In the pancreas, treatment of DM rats with LIK066 caused a significant increase in GSH compared to untreated DM rats. I would also like to express my gratitude to all the instructors in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology for the knowledge they provided.
Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus
Epidemiology of DM
Classification and Diagnosis
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
All these will lead to obesity, a key factor for the development of insulin resistance, an important phenomenon in the pathogenesis of T2DM. Three tests can show whether diabetic patients are in the pre-diabetes stage or not.
Pancreatic β-cell Dysfunction and Obesity
When β-cells are stable, an adaptive response to insulin resistance occurs, resulting in the maintenance of normal glucose levels. Moreover, the presence of insulin resistance in vivo, as well as a lack of compensatory β-cell function, will lead to an increase in NEFA levels produced from lipids (Al-Goblan et al., 2014).
Diabetes Mellitus Risk Factors
- Lifestyle and Environmental Risk Factors
- Genetic Risk Factors
BAT activity and risk of diabetes are negatively associated, meaning that the higher activity of brown adipose tissue will reduce obesity and the risk of T2DM (Khan et al., 2019). The KCNJ11 is a gene that increases the risk of T2DM and is regulated by the PPAR-γ.
Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetic Microvascular Complications
- Diabetic Macrovascular Complications
In non-PDR, the biochemical change at this stage is initiated by a lesion in the blood vessel due to retinal hypoxia. In vivo experiments show hyperglycemia as a factor in facilitating the production of collagen in the arterial wall.
Oxidative Stress
- Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus
- Oxidative Stress in the Heart
The heart is a muscular pump located in the middle of the chest between the lungs and slightly to the left. This process results in the production of an excessive amount of ROS (Giacco & Brownlee, 2010).
Management of Diabetes Mellitus
- Lifestyle Modification
- Pharmacotherapy
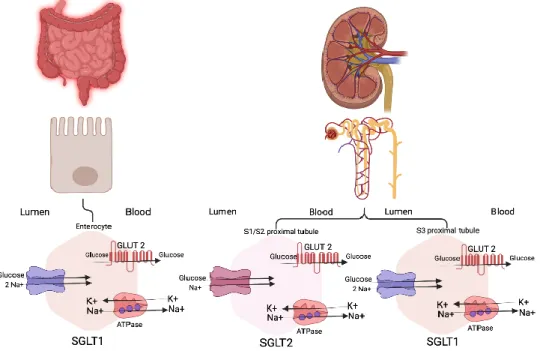
GLP-1 receptor agonists have been established to lower liver enzymes and affect reduction of oxidative stress and weight loss, all of which aid in diabetes management (Sumida et al., 2020). It also contributes to the reabsorption of glucose in the kidney, as it is found in the S3 segment of proximal tubule renal epithelial cells (Abdul-Ghani et al., 2011). SGLT1 inhibitors are designed to prevent the normal function of the SGLT1 transporter in the small intestine and kidney and increase glucosuria.
It inhibits glucose uptake in microvilli and glucose reabsorption in PCT, and this is important in carbohydrate metabolism (Adeghate et al., 2019). In a euglycemic state, renal reabsorption of glucose by SGLT2 is highly significant, up to 90%, which is considered to be its major function. SGLT2 inhibitors were used to prevent the reabsorption of glucose in PCT precisely in segment 1 (S1) (E. Adeghate et al., 2019).
This group of inhibitors increases the release of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) from intestinal L cells when used with dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors (Tsimihodimos et al., 2018).
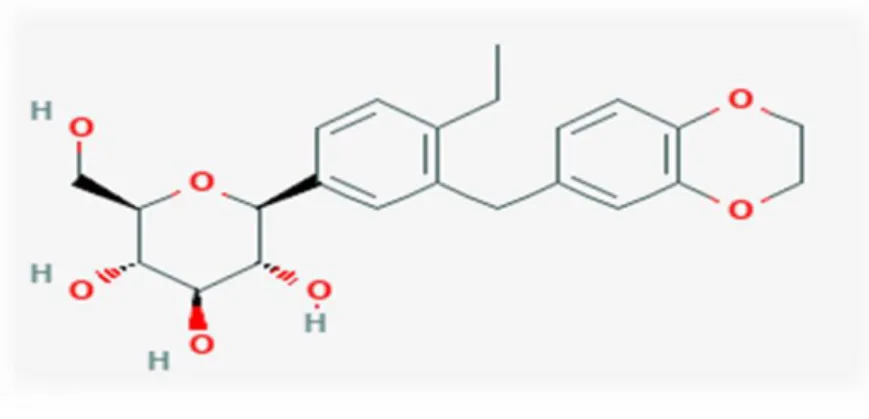
Licogliflozin
- Structure of LIK066
- Licogliflozin’s Mechanism of Action
- The Clinical Benefits of Licogliflozin
On the other hand, the negative effect includes diarrhea, diabetic ketoacidosis and a higher risk of hypoglycemia (E. Adeghate et al., 2019). This study shows the significant effect of LIK066 in reducing body weight by 6% compared to placebo (Bays et al., 2020). Inhibition of SGLT2 results in weight loss, glucosuria, and a decrease in glucose levels in patients with T2DM as well as controls in many clinical trials (He et al., 2020).
Its role is involved in the transport of glucose from vessels to cardiomyocytes, and SGLT2 is absent in the heart (Sano et al., 2020). This study also demonstrated the effect of LIK066 on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) (He et al., 2021). Aldosterone is thought to increase renal perfusion and cause renal hyperfiltration by increasing sodium reabsorption and synthesis in the adrenal cortex (Kobayashi et al., 2020).
Furthermore, LIK066 shows an improvement of transaminases and reduces steatosis in NASH patients, according to results (Dewidar et al., 2020).
Hypothesis, Aims, and Objectives
Methods
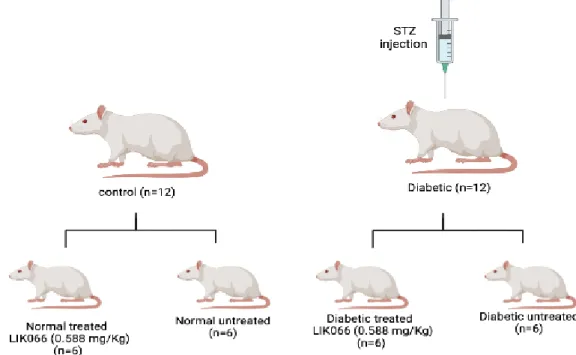
- Animal Model
- Establishing the Experimental Diabetes Model
- Experimental Design
- Blood/Tissue Collection and Tissue Processing
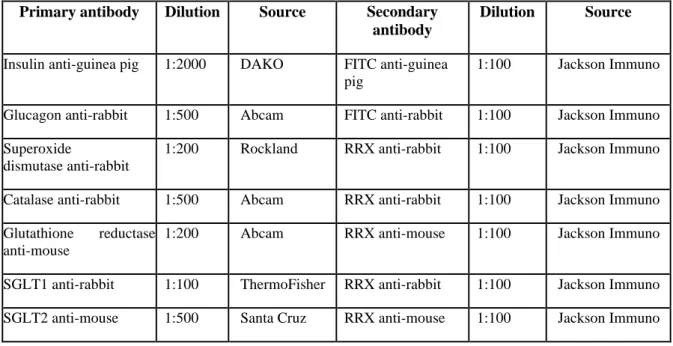
- Immunofluorescence Staining of Paraffin Sections
- Immunoelectron Microscopy
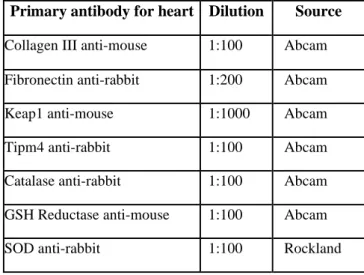
- Markers of Oxidative Stress in the Heart and Serum
- Measurement of Catalase
- Measurement of Glutathione
- Superoxide Dismutase
- Nitric Oxide
- Masson Staining for Heart Tissue
- Statistical Analysis
Heart and pancreas samples were isolated and sectioned for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and electron microscopy (EM) investigation. Then block the tissue sections by adding blocking buffer and incubate for 45 minutes at room temperature to prevent any non-specific binding. A home-made glutathione assay kit was used to measure reduced glutathione in serum and heart homogenates, 50 µL of samples and 50 µL of 5% were taken.
150 µL of the working mixture was added to all wells and incubated for 5 min on the shaker at room temperature followed by the addition of 50 µL of diluted NADPH. To determine the reaction rate, calculate the average absorbance of all standards and samples. Calculate the SOD activity of the samples using the linear regression graph created for the standard (Cayman Chemical, 2008).
This test was used to measure nitric oxide in serum and cardiac homogenate, 50 µl of the samples were taken and 50 µl of 5% sulfosalicylic acid was added (ratio 1:1) for the deproteinization process, then vortexed and incubated on ice for 10 minutes. .
Results and Discussions
Metabolic Parameters
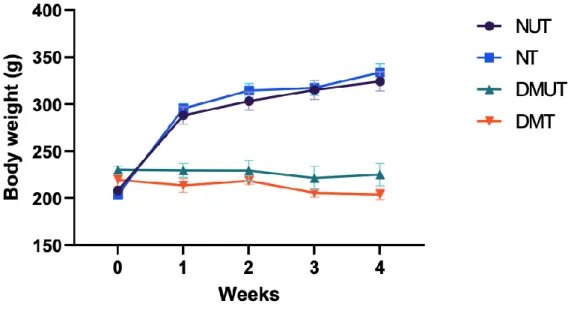
- Body Weight
- Blood Glucose Levels
- IPGTT
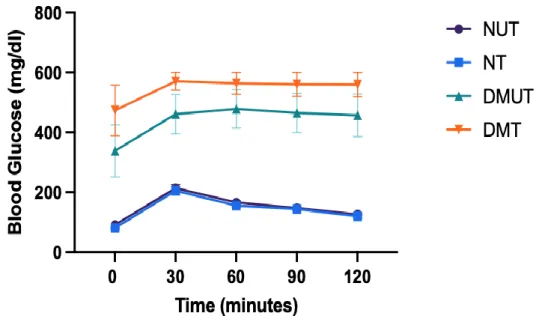
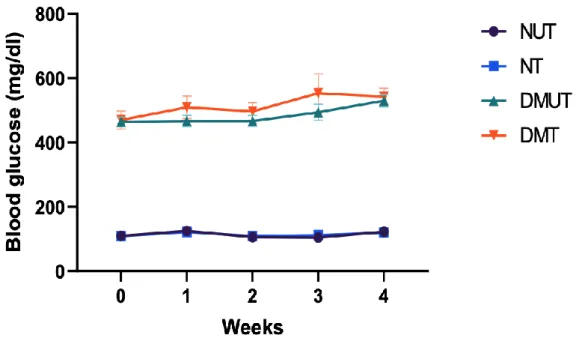
The result shows a significant weight reduction higher than 5.7% from baseline in patients with dysglycemia seen with an optimal dose of 150 mg LIK066 compared to placebo-controlled individuals (Kalra et al., 2020). The mechanism of LIK066 in reducing weight is the inhibition in intestinal L cells that increase the production of weight-controlling incretin hormones such as GLP-1 and peptide YY that affect appetite and this mechanism has an indirect effect on satiety so it can body weight reduced (Hy et al., 2019). The effect of LIK066 on blood glucose levels in both normal and diabetic animals over the 4 weeks of the study is shown in Figure 5.
The STZ-induced diabetic rats had significantly elevated blood glucose levels compared to normal rats. Time course graphs representing the effect of LIK066 treatment on blood glucose levels in normal untreated, normal LIK066-treated, diabetic untreated and diabetic LIK066-treated rats. The effect of LIK066 on blood glucose in the IPGTT for both normal and diabetic animals at the end of the 4-week study is shown in Figure 6.
A study was conducted to investigate the improvements in glycemic control in mice deficient in SGLT1 and SGLT2, which mimics the mechanism of LIK066 to inhibit SGLT1 and SGLT2.
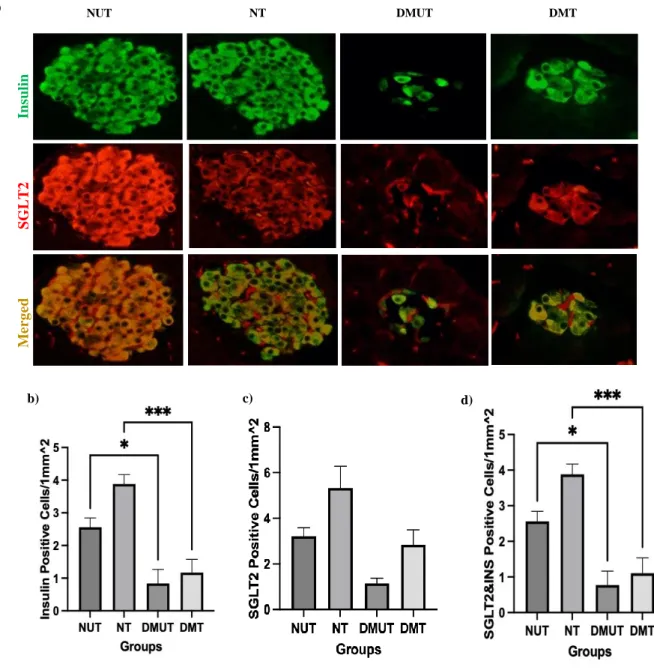
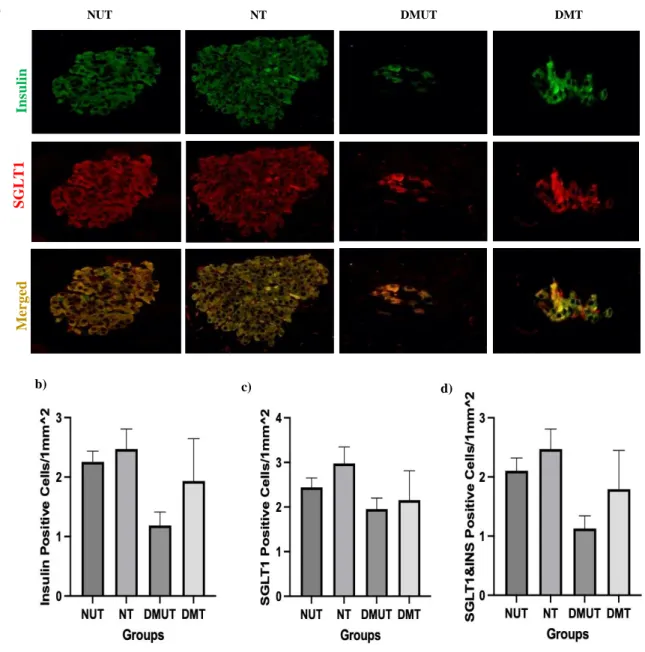
Immunohistochemical Analysis
- Immunohistochemical Study in the Pancreas
- Immunohistochemical Study of the Remodeling of the Myocardium
The effect of LIK066 on collagen III was examined in the myocardium using immunofluorescence analysis. To our knowledge, there are no reported data on the effect of LIK066 on collagen III in the myocardium. There is no significant difference in the percentage distribution of fibronectin-positive cells between groups.
The results show no significant effect of LIK066 on the myocardium of normal and diabetic rats, regardless of LIK066 treatment. No data have been reported on the effect of LIK066 on fibronectin in the heart of experimental animals. The effect of LIK066 on TIMP4 expression was examined in the myocardium of normal and diabetic rats treated with LIK066 using immunofluorescence analysis.
A significant increase in the number of TIMP4-positive cells was observed in diabetic rats treated with LIK066 compared to non-diabetic rats.
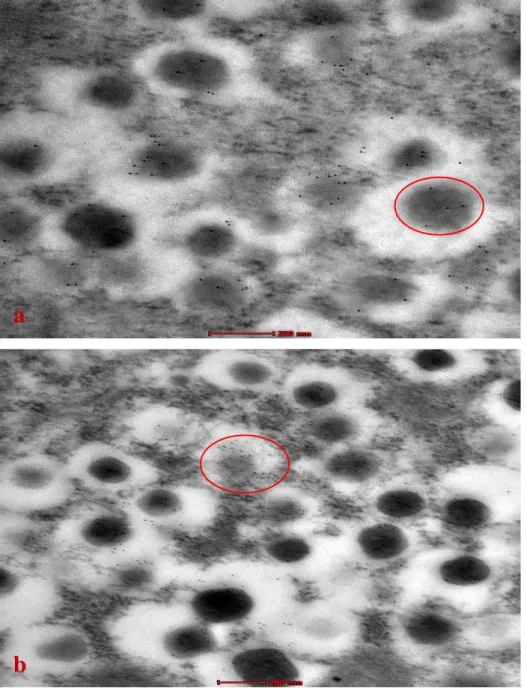
Electron Microscopy
MMP remodeling is one mechanism by which the extracellular matrix (ECM) is altered by ECM degradation by proteases. In diabetes, hyperglycemia and ROS can induce the production of MMPs, and one example of MMPs associated with a higher incidence of macrovascular disease is an increase in MMP-2, which is associated with endothelial dysfunction and also increases fibrosis, thrombus formation, and lower elastin content (Peeters et al ., 2017). Electron micrographs are representative of 6 different animals in each group, and images were taken at a scale of 200 nm.
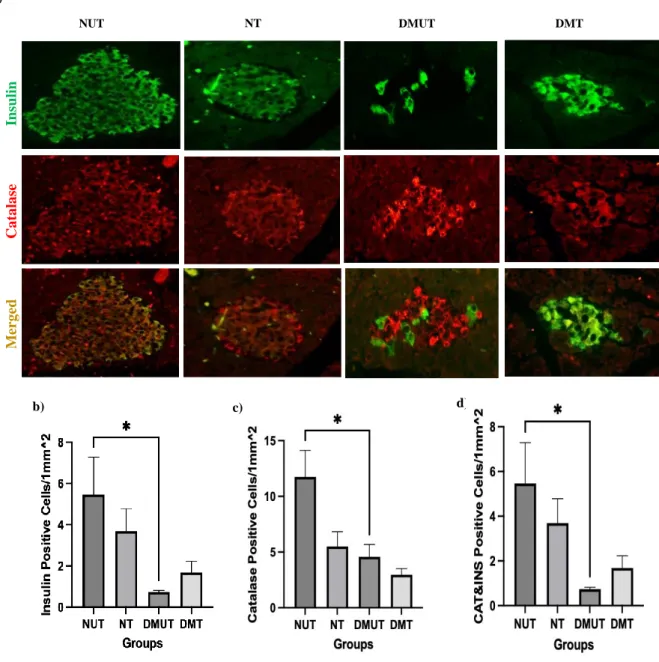
Markers of Oxidative Stress
- Oxidative Stress Markers in the Pancreas
- Effects of LIK066 on Antioxidant Enzymes Activities in the Heart
- Effects of LIK066 on Antioxidant Enzymes Activities in Serum and
A highly significant increase in the percentage distribution of catalase-positive cells was observed in the heart of diabetic rats treated with LIK066. The results show that catalase is present in the heart of diabetic and normal rats. Treatment with LIK066 in vivo results in a significant enlargement of the heart of diabetic rats compared to diabetic untreated rats.
The treatment with LIK066 had no significant effect on the number of SOD-positive cells in the heart. A significant increase in the number of GSH reductase-positive cells was observed in the heart of diabetic rats 4 weeks after being treated with LIK066. The antioxidant activity of LIK066 was tested in the serum and the heart tissue homogenate using colorimetric analysis.
Cardiac SOD activity was ..significantly higher in the heart of diabetic rats compared to untreated diabetics, shown in Figure 24b.
Heart Morphology
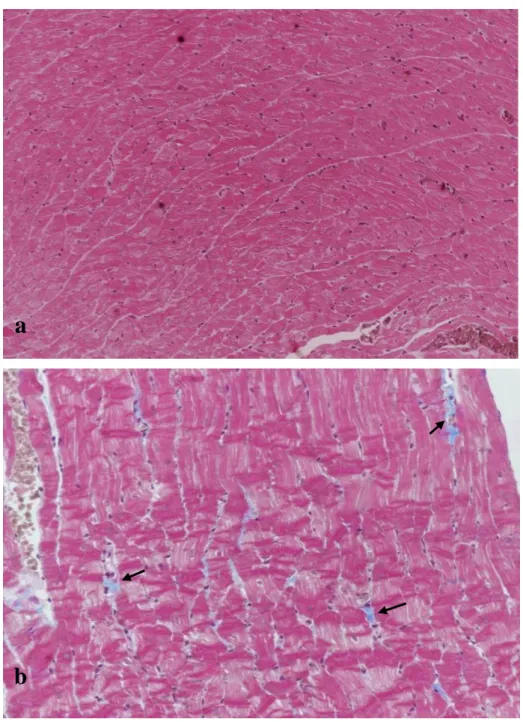
- Masson Staining of heart tissue fibrosis
Both (a) and (b) represent the colorimetric analysis of NO activity in NUT, NT, DMUT and DMT groups showing significance in heart homogenate while comparing diabetic treated and control treated people and no significance in serum comparing all groups be compared. In diabetes, the hallmark of vascular complications is the elevation of ROS and endothelial dysfunction due to a decrease in NO levels involved in the diabetes. One study reported that STZ-induced diabetic rats showed higher NO levels and NO metabolites excreted in the urine, which is related to the glomerular.
We found that STZ-induced diabetic treated rats show a significant increase in cardiac NO activity compared to normally treated animals. In non-diabetic rat hearts, the arrangement of cardiomyocytes is random, with many spaces, but in diabetic rats, the arrangement of cardiomyocytes is more regular.
Conclusions
SGLT2 inhibitors reduce cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations in patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Effects and safety of SGLT2 inhibitors compared with placebo in patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nrf2/Keap1/ARE pathway and oxidative stress as a therapeutic target in type II diabetes mellitus.
Effects of the dual sodium-glucose-coupled transporter inhibitor licogliflozin vs placebo or empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and heart failure. The effects of licogliflozin, a dual SGLT1/2 inhibitor, on body weight in obese patients with and without diabetes. Plasma extracellular superoxide dismutase concentration, allelic variations in the SOD3 gene, and risk of myocardial infarction and all-cause mortality in humans with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Impact of receptor selectivity on the benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with heart failure: a systematic review and comparative effectiveness network meta-analysis.