Questions regarding the use of the book should be directed to the Rights and Permissions Department of INTECHOPEN LIMITED ([email protected]). The publisher assumes no responsibility for any damage or injury to persons or property resulting from the use of materials, instructions, methods, or ideas contained in the book.
107 Optimizing a Centralized Control Topology of an IoT Network Based
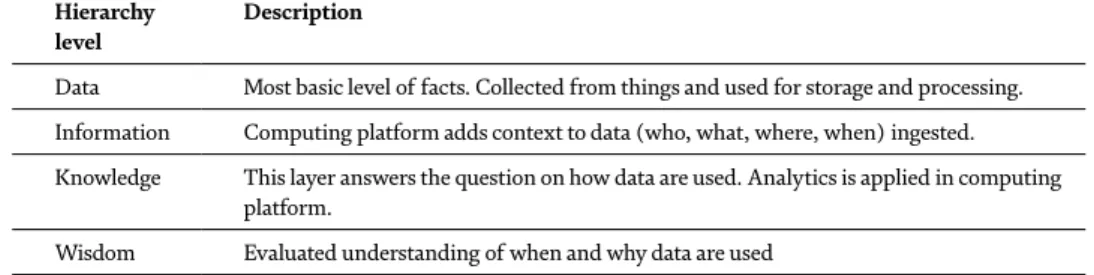
What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things is a cutting-edge technology that creates a global network of machines and devices that are able to communicate and exchange data with each other over the Internet. Security cameras, sensors, vehicles, buildings and software are examples of things that can exchange data between each other.
Internet of Things challenges
- Smart connectivity
- Keeping high privacy and security of all connected devices
- Treating big data
- Reducing the overall data latency among machine-to-machine interactions While connecting many devices through the Internet of Things infrastructure,
- Reducing bandwidth and power consumption
- Complexity
The main challenge of using the Internet of Things is the tremendous growth of the data transferred between the connected devices. As a result, there is a challenge to reduce the complexity of the Internet of Things technology as the number of connected devices increases.
Internet of Things applications
The smart home is one of the main applications that use the Internet of Things infrastructure to connect multiple sensors. There are many other applications that use Internet of Things infrastructures such as smart bridges and smart tunnels.
Introduction
Through this chapter, we present current emerging trends in IoT in different industry sectors, as well as discuss the main privacy challenges that hinder the growth of IoT to reach its potential in the smart home context. The findings of this research aim to help practitioners and researchers interested in the privacy of IoT-enabled smart systems.
Review of privacy literature with specific IoT focus
- Potential scenarios of privacy violation in smart home
- Legal aspects of privacy in IoT era
- People aspects of privacy in IoT era
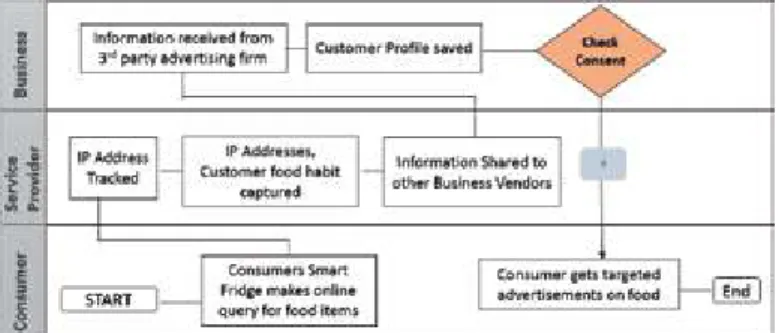
An inherent part of the privacy issue is the exposure of sensitive data such as personally identifiable information (PII) to unintended recipients. According to McKinsey's global report, consumers are wary of embracing IoT-based systems, especially due to lack of privacy and the data at risk.
Consumer-centric approach
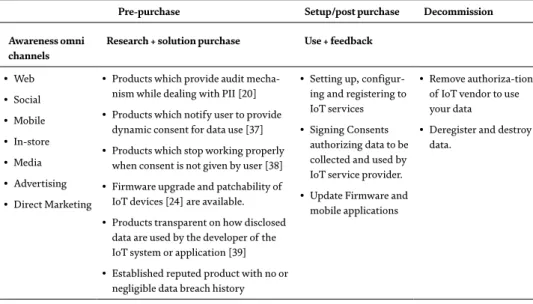
PbD is one of the highly recommended approaches to protect individual privacy [31, 33] concerns in IoT. The products are transparent about how the disclosed data is used by the developer of the IoT system or application [39].
Proposed framework
- The 4I framework applied to privacy context
The identification phase of the 4I framework (Figure 4) consists of seven key dimensions such as risk, compliance, policy, process, people, data assets and technology (Table 6). The Identify phase of the 4I framework distinguishes the potential risks associated with consumer data shared between data processors in the data supply chain.
Conclusion
Overview of Smart Home Current Status and Challenges: Connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) with Context Aware. Classic smart home, IoT, cloud computing and rule-based event processing are the building blocks of our proposed advanced integrated smart home mix.
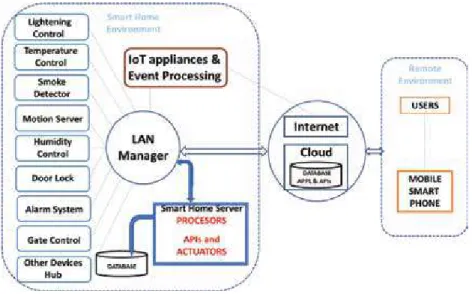
Classic smart home overview
- Smart home services .1 Measuring home conditions
- The main components
These sensors are connected to the home itself and to the devices connected to the home. The sensors' data is collected and continuously transmitted via the local network to the smart home server.
Internet of things [IoT] overview
Cloud computing and its contribution to IoT and smart home Cloud computing is a shared pool of computing resources ready to provide a
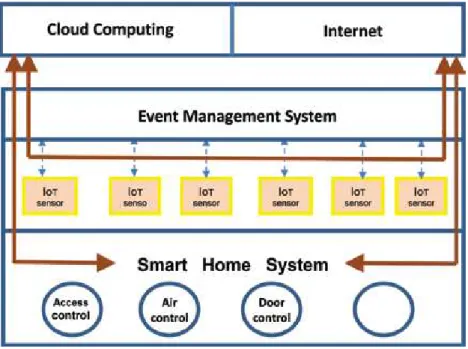
Centralized event processing, a rule-based system
- Event processing languages
- Rediscovering workflow from events
Smart home and IoT will focus on data collection, basic processing and transmission to the cloud for further processing. A computing task can either be performed on IoT and smart home devices or outsourced to the cloud.
Advanced smart home
New event conditions or event patterns can be added or removed from the rule model. The rules engine assembles sequences of events relevant to a particular rule condition to allow events to be linked according to their context information.
Practical aspects and implementation considerations for IoT and smart home
Referring to the RSA example, an IoT device triggers the need to generate an encryption key and thus sends a request message to an RSA application running on a smart home computer. In a later stage, the IoT device issues a request to the smart home computer to encrypt the message using the recently generated RSA encryption key.
Smart home and IoT examples
- Discovery of water leaks and its prevention
- Smoke detectors
The underlying configuration assumes an integration via messages and commands between the smart home and the IoT control system. Therefore, this scenario is possible due to the integration between smart home and IoT systems.
Conclusions and summary
Consider the scenario where you leave the house while some of the devices are still on. On the other hand, it has been found that most hospitals in different countries are still facing many problems regarding the exchange of their health information. Recently, various studies in the field of health care information system mention that the fragmentation of health information is one of the most important challenges with the distribution of patient information data.
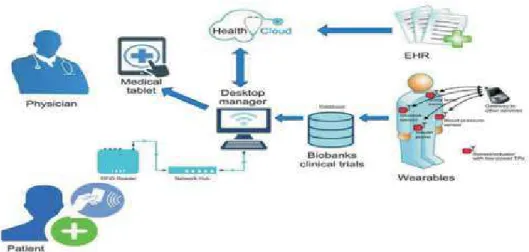
Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare
Healthcare professionals also rely on this technology to deliver high-quality and affordable healthcare services, minimize medical errors, ensure the safety of their patients and optimize their care processes [14]. The IoT technology is yet to be used in the health sector in different regions to combine the information with control and monitoring, such as in China, USA, Canada, etc. Security and privacy Tracking a location and collecting inappropriate information for each person using it sees the use of IoT services in healthcare as a challenge.
HIoT applications and device features
Many outstanding challenges need to be addressed through new research and research, mainly due to the complex implementation characteristics of such systems and the stringent requirements imposed by various services seeking to make use of such complex systems. Thus, it becomes critical to study how to improve current approaches to standardization in this field while better understanding the opportunities for the research community to contribute to the IoT field [36].
IoT scenario in the healthcare industry
Wearability: most of the HIoT applications provide sensing on the human body so that they collect data precisely and take vital signs of the human body as targets. Therefore, most of the existing medical health devices make the portability as the basic requirement for collecting vital signs of the human body. In this way, the users feel more comfortable and can be improved and the accuracy of the collected health data can be guaranteed through the collection procedure.
Healthcare system challenges
However, with the increasing complexity of healthcare, the availability of patient information is considered very important. The full potential of teamwork is rarely realized due to training difficulties and lack of confidence in the reliability of health care. As in other countries, substantial concerns about privacy and security in the UK and the Netherlands have fueled resistance from healthcare professionals to HIE, despite the benefits of this practice.
Models/frameworks for IoT use in healthcare
- Tyagi et al
- Manate et al
- Datta et al
- Prayoga and Abraham
- Roy et al
- Jagatheesan et al
- Bui et al
- Manashty et al
- Sheriff et al
- Pir et al
- Chatterjee and Armentano
- Gupta et al
However, the benefits of the cloud-IoT-based healthcare framework are offset by issues related to trust, privacy and security, all of which need to be addressed before healthcare providers decide to adopt this framework. Although this system can provide exciting benefits to the healthcare industry stakeholders, several complexities and challenges in hospital environments need to be addressed before ICADS is implemented [31]. However, this method does not allow patients to receive a high-level abstract abstraction of data collected by wearable devices [58].
Conclusion
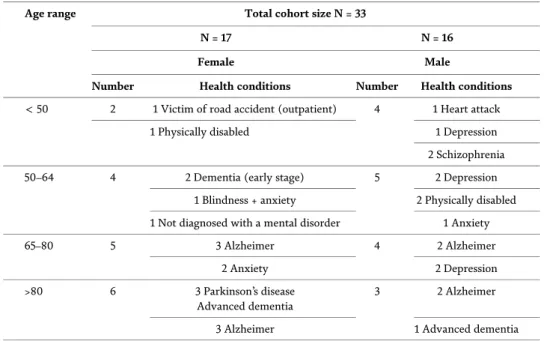
The demographic structure of the developed countries (DC) or high-income countries (HIC) contains a large number of elderly (from 85+ years) and elderly (from 60+ years) than young people (up to 59 years) and a very small number of teenagers (up to 15 years) in their population. IoHT is a special case of the Internet of Things (IoT) that combines health technologies and IoT and takes full advantage of IoT technology, such as the ability to initiate actions based on collected and analyzed data [ 24 ]. The first three stages of the Hilbert curve, (b) scattering matrix orγof∑4i¼1nMCUið Þt inside a convection space, and (c) matrix!γordered as a vector.
The first three stages of the Hilbert curve, (b) the dispersion matrix or γof∑4i¼1n MCUið Þt inside the convection chamber and (c) the!γ matrix ordered as a vector. In the same way, we make all the nodes and interconnections for the simulation of the next section.
![Figure 2 (Source Figure 23.1 in [21]) presents a sample of home control devices.](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/1libvncom/9200637.0/91.765.119.646.81.451/figure-source-figure-presents-sample-home-control-devices.webp)
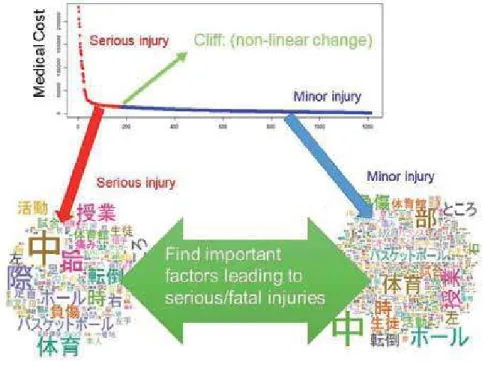
Issues in building a living function-resilient society
- Gap between efficacy and effectiveness
- Fragmented living data and support services
- Variety in privacy exposure
There is an expectation that in the next 10 years, a new industry that helps translate the need for living functional resilience into innovation will grow significantly. We need to reveal the whole picture of problems associated with changes in the life function of the elderly and base intervention design (precision intervention [2]) on this picture. On the other hand, a universal strategy does not allow the diversity of living function to be addressed.
Problem solving by connective AI 1 Description of connective AI
- Smart living lab coevolving with connective AI
A collective impact model has been proposed to achieve efficiency through joint use of stakeholders and social resources with a common goal [5]. There is a need for a system for implementing the collective impact model based on the data. This means that there is a "one-size-fits-all" issue in privacy policy as well; we need a system and technology to control information according to the variety of ideas of individuals and facilities about privacy, instead of developing a privacy policy common to all people and facilities.
Attempt to demonstrate safety in daily life using AI and IoT technology
- Raising awareness using data scattered across multiple organizations in an integrated manner (issue identification)
- Monitoring changes in living function using IoT technology
- Supporting community involvement of people with different living functions by using a daily life database
- Trial of precision care at IoT-based care facilities
- Elderly behavior library for searching for product usage by those with changing living function
There is a need for IoT sensors to detect changes in the lifestyle function of individual seniors as they occur and prompt appropriate interventions. This person's walking pace tends to be slow in the morning and varies a lot. Staff can monitor day-to-day changes in the elderly's gait and can relate changes to medication, mental status (dementia), discharge and pain.
Conclusions
This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/ . by/3.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. In this report, based on our research, we describe "a living function-resilient society" as a desirable society and show the potential of AI and IoT technology to identify and solve problems. The type of innovation required today is the transformation of society into an advanced, interconnected society by using the ubiquity of data and intelligence in modern society to address new emerging issues.