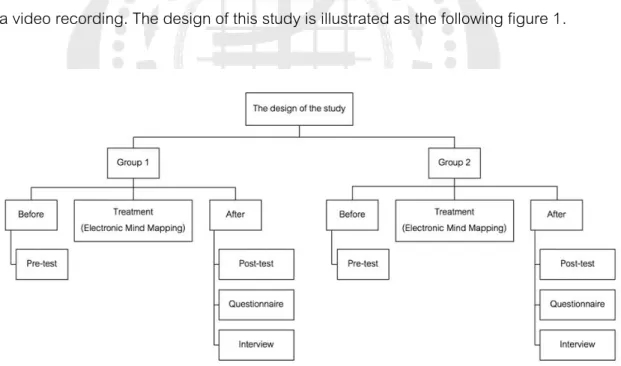
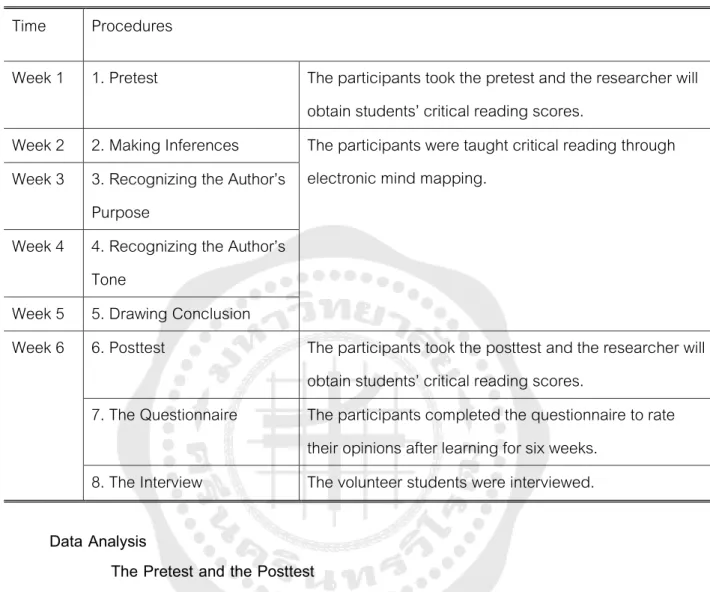
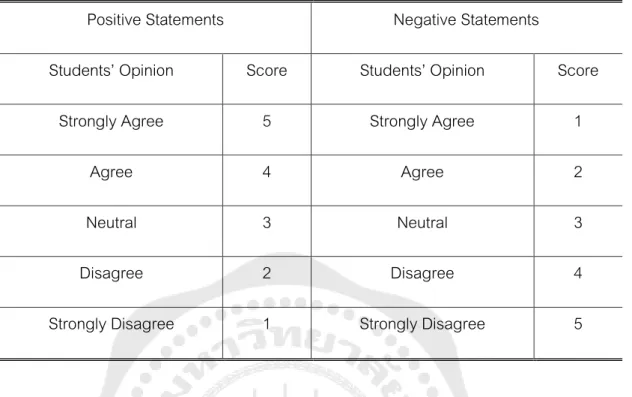
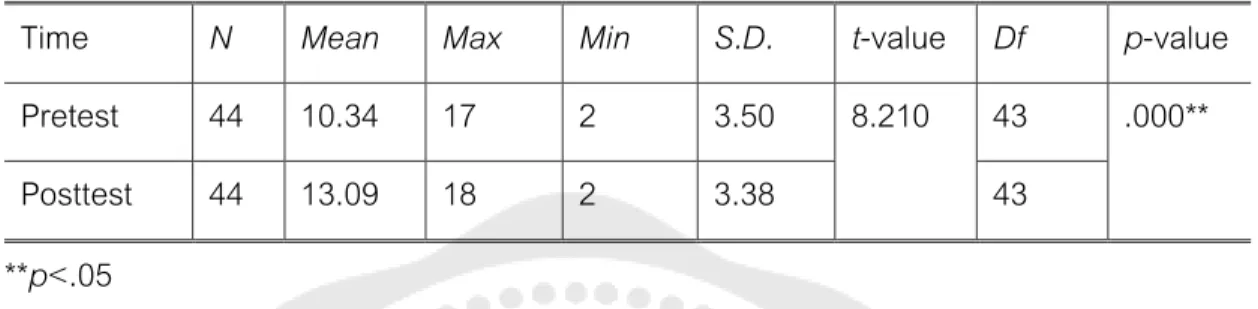
INTRODUCTION
LITERATURE REVIEW
In summary, electronic mind mapping is an online tool that allows students to create mind maps. The results showed that electronic mind mapping has greater potential than conventional mind mapping. Two groups of students were asked to use electronic and conventional mind mapping.
Sabbah (2015) investigated the effects of electronic mind mapping (computerized mind maps) on students' reading comprehension and attitudes towards learning through electronic mind mapping. The results of this study indicated that electronic mind mapping affected students' reading comprehension performance. The results showed that the use of electronic mind mapping had a medium effect on the learning of reading comprehension.
There are several applications of electronic mind mapping in the language classroom, but studies have been conducted on reading comprehension. Therefore, this study proposed to explore the effects of electronic mind mapping on critical reading skills.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The vision of the school emphasizes students' English language skills and the importance of critical reading. The participants were 83 eleventh grade students studying at a demonstration school in Bangkok, Thailand in the second semester of the 2021 academic year. The participants passed the English Reading I, an English course in the first semester of the 2021 academic year, and they enrolled in the English Reading II course in the second semester.
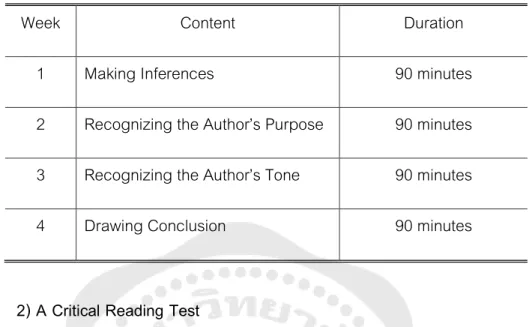
In the pre-reading phase, electronic mind maps were used to activate the students' background knowledge and prepare students for reading texts as well as to motivate students to read. The questionnaire was used to study the students' opinions about learning critical reading by means of electronic mind maps. A semi-structured interview was conducted to obtain more information besides the questionnaire and to ensure the accuracy of the questionnaire.
To avoid a language barrier in communication, the interview was conducted in the students' mother tongue (Thai). In the last week of the study, the researcher asked five students from each class to volunteer for interviews. The data from the video was triangulated with the data from the open-ended part of the questionnaire and the interview.
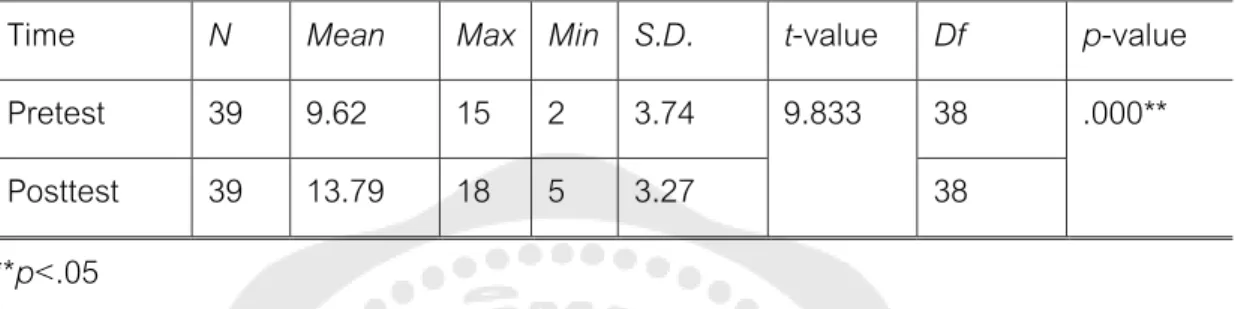
Pretest The participants have taken the pretest and the researcher will obtain the critical reading scores of the students. Posttest The participants took the posttest and the researcher calculates the critical reading scores of the students. The data from the first part was analyzed by mean scores and standard deviations to find out students' opinions about studying critical reading through electronic mind mapping.
The value of students' thoughts in learning critical reading through electronic mind mapping was interpreted using the criteria in Table 4. Data from the video recording was analyzed using content analysis and triangulated with data from the open-ended questionnaire and interviews. to probe students' thoughts. They have been informed about the study procedures and understand that this study has not put them at a disadvantage.
FINDINGS
Students’ Critical Reading Skills
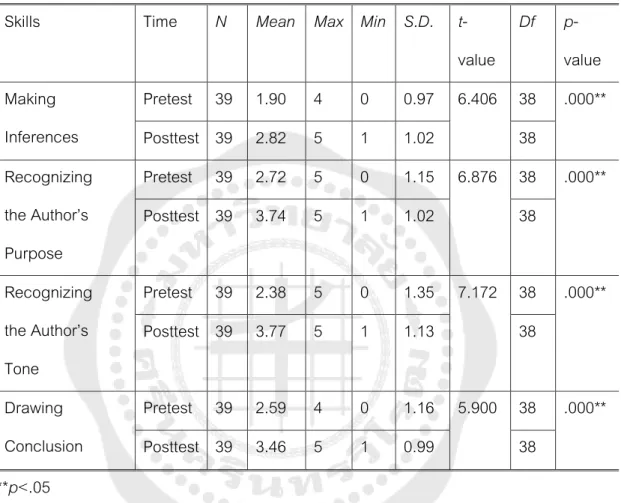
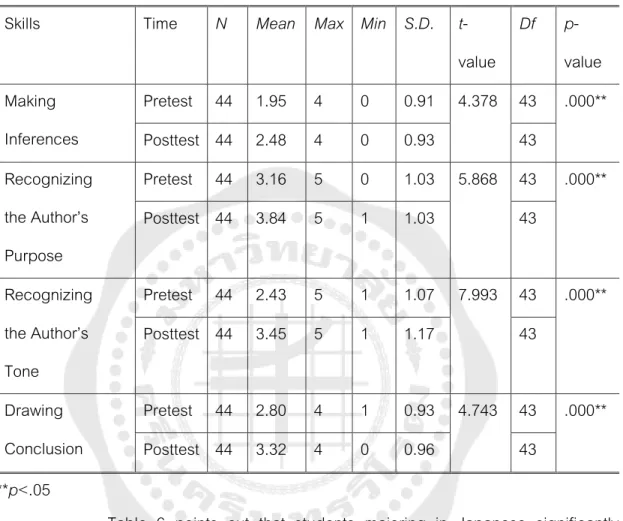
The t-test analysis reveals that there were statistically significant differences in the pretest and posttest mean scores of critical reading skills of students majoring in Japanese (t p<.05). In particular, the results also show that students majoring in Japanese made the highest gains in recognizing the author's tonal skill. In summary, the results indicate that teaching critical reading skills through electronic mind mapping potentially improved all of the students' subskills.
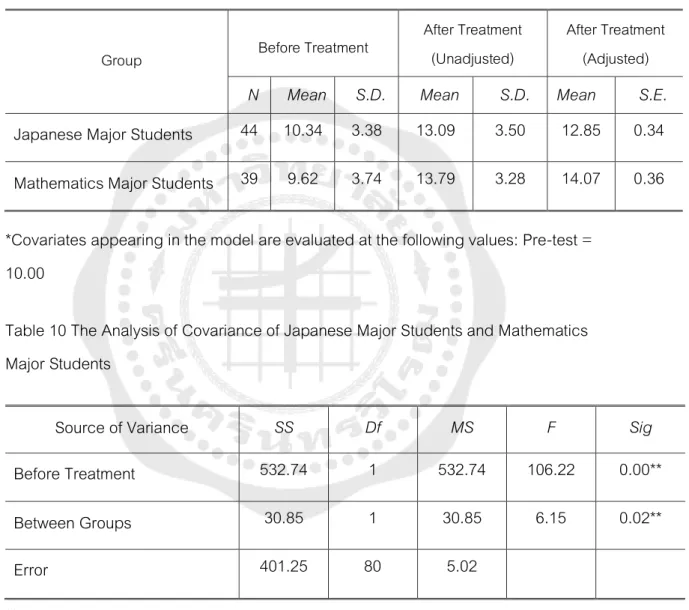
Similar to the students majoring in Japanese, the results also show that students gained the highest gain in recognizing the writer's tone sub-skill. Therefore, the results indicate that teaching critical reading skills through electronic mind maps potentially improved students' all sub-skills. To specify, the pretest mean score of students majoring in Japanese was higher than that of students majoring in Mathematics.
After the treatment, the analysis shows that there were statistical differences in the average scores of students studying as a major. The electronic mind map can improve critical reading skills of students majoring in Mathematics better than students majoring in Japanese.
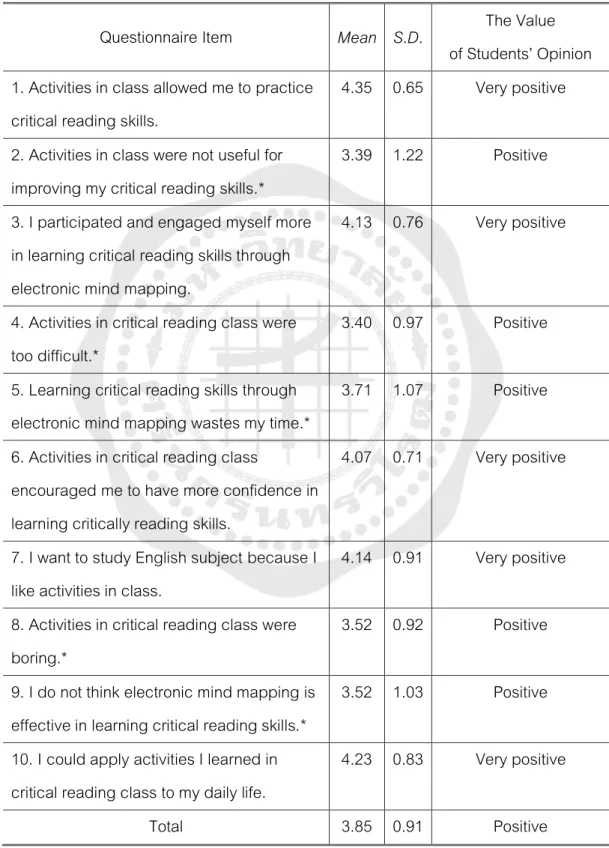
Students’ Opinions about Learning Critical Reading Skills through Electronic Mind
The statement that received the highest mean score was "Activities in class allowed me to practice critical reading skills" (4.35), followed by the statement "I was able to apply activities I learned in critical reading class to my daily life " (4.23). The next two following statements were "I want to study the subject of English because I like activities in the class" (4.14) and, "I participated and involved myself more in learning critical reading skills through electronic mind maps" (4.13). The statement that received the lowest average score was "Activities in critical reading class were too difficult" (3.40).
First of all, most of the students reported that the electronic brain mapping enhanced their enjoyment during learning. One student said, "It was easier to look at the information in the mind map than to read the text itself." One student also expressed that using electronic mind maps is similar to the game that can be played happily with the classmates. In the first lesson, they noted that they were not familiar with the software tools, and it took more time to do mind mapping; however, when they were familiar with using tools in later classes, they enjoyed creating mind maps.
All students reported that electronic mind mapping improved their critical reading skills because of the collaboration among their friends. Several students mentioned that while creating an electronic mind map, they were able to see their friends' points of view, which helped them better understand the texts they read and did not miss important points and key words. One student mentioned, "I could apply using electronic mind mapping to read articles and different media." One student also added, "I could use electronic mind mapping in reading in everyday life."
As concluded from the interviews, students had positive thoughts about learning critical reading skills through electronic mind mapping. In addition, all students agreed that electronic mind mapping promotes enjoyment and can improve their critical reading skills. In terms of student interaction and behavior, students participated well in creating the electronic mind map.
However, in the first few weeks there were some problems in the classroom using the electronic mind mapping software. By triangulating the results of the questionnaire, interview and video recording, the students had positive opinions about learning critical reading skills through electronic mind mapping. The students agreed that the use of electronic mind mapping could help them improve their critical reading skills and comprehension while reading texts.
CONCLUSION AND DISCUSSION
The results of the questionnaire, the semi-structured interview and the video recording showed that students had a positive attitude towards learning critical reading skills through electronic mind mapping. In conclusion, electronic mind mapping had a positive effect on critical reading skills and opinions of EFL students. Based on the first and second research questions, the analysis shows that EFL students improved their critical reading skills by learning through electronic mind mapping.
First of all, electronic mind mapping helped students organize information and ideas for the reading texts. In this activity, the electronic mind mapping helped the students organize the ideas and also remember the information from the reading text better. The information and ideas were better arranged and organized when the students used electronic mind mapping.
Regarding the results of each sub-skill, electronic mind mapping potentially improved students' sub-skills. The electronic mind mapping visualized this information and helped them better understand the meaning of the words. The results also reveal that electronic mind mapping better improved critical reading skills in students majoring in mathematics than students majoring in Japanese.
These results confirm the study of Samonlux (2020) which revealed that electronic brain mapping improved students' performance. To compare with the traditional mind map, electronic mind map is more attractive to students. This discussion is in line with the study of Sabbah (2015) who investigated the effects of electronic mind maps.
In the first lesson, it took students much more time to create mind maps. Although there were some difficulties in the classroom, the electronic mind mapping was effective in increasing the critical reading ability of EFL students. The results of the study found that EFL high school students developed their critical reading skills after learning through electronic mind mapping.
Electronic Mind Mapping - PowerPoint presentation - The reading passage on how global warming is changing our world”. Directions: Ask five volunteers from each group how they can teach critical reading skills through electronic mind mapping.