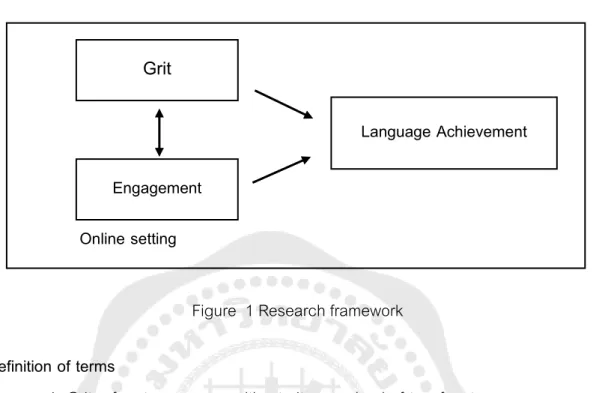
INTRODUCTION
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Second Language Acquisition
- Individual Differences
- Language Learning Strategies
- Agency
- Autonomy
- Self-regulation
- Self-efficacy
- Personality
- Motivation
- Grit
- Definition of grit
- Grit in the field of education
- Criticism of grit
- Related research
- Learner Engagement
- Definition of learner engagement
- Measuring behavioral engagement
- Measuring emotional engagement
- Measuring cognitive engagement
- Importance of learner engagement to online learning
- Related research
- English Learning in Online Setting
Holec (1979) described learner autonomy as "the ability to take responsibility for one's own learning". The learner's autonomy consists of several elements: "determination of goals, definition of content and progression, choice of methods and techniques, monitoring of the acquisition process and evaluation of what has been acquired". Furthermore, Gathercole (1990) defined it as the ability of students to take responsibility for their learning. Due to the correlational analysis of total items, some items in the L2 granulation scale were removed. The study found that black males with higher levels of hardness earned higher scores.
In addition, the study found other links between L2 grit (e.g., multilingualism, L2 joy, age, and gender). As summarized in the work of Fredricks et al. 2004), many researchers chose to measure both positive and negative behavior. The instrument used in the study by Fredricks et al. 2004) is designed to assess students' goals, metacognition, and effort control.
The importance of learner engagement was also highlighted in the work of Han (2021), who found that students' language achievement depends on learner engagement. Furthermore, the importance of learning strategies in online learning was shown in the study of Lin et al.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The researcher calculated the size of the sample in this study using the Taro Yamane formula with a 96% confidence level. The participants in this research were 563 grade 11 Thai ELL students in the second semester of the 2021 academic year as determined by the Taro Yamane formula. To avoid the misunderstandings due to language barriers, the researcher translated the scales from English to Thai for the convenience of the participants.
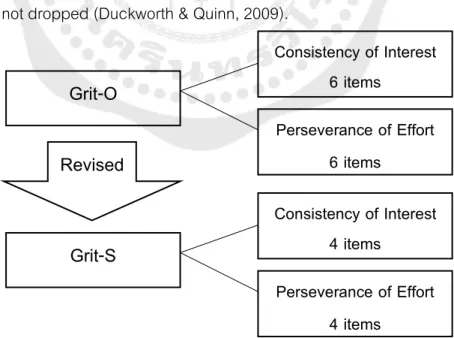
The questionnaire was organized and administered via the platform of Google Form for the convenience of the participants during the data collection process. The second section of the questionnaire containing 12 items is based on a self-report measure of grit-O (Duckworth et al., 2007) and L2-Grit scale (Teimouri et al., 2020). The first half of the items referred to the persistence of effort and the second half was concerned with the consistency of interest.
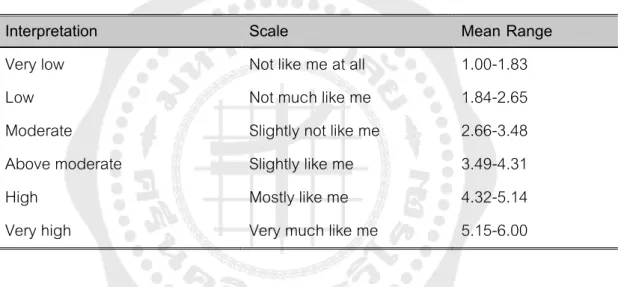
All items were based on a 6-point rating scale ranging from 1 Not me to 4 Very much like me. This part of the questionnaire was also based on a 6-point rating scale from 1 do not agree at all to 4 completely agree. In addition, 3 open-ended questions were added in the last section at the end of the questionnaire to reconfirm the data with the previous sections.
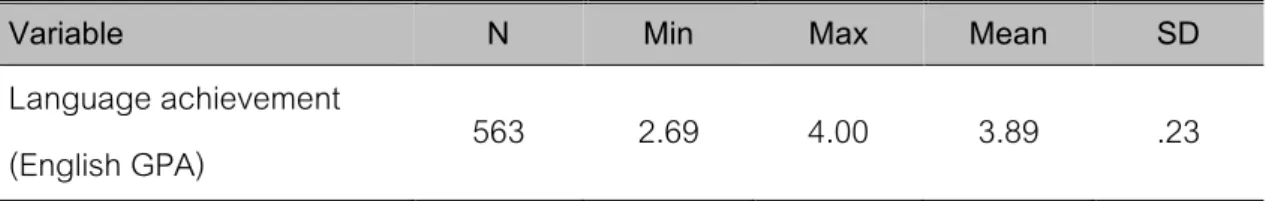
The data was collected at the end of the second semester of the academic year 2021. The data from the first part of the questionnaire, the demographic information of the participants, was analyzed and presented in terms of frequency and percentage. The students' language performance was presented with descriptive statistics in the form of mean and standard deviation.
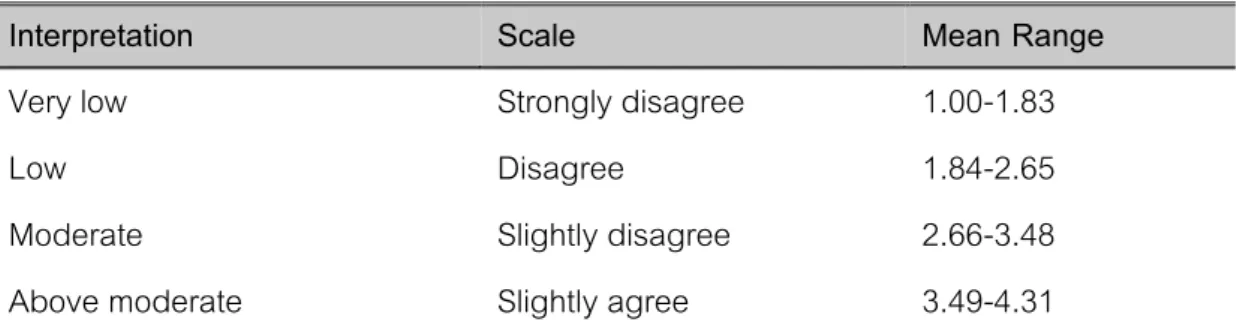
To answer the first research question, the researcher used descriptive statistics to determine the mean and standard deviation of the scores of the 6-point rating scales, the grit scale and the involvement scale using the SPSS program. The researcher adopted the criteria for interpretation of the mean values from the work of Gyamfi and Lai (2020). Further, the researcher designs the opposite scoring system to calculate the scores of the negative items.
Results of the study
- Demographics
- Thai ELLs’ grit scores
- Thai ELLs’ engagement scores
- The relationship between Thai ELLs’ grit, their engagement, their language
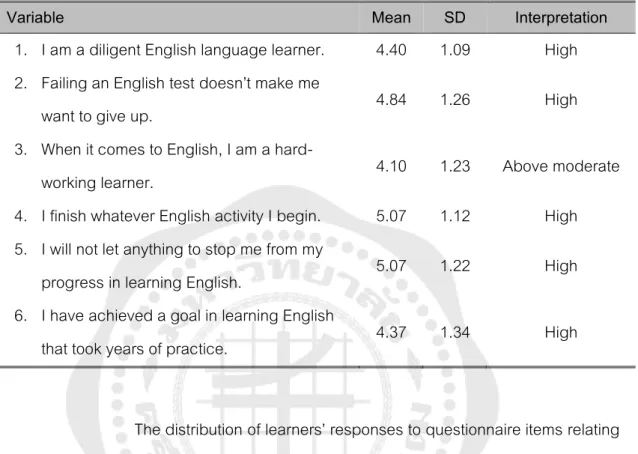
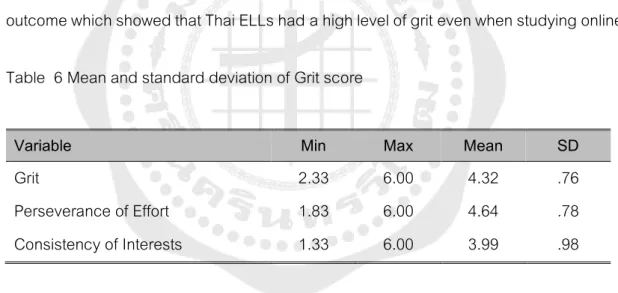
Descriptive statistics were provided in this section to show the size of Thai ELL's grit. The results also suggested that the grit of Thai ELLs was rated at a high level due to effort persistence. In addition, the results of the participants' statements obtained from the open-ended questions suggested a similar result, showing that Thai ELLs had high levels of perseverance even when studying online.
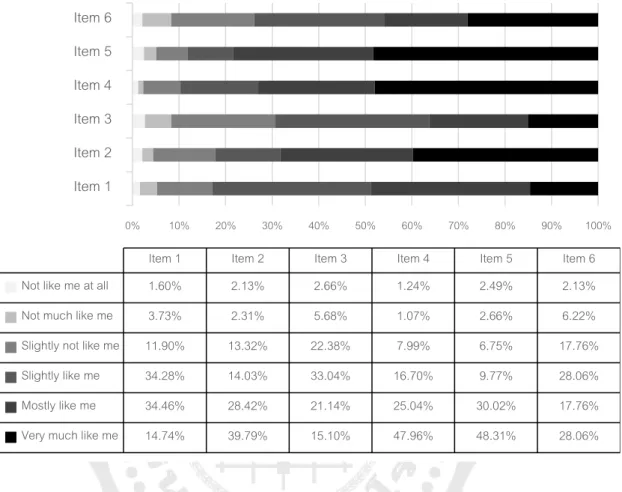
The distribution of students' responses to questionnaire items related to persistence of effort was shown in Figure 4. In this section, descriptive statistics were provided to show the extent of engagement of Thai ELLs. The distribution of student responses to the questionnaire questions regarding behavioral engagement was demonstrated here (Figure 6).
The distribution of learners' responses to questionnaire items related to cognitive engagement is shown in Figure 8. The relationship between Thai ELLs' grit, their engagement, their language performance in online English learning performance in online English learning. Thai ELLs' grit was found to be moderately and positively correlated with their language achievement, r = .345.
Another Pearson correlation analysis was performed to examine the correlation between the involvement of Thai ELLs and language performance. In addition, to investigate whether determination and engagement were predictors of language performance of Thai ELLs, a multiple regression analysis was performed. The qualitative results confirmed the positive correlation between the determination of Thai ELLs and their language performance.
However, it was also found that the qualitative data provided a different argument about the positive correlation between Thai ELLs' engagement and their language achievement. The findings showed that the Thai ELL students participating in the study have a high level of determination in learning English online. In terms of level of involvement, Thai ELL learners have a moderate level of involvement in online English learning.
CONCLUSION AND DISCUSSION
As to why grit was rated at a high level, the nature of the study sample must be taken into account. The participants in this study were from one of the top 5 prestigious public high schools and guts is a predictor of success. students are more often grim. The result of the study showed that the hypothesis stated 'is a significant predictor of language performance in online settings'.
Mohandas and Vinitwatanakhun (2020) found that the behavioral engagement of students in their study was at a high level due to the following components: class attendance and punctuality. The hypothesis which is 'Tai ELLs'. Engagement is significantly positively related to language achievement in online environments, the study found to be true. This suggested that the learning transition. environment influenced the correlation between student engagement and academic achievement.
Since in an online environment a number of uncontrollable obstacles can arise during the class, e.g. the instability of the internet connection and a short concentration period. This result of the study suggested that the hypothesis which was 'engagement significantly predicts language performance in an online environment' was rejected. Due to the limitations of the online setting, learners could not participate in learning activities, resulting in a loss in their engagement.
First, the data in the current study were collected from high school students from one of the top 5 prestigious public high schools ranked highest for academic excellence in Thailand. Most of the language achievements of the participants are considered to be at a high level compared to the national standard. From the results of the study, some recommendations emerge for students and teachers of the English language.
The findings obtained from this study provide a better understanding of the personality construct, grit, which is believed to influence the language learning process. Teachers should encourage learners, raise awareness of the importance of English and guide them to set their long-term goal in English learning, which can lead to the increase of their proficiency. First, as mentioned in the limitations section, the language performance of the participants is considered to be at a high level compared to the national standard.
Self-regulation of the use of digital resources in an online language learning course improves learning outcomes. E-learning of English in a virtual classroom and factors affecting ESL (English as a second language): Taiwan citizens' acceptance and use of a modular object-oriented dynamic learning environment.