First, it will provide important data on the impact of country brand communication strategies on country brand image. Thus, the inclusion of country brand and country brand image in the model will be very rewarding to have a stronger view of FDI attraction.
Research context
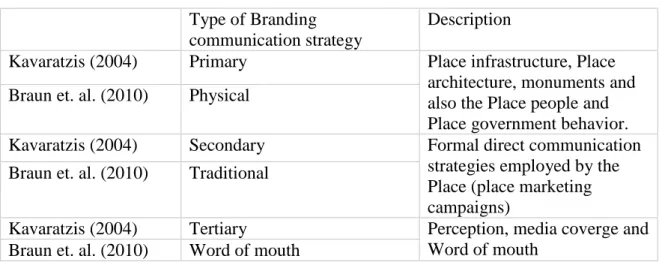
First, it will provide important data on the impact of a placemark communication strategies on a placemark's image and, consequently, its relationship to FDI appeal. The model suggests that there are three types of place brand communication strategies (primary communication, secondary communication and tertiary communication) that have an effect on place brand image (Kavaratzis.
Research problem
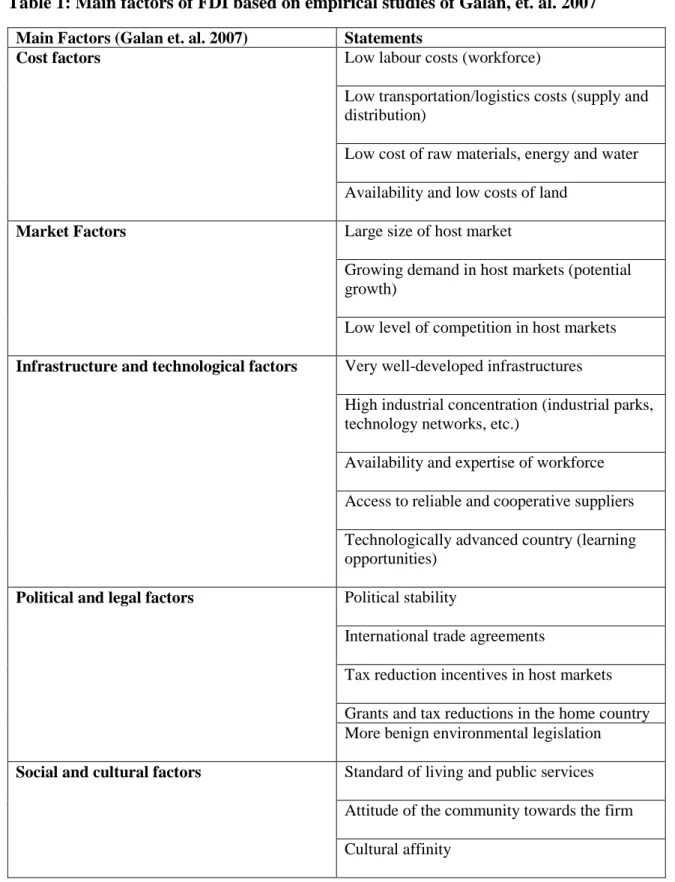
The most prominent research sub-theme is related to market-related determinants (Bretas et.al. 2021). That said, various theoretical frameworks attempted to explain FDI, with Dunning's work as the most significant theoretical foundation for FDI studies (Bretas et. al. 2021).
Research purpose
Moreover, the concept of place branding still remains a complicated and somewhat confused construct, even with the growing interest of academics and researchers in the field (Fan, 2006; Dinnie, 2008). Only a few studies have recognized that region branding, nation branding and city branding are concepts that fall under the umbrella term of place branding (Lucarelli & Berg, 2002).
Research questions
Are there any differences in the perception of employees working in FDI, from the point of view of the public sector, which mainly seeks to attract FDI, and the private sector, which mainly seeks to determine the location, regarding the importance of the place's brand image and place branding communication strategies in attracting FDI. As for the government employees, they should specifically work in FDI attraction, while the private sector employees have worked on choosing location for FDI.
Research objectives
That said, a limited amount of quantitative research has been conducted to examine the impact of place brand communication strategies on place brand image and ultimately on the appeal of FDI. As noted, different communication strategies can have different effects on a placemark's image and ultimately its relationship to FDI appeal.
Research strategy
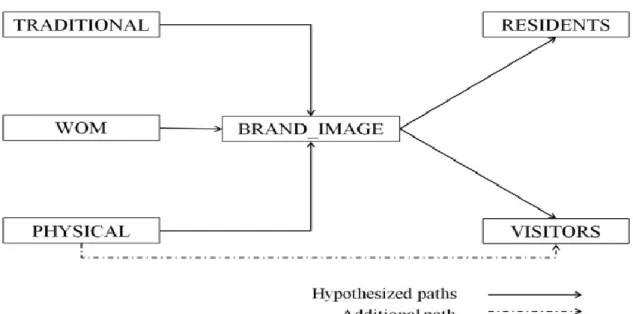
This thesis will assess the impact of three types of place branding communication strategies on the relationship between place branding image and FDI attraction. The conceptual model states that there is a relationship between place brand communication strategies and FDI where place brand image serves as a mediating variable.
Conclusion
The main research questions of the study are: How important is the brand image of a place in attracting foreign direct investment. Thus, the main research objectives of the study are to understand the relationship between placemark communication strategies and the attraction of foreign direct investment and the impact of placemark image as a mediating variable on the relationship.
Introduction
As industrialization made it easier to travel, Harvey (1996) claims that reducing the place barrier between any two locations transformed a "place" into a "product". Organizations are allowed to risk a certain kind of rigidity in order to get a larger share of the transportable investment” (p. 58).
Soft Power
Due to the diversity of sources, soft power is difficult to assess and control. Hard power, in which governments enforce their will by force, could be seen as the opposite of soft power.
Place Brand Image
According to Nye, power in the global period would entail a soft dimension of appeal in addition to the hard dimensions of coercion and inducements (2008, p. 107). Nations obviously mix soft and hard power in the current global environment to achieve their goals and expand their influence.
Place Branding
Place Branding/Nation Branding
This approach takes nation branding as a strategic tool to increase nations' competitive advantages. Apart from the latter approach, most agree that nation branding is a tool for competitive advantage.
Place Branding/ Investment Promotion
Two schools of thought have emerged in this regard, one argues that the two concepts are different but related, while the other argues that they are essentially the same (Kaneva, 2011). Nevertheless, it can be argued that the main difference between city, nation and region branding is that city branding strategies are smaller in scale (Oguztimur & Akturan, 2016).
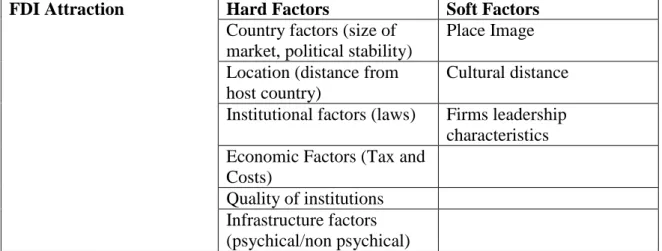
Foreign Direct Investment (hard / soft Factors)
Institutional factors are also taken into consideration, mainly looking at the laws of the country, especially in relation to foreign direct investments. There have also been researchers who have investigated the influence of host countries' institutions on the flow of FDI.
Place Brand Image and FDI attraction
Place branding strategies can be understood as an important tool used by different places to promote, create and change the image of the place (Moilanen & Rainisto, 2009). In addition, research has shown that place branding plays an important role in the sustainable development of a place (Maheshwari et. al. 2011).

Place Brand Communication Strategies
Taglines and insignia can be useful in a place's branding; however, they cannot be considered the strategy in itself, according to Kavaratzis and Ashworth (2005). According to Jones and Kubacki (2014), a comprehensive study, government support is essential for the growth of place-branding in places with socio-economic challenges.
Conclusion
Many authors, including Fan (2006), believe that branding will not solve a country's problems, but others (e.g. Konecnik Ruzzier & de Chernatony, 2013; Cleave et al., 2016; Jones & Kubacki, 2014) argue, that place branding should be a top priority for government agencies and therefore should not be overwhelmed with its functionality (de Noronha, Coca-Stefaniak, & Morrison, 2017). Not only does people's confidence increase when place branding is made official, but so does their engagement, according to Zhao, Sun, and Kakuda (2017).
Proposed Framework
Research Hypothesis
H8b Private sector perception Communication strategies for the place brand positively influence the attraction of FDI mediated by the image of the place brand. H9a Government Sector sees primary placemark communication as positively impacting the attraction of FDI mediated by the placemark image.
First Hypothesis
H10a: The public sector perceives that secondary communication of the place brand has a positive impact on attracting foreign direct investment, which is mediated by the place's brand image. As discussed in the literature, place brand image is said to have an impact on FDI attraction (Papadopoulos et. al., 2016).
Second Hypothesis
It is a strategy that educates consumers about the uniqueness of the brand and the benefits of interacting with it. In addition to the fact that increased knowledge helps consumers associate marketed items with higher quality, this is often seen as an advantage for buyers (Rubio, Oubia, & Villaseor, 2014).
Third Hypothesis
H2: Country brand communication strategies have a positive impact on FDI attraction that is mediated by country brand image. H3: Primary country brand communication has a positive impact on FDI attraction that is mediated by country brand image.
Fourth Hypothesis
They reinforced pre-existing troubling portrayals in advertising (especially in the film and TV industry) "that portray New York City as a decaying, decaying metropolis". The first official "I love New York" advertising campaign started in the post-industrial era and then became a worldwide hit.
Fifth Hypothesis
Word of mouth refers to informal conversations about a product or brand aimed at other customers (Westbrook, 1987). For a number of reasons, word-of-mouth marketing has attracted a lot of attention in recent years.
Sixth Hypothesis
Tertiary placemark communications can be used to enhance a location's image to attract foreign direct investment (FDI). H5: Tertiary placemark communication has a positive impact on the attraction of foreign direct investment mediated by the placemark image.
Additional Hypothesis
H8a: The public sector believes that place brand communication strategies have a positive impact on attracting foreign direct investment, mediated by place brand image. H11a: The public sector believes that the tertiary communication of the place brand has a positive effect on the attraction of foreign direct investment, which is mediated by the image of the place brand.
Conclusion
H7a: The public sector believes that the brand image of a place is an important soft factor in attracting foreign direct investment. H6: Place brand communication strategies have a positive effect on attracting FDI. H7a: The public sector sees the brand image of a place as an important soft factor in attracting FDI.
Introduction
Research philosophy
Therefore, the philosophy will match the plan that the researcher has in place regarding the study. Moreover, philosophy will be suitable for study because it is meant for quantitative studies.
Research approach
The philosophy is suitable for studies that seek to find out the relationship between variables, which is part of the aim and objective of the study. Because the inductive approach is based on subjectivity and is not deterministic, unlike deductive approach, the researcher in this study did not find it appropriate for this research.
Research Method
Using the quantitative research design will help generate data that will be effective in disproving or proving the pre-developed hypothesis. Accordingly, the present study has concentrated on using the quantitative methodology, as this approach allows for numerical evaluations and comparisons between a large number of respondents.
Research Strategy
The findings of the closed survey enabled the researcher to identify a consistent pattern in the responses of the participants. The requirements for the potential participants to work in the field of FDI were clearly stated to the HR department of each institution to ensure the requirements of the research.
Time Horizons
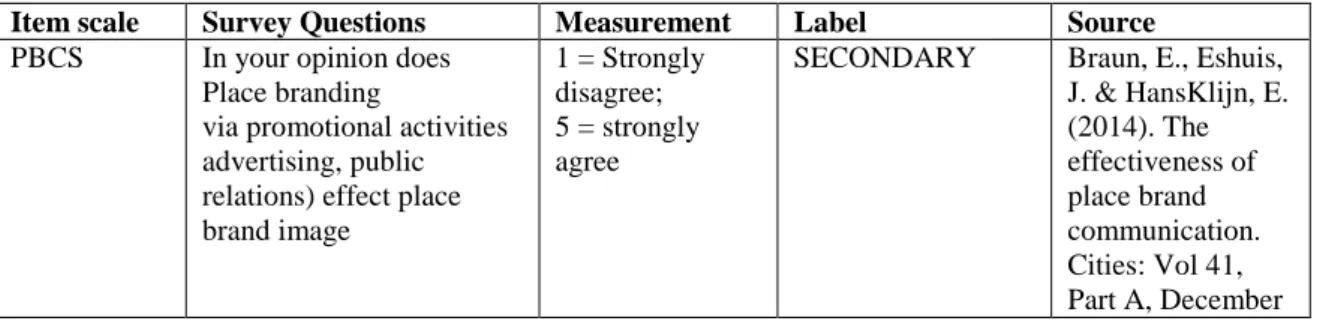
The dissertation was first intended to get institutions' permission to disseminate the research to their employees. The survey was based on a five-point Likert scale to ensure an appropriate degree of variability in the answers.
Sampling strategy and size
However, since the population size is unknown, the sample size can be determined based on the number of latent variables (Pallant, 2016). Thus, in the present study, the sample size chosen is 200 based on the above information.
Data Collection
FDI_Tech Galan, J., Gonzalez-Benito, J. Factors determining location decisions of Spanish MNEs:. an analysis based on the investment development path. FDI_trade Galan, J., Gonzalez-Benito, J. Factors determining location decisions of Spanish MNEs:. an analysis based on the investment development path.
Data Analysis
Theoretical frameworks can be used by researchers to construct predictive perspectives, while also conducting studies to analyze the many relationships between the factors (Fornell & Bookstein, 1982; Hair et al., 2019; Chin, Marcolin & Newsted 2003; Henseler et al. al., 2009). PLS-SEM and SmartPLS 3.3 were used to analyze the data in this investigation (Ringle et al., 2015).
Reliability and Validity
PLS should be used in research to identify new fundamentals as models are complex and sample size is small (Henseler et al., 2009; Hair et al., 2019). Finally, the Fornell-Larcker and heterotrait-monotrait ratios were used to examine discriminant validity (Hair et al., 2017).
Pilot Study
There were also evaluations of the internal performance and durability of the product, as well as the reliability of composites. To remedy these issues, the researcher signed a non-disclosure agreement with the organization and obtained the direct e-mail from the employees.
Ethical considerations
Third, respondents will be informed that their data will not be forwarded to any other party. Finally, respondents will be told that if they choose to withdraw their data at any time during the survey, they can do so without any negative consequences or consequences.
Conclusion
This research will be conducted with the highest ethical standards to ensure the health and ethical behavior of the participants. The second stage will be to inform respondents that their information will be used for educational purposes only and will be treated with the strictest possible confidentiality and anonymity.
Introduction
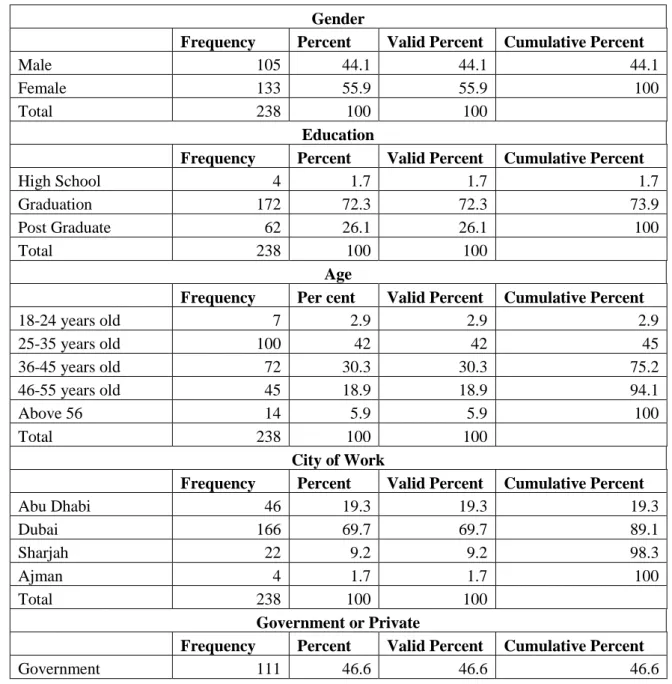
Response Rate and Completeness
Preliminary Analysis
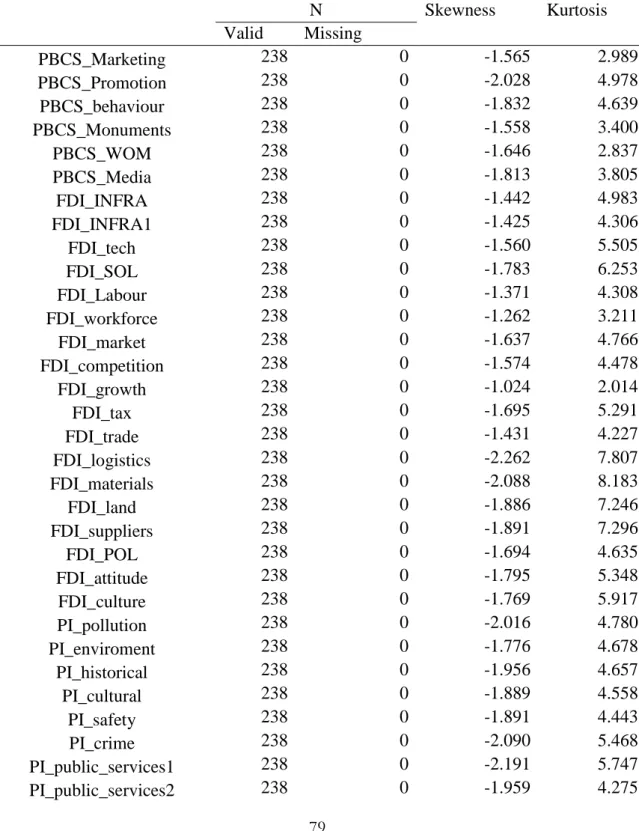
Since the results in the table above are significant, the hypothesis that the data does not follow a normal distribution is accepted. Skewness measures the symmetrical arrangement of the data, while kurtosis measures the peakedness of the data” (Hair et al., 2017).
EFA and Reliability Analysis
Rotation is a data model optimization technique that rotates the reference axis of the components until they reach a new location (Hair et al., 2014; Thomson, 2004). Due to the limited availability of oblique rotation in statistical programs and the limitations of the underlying analytical methods, it was not selected (Hair et al., 2014).
Common Method Bias
Initial Eigenvalues Extraction Sums of Charges Squared Total % of Variance Cumulative % Total % of Variance Cumulative.
Descriptive Statistics
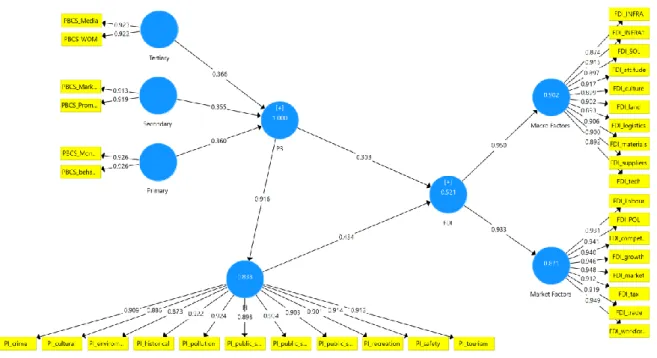
Structural Equation Modelling
Outer Model
It was also hypothesized that country brand communication strategies have a positive impact on FDI attraction (H6). Furthermore, it was also hypothesized that country brand communication strategies have a positive impact on FDI attraction (H6).
Construct Reliability & Validity
Convergent & Discriminant Validity
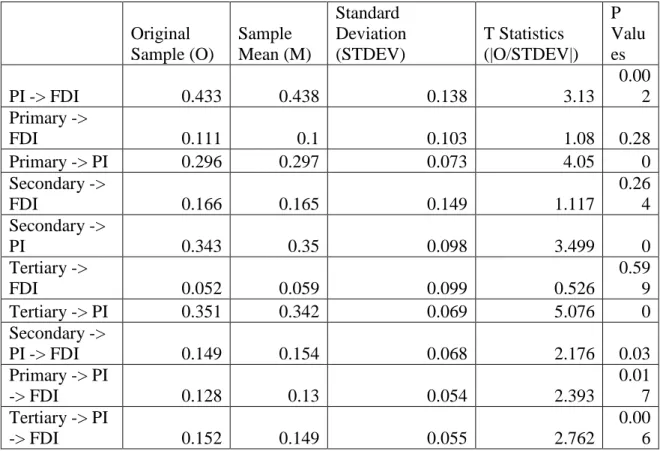
Hypothesis Testing
Direct and Mediating Influences
It was hypothesized that secondary country brand communication has a positive impact on FDI attraction that is mediated by country brand image (H4). 0.00 6 It was also hypothesized that country brand communication strategies have a positive impact on FDI attraction (H6).
Multi-Group Analysis
H4: Secondary place brand communication has a positive effect on FDI attraction, mediated by place brand image. In addition, there was an indirect effect of place brand communication techniques on FDI through place brand image.
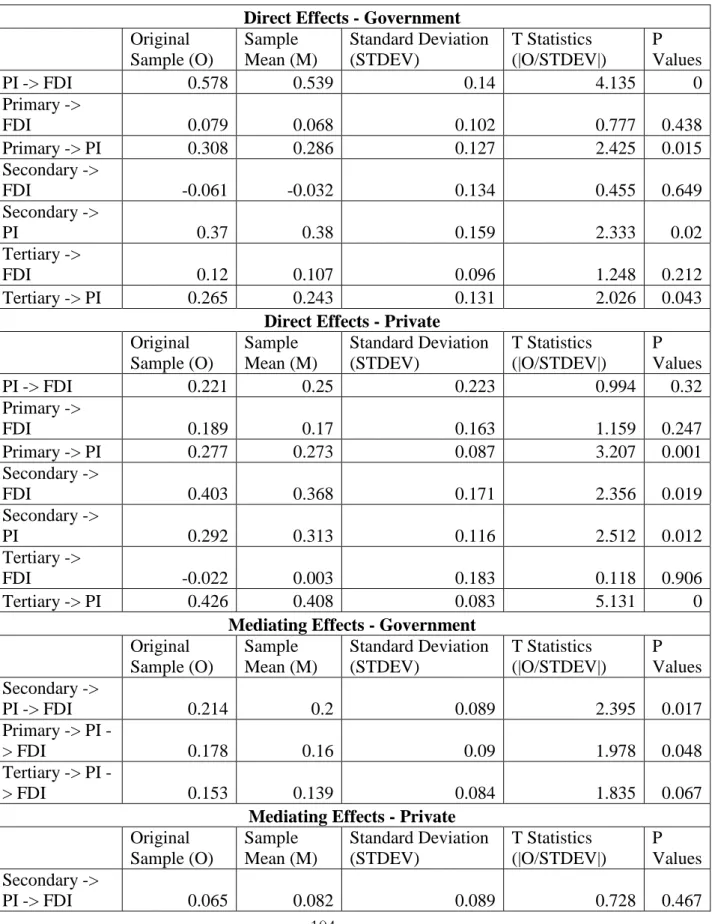
Group Differences
Conclusion
Introduction
The main objective of this study is to understand the relationship between country brand communication strategies and FDI attraction and the influence of country brand image as a mediating variable in the relationship. Furthermore, the mediating influence of country brand image on the relationship between each of the three strategies (primary, secondary and tertiary) is highlighted.
Place Brand Image and FDI Attraction
First, the chapter begins with a discussion of place branding and its impact on FDI attraction. One possible reason why a place's brand image affects FDI attractiveness is by influencing stakeholders' perceptions of the nature of the place, which can help stakeholders decide whether to invest in a country or not (Henninger et al., 2016 ).
Place Brand Communication Strategies and Place Brand Image
Primary Brand Communication Strategies
It was hypothesized that the main placemark communication has a beneficial effect on attracting FDI through the placemark image (H3). Another infrastructure necessary for attracting FDI is the country's financial infrastructure.
Secondary Place Brand Communication
Nunnenkamp (2002a) still presents the most important conventional market characteristics in attracting foreign direct investment (FDI). Research shows that countries that spend more time and money advertising their investment potential are more likely to attract foreign direct investment (FDI).
Tertiary Place Brand Communication
A wide range of government tactics and policies can affect foreign direct investment (FDI). To attract foreign direct investment (FDI), tertiary place brand communication can be used to create a favorable impact on the place brand image.
Perceptions of the Government and Private Sector
Furthermore, it was assumed that the government sector believes that primary placemark communication has a favorable influence on FDI acquisition through the placemark image (H9a). It was assumed that the government sector believes that tertiary placemark communication has a beneficial effect on FDI recruitment through the placemark image (H11a).
Conclusion
However, there is a significant indirect influence of tertiary placemark communication on DBI through the placemark image. Similarly, the government sector believes that placemark communication methods favorably affect FDI recruitment through the image of the placemark (H8a).
Recommendations
Theoretical Contributions
Finally, no study has previously identified the perceptual differences between the government sector and private sector in the context of place brand communication strategies, place brand image and FDI attraction.
Practical Recommendations
Limitations and Future Recommendations
According to the researcher's knowledge, this study was new in applying place brand communication strategies, placing brand image in the IDP framework to understand FDI attraction. In addition, future studies can also use other types of methods to delve deeper into the understanding of the role of place branding, place brand image on FDI attraction.
Summary of the study and Conclusion
From nation branding to competitive identity – The role of brand management as a component of national policy. 2010) Definitions of placemarking - Working towards a solution. 2008), “Country branding: the state of the art”, Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Sciences, Vol.