Course Title: Introductory Mathematics Course Code:
MTH101Program: B. Sc. Mathematics Department: Mathematics College: Science
Institution: Jouf University
2
Table of Contents
A. Course Identification ... 3
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply) ... 3
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes ... 3
1. Course Description ... .ةف ّرعم ريغ ةيعجرملا ةراشلإا !أطخ 2. Course Main Objective ... 3
3. Course Learning Outcomes ... 4
C. Course Content ... 4
D. Teaching and Assessment ... 4
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods ... 4
2. Assessment Tasks for Students ... 5
E. Student Academic Counseling and Support ... 5
F. Learning Resources and Facilities ... 5
1.Learning Resources ... 5
2. Facilities Required ... 6
G. Course Quality Evaluation ... 6
H. Specification Approval Data ... 6
A. Course Identification
1. Credit hours: 3 2. Course type
a. University College Department ✓ Others
b. Required ✓ Elective
3. Level/year at which this course is offered: Level 1.
4. Pre-requisites for this course (if any):
5. Co-requisites for this course (if any): None
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply)
No Mode of Instruction Contact Hours Percentage
1 Traditional classroom 4 100 %
2 Blended 3 E-learning 4 Distance learning
5 Other
7. Contact Hours (based on academic semester)
No Activity Contact Hours
1 Lecture 2
2 Laboratory/Studio 0
3 Tutorial 2
4 Others (specify)
Total 4
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes
1) Outline the basic concepts, definitions and areas of applications of general Mathematics.
2) Produce solutions for polynomial equations of first and second degree, mathematical problems in geometry trigonometry which meet the desired needs.
3) Operate orally and written communication effectively.
4) Analyze work independently and within effectively to establish goals, plan tasks, meet deadlines.
2. Course Main Objective
To make the Students aware of the mathematical applications which will be further applicable in their stream studies.
4
3. Course Learning Outcomes
After finishing this course, student should be able to
CLOs AlignedPLO
s 1 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1 Outline the basic concepts, definitions and areas of applications of general Mathematics.
K1 2 Skills:
2.1
Produce solutions for polynomial equations of first and second degree, mathematical problems in geometry trigonometry which meet the desired needs
S2
2.2 Operate orally and written communication effectively. S5
3 Values:
3.1 Analyze work independently and within effectively to establish goals,
plan tasks, meet deadlines. V3
C. Course Content
No List of Topics Contact
Hours 1 Review of Basic concepts of Algebraic Operations, Equations and Inequalities,
transformation and rotation of axes.
8 2 Cartesian coordinates systems, Distance in plane and Equation of line 4 3 Functions, Polynomials and Rational Functions, complex numbers, partial fractions
functions, Quadratic functions and inverse function .
Graphing
8 4 Inverse, Exponential and Logarithmic Functions, Trigonometric Functions and Inverse
Trigonometric Functions.
8
5 Circular functions and their graphs, Trigonometric Identities and Equations
8
6 Systems of linear Equations and Matrices 8
7 Analytic geometry: line, pair of lines, circle 8
8 conic sections: parabola, ellipse, hyperbola. 8
Total 60
D. Teaching and Assessment
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods
Code Course Learning Outcomes TeachingStrategie
s AssessmentMethods 1.0 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1
outline the basic rules, formulas, principles, and theorems in general mathematics (such as:
equations and inequalities, complex numbers, circles, functions and their invariances, Trigonometric functions, solving linear systems correctly, determinants and its properties.
- Lectures
- Flipped class rooms
- Quizzes, - Midterm exams - Final exams
Code Course Learning Outcomes TeachingStrategie
s AssessmentMethods 2.0 Skills
2.1
Solving the equations and inequalities and reviewing basic concepts of algebraic operations plus transformations and rotation od axes.
- Lectures
- Problem solving and decision making - Flipped class rooms
- Quizzes, - Midterm exams - Final exams
2.2
Operate orally and written communication effectively.
- Flipped class rooms
- Written
communications are assessed through students written answers during the course
- Oral
communications are assessed through class discussion & oral exams
3.0 Values 3.1
Analyze work independently and within effectively to establish goals, plan tasks, meet deadlines.
- Working in groups - Presentations
2. Assessment Tasks for Students
# Assessment task* Week Due Percentage of Total
Assessment Score
1 Quizzes 6 &12 10%
2 Assignments & homework 7&13 20%
3 Midterm exam. 7 20%
4 Class discussions 14 10 %
5 Final Exam 16 40%
*Assessment task (i.e., written test, oral test, oral presentation, group project, essay, etc.) E. Student Academic Counseling and Support
The weekly office hours, academic counseling and support hours are available to each student through Blackboard. The ways of contact are available through Blackboard and meetings in the department as well.
F. Learning Resources and Facilities
1.Learning Resources
Required Textbooks College Algebra& Trigonometry, Margaret L. Lial & Others, 2017 Essential References
Materials College Algebra& Trigonometry, Margaret L. Lial & Others, 2017.
www.springer.com –
6
Other Learning
Materials --
2. Facilities Required
Item Resources
Accommodation
(Classrooms, laboratories, demonstration rooms/labs, etc.)
Classroom
Technology Resources
(AV, data show, Smart Board, software, etc.) Smart Board
Other Resources (Specify, e.g. if specific laboratory equipment is required, list requirements or
attach a list)
Blackboard
G. Course Quality Evaluation Evaluation
Areas/Issues Evaluators Evaluation Methods
Extent of achievement of course
learning outcomes Program Leaders Direct
Effectiveness of teaching and
assessment Students Indirect
Quality of learning resources Students Indirect
Course content Peer Reviewer Direct
Evaluation areas (e.g., Effectiveness of teaching and assessment, Extent of achievement of course learning outcomes, Quality of learning resources, etc.)
Evaluators (Students, Faculty, Program Leaders, Peer Reviewer, Others (specify) Assessment Methods(Direct, Indirect)
H. Specification Approval Data Council / Committee Reference No.
Date
Course Title: Differential Calculus Course Code:
MTH102Program: B. Sc. Mathematics Department: Mathematics College: Science
Institution: Jouf University
2
Table of Contents
A. Course Identification ... 3
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply) ... 3
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes ... 3
1. Course Description ... 3
2. Course Main Objective ... 3
3. Course Learning Outcomes ... 4
C. Course Content ... 4
D. Teaching and Assessment ... 5
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods... 5
2. Assessment Tasks for Students ... 5
E. Student Academic Counseling and Support ... 5
F. Learning Resources and Facilities ... 6
1.Learning Resources ... 6
2. Facilities Required ... 6
G. Course Quality Evaluation ... 6
H. Specification Approval Data ... 6
A. Course Identification
1. Credit hours:3 2. Course type
a. University College Department √ Others
b. Required Elective √
3. Level/year at which this course is offered:
2nd Level - 1st Year
4. Pre-requisites for this course (if any): Introductory Mathematics MTH 101 5. Co-requisites for this course (if any): --
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply)
No
Mode of Instruction
Contact Hours Percentage1 Traditional classroom 2 Blended
3 E-learning
4 Distance learning 3 100%
5 Other
7. Contact Hours (based on academic semester)
No Activity Contact Hours
1 Lecture 2
2 Laboratory/Studio 0
3 Tutorial 2
4 Others (specify)
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes 1. Course Description
Real numbers, Limits, Continuity and its Consequences, domain and range of functions, hyperbolic and inverse hyperbolic functions, Differentiation, The Chain Rule,
Derivatives of polynomial, Exponential and Logarithmic Functions, Trigonometric and Inverse Trigonometric Functions, hyperbolic and inverse hyperbolic functions, Implicit Differentiation , Higher Order Derivatives and, Indeterminate Forms and L’Hopital’s rule, local extrema, concavity, horizontal and vertical asymptotes, graphing curves, applications of extrema, related rates, Rolle’s theorem ,mean value theorem ,Taylor and maclorine series in one variable.
2. Course Main Objective
1- To define to the student on Real numbers, Limits, Continuity and .Differentiation 2- To define to the students on graphics: their types, properties and applications.
3- To define to the student on Theories: Applications of Differentiation.
4
3. Course Learning Outcomes
CLOs Aligned
PLOs 1 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1 Tell about characteristics and properties of Differential Calculus.
1.2 Define the most important applications of Differential Calculus.
1.3 1.4
2 Skills : 2.1
2.2
2.3 Explains different theories, algorithms and application fields.
2.4 Use mathematical theories in solving of problems relating to the calculus 3 Values:
3.1 Use a method of discussing problems scientifically by asking questions and answering them.
3.2 3.3 3.4
C. Course Content
No List of Topics Contact
Hours
1 Real numbers, Limits, 3
2 Continuity and its Consequences 3
3 The Limit of a Function,Calculating Limits Using the Limit Laws,. 3 4 domain and range of functions, hyperbolic and inverse hyperbolic functions
3 5
Limits at Infinity, Horizontal Asymptotes ,Derivatives and Rates of Change , The
Derivative as a Function 3
6
The Chain Rule ,The Product and Quotient Rules ,Derivatives of polynomial
,Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3
7 Derivatives of Trigonometric and Inverse Trigonometric Functions 3 8 hyperbolic and inverse hyperbolic functions. Implicit Differentiation 3
9 Higher Order Derivatives ,. Intermediate Forms and 3
10 L’Hospital Rule, Rates of Change in the Sciences. 3
11 local extrema, concavity, horizontal and vertical asymptotes
3 12 graphing curves, applications of extrema, related rates
3 13 Rolle’s theorem ,mean value theorem ,
3
14 Taylor and maclorine series in one variable 3
15 Revision 3
Total 45
D. Teaching and Assessment
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods
Code Course Learning Outcomes Teaching Strategies Assessment Methods 1.0 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1
Tell about characteristics and Differential Calculus
Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
Home works &
quizzes and assessment 1.2
Define the most important applications of Differential Calculus.
Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
discussion
1.3
2.0 Skills 2.1
2.2
Explains different theories, and Applications of Differentiation
Solve problems accurately
Exercise and use of references
Midterm Exams, final exams 2.3
3.0 Values 3.1
Use a method of discussing problems scientifically by asking questions and answering them.
Solve problems accurately
Exercise and use of references
Exams 3.2
3.3
2. Assessment Tasks for Students
# Assessment task* Week Due Percentage of Total
Assessment Score
1 written test 5 5%
2 written test Midterm 8 20%
3 Assignment Problem 9 10%
4 Quizzes 3 10%
5 Quizzes 6 5%
6 Final exam 16 40%
7 Homeworks 7 10%
8
*Assessment task (i.e., written test, oral test, oral presentation, group project, essay, etc.)
E. Student Academic Counseling and Support
Arrangements for availability of faculty and teaching staff for individual student consultations and academic advice :
4 hr / week office hours , 6hr/week guidance hours
6
F. Learning Resources and Facilities 1.Learning Resources
Required Textbooks
J. Stewart ,”Calculus: Early Transcendentals”, Brooks/cole, cengage Learning, 2012.
ISBN-13: 978-0-538-49790-9 Essential References
Materials S. Lang “A First Course in Calculus” 3th edition Springer Verlag 1986
Electronic Materials
www.googe.come www.youtube.com
https://www.sciencedirect.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Other Learning
Materials --
2. Facilities Required
Item Resources
Accommodation
(Classrooms, laboratories, demonstration rooms/labs, etc.)
Classroom
Technology Resources
(AV, data show, Smart Board, software, etc.) None
Other Resources (Specify, e.g. if specific laboratory equipment is required, list requirements or
attach a list)
None
G. Course Quality Evaluation
Evaluation
Areas/Issues Evaluators Evaluation Methods
Effectiveness of teaching and
assessment Faculty Direct
Evaluation areas (e.g., Effectiveness of teaching and assessment, Extent of achievement of course learning outcomes, Quality of learning resources, etc.)
Evaluators (Students, Faculty, Program Leaders, Peer Reviewer, Others (specify) Assessment Methods(Direct, Indirect)
H. Specification Approval Data
Council / Committee Reference No.
Date
Course Title:
Real Analysis -1-Course Code:
MTH211Program: B. Sc. Mathematics Department: Mathematics College: Science
Institution: Jouf University
Table of Contents
A. Course Identification ... 3
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply) ... 3
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes ... 3
1. Course Description ... 3
2. Course Main Objective ... 3
3. Course Learning Outcomes ... 4
C. Course Content ... 4
D. Teaching and Assessment ... 4
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods ... 4
2. Assessment Tasks for Students ... 5
E. Student Academic Counseling and Support ... 5
F. Learning Resources and Facilities ... 5
1.Learning Resources ... 5
2. Facilities Required ... 5
G. Course Quality Evaluation ... 6
H. Specification Approval Data ... 6
3
A. Course Identification
1. Credit hours: 3 2. Course type
a. University College Department √ Others
b. Required √ Elective
3. Level/year at which this course is offered: 4th level.
4. Pre-requisites for this course (if any): Basic of Mathematics MTH231
5. Co-requisites for this course (if any): None
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply)
No
Mode of Instruction
Contact Hours Percentage1 Traditional classroom 4 100 %
2 Blended 3 E-learning 4 Distance learning
5 Other
7. Contact Hours (based on academic semester)
No Activity Contact Hours
1 Lecture 2
2 Laboratory/Studio 0
3 Tutorial 2
4 Others (specify)
Total 4
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes 1. Course Description
Basic Properties of the field of real numbers- completeness axiom, Sequences and their convergence- monotone sequence, monotone sequence -Cauchy criterion, Basic topological properties of the real numbers, Limit of a function , continuous functions and their properties- Uniform continuity , compact sets and its properties. The derivative of a function, Mean value theorem. L'Hospital rule-Taylor theorem.
2. Course Main Objective
To make the Students aware of the mathematical counting concepts, which will be further applicable in their stream studies.
3. Course Learning Outcomes
After finishing this course, student should be able to
CLOs AlignedPLO
s 1 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1 Basic Properties of the field of real numbers- completeness axiom K1 2 Skills:
2.1 Dealing with most bases mathematical problems.
S2
2.2 Interactive discussions with students in the class. S5
3 Values:
3.1 Use a method of discussing problems scientifically by asking questions and answering
them V3
3.2 Tests his self-confidence by doing homework V3
C. Course Content
No List of Topics Contact
Hours 1 Basic Properties of the field of real numbers- completeness axiom 8 2 Sequences and their convergence-monotone sequence monotone sequence -Cauchy
criterion 8
3 Basic topologyical properties of the real numbers 8
4 Limit of a function, continuous functions and their properties- Uniform continuity 8
5 Compact sets and its properties. 8
6 The derivative of a function 12
7 Mean value theorem. L'Hospital rule-Taylor theorem. 8
Total 60
D. Teaching and Assessment
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods
Code Course Learning Outcomes TeachingStrategies AssessmentMethods 1.0 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1 Demonstrate basic concepts, theorems, and principles in real analysis.
- Lectures
- Flipped class rooms
- Quizzes Assignments Midterm exam Final Exam 2.0 Skills
2.1
Develop critical thinking methods and mathematical reasoning to solve problems in real analysis and draw correct conclusions
- Lectures
- Problem solving and decision making - Flipped class rooms
- Quizzes Assignments Midterm exam Final Exam
2.2
Research about the impact of the
application of real analysis in - Flipped class rooms Class Discussion
5
Code Course Learning Outcomes TeachingStrategies AssessmentMethods and societal contexts.
3.0 Values 3.1
Work effectively in teams to establish goals, plan tasks to meet deadlines
- Working in groups - Presentations 3.2 Tests his self-confidence by doing homework
2. Assessment Tasks for Students
# Assessment task* Week Due Percentage of Total
Assessment Score
1 Assignments & Homework&Quizzes Weekly 10%
2 Participations during the course Weekly 5%
3 Midterm exams(First & Second) 6&12 20%
4 Oral Examination 14 5 %
5 Final Exam 16 60%
*Assessment task (i.e., written test, oral test, oral presentation, group project, essay, etc.) E. Student Academic Counseling and Support
The weekly office hours, academic counseling and support hours are available to each student through Blackboard.
The ways of contact are available through Blackboard and meetings in the department as well.
F. Learning Resources and Facilities
1.Learning Resources
Required TextbooksIntroduction to real Analysis(Third edition) Robert G.Bartle and Onald R.Sherbert
Essential References Materials
1.
uction to Real Analysis, Volume I,
by Jirí Lebl ˇ June 10, 2020 (https://www.jirka.org/ra/realanal.pdf).
Electronic Materials
www.googe.com www.youtube.com
https://www.sciencedirect.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Other Learning
Materials --
2. Facilities Required
Item Resources
Accommodation
(Classrooms, laboratories, demonstration rooms/labs, etc.)
Classroom
Item Resources Technology Resources
(AV, data show, Smart Board, software, etc.) Smart Board
Other Resources (Specify, e.g. if specific laboratory equipment is required, list requirements or
attach a list)
Blackboard
G. Course Quality Evaluation Evaluation
Areas/Issues Evaluators Evaluation Methods
Extent of achievement of course
learning outcomes Program Leaders Direct
Effectiveness of teaching and
assessment Students Indirect
Quality of learning resources Students Indirect
Course content Peer Reviewer Direct
Evaluation areas (e.g., Effectiveness of teaching and assessment, Extent of achievement of course learning outcomes, Quality of learning resources, etc.)
Evaluators (Students, Faculty, Program Leaders, Peer Reviewer, Others (specify) Assessment Methods(Direct, Indirect)
H. Specification Approval Data Council / Committee
Reference No.
Date
Course Title: Integral Calculus Course Code:
MTH 203Program: B. Sc. Mathematics Department: Mathematics College: Science
Institution: Jouf University
Table of Contents
A. Course Identification ... 3
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply) ... 3
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes ... 3
1. Course Description ... 3
2. Course Main Objective ... 3
3. Course Learning Outcomes ... 4
C. Course Content ... 4
D. Teaching and Assessment ... 5
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods ... 5
2. Assessment Tasks for Students ... 5
E. Student Academic Counseling and Support ... 5
F. Learning Resources and Facilities ... 6
1.Learning Resources ... 6
2. Facilities Required ... 6
G. Course Quality Evaluation ... 6
H. Specification Approval Data ... 6
3
A. Course Identification
1. Credit hours: 3(2+1) 2. Course type
a. University College Department √ Others
b. Required √ Elective
3. Level/year at which this course is offered:
Third
4. Pre-requisites for this course (if any): Differential Calculus MTH 102
5. Co-requisites for this course (if any): --
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply)
No
Mode of Instruction
Contact Hours Percentage1 Traditional classroom 3 100%
2 Blended 3 E-learning 4 Distance learning
5 Other
7. Contact Hours (based on academic semester)
No Activity Contact Hours
1 Lecture 30
2 Laboratory/Studio 0
3 Tutorial 30
4 Others (specify) 0
Total 60
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes 1. Course Description
The definite integral, fundamental theorem of calculus, the indefinite integral, changes of variable, integration of trigonometric and inverse trigonometric functions. Integration of the hyperbolic and inverse hyperbolic functions. Techniques of integration: substitution, by parts, trigonometric substitutions, partial fractions, indeterminate forms, improper integrals, numerical integration. Application of definite integral: Area, volume of revolution, work, arc length. Polar coordinates.
2. Course Main Objective
1- An ability to understand the definite and indefinite integrals.
2- Apply integration to find the area between to curves, volumes, arc length and surface area of the solid of revolution.
3- Integrate various types of functions: logarithmic, exponential trigonometric, inverse trigonometric, hyperbolic functions and inverse hyperbolic functions.
4- Use various integration methods such as integration by parts, by trigonometric substitution, partial fractions to integrate various types of function.
5- Evaluate numerical integration and improper integrals.
6- Evaluate tangent lines and arc lengths for parametric and polar curves.
3. Course Learning Outcomes
CLOs Aligned
PLOs 1 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1 Identify The Definite Rules Properties and Notation, example and exercise.
Change of Variables in Indefinite Integral Summation Notation, example and exercise.
1.1 1.2 Demonstrate between Indefinite Integral and Definite Integral and its
Applications in Engineering College.
1.2 2 Skills :
2.1 Distinguish the basic Concept of Integration, Differentiation. 2.2 2.2 Perform appropriate solutions for engineering problems based on
analytical thinking.
2.3 3 Values:
3.1 Illustrate how take up responsibility. 3.1
3.2 Assess the skills to practice team work and present results. 3.2
C. Course Content
No List of Topics Contact
Hours 1
The Definite Rules Properties and Notation, example and exercise.
The definite integral, fundamental theorem of calculus.
Change of Variables in Indefinite Integral Summation Notation, example and exercise.
8
2 Integration of Trigonometric and Inverse Trigonometric functions, Definition, theorem and examples.
8 3 Integration of Hyperbolic functions and Inverse Hyperbolic functions 8 4
Techniques of Integrations: substitution, by parts, their rules and examples.
Techniques of Integrations, reduction formula of sin, cosine, tan, secant, cot and cosec.
8
5
Guidelines for evaluating even and odd integers, Trigonometric substitutions expression Integrand.
Integrals of partial fractions, Guidelines for partial fractions. Properties and related examples and solved exercises.
8
6 Indeterminate forms, Improper integrals, Polar Coordinates, related examples. numerical integration
4
7
The Definite Integral, Definition, Partition of Interval, subinterval and norm of partition.
Applications of the Definite Integral- Area, Volume of revolution, work, arc length Related definitions and questions
12
Total 60
5
D. Teaching and Assessment
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods
Code Course Learning Outcomes Teaching Strategies Assessment Methods 1.0 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1
Identify The Definite Rules Properties and Notation, example and exercise. Change of Variables in Indefinite Integral Summation Notation, example and exercise.
Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
Midterm 1 Quiz 1 Final Exam
1.2
Demonstrate between Indefinite Integral and Definite Integral and its Applications in Engineering College.
Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
Quiz 1 Homework Final Exam 2.0 Skills
2.1
Distinguish the basic Concept of Integration, Differentiation.
Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
Midterm 1 Final Exam 2.2
Perform appropriate solutions for engineering problems based on analytical thinking.
Solve problems accurately
Exercise and use of references
Quiz 1 Quiz 2 Final Exam 3.0 Values
3.1 Illustrate how take up responsibility.
Solve problems accurately
Exercise and use of references
Midterm 2 Homework
3.2 Assess the skills to practice team work and present results.
Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
Assignment Class Discussion
2. Assessment Tasks for Students
# Assessment task* Week Due Percentage of Total
Assessment Score
1 Midterms 8-12 20%
2 Quizzes - class discussion 4 -11 10%
3 Final exam 16 60%
4 Homework’s 3- 7 10%
*Assessment task (i.e., written test, oral test, oral presentation, group project, essay, etc.)
E. Student Academic Counseling and Support
Arrangements for availability of faculty and teaching staff for individual student consultations and academic advice :
4 hr / week office hours , 6hr/week guidance hours.
F. Learning Resources and Facilities 1.Learning Resources
Required Textbooks
J. Stewart ,”Calculus: Early Transcendentals”, Brooks/cole, cengage Learning, 2012.
ISBN-13: 978-0-538-49790-9 Essential References
Materials S. Lang “A First Course in Calculus” 5th edition Springer Verlag 1986.
Electronic Materials
www.googe.come www.youtube.com
https://www.sciencedirect.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Other Learning
Materials --
2. Facilities Required
Item Resources
Accommodation
(Classrooms, laboratories, demonstration rooms/labs, etc.)
Classroom
Technology Resources
(AV, data show, Smart Board, software, etc.) None
Other Resources (Specify, e.g. if specific laboratory equipment is required, list requirements or
attach a list)
None
G. Course Quality Evaluation
Evaluation
Areas/Issues Evaluators Evaluation Methods
Effectiveness of teaching and
assessment Faculty Direct
Evaluation areas (e.g., Effectiveness of teaching and assessment, Extent of achievement of course learning outcomes, Quality of learning resources, etc.)
Evaluators (Students, Faculty, Program Leaders, Peer Reviewer, Others (specify) Assessment Methods(Direct, Indirect)
H. Specification Approval Data
Council / Committee Reference No.
Date
Course Title:
Basics of MathematicsCourse Code:
MTH 231Program:
B. Sc. MathematicsDepartment:
MathematicsCollege:
ScienceInstitution:
Jouf UniversityTable of Contents
A. Course Identification ... 3
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply) ... 3 B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes ... 3
1. Course Description ... 3 2. Course Main Objective ... 3 3. Course Learning Outcomes ... 4 C. Course Content ... 4
D. Teaching and Assessment ... 5 1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment
Methods ... 5 2. Assessment Tasks for Students ... 6 E. Student Academic Counseling and Support ... 6
F. Learning Resources and Facilities ... 6
1.Learning Resources ... 6 2. Facilities Required ... 6 G. Course Quality Evaluation ... 7
H. Specification Approval Data ... 7
3
A. Course Identification
1. Credit hours:
2. Course type
a. University College Department √ Others
b. Required √ Elective
3. Level/year at which this course is offered:
Third
4. Pre-requisites for this course (if any): Differential Calculus, MTH 102
5. Co-requisites for this course (if any):
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply)
No
Mode of Instruction
Contact Hours Percentage1 Traditional classroom 2 Blended
3 E-learning
4 Distance learning 3 100%
5 Other
7. Contact Hours (based on academic semester)
No Activity Contact Hours
1 Lecture 2
2 Laboratory/Studio 0
3 Tutorial 2
4 Others (specify)
Total 3
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes 1. Course Description
Introduction to Mathematical Logic- Methods of proofs- Mathematical induction- Set theory- The product of a sets- Binary operations- Equivalence relations - Equivalence classes and partitions – Mappings -The images and inverse images of a sets under mappings - Equivalence sets- Countable and finite sets - Morphisms- Definition and examples of groups- Definition and examples of rings and fields- Polynomials-Partial fractions.
2. Course Main Objective
1. Recognizes student about mathematical logic and methods of proof.
2. Recognizes student about groups and operations.
3. Recognizes student the binary relations and mappings and their characteristics.
4. Recognizes student the equivalence of groups and countable groups.
5. Recognizes student about the binary operations, the group, the ring and the field.
3. Course Learning Outcomes
CLOs Aligned
PLOs 1 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1 Demonstrate deep, wide, consistent and advanced understanding to the basic definitions of logical equivalence, quantifiers, the Contra positive of a conditional statement, the power set, set operations, Cartesian product, binary relation, equivalence relation, equivalence classes, partitions, mappings (functions), injections, surjections, bijections, composition, equivalence of sets, finite sets, countable sets, inverse mappings (functions), binary operations, algebraic systems and their homomorphisms, groups, rings and fields.
1.2 1.3 1.4
2 Skills :
2.1 Apply basic definitions, axioms, principles, theories to produce the proofs and solutions of logical equivalence, set operations, equivalence relations, equivalence classes, partitions, mappings (functions), injections, surjections, bijections, composition, equivalence of sets, finite sets, countable sets, inverse mappings (functions), binary operations, algebraic systems and their homomorphisms, groups, rings and fields.
2.2 Solve complex and unanticipated mathematical problems in logical equivalence, set operations, equivalence relations, mappings (functions), groups, rings and fields.
2.3 2.4
3 Values:
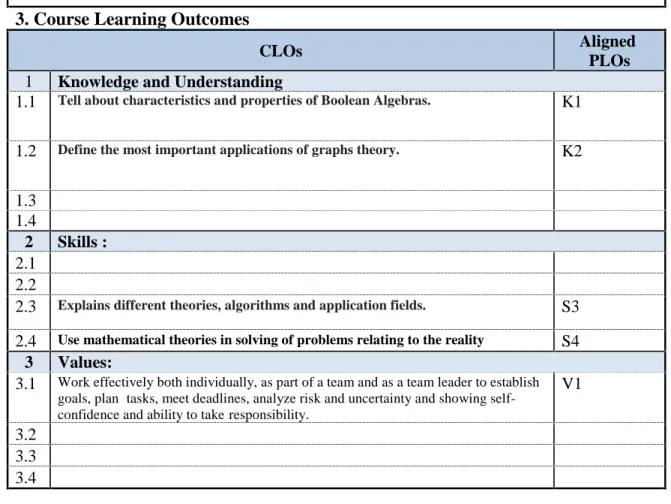
3.1 Work effectively both individually, as part of a team and as a team leader to establish goals, plan tasks, meet deadlines, analyze risk and uncertainty and showing self- confidence and ability to take responsibility.
3.2 3.3 3.4
C. Course Content
No List of Topics Contact
Hours
1 Introduction to Mathematical Logic 3
2 Methods of proofs. 3
3 Mathematical induction 3
4 Sets theory, the product of sets. 3
5 Binary oprations.
3
6 Equivalence relations, equivalence classes and partitions. 3
7 Mappings, the image and inverse image under mapping. 3
8 Equivalence sets. 3
9 Countable and finite sets 3
10 Morphisms. 3
11 Definitions and examples of groups. 3
12 Polynomials: operations on polynomials and its roots.
3
5
13 Decomposition of polynomials. 3
14 Partials Fractions: operations, poles and decomposition.
3
15 Definitions and examples of groups. 3
Total 45
D. Teaching and Assessment
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods
Code Course Learning Outcomes Teaching
Strategies Assessment Methods 1.0 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1
Demonstrate deep, wide, consistent and advanced understanding to the basic definitions of logical equivalence, quantifiers, the Contra positive of a conditional statement, the power set, set operations, Cartesian product, binary relation, equivalence relation, equivalence classes, partitions, mappings (functions), injections, surjections, bijections, composition, equivalence of sets, finite sets, countable sets, inverse mappings (functions), binary operations, algebraic systems and their
homomorphisms, groups, rings and fields.
- Lectures - Problem-solving strategy.
-Quizzes, -Midterm exams - Assignments
1.2 1.3
2.0 Skills
2.1
Apply basic definitions, axioms, principles, theories to produce the proofs and solutions of logical equivalence, set operations, equivalence relations, equivalence classes, partitions, mappings (functions), injections, surjections, bijections, composition, equivalence of sets, finite sets, countable sets, inverse mappings (functions), binary operations, algebraic systems and their homomorphisms, groups, rings and fields.
- Lectures - Problem-solving strategy.
-Quizzes, -Midterm exams -Final exams
2.2
Solve complex and unanticipated mathematical problems in logical equivalence, set operations, equivalence relations, mappings (functions), groups, rings and fields.
- Lectures - Problem-solving strategy.
-Assignments.
-Final exams
2.3
3.0 Values 3.1
Work effectively both individually, as part of a team and as a team leader to establish goals, plan tasks, meet deadlines, analyze risk and uncertainty and showing self-confidence and ability to take responsibility.
Students’
discussions, Group work, Co-operation s
Class discussion
3.2 3.3
2. Assessment Tasks for Students
# Assessment task* Week Due Percentage of Total
Assessment Score
1 Quizzes From 2nd week 10%
2 Assignments Agreement in (4-15) th week 20%
3 Class discussion From 2nd week 10%
4 Midterm Exam 7thweek – 9th week 20%
5 Final Exam After 15th week 40%
*Assessment task (i.e., written test, oral test, oral presentation, group project, essay, etc.)
E. Student Academic Counseling and Support
Arrangements for availability of faculty and teaching staff for individual student consultations and academic advice :
F. Learning Resources and Facilities 1.Learning Resources
Required Textbooks
R. A. Dean : Classical Abstract Algebra , Harper and Row. Inc., 1990 .
Essential References Materials
D. Saracino : Abstract Algebra, A first Course, Addison Wesley , 1980 .
Electronic Materials
www.google.come www.youtube.com
https://www.sciencedirect.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Other Learning
Materials --
2. Facilities Required
Item Resources
Accommodation
(Classrooms, laboratories, demonstration rooms/labs, etc.)
Classroom
Technology Resources
(AV, data show, Smart Board, software, etc.) None
7
Item Resources
Other Resources (Specify, e.g. if specific laboratory equipment is required, list requirements or
attach a list)
None
G. Course Quality Evaluation
Evaluation
Areas/Issues Evaluators Evaluation Methods
Effectiveness of teaching and
assessment Faculty Direct
Evaluation areas (e.g., Effectiveness of teaching and assessment, Extent of achievement of course learning outcomes, Quality of learning resources, etc.)
Evaluators (Students, Faculty, Program Leaders, Peer Reviewer, Others (specify) Assessment Methods(Direct, Indirect)
H. Specification Approval Data
Council / Committee Reference No.
Date
Course Title: General Statistics Course Code:
MTH 271Program: B. Sc. Mathematics Department: Mathematics College: Science
Institution: Jouf University
2
Table of Contents
A. Course Identification ... 3
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply) ... 3 B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes ... 3
1. Course Description ... 3 2. Course Main Objective ... 3 3. Course Learning Outcomes ... 4 C. Course Content ... 4
D. Teaching and Assessment ... 5 1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment
Methods ... 5 2. Assessment Tasks for Students ... 6 E. Student Academic Counseling and Support ... 6
F. Learning Resources and Facilities ... 6
1.Learning Resources ... 6 2. Facilities Required ... 6 G. Course Quality Evaluation ... 6
H. Specification Approval Data ... 7
A. Course Identification
1. Credit hours: 3(2+1) 2. Course type
a. University College Department √ Others
b. Required √ Elective
3. Level/year at which this course is offered:
Third
4. Pre-requisites for this course (if any): General Statistics MTH 271
5. Co-requisites for this course (if any): --
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply)
No Mode of Instruction Contact Hours Percentage
1 Traditional classroom 3 100%
2 Blended 3 E-learning 4 Distance learning
5 Other
7. Contact Hours (based on academic semester)
No Activity Contact Hours
1 Lecture 30
2 Laboratory/Studio 0
3 Tutorial 30
4 Others (specify) 0
Total 60
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes
1. Course DescriptionIntroduction and overview of statistics and the definition of some statistical concepts – Organization and presentation of statistical data - Measures of central tendency (Mean, Median, Mode, …) of the simple data and the frequency distribution - Measures of dispersion (The Range – The Mean Deviation – The Variance and the standard deviation - Coefficient of variation of the simple data and the frequency distribution – Sets and the operations on sets - Sample space and Events - Counting Techniques (Fundamental basics, Addition Rule – Multiplication Rule- Permutation and Combinations) - Definition of the probability and its applications – Conditional probability - Independence of events and Bayes theorem and its applications - Definition of therandom variable- The probability function (The probability Distribution)- The Expectation and the variance of the random variable (Discrete and Continuous) .
2. Course Main Objective
4
2- Measures of central tendency (Mean, Median, Mode, …) of the simple data and the frequency distribution
3- Measures of dispersion (The Range – The Mean Deviation – The Variance and the standard deviation - Coefficient of variation of the simple data and the frequency distribution – Sets and the operations on sets –
4- An ability to understand Sample space and Events - Counting Techniques (Fundamental basics, Addition Rule – Multiplication Rule- Permutation and Combinations) - Definition of the probability and its applications – Conditional probability - Independence of events and Bayes theorem and its applications - Definition of therandom variable- The probability function
5. An ability to understand the Expectation and the variance of the random variable (Discrete and Continuous) .
3. Course Learning Outcomes
CLOs Aligned
PLOs 1 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1
Tell about statistics and how to organize and display statistical data
1.1
1.2 Define the probability and list its general laws 1.2
2 Skills :
2.1 Compares various statistical methods 2.2
2.2 Summarizes and analyzes many statistical and probabilistic problems 2.3 3 Values:
3.1 Use a method of discussing problems scientifically by asking questions and answering them.
3.1
3.2 Tests his self-confidence by doing homework. 3.2
4 Communication, Information Technology, Numerical:
4.1 Calculate the results using IT 4.1
4.2 Explains and compares computational results. 4.2
C. Course Content
No List of Topics Contact
Hours 1
Introduction and overview of statistics and the definition of some statistical concepts
Organization and presentation of statistical data
8
2 Measures of central tendency (Mean, Median, Mode, …) of the simple data and the frequency distribution.
8
3
Measures of dispersion (The Range - The Mean Deviation. The Variance and the standard deviation.
Coefficient of variation of the simple data and the frequency distribution
8
4
Definition of the probability and its applications – Conditional probability
The probability function (The probability distribution of a discrete random variable)
The expectation and variance of the random variable.
Sampling c of mean
Sampling distribution of sample variance
8
5
T sampling distribution
F sampling distribution
Central limit theorem
8
6 Estimating the mean of the single sample and one proportion
Estimating the difference between two means of the two sample
4
7
Test hypotheses about the mean of the single sample and one proportion
Tests hypotheses about the difference between two means of the two sample.
Correlation (Person and Sperman)
12
Total 60
D. Teaching and Assessment
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods
Code Course Learning Outcomes Teaching Strategies Assessment Methods 1.0 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1
Tell about statistics and how to organize
and display statistical data Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
Midterm 1 Quiz 1 Final Exam
1.2
Define the probability and list its general laws .
Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
Quiz 1 Homework Final Exam 2.0 Skills
2.1
Compares various statistical methods. Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
Midterm 1 Final Exam 2.2
Summarizes and analyzes many statistical and probabilistic problems
Solve problems accurately
Exercise and use of references
Quiz 1 Quiz 2 Final Exam 3.0 Values
3.1
Use a method of discussing problems scientifically by asking questions and answering them.
Solve problems accurately
Exercise and use of references
Midterm 2 Homework
3.2
Tests his self-confidence by doing homework.
Lectures Office hours Discussion Boards
Assignment Class Discussion
4 Communication, Information
Technology, Numerical:
4.1 Calculate the results using IT Solve problems accurately
Exercise and use of references
Midterm 2 Homework 4.2 Explains and compares computational
results.
Lectures Office hours
Discussion Boards
Assignment Class Discussion
6
2. Assessment Tasks for Students
# Assessment task* Week Due Percentage of Total
Assessment Score
1 Midterms 8-12 20%
2 Quizzes - class discussion 4 -11 10%
3 Final exam 16 60%
4 Homework’s 3- 7 10%
*Assessment task (i.e., written test, oral test, oral presentation, group project, essay, etc.)
E. Student Academic Counseling and Support
Arrangements for availability of faculty and teaching staff for individual student consultations and academic advice :
4 hr / week office hours , 6hr/week guidance hours.
F. Learning Resources and Facilities
1.Learning Resources
Required Textbooks Prem S. Mann, Introductory Statistics, 9th Edition.John Wiley and sons, Inc., 2016. ISBN 978-1-119-14832-6
Essential References Materials
Prem S. Mann, Introductory Statistics, 9th Edition.John Wiley and sons, Inc., 2016. ISBN 978-1-119-14832-6
Electronic Materials
www.googe.come www.youtube.com
https://www.sciencedirect.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Other Learning
Materials --
2. Facilities Required
Item Resources
Accommodation
(Classrooms, laboratories, demonstration rooms/labs, etc.)
Classroom
Technology Resources
(AV, data show, Smart Board, software, etc.) None
Other Resources (Specify, e.g. if specific laboratory equipment is required, list requirements or
attach a list)
None
G. Course Quality Evaluation
Evaluation
Areas/Issues Evaluators Evaluation Methods
Effectiveness of teaching and Faculty Direct
Evaluation
Areas/Issues Evaluators Evaluation Methods
assessment
Evaluation areas (e.g., Effectiveness of teaching and assessment, Extent of achievement of course learning outcomes, Quality of learning resources, etc.)
Evaluators (Students, Faculty, Program Leaders, Peer Reviewer, Others (specify) Assessment Methods(Direct, Indirect)
H. Specification Approval Data
Council / Committee Reference No.
Date
Course Title: Advanced Calculus Course Code:
MTH204Program: B. Sc. Mathematics Department: Mathematics College: Science
Institution: Jouf University
Table of Contents
A. Course Identification ... 3
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply) ... 3 B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes ... 3
1. Course Description ... 3 2. Course Main Objective ... 3 3. Course Learning Outcomes ... 4 C. Course Content ... 4
D. Teaching and Assessment ... 4 1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment
Methods ... 4 2. Assessment Tasks for Students ... 5 E. Student Academic Counseling and Support ... 5
F. Learning Resources and Facilities ... 5
1.Learning Resources ... 5 2. Facilities Required ... 6 G. Course Quality Evaluation ... 6
H. Specification Approval Data ... 6
3
A. Course Identification
1. Credit hours: 3 2. Course type
a. University College Department √ Others
b. Required √ Elective
3. Level/year at which this course is offered: 4th level.
4. Pre-requisites for this course (if any): Integral calculus MTH203
5. Co-requisites for this course (if any): None
6. Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply)
No Mode of Instruction Contact Hours Percentage
1 Traditional classroom 4 100 %
2 Blended 3 E-learning 4 Distance learning
5 Other
7. Contact Hours (based on academic semester)
No Activity Contact Hours
1 Lecture 2
2 Laboratory/Studio 0
3 Tutorial 2
4 Others (specify)
Total 4
B. Course Objectives and Learning Outcomes 1. Course Description
Cylindrical and spherical coordinates. Partial derivatives: Functions of several variables. Limits and continuity. Partial derivatives. Tangent planes and linear approximations. The chain rule. Directional derivatives and the gradient vector. Maximum and minimum values.Lagrange multiplies. Multiple integrals: Double integrals over rectangles.Iterated integrals. Double integrals over general regions.
Double integrals in polar coordinates. Application of double integrals. Surface Area. Triple integrals.
Triple integrals in cylindrical and spherical coordinates. Change of variables in multiple integrals
2. Course Main Objective
To make the Students aware of the mathematical counting concepts, which will be further applicable in their stream studies.
3. Course Learning Outcomes
After finishing this course, student should be able to
CLOs AlignedPLO
s 1 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1 Basic Properties of the field K1
2 Skills:
2.1 Dealing with most bases mathematical problems.
S2
2.2 Interactive discussions with students in the class. S5
3 Values:
3.1 Use a method of discussing problems scientifically by asking questions and answering
them V3
3.2 Tests his self-confidence by doing homework V3
C. Course Content
No List of Topics Contact
Hours
1 Function of two or more variables and its domain 4
2 Limits-Continuity. 4
3 Partial derivatives-Higher order partial derivatives- Total derivative 6
4 Chain rule - Harmonic functions – Homogenous functions 4
5 Euler's theorem for homogenous functions – Jacobian 4
6 Maxima and minima-Method of Lagrange multipliers for maxima and minima
6 7 Taylor's and Maclaurin's series for functions of two variables 4 8 Double integrals in Cartesian and Polar coordinates and applications 4
9 Double integrals in Cartesian and Polar coordinates 4
10 Double integrals in Cartesian and Polar coordinates and applications 4 11 Triple integrals in spherical and cylindrical coordinates and applications 4 12 Triple integrals in spherical and cylindrical coordinates and applications 4 13 Triple integrals in spherical and cylindrical coordinates and applications 4 14 Line integral – Green's theorem in a plan – Improper integrals 4
Total 60
D. Teaching and Assessment
1. Alignment of Course Learning Outcomes with Teaching Strategies and Assessment Methods
Code Course Learning Outcomes TeachingStrategies AssessmentMethods 1.0 Knowledge and Understanding
1.1 Demonstrate basic concepts, theorems, and principles in real analysis.
- Lectures
- Quizzes Assignments