I understand that a copy of my research will be deposited in the University Library for permanent safekeeping. I understand that the British University in Dubai may make a digital copy available in an institutional repository. The author, whose copyright is indicated on the title page of the work, has granted the British University in Dubai the right to lend his research work to users of its library and to make partial or single copies for educational and research use.
The author has also granted permission to the University to store or make a digital copy for similar use and for the digital preservation of the work. Research Questions/Problem: What is the current practice of PSIAs in IBWs in Oman compared to AAOIFI standards. Objective: The main objective of this research is to reveal the practice of PSIAs in Oman's IBWs as compared to AAOIFI's standards, particularly with regard to Sharia and disclosure issues.
Research Methodology: In order to study this research issue, the researcher collected the relevant data from two full-fledged Islamic banks and five Islamic windows in Oman, using their annual reports and published contracts in the year 2021. In addition, the practice of PSIAs was found to be largely compatible with AAOIFI's standards.
LIST OF ACRONYMS
INTRODUCTION
- Background
However, the contractual relationship between the bank and depositors differs greatly between Islamic banks and conventional banks. Similarly, Kusuma (2018) studied the phenomenon of unfairness related to profit margin determination in Mudarabah contract in Indonesian Islamic banks. In addition, he found that returns on investment deposits in Islamic banks do not reflect the risk-taking characteristics inherent in Islamic deposits compared to shareholders.
However, AlShattarat and Atmeh (2016) investigated the problems and challenges of Islamic banks in implementing the Mudarabah contract. In contrast, Hamza (2016) found that investment accounts in Islamic banks do not reflect the principle of profit and loss sharing due to moral hazard and excessive risk behavior of the Islamic bank. It is found that there are two types of risks in the context of Islamic banks.
The study found that accounting practices of PSIAs have varied significantly due to the variation in standards applied in Islamic banks. The study took a descriptive approach and sampled two Islamic banks and five conventional banks.
METHODOLOGY
- definition of investment accounts
- Types of investment accounts
- Investment accounts risks
- AAOIFI’s investment accounts standards
- Background of AAOIFI
- AAOIFI’s Structure
- Investment Accounts in Oman’s Islamic Banking Sector
- Investment accounts practice in Oman’s Islamic banks in comparison with AAOIFI’s standards
- Classification and Presentation of PSIAs
- Valuation of PSIAs
- Profit and Expenses
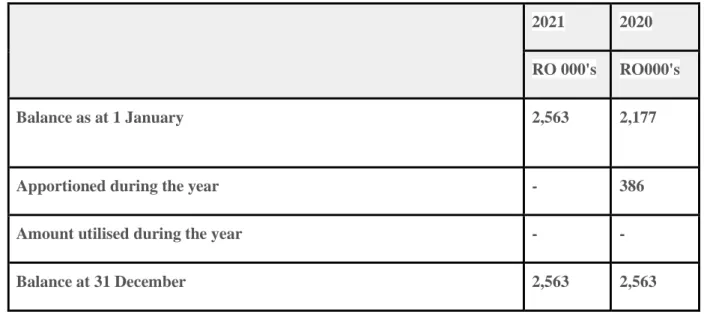
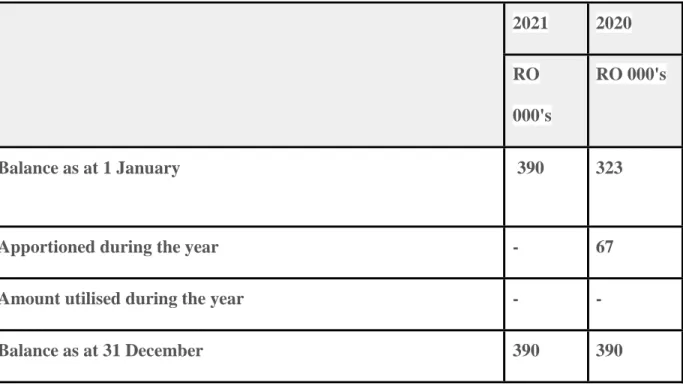
- Risk Reserves (PER and IRR)
If this does happen, the loss will be borne according to the percentage of each party's share in the capital. Moreover, as Mudarib, the bank does not bear the loss except in the case of negligence, misconduct and breach of terms. In the context of investment accounts, Islamic banks could structure these accounts based on the wakalah contract in which the depositors designate and delegate the bank to manage and invest their money against agreed and identified fees.
Second, from a practical point of view and despite the above fact, IAHs are not represented in the bank. IAs are covered by this standard because they can be built based on the Wakalah contract mentioned in the. As is known, deposits are considered an important source of funding in the general banking sector.
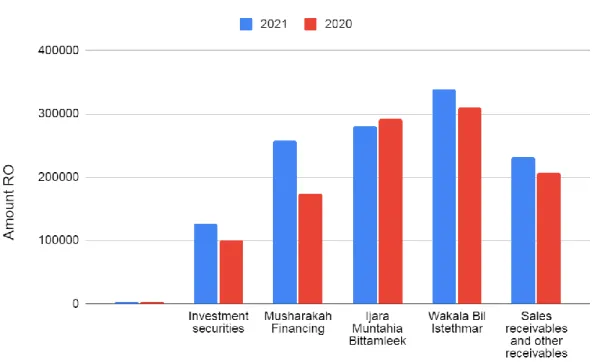
In the notes to the financial statement, they reported that the funds of IAHs and shareholders have been combined and mixed to create a large group of Mudarabah. Although AAOIFI standards do not require it, IBWs in Oman distinguish in the notes to their financial statements between assets that are jointly financed by IAHs and shareholders and assets that are solely financed by the bank. In the context of the Islamic banking experience in Oman, all assets and liabilities attributable to PSIAs are measured at fair value.
This is part of the complex nature of the contractual relationship between the Islamic bank and depositors. However, this could be explained by the fact that PSIAs benefit shareholders from both sides; first, like a Rub Al Mall, the bank mixes its funds with the funds of other IAHs in the Mudarabah Pool. The first is the pool method, where all sources of money at the bank share all income and losses generated.
In the notes, they even state precisely the assets that are jointly financed and the assets that are financed only by the bank. Essentially, the nature and effects of the contractual relationship in the Wakalah contract are different from the Mudarabah contract. Therefore, the Islamic bank's share of reserves should be disclosed under equity in the statement of financial position.
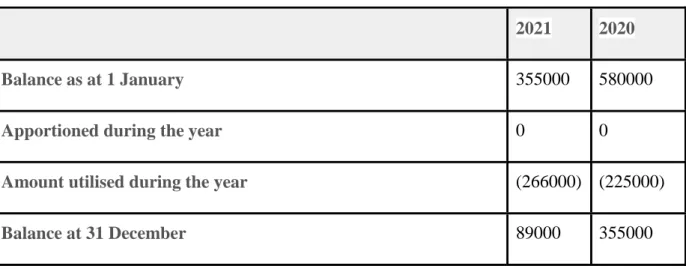
Third, there is unfairness in the distribution of reserves after the end of the financial period. Also, the IAH that will withdraw its fund before the end of the financial period will have its share in the reserves removed. In addition, some IBWs stated that the bank could cover the loss or decrease in returns caused to the PSIA by its fund.
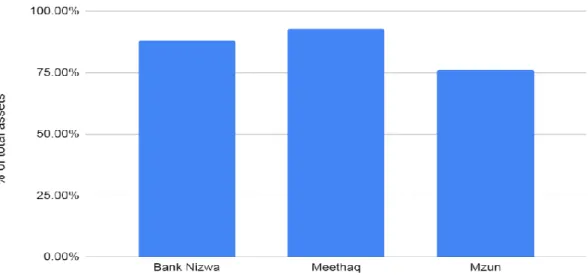
As a result, IAH's equity in the Islamic banking sector was found to consist of approximately 62% of the total liabilities and equity of IBW in Oman.
The Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex PO19 8SQ, England: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. RISK MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR INSTITUTIONS (OTHER THAN INSURANCE INSTITUTIONS) OFFERING ONLY ISLAMIC FINANCIAL: www.b.s. org. Time-series analysis of equity-based financing, deposit and investment accounts: Evidence from Islamic banks in Malaysia.
Profit Sharing Deposit Accounts in Islamic Banking: An Analysis of Malaysian Depositors' Perceptions and Attitudes. Contracts and Transactions in Islamic Finance: A User's Guide to Cash Flows, Balance Sheets and Capital Structures. Accounting Issues in the Reporting of Profit Sharing Investment Accounts in the Financial Statements of Islamic Banks under IFSA 2013.
Establishing a Fair Mudarabah Profit Sharing Ratio: A Case Study of Islamic Banks in Indonesia. Classification of investment accounts with profit sharing: A study of financial statements of Islamic banks in Asia.