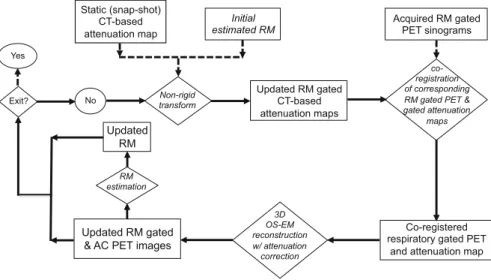
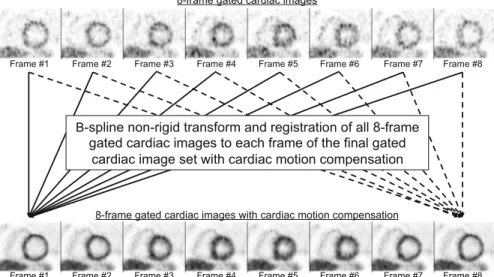
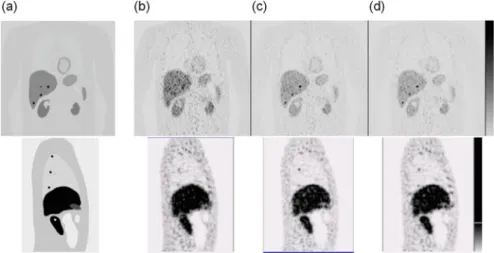
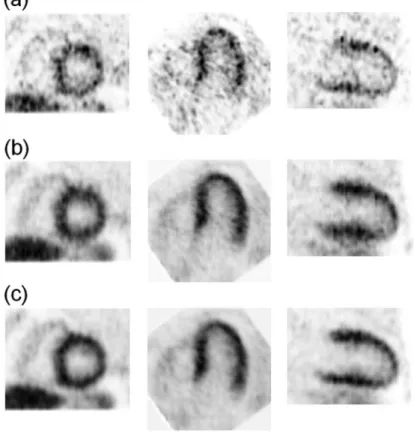
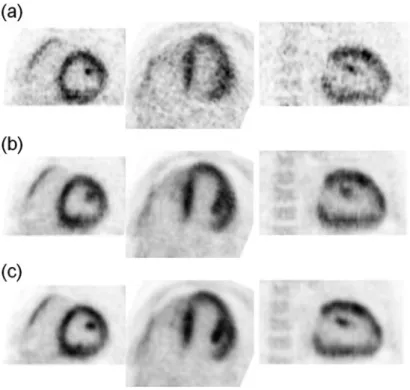
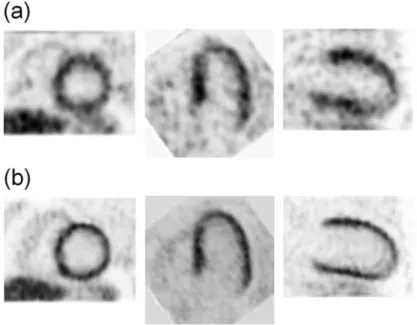
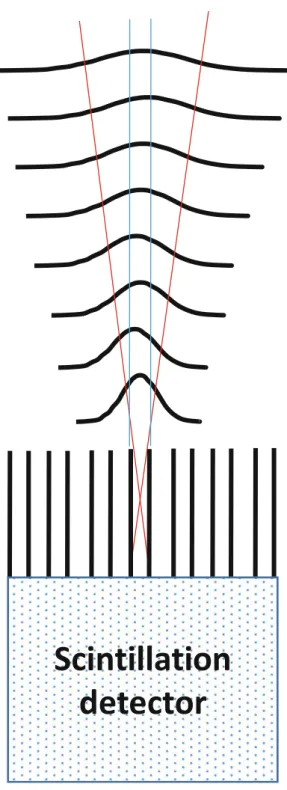
We evaluated the 4D image reconstruction method with respiratory and attenuation compensation for two clinical applications. The 4D PET image reconstruction method with RM and attenuation compensation was applied to the simulated RM-gated projection data.
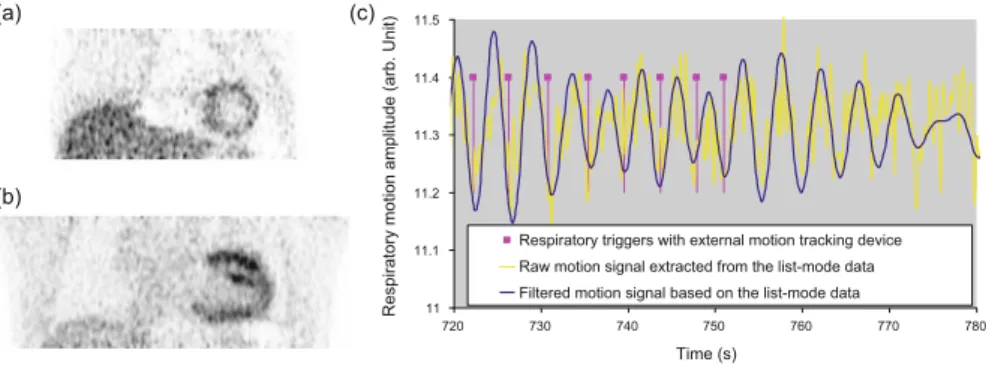
Improvement of Gated Cardiac PET Images with Dual Respiratory and Cardiac Motion Compensation
Conclusions
Evaluation of a new 4D PET image reconstruction method with respiratory motion compensation in a CHO study. Proceedings of the meeting Full three-dimensional image reconstruction in radiology and nuclear medicine.
Introduction
Abstract This report details the requirements and practical procedures for quantitative assessments of biological functional parametric images of the brain using 123I-labeled tracers and clinical SPECT systems. With SPECT scans, there is the advantage over PET of the availability of the necessary scanner in clinical institutions.
Requirements for Quantitative Reconstructions in SPECT
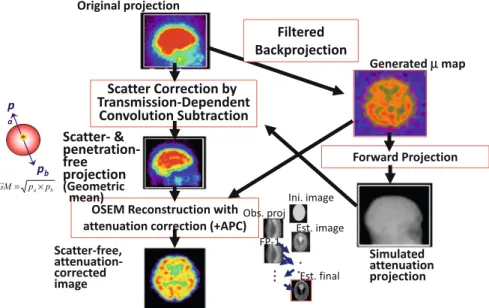
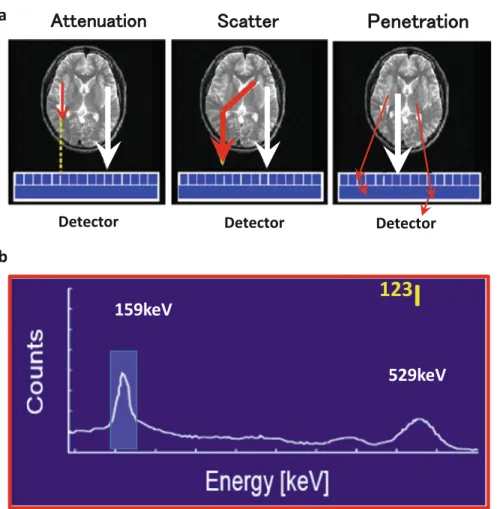
- Scatter Correction
- Septal Penetration in the Collimator
- Attenuation Correction
- Attenuation Coefficient Map
- Implementation of the Collimator Aperture Model
- SPECT Reconstruction
- Calibration to Bq/mL
- Dead Time Count Loss
It should be noted here that the magnitude of the shift in the projection data due to penetrating photons varies depending on the collimator. In the striatum phantom projection data, the striatum to whole brain ratio is also altered due to penetrating photons.
Phantom Experiments
Uniform Cylindrical Phantom
However, it should be noted that inappropriate definition of the head contour and inconsistently defined attenuation coefficient values in relation to the presence of the skull may not be evaluated from the uniform cylinder phantom experiment. Geometrically shaped phantoms are limited in simulating realistic head contours, the presence of the bone and trachea, and also the realistic radioactivity distribution. 2.5, the accuracy of the QSPECT software can be evaluated by referencing regional radioactivity concentration on the reconstructed images with that of design images of this phantom.
22] showed that spatial resolution smoothing significantly reduced the inter-institutional variation of the normal database of resting and acetazolamide CBF images between three institutions.
Striatum Phantom for Dopamine Transporter Imaging
The QSPECT reconstruction program was also evaluated using this phantom to assess the accuracy of the specific binding ratio (SBR) values [24], referring to values calculated from the true radioactivity in the striatum regions relative to the whole brain background concentration. - tration. The results showed that the SBR values measured by the QSPECT software were in good agreement with those determined from the actual radioactivity concentrations. This suggested minor inter-institution/inter-vendor variation of less than 1/3 for QSPECT compared to FBP.
This change corresponds to the decrease in sensitivity and specificity from 97 to 78% in our preliminary simulation study.
QSPECT Program Packages
Adequacy and Impact in Clinical Scans
Dopamine Transporter Function (SBR Quantitation) Using 123 I-FP-CIT
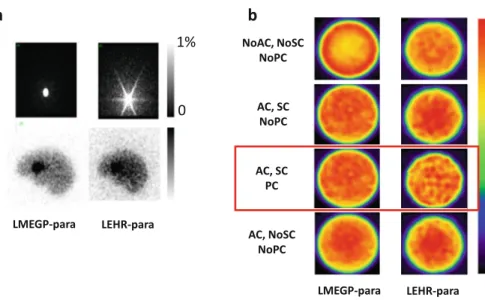
It is therefore of critical importance to establish an accurate reconstruction methodology to provide good diagnostic performance in clinical settings. There can be many areas of application where improved image quality can contribute in clinical settings. The scanning was done using Toshiba 9300R (three-head camera) equipped with an LMEGP-fan collimator.
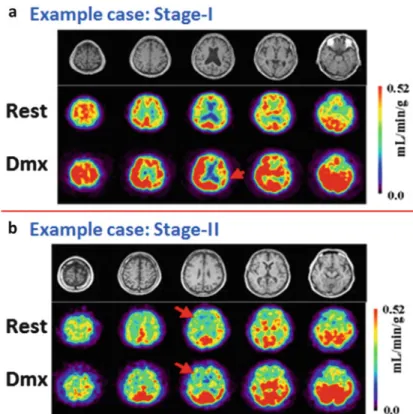
The main contour is well delineated using the edge detection method implemented in the QSPECT software, as shown by the arrows.
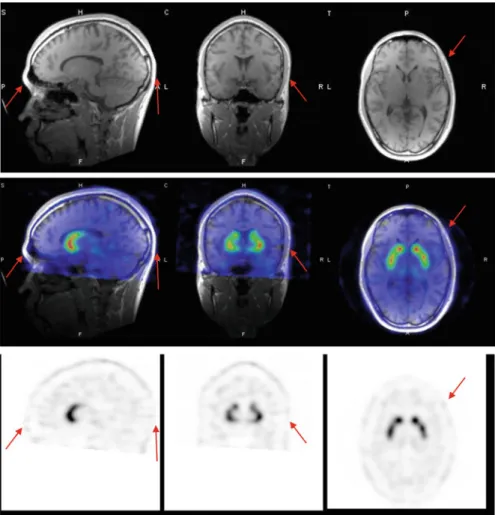
Central Benzodiazepine Receptor Imaging Using
Rest- and Acetazolamide-CBF Using 123 I-IMP (The Dual-Table Autoradiography Method)
A number of studies were carried out to verify the method in a clinical setting, funded by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare Research Fund from the year 2007 for 3 years as follows:. This study is a good example showing the contribution of quantitative SPECT in a clinical setting. Results of 3D-SSP shown in Fig.2.8 are useful to understand the severity of ischemia and risk status in patients with major artery occlusion or stenosis.
Quality Control of the SPECT Scanner
Of the 139 cases identified, no errors were suggested in the data or in the calculation process, as the observed CFR or small CBF values could be confirmed by the results of the tTAC analysis, both in the dynamic reconstructed images and in the projection data. The feedback given in the information about the clinical institution was evaluated to be effective in improving the quality of the examination results. It was clear that vendor engineers should be encouraged to put effort into improving the quality of reconstructed images and not just projection data.
Active feedback to users in clinical institutions is also essential to improve the quality of quantitative screening.
![Fig. 2.8 Stereotactic extraction estimates based on the JET study (SEE-JET) images [4] of a patient obtained in institutions O and Y](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/1libvncom/10207169.0/34.659.83.580.96.517/stereotactic-extraction-estimates-based-images-patient-obtained-institutions.webp)
Summary and Future Directions
Effects of scatter and attenuation correction on quantitative assessment of regional cerebral blood flow with SPECT. A multicenter validation of regional cerebral blood flow quantification using [123I] iodoamphetamine and single photon emission computed tomography. Quantitative mapping of basal and vasoreactive cerebral blood flow using split-dose (123) I-iodoamphetamine and single-photon emission computed tomography.
Multicenter evaluation of a standardized resting protocol and assessment of cerebral blood flow with acetazolamide using a quantitative SPECT reconstruction program and split-dose 123I-iodoamphetamine.
Introduction
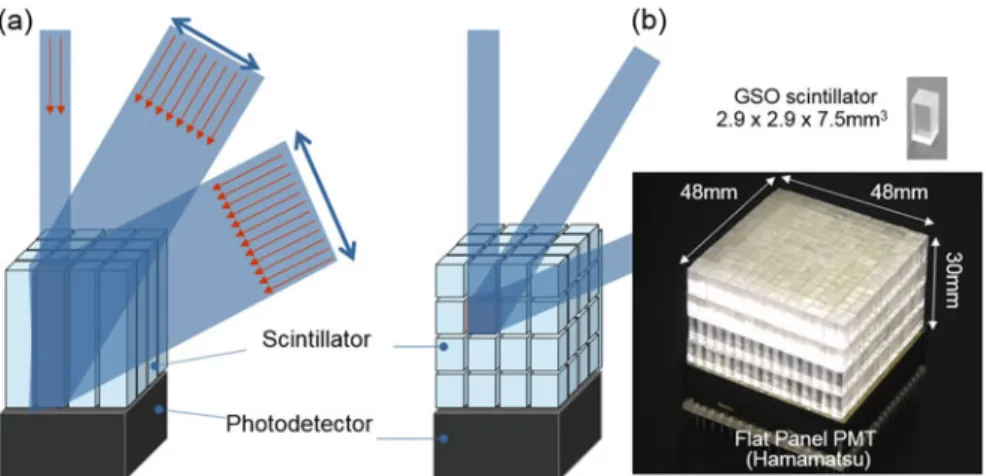
The DOI detector itself continues to evolve with the help of recently developed semiconductor photodetectors, often referred to as silicon photomultipliers (SiPM). X’tal” cube to achieve sub-mm spatial resolution, which is reaching the theoretical limitation of PET imaging. The DOI detector (b) eliminates the parallax error, which is caused by the thickness of the crystals in conventional 2D detectors.
We are developing a SiPM-based DOI detector “X'tal cube” to achieve sub-mm spatial resolution, which achieves the theoretical limitation of PET imaging.
The OpenPET: A Future PET for Therapy Imaging
Using our SiPM-based DOI detectors, we are developing a novel, high-performance, low-cost brain PET/MRI to meet the requirements for early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. The main concept is an RF coil with PET DOI detectors, which has a potential to improve any existing MRI in PET/MRI. The prototype consisted of two detector rings and each detector ring had two sub-rings of 40 detectors.
The portable gantry had a compact design; each detector ring had an outer diameter of 940 mm and a thickness of 171 mm, while the inner bore of the detector had a diameter of 640 mm and a thickness of 113 mm.
The Helmet-Chin PET for Super High-Sensitive Brain Imaging
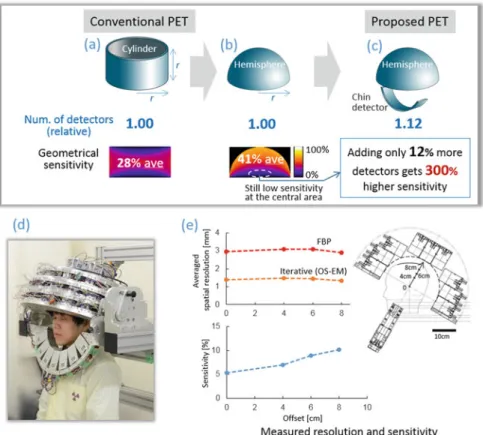
Our basic idea is based on the evidence that the average sensitivity of a hemispherical PET is about 1.5 times higher than that of a PET cylinder of the same radius and height, while the area is the same for both geometries (Fig.3.3a ,b). ). In addition, the use of 12% more detectors for “chin detectors”, placed like a chinstrap, improves sensitivity, especially in the central region (Fig. 3.3c). In the prototype, 47 block detectors were used to form a hemisphere with an inner diameter of 25 cm and an outer diameter of 50 cm, and seven block detectors were used for the chinstrap (Fig.3.3d).
The measured sensitivity was 5% in the cerebellar region and 10% in the parietal region for a standard energy window of 400–600 keV.
The X ’ tal Cube: 0.8 mm Isotropic Resolution, a World Record
The Add-On PET: A PET Insert to Upgrade Existing MRI to PET/MRI
While obtaining a uniform static magnetic field, approximately a 20 % decrease in signal-to-noise ratio was observed in MR images; we suspected it was due to noise pollution from outside the MRI room. Although further optimization is needed for shielding, we have demonstrated a proof of concept of the proposed head coil with DOI PET detectors (Fig.3.5g).
Conclusions
Initial results of simultaneous PET/MRI experiments with an MRI-compatible silicon photomultiplier PET scanner. Feasibility of a dedicated brain PET-MRI system using four-layer detectors integrated with an RF head coil.
Introduction
The feasibility of using CdTe-SPECT for simultaneous imaging with two radionuclides was evaluated through scans of phantoms and healthy volunteers. The results suggest that the prototype CdTe-PET can identify heterogeneous intratumoral metabolic distribution and that CdTe-SPECT can accurately acquire dual radionuclide images at the same time. A high energy resolution is expected to reduce the scattered components in the detected signals and improve the quantitative accuracy of the reconstructed images.
The physical and clinical performance of the systems was evaluated through phantom, animal and clinical studies.
Materials and Methods
Development and Performance Evaluation of Prototype CdTe-PET
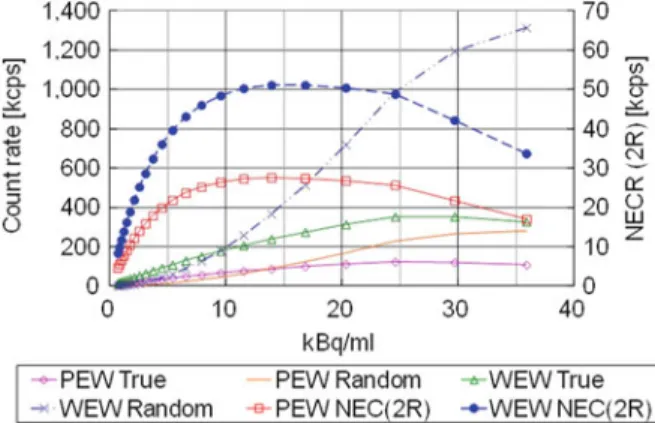
The effective atomic number of the CdTe is smaller than the scintillation detectors of the current PET scanner. A reconstruction system of the developed scanner dealt with the sensitivity problem and avoided unexpected statistical fluctuation in reconstructed images. The sensitivity of the scanner was also evaluated using the measurement data of count rate performance.
All sectioned parts were integrated into a 3-D volume using a slice-by-slice image registration technique.
Development and Performance Evaluation of Prototype CdTe-SPECT
The ability to use CdTe-PET to measure the metabolic distribution of tumor was evaluated. The ordered subset expectation maximization (OSEM) ( Hudson and Larkin 1994 ) including PSF and attenuation correction was used. A character-shaped dual-radionuclide phantom, which has three kinds of radioactivity, was scanned (Fig. 4.2).
A healthy volunteer was injected with Tc-99m HAS-D and I-123 IMP and then scanned with CdTe-SPECT for 21 minutes as a simultaneous dual radionuclide brain study.
Results and Discussion
Performance Evaluation of CdTe-PET by Phantom Experiment and Clinical Study
Therefore, the border between gray matter and white matter was well defined in the PSC-MAP image. The heterogeneous intratumoral FDG distribution in each tumor was visualized by both CdTe-PET and ARG (Fig.4.5 and 4.6). Reconstructed images of brain tumor and nasopharyngeal cancer patients scanned by CdTe-PET are shown in Fig.4.7.
CdTe-PET identified intratumoral heterogeneity and visualized the tumor edge sharply for both cancers.
Performance Evaluation of CdTe-SPECT by Phantom Experiment and Clinical Study
Conclusion
Semiconductor detectors have the potential to play a significant role in the future of nuclear medicine. Therefore, in this study we aimed to evaluate whether HED was washed out from the myocardium using compartment model analysis. We estimated RI, influx rate K1 and washout rate k2 using single-compartment model analysis using 11C-HED PET.
This result may mean that HED PET is able to evaluate washout parameter using spatial model.
Introduction
Methods
- Study Subjects
- Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography 11 C-HED PET/CT Imaging
- RI Estimation
- Compartment Model Analysis
- Statistical Analysis
11C-HED was prepared from 11C-methyl iodide and metaraminol (free base) using standard methods with high purity and high specific activity [13]. PET/CT imaging was performed with a 64-slice PET/CT scanner (Biograph Siemens/CTI, Knoxville, TN, USA). The time-activity curve was derived from a small circular region of interest in the left ventricular cavity (Fig. 5.1, [10]).
In single-compartment model analysis, the tracer kinetics consists of only two parameters, which are inflow rate K1 and washout rate k2 (Fig.5.1,[6]).
Results
Subjects ’ Background
HED PET Data Normal Volunteers and HF Patients
Discussion
Study Limitation
Conclusion
Quantification of myocardial blood flow using dynamic 320-line multidetector CT versus (1)(5)O-H(2)O PET. Quantification of myocardial blood flow using positron emission tomography: analysis and practice in the clinical setting. Test-retest reproducibility of quantitative cardiac measurements of 11C-meta-hydroxyephedrine in rats by small animal positron emission tomography.
Iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging and carbon-11 hydroxyephedrine positron emission tomography compared in patients with left ventricular dysfunction.