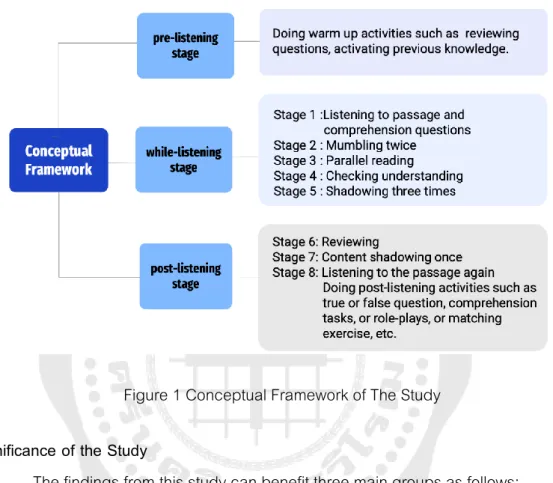
INTRODUCTION
LITERATURE REVIEW
Listening Skills
- Definition
- Listening Process
- Listening Strategies
- Components of Listening Skills
- Teaching Listening Skills
Sevik (2012) states that listening skills are receptive skills, like reading, because they concentrate on obtaining data from external sources. Furthermore, Bostrom (2011) argues that listening skills are the acquisition, processing and storage of information in the interpersonal context. Listening skills can also mean interpreting communicative behavior to understand the meaning and behavior of the sender (Burleson, 2011).
Moreover, Gilakjani and Sabouri (2016, p. 124) defined listening comprehension as the process of receiving and understanding a message from the sender and creating meaning through participation, creativity and empathy. Ranggen (2016) defines listening comprehension as the process of actively focusing on dynamic sounds with precision and speed in analyzing the information. Basically, listening skills are the ability to hear information and understand messages that senders are trying to communicate.
Therefore, listening skills can be considered as a complex and dynamic process involving different aspects of knowledge and communicative abilities. In short, although many researchers have proposed different components of listening skills, they share some similarities: the ability to understand the main ideas, distinguish between different sounds, and identify important points.

A Shadowing Technique
- Stages of A Shadowing Technique
Finally, a Shadowing technique has two main advantages: it stimulates students' listening strategies and their working memory and supports communication skills. However, in reality, meaning will always be processed, so A Shadowing Technique should be explained to students before they begin the learning process (Hamada, 2011b). In summary, some disadvantages of A Shadowing Technique include the involvement of classmates' voices, which can cause distraction and focus on phonological information without accessing the meaning.
Students listen to the target passage to prepare for shadowing and can begin shadowing without vocalizing the words. Therefore, the aim of this stage is to focus on phonemic aspects by imitating words/phrases. According to Iwashita (2010), this step helps students reproduce sounds better, but they focus more on shadowing than hearing the sound.
At this point, students listen to the words/phrases one last time and shade them. This is one of the most challenging stages for students, according to Hamada (2011b), because students may struggle to focus on both the sounds and their meanings.

Attitudes
The purpose of this phase is to identify words/phrases that may still be challenging for students. In the linguistic field there is also a type of attitude that shows the expression of favorable or unfavorable feelings of a language. This type of attitude is called language attitudes, which reflects "impressions of language difficulty or simplicity, ease or difficulty of learning, degree of importance, elegance, social status, etc.".
This means that language attitudes are essential factors either for enhancing students' competence or for discouraging their potential in language learning. Students with positive attitudes toward the target language, their instructors, and native speakers tend to promote their language acquisition and learning process (Hismanoglu, 2016). On the other hand, students with a negative attitude will exhibit hesitant behavior while learning the target language, leading to anxiety and failure.
According to Dehbozorgi (2012), attitudes and language are key variables in determining language learning success. It can be said that attitude towards language is critical to the progress or failure of language learning (Baker, 1992).
English as a Foreign Language (EFL) Students
In conclusion, EFL can be considered as a language that is not imperative for native citizens' everyday communication (Bern, 1990; Si, 2019; . Tarnopolsky, 2002). Interestingly, many English learners tend to have a motivation to learn the foreign language, which Iwai (2011) and Peng (2012) called EFL learners - the students who study English in non-English speaking countries. For EFL students, the motivational reasons for learning English as a foreign language have a clear intention: they want to be able to communicate with English-speaking tourists or friends, or they want to be able to read English in books, newspapers or other media (Broughton et al., 2002 ).
The first problem is students' limited opportunities to use English in the classroom due to teaching strategies where teachers provide passive learning for students (Peng, 2012). Consistent with this claim, EFL learners lack the ability to display their language potential (Maskhao, 2002; Simpson, 2011; Zhao, 2011). Students who study English as a foreign language hardly experience the use of the target language in social occasions and even in their daily life, since the environment in the classrooms and in the home country is not beneficial for active learning activities, such as speaking and listening. (Yuthana, 2 0 1 7 as cited in Rakangthong, 2019).
In conclusion, considering the above-mentioned major difficulties, the teaching methods should be changed from passive learning to active methods, which provide more opportunities for students to use English appropriately in terms of speaking, writing, reading and listening.
Related Research
Likewise, Sugiarto, Prihantoro and Edy (2020) conducted studies on the impact of the shadowing technique on higher education students' English pronunciation. The results indicated that the shadowing technique had a positive impact on the target learners' English pronunciation. The results showed that imitation and shadowing techniques using English transcription video helped improve students' speaking skills.
Studies have also been carried out on the development of pupils' listening skills using the shadowing technique. In the study, 73 students were divided into two experimental studies to investigate how difficult lessons can improve students' listening comprehension. The results of the study suggested that shadowing with difficult materials could improve students' listening comprehension, particularly the ability to identify the sounds they were listening to.
Even though the effectiveness of the shadowing technique was confirmed, Hamada found the limitation of the study of shadowing technique: students' individual differences. The results of the study showed that students' listening skills were significantly improved after applying the shadowing technique.
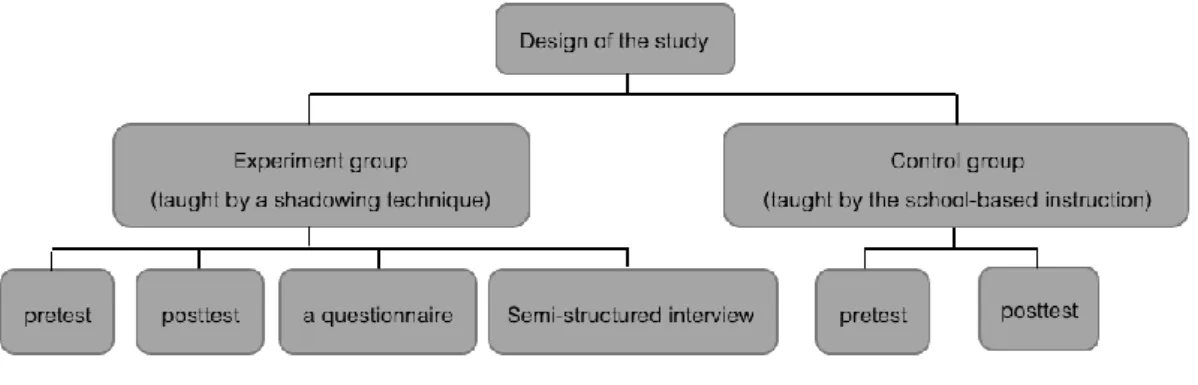
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
26 To design lesson plans, Hamada's instructional listening using the shadowing technique (Hamada, 2017) and Gilakjani and Ahmadi's listening teaching method were used as a framework (Gilakjani & Ahmadi, 2011). In stage 4 of the shadowing technique, namely 'quietly check students' understanding', the teacher checks students' understanding using various exercises such as filling in a blank or matching. The process was adapted from the suggestions of Pope and Mays (2020). The process was 1) interviewing five volunteers from the experiment group taught by A Shadowing Technique, 2) transcribing the data, 3) finding the frequency of information, 4) identifying interesting data, 5) organizing them into a category -- improving listening skills, motivation and learning environment, and 6) descriptive discussion with reliable explanation.
As shown in Table 10, the statements "I enjoyed doing activities in class" (M= 4.07) and "The teacher's techniques were ineffective in improving my listening skills" (M= 4) * were rated at a very positive level. To investigate Thai EFL high school students' attitudes towards learning listening skills through A Shadowing Technique. According to the results of the research, both A Shadowing Technique and the school-based teaching improved students' listening skills.
First, a specific set of students - the 8th graders at a secondary school -. were included in this study. For example, if the word is "actor", the learners are expected to act as an actor.
FINDINGS
The effects of A Shadowing Technique on Thai EFL secondary school students’
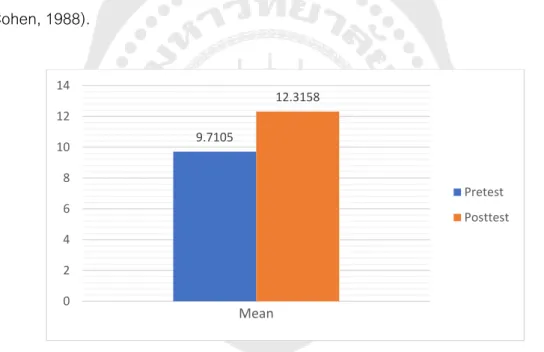
To investigate the effects of A Shadowing Technique on the listening comprehension of Thai EFL high school students, mean scores, standard deviations and the Dependent Samples t-test were used to analyze the pre-test and post-test. 34 It turned out that the first hypothesis, the mean post-test score of students teaching A Shadowing Technique was higher than the mean pre-test score, was supported by the data. There were statistically significant differences in the pretest and posttest mean scores of students' listening skills (t p<.001).
Therefore, the results indicate that A Shadowing Technique had the potential to improve Thai EFL high school students' listening skills. Furthermore, Cohen's effect size value (d=0.91) suggests a large effect of A Shadowing Technique on Thai EFL high school students' listening skills (Cohen, 1988).
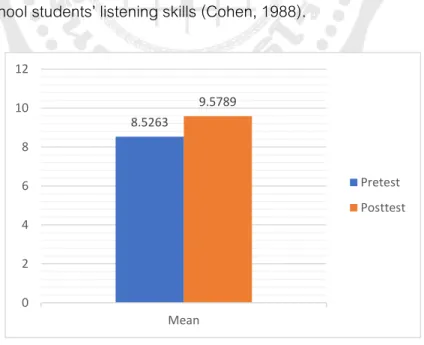
The effects of the school-based instruction on Thai EFL secondary school
The results show that there were statistically significant differences in the mean scores of the pretest and posttest (t p<.001). This means that the mean post-test score was significantly higher than the mean pre-test score. Also, Cohen's effect size value (d=0.33) suggests a small effect of school-based instruction on the listening skills of EFL Thai high school students (Cohen, 1988).
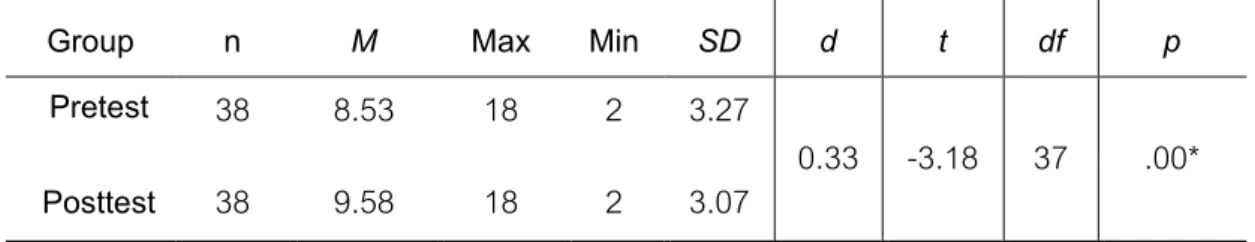
The comparison of A Shadowing Technique to the school-based instruction
In summary, the results show that both the Shadowing Technique and school-based instruction improve students' listening skills, but a shadowing technique improved students' listening skills better. The following section deals with the results from the questionnaire and semi-structured interviews to show students' attitudes towards learning listening skills through the Shadowing Technique.
Students’ attitudes toward learning listening skills through A Shadowing
The results show that students had a positive attitude towards learning listening skills through A Shadowing Technique (M = 3.89). In conclusion, the results of the questionnaire and the interviews showed that students preferred to learn listening skills through A Shadowing Technique. This study aimed to investigate the effects of A Shadowing Technique on the listening skills of Thai EFL high school students.
Furthermore, the aim was to examine the attitudes of EFL students towards learning listening skills through A Shadowing Technique. To investigate the effects of A Shadowing Technique on the listening comprehension of Thai EFL high school students. Comparing the effects of A Shadowing Technique with that of school education on the listening comprehension of Thai EFL high school students.
Then, the students in the experimental group were asked to fill out a questionnaire about their attitudes towards learning listening skills through A Shadowing Technique. The results of the study showed that both A Shadowing Technique and the school-based teaching effectively improved students' listening skills. The students also had positive attitudes towards learning listening skills through A Shadowing Technique.
This study proved that using the shadowing technique is a good method to improve students' listening skills. The teacher asks the students to shadow the sound while reading and listening to the passage.
CONCLUSION AND DISCUSSION