect between self-efficacy and informal learning (Sobel test = 0.403, p < 0.687).
DISCUSSION, CONCLUSION, AND RECOMMENDATION
- Discussion of Research Findings
- Relationship between Job Demand-Control-Support and Burnout as well as Informal Learning
- Relationship between Self-Efficacy and Burnout as well as Informal Learning
- Relationship between Self-Efficacy and Job Demand-Control- Support
- Mediating Role of Job Demand-Control-Support in the
- Relationship between Burnout and Informal Learning as well as Job Performance
- Analytical Findings for Bank A, B, C
- Bank A
- Bank B
- Bank C
- Conclusion
- Practical Implications
- Contributions of the Study
- Limitations of the Study
- Directions for Future Research
The result showed that there was a significant relationship between self-efficacy and job demand-control-support. The result showed that there was a significant relationship between self-efficacy and job demand-control-support.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Hidden dimensions of work and learning: the meaning of unpaid work and informal learning in global capitalism. The effects of formal learning and informal learning on job performance: the mediating role of the value of learning at work.
APPENDIX
Demography of Respondents
Please check in your opinion towards the following items
The Empirical Study of the Relationship between Workplace Characteristics, Work-Related Informal Learning and Job Performance”. I can stay calm when I face problems in my work because I can rely on my abilities.
แบบสอบถาม
ฉันสำมำรถก ำหนดรูปแบบกำรท ำงำนของตัวเองได้
ข้อค าถาม
พวกเขำเห็นคุณค่ำในตัวฉัน
ระดับควำมถี่
35. งานของฉันใช้เวลานานในการทำ 36. งานของฉันจะต้องทำให้เสร็จ เราทำอย่างเร่งรีบตลอดเวลา 36. งานของฉันจะต้องทำให้เสร็จ เราทำอย่างเร่งรีบตลอดเวลา 37. ฉันไม่มีเวลาพอที่จะทำมัน. 38. งานของฉันถูกขัดจังหวะบ่อยครั้งทำให้ฉันต้องกลับไปเริ่มต้นใหม่
41.งำนของฉันต้องใช้ควำมรวดเร็ว