This dissertation does not contain the writings of other persons, unless they are specifically acknowledged as originating from other researchers. KZN DoH, Hlabisa Hospital Manager and Clinic Managers for permission to conduct the study.
List of Tables
Summary of the study
Aim of the study
Specific Objectives
Although only 12.0% of patients were nonadherent to ART, other recommendations include strengthening the tracking of patients who missed a follow-up visit. The missing data may be those of patients who did not adhere to appointments and ART.
Chapter One
Introduction
Background of the study
They interpreted the results in relation to the virological and immunological response to antiretroviral treatment and factors influencing treatment adherence, such as demographic characteristics, medications, alcohol/substance abuse, health beliefs, etc.12. In this study, the researcher measured adherence using recorded patient self-reports and the results were interpreted in combination with virological and immunological responses to antiretroviral treatment, taking into account the relationship between demographics, socio-economic factors, disclosure and support , and symptoms and side effects.
Assumption
Antiretroviral therapy reduces the morbidity and mortality associated with AIDS-defining diseases,8,9 but the success of antiretroviral therapy depends on adherence to treatment. The program was gradually expanded to the remaining fourteen sub-district clinics in 2005-2006.
Research Questions
To analyze the associations between adherence, disclosure, socio-demographic characteristics, symptoms and side effects, and CD4 and VL outcomes 12 months after initiation of antiretroviral therapy. This chapter laid the groundwork for the study in terms of background, aim and objectives, and the next chapter will present a literature review related to the objectives of the study.
Chapter Two
Literature Review
Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)
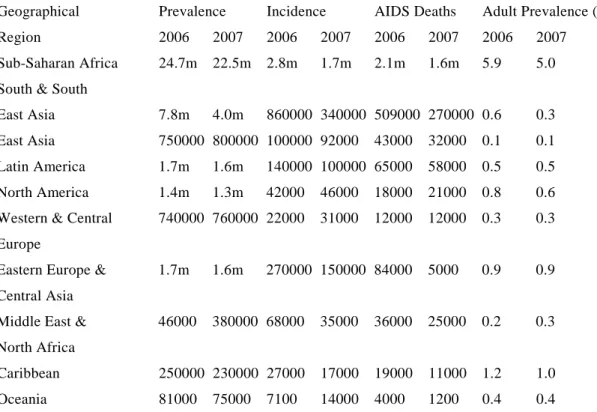
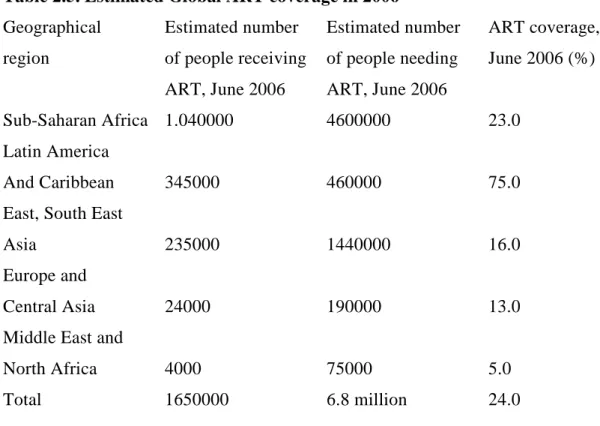
Antiretroviral treatment coverage increased fourfold in low- and middle-income countries between December 2003 and June 2006.1 ART coverage increased by 45.0% in 2007.1 An estimated two million life years have been gained since 2002 in countries with low and middle income.20 About 3 million people (31.0% coverage) in low and middle income countries were on ART in 2007.1. Today South Africa has the largest number of people on ART in the world,1 however, many more people need ART to keep them healthy and prevent deaths from HIV/AIDS.1 More adults how many children use ARVs and co-infection with TB are challenges.1 South African National ART Guidelines13 and international guidelines (Department of Health and Human Services, International AIDS Society of the United States of America (DHHS, IAS-USA ) and European guidelines) are based on the WHO ART guidelines cited below.21.
Adherence - a key component of ART
Some of the patients (16%) who were lost to follow-up before completing 48 weeks of follow-up had been excluded from the study. Rosen, Fox, and Gill,93 used online ART program reports to estimate retention of patients in ART programs in sub-Saharan Africa and what causes loss to follow-up.
Side effects of ART
The incidence of anemia before ART and ON ART was the same, so there was no progressive anemia on ART. The incidence of peripheral neuropathy was also similar before and during antiretroviral therapy. In this study, the regimen appeared to be safer because it was difficult to distinguish adverse effects from drug toxicity.
Most of the patients switched due to adverse events were switched to zidovudine-based (42.7%) and tenofovir (32.8%)-based regimens. More women (obese) changed due to hyperlactatemia than men before six months of treatment. These results also call for careful monitoring of patients on ART for serious side effects such as hyperlactatemia.
Those patients whose treatment was changed before two VL results were greater than 1000, and those who were switched due to treatment failure rather than treatment nonadherence were more likely to achieve viral suppression.
Summary of literature review
Another study in Johannesburg, South Africa,121 was conducted to determine patient outcomes after one year of second-line therapy. These results are encouraging for patients with treatment failure, and prescription of second regimen should not be delayed for those patients in need.
Chapter Three
Research Methodology
- Study design
- Study limitations
- Definition of terms Adherence
- Methods 1. Study Sites
- Validity and reliability
- Data management
- Statistical Analysis
- Ethical Considerations
- Summary
Coetzee et al 2004 Defined loss to be followed as a patient of unknown location for 3 months or more.40. Loss to follow-up is described as missing a visit for one month, six weeks, 3 months or more up to two years. There appears to be no consensus on the definition of a loss to be monitored.
Standard operating procedures were in place regarding the clinical care of patients during follow-up visits. To describe the current Daily clinic Structured Date of initiation, regimen, Registered the patient's state of compliance with observation, treatment collected on scheduled follow-up visits. To describe death and patient records Still structured in ART program, If no, death or loss to dropout rates under Daily registry observation follow-up, date of death/loss to follow-up.
Treatment adherence was defined as >95.0% adherence, and attendance adherence was defined as not missing monthly follow-up visits.
Chapter Four
Results
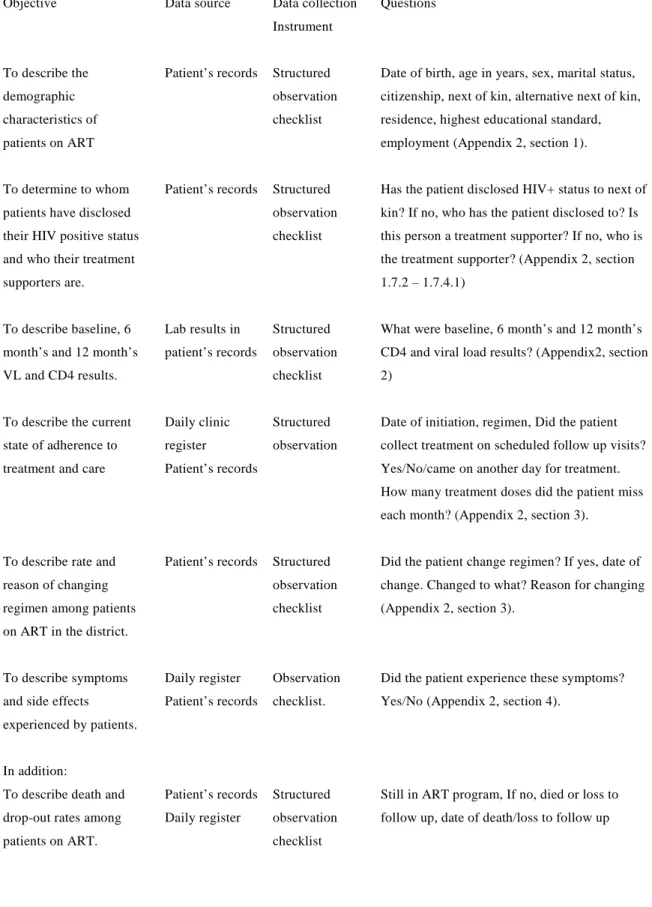
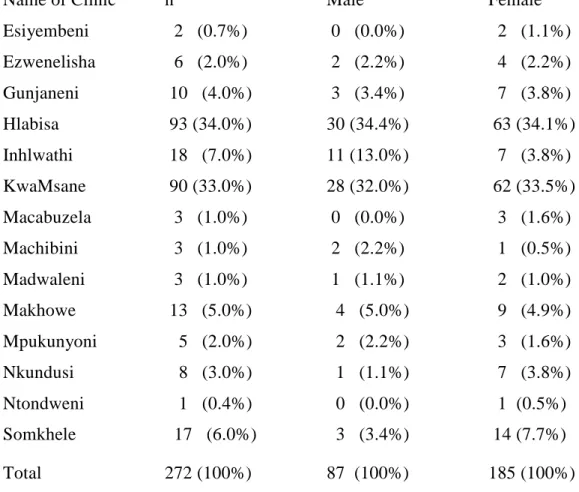
Description of patients (receiving ART at Hlabisa public clinics) 1 Socio-demographic characteristics of the study sample
All nurses and counselors were trained to manage patients on ART before patients were transferred from Hlabisa to other clinics. Educational standard of patients receiving ART in Hlabisa public clinics by gender, n=249 Education Total Men Women. Closest relatives of patients receiving art in Hlabisa public clinics by gender, n=257 Closest relatives Total Men Women.
None of the patients who had not registered partners as next of kin registered them as alternative next of kin. The majority of patients received regimen 1a (stavudine, lamivudine, and stocrin) when they initiated ART. SD = Standard deviation, n = Total number of patients for whom information on the variable was available.
SD = standard deviation, n = Total number of patients for whom information on the variable was available differed.
Adherence
After six months there was a sharp decrease in viral load and the majority of viral loads for both male (95.2%) and female (94.7%) patients were <400 copies/ml. Female patients were less likely to miss a follow-up visit than male patients receiving ART. The higher the CD4 count, the more likely they are to miss a follow-up visit.
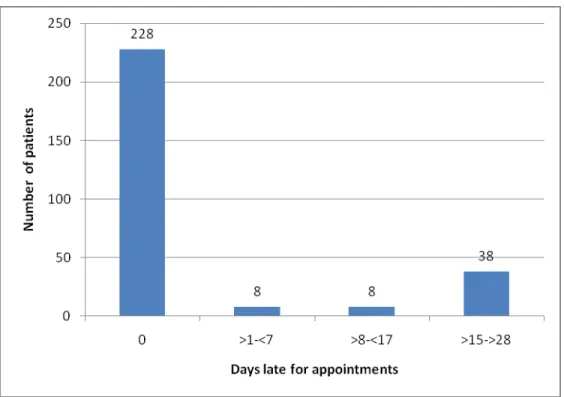
Patients from Hlabisa were more likely to miss a follow-up visit than all the other clinics. This graph shows the proportion of patients who were adherent to ART in the first year of treatment. Comparison of patients' adherence to ARV treatment by symptoms and side effects in the first year of treatment, n=272.
Adherence was not associated with baseline and six-month viral load outcomes, but at 12 months, non-adherence was associated with failure of viral suppression.
Chapter Five
Discussion
Summary
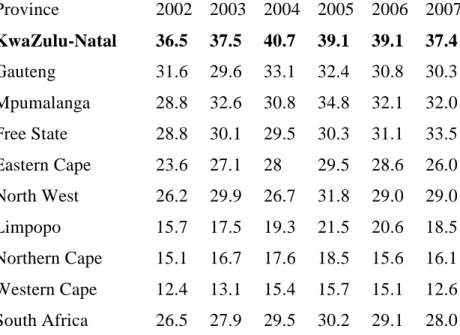
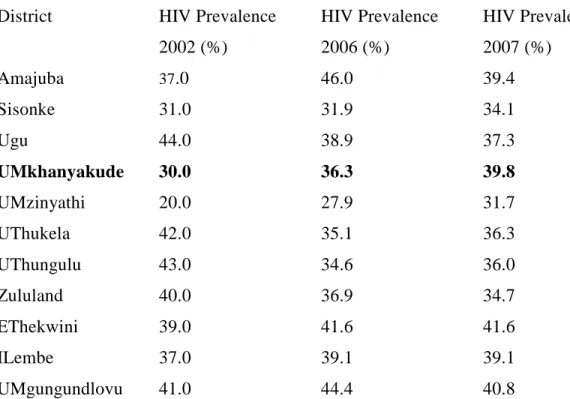
This chapter presented a discussion of ARV adherence and appointments, that is, higher education level, employment, being single, and a CD4 count >50 cells/mm3 increased the probability of missing ART doses. Other determinants of adherence included demographic characteristics, disclosure, support, and signs and symptoms and side effects.
Chapter Six
Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusions
Only marital status was predictive, and being married was associated with a high likelihood of adherence to ART. The top five most common symptoms were weight loss, headache, rash and cough, but these were not associated with medication adherence. Although fatigue was only experienced by 9.0% of patients, those who experienced it tended to be less adherent to ART than those who did not experience this symptom.
The nurse/consultant-led model used to decentralize treatment and care for patients with HIV and AIDS has proven useful and provides support for scaling up rollout without fear of lack of adherence. The feasibility of referral to PHC clinics is confirmed by the results of this study, which shows that more people who need treatment can receive it without treatment.
Generalizability
In this study, adherence was based on the recall of medication in the past seven days, meaning that memory of medication intake was likely to be good. Due to the likelihood that patients with higher levels of education will miss a follow-up visit, it is recommended that more emphasis be placed on adherence counseling of the more educated group of patients who appear to be neglected because they are believed to have more knowledge and to understand the importance of adherence to ART. Because the majority of patients in the ART program were older women, awareness strategies and campaigns aimed at engaging .youth and men are needed.
Although disclosure and treatment partner were not associated with adherence, qualitative studies are needed to investigate disclosure and discrimination in this community because most patients would prefer not to disclose their sexual partners. In order to monitor the effectiveness of the ART program, timely access to VL results is extremely important and these systems need to be improved. In relation to these recommendations, the researcher will present the results of the study to the management teams of the sub-district and district offices.
A copy of the report will be sent to all clinics in the sub-district, the provincial DoH HIV and AIDS office and the national HIV and AIDS directorate.
Observation Checklist
Adherence
Ethics Clearance
Permission from KZN DoH
- rranlciPant .::26· 06 Date OJ
Vou can contact the Medical Research Office at the Nelson R Mandela School of Medicine OIl if you have questions about your rights as a research subject. You have been asked to have your clinic participate in a research study. You were sent by Mrs. L informed about the study. You can contact the Medical Research Office at the Nelson R Mandela School of Medicine at if you have questions about your rights as a research subject. .
You can contact the Medical Research Office at the Nelson R Mandela School of Medicine at If you have any questions about your rights as an e-research subject. If you have any questions about the study, you can contact Ms Mthlyane at any time. You can contact the Medical Research Office of the Nelson R Mandela School of Medicine if you have any questions about your rights as a research subject.
Yoo can contact the MediCal Research Office at the Nelson R. Mandela School of Medicine if you have questions about your rights as a researcher. Permission was obtained from KZN DoH 10 to conduct this study.
Process evaluation of the pilot study
Patients who were no longer in the ART programme, n=21