It is true of thousands of private sector leaders – the startup innovator, the niche marketer, the neighborhood entrepreneur. It confronts such misconceptions as "research is only for big decisions" or "most research is waste" or, the most important myth, "market research is too expensive." The simple truths that put the lie to these myths go a long way toward helping the reluctant investigator move out of the marketplace fog into crisp, clear insights into what is happening with key audiences, major competitors, regulators, and others whose perceptions , attitudes, actions and future plans will greatly influence the marketer's success.
Preface
The middle two parts focus more on the core of specific, low-cost research techniques. The chapter emphasizes the need to be systematic in developing a low-cost research program and provides a general procedure for doing so.
Acknowledgments
The original book and this revision would not have appeared without the encouragement and contributions of my wife, Jean Manning.
The Author
Planning a Low-Cost Research Program
Myths of Marketing Research
- I’m Already Doing Enough Research”
- Research Is Only for Big Decisions”
- Losing Control”
- Market Research Is Survey Research”
- Market Research Is Too Expensive”
- Most Research Is a Waste”
Sometimes research is wasted because the manager has personal motives for not using the research effectively after it is completed. They just don't think about research. In part, this is because too many managers are unaware of the variety of uses to which research can be put.
Planning a Research Program
A suggested list of the types of research projects that may develop is included in Table 2.1. The second point to make regarding the planning process is that many of the options listed may not be relevant.
Evaluating Individual Research Projects
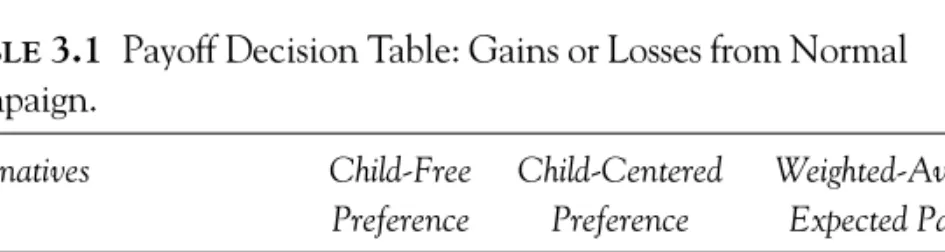
You can easily justify the increase by pointing out that last year's spending was only half of 1 percent of the investment made in new product development, and — lo and behold — the current budget is also half of 1 percent of the product investment of young. The main flaw in this commonly used approach is that the manager expects the bid cost to magically match the decision. It requires the manager to explicitly use the probabilities of different future environments to weigh the outcomes under each decision alternative.
Playing It Safe. The other extreme is to look at the worst outcome under each alternative course of action and choose the action that involves the best worst outcome. It is not how uncertain the manager is about the state of the current market or what it will be in the future. Alternatively, research can be very important if the manager has strong feelings about the nature of the market but is quite uncertain about what to do.
A fishing expedition can be enjoyable, and if only the manager's own time and money is involved, it is not irresponsible. Indeed (like all anglers, I suppose) the manager may fish just often enough to be convinced that the activity is justified by the payoff.
Backward Marketing Research
- Determine What Decisions Are to Be Made
- Determine Information Needed for Decision
- Prepare a Prototype Report
- Determine the Analysis Needed
- Decide on the Questions to Be Asked in the Study
- See If the Data Already Exist Somewhere
- Design the Sample
- Through 11
We develop each stage of the process based on what comes after, not before. To determine whether this is a good decision, she must predict the reactions of both old and new customers to the elimination of the discount. This new formulation of the decision leads to a discussion of the results indicating that the study should really ask not only about the permanent discount, but also about a one-time discount.
As the manager thinks about this table, she realizes she still needs a way to minimize the chance that old customers will take advantage of the one-time discount. Usually this is a reason to do away with that part of the research design altogether. It deepens their understanding of many details of the study itself and their appreciation of both its strengths and weaknesses.
If the management is satisfied with the higher achievements of the statistics, the researcher can derive some of the more advanced analytical procedures. Similarly, script writing will also usually reveal that management wants more breakdowns of results than the researcher anticipates, requiring larger sample sizes or more precise stratification procedures than originally planned.
Alternative Low-Cost Research Techniques
Using Available Data
The advantage of the techniques we will discuss here and in the next chapter is that they can eliminate this potentially large source of bias. A simple summary or coding of the data into measured or measurable records can provide a marketing manager with interesting new insights. Further use of the comparisons to explore alternative marketing mixes was considered for the future.
Evaluation of the quality of such reports can be used as one measure of staff performance. In most cases it is possible to go directly to the original sources of the data. The selection of the material to be analyzed must be objective and somehow random.
Trial analyzes of a subset of materials should be performed and rules should be established for ambiguous cases. Repeated archival records of the activities of key actors in an organization's environment can tell managers a great deal about systematic changes in their strategies and tactics over time.
Systematic Observation
A major virtue of simple counting is that it can be performed by untrained researchers. Careful training is still necessary and procedures must be carefully specified, but costs can be kept low. Even the individual researcher with the best intentions can be distracted or tired or count the wrong thing.
These devices count bodies that refract a beam of light and can be used to unobtrusively note the number of people passing an exhibit or entering a room or building. Websites can be programmed to record items viewed on a web page or the time a visitor spent viewing a particular page. A good example of the kind of insight that can be gained by looking for patterns through low-cost, relatively unobtrusive observation of naturally occurring consumer behavior is in supermarket observations.
The results can be very biased if the observers always go at the same time, for example, when it is convenient for them or when there are few people in the place. The observer can be told to observe every ninth event, for example, every fifth person passing the north side of the ficus tree just inside the southeast entrance to the Children's Museum.
Low-Cost Experimentation
They all look like experiments in the sense that something is changed and there appear to be consequences of the something. Third, in the case of California, since we did not control the timing of the treatments, we cannot even say that the fee reduction preceded it. One possibility is that the post-measures simply reflect differences in the groups (centers) that existed before the study and that the treatment had no effect.
The posters are displayed in the treatment centers, and after six weeks the same parents are interviewed again in both areas. It appears from the results that the posters in the treatment group were a great success. Recall that the reason for the premeasure in the first place was to account for just such sampling differences between groups.
Mechanical or electronic measuring equipment may be used in the laboratory that would be cumbersome in the field. Often there is little need for representativeness in the samples, as long as the participants belong to the target market and, where appropriate, are randomly assigned.
Low-Cost Survey Designs
Another effect of research consciousness is that some respondents try to please the researcher. One group of respondents will be interested in the topic of the study. It is possible to obtain a mailing list (or sampling process) that is truly representative of the population of interest.
There is a good chance that a large proportion of the respondents will be interested in the subject and respond to it. Even in such situations, it is essential to estimate the non-response bias. If the research sponsor can be disclosed and awareness of it would motivate respondents (e.g. UNICEF or a major professional body), the letter should do so.
Facial expressions can be observed to indicate which parts of messages are confusing to respondents and need to be processed. The respondent is the sole focus of the interviewer's attention and is therefore more likely to open up.
Making Low-Cost Research Good Research
Producing Valid Data
The question used to measure preference may be vaguely worded or may not reflect the true relationship between the charities. The interviewer may misrecord the answer because he or she misheard the respondent, misinterpreted what the respondent meant, or accidentally wrote down the wrong number or symbol (or someone else assigned the wrong number or code to what the interviewer has written down). If one or more of these events occur (or many others listed below), the researcher has a clear case of "garbage in." No amount of sophisticated statistical manipulation can wring the truth out of biased data; it is always 'garbage outside'.
Following the retrospective approach introduced in Chapter Four, we will first address data entry and coding errors before turning to the more complex problems of eliciting and recording human responses. In expensive studies, input error can be almost eliminated by checking each input (that is, double input). First, separate data entry can be eliminated by using computers during the interview, conducting surveys over the Internet, or having respondents sit at a computer terminal and record their responses (the latter two would