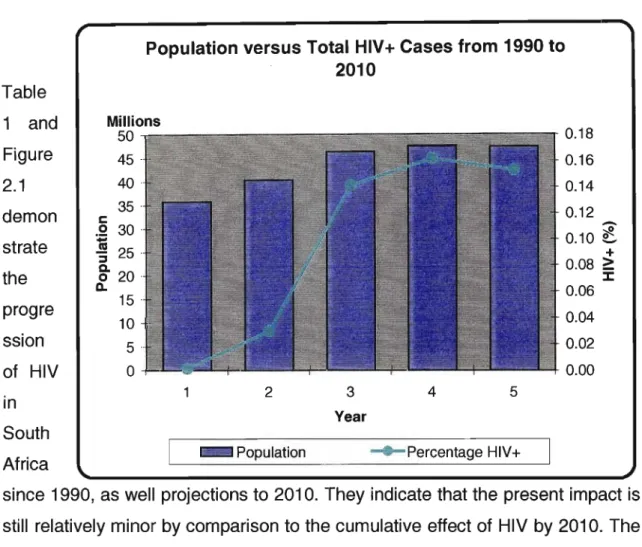
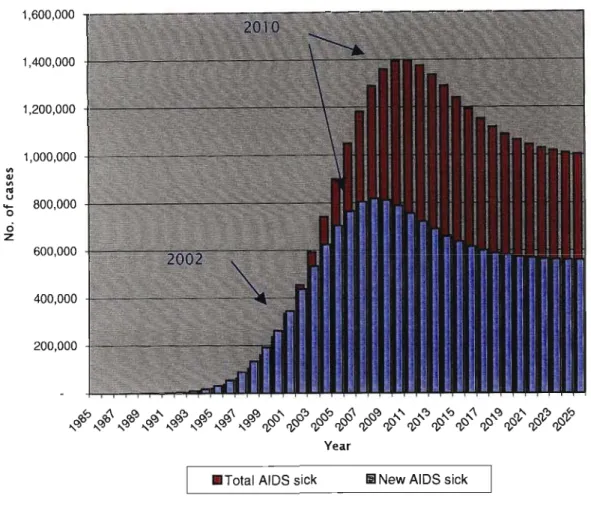
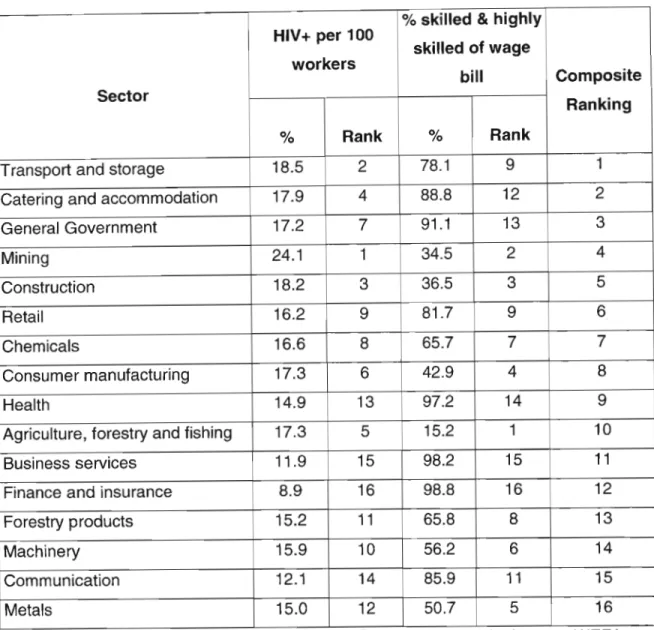
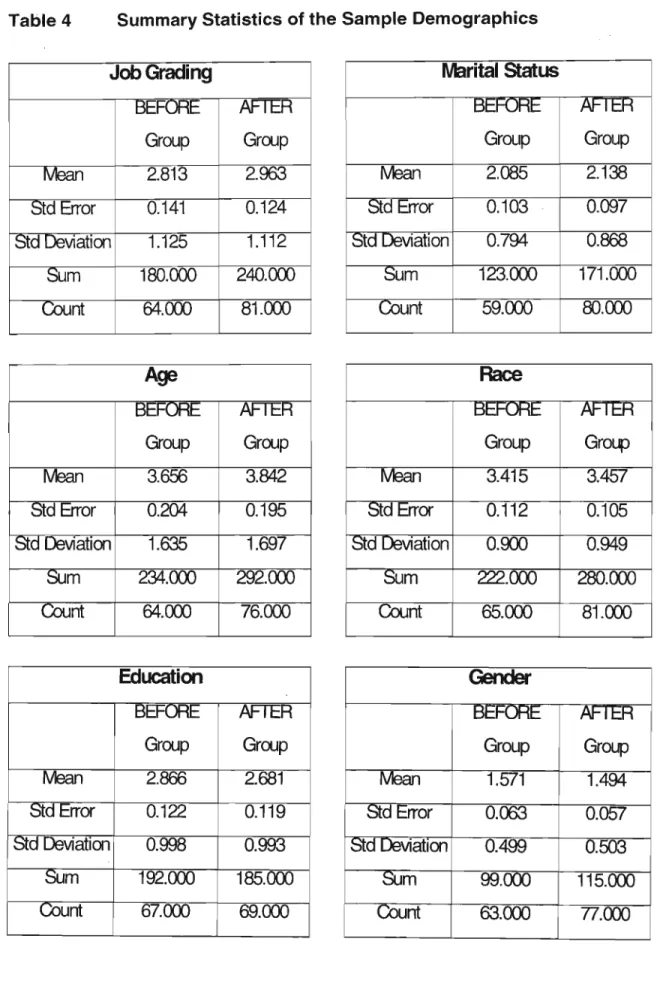
The primary purpose of this study is to examine the impact of HIV/AIDS on business with an assessment of the risk facing business in the short and long term. Case studies of workplace HIV/AIDS programs are used to identify and analyze successful interventions that can be used in the South African context. Issues of discrimination and intolerance pervade the environment where employers are required to implement programs that change knowledge, attitudes and behavior around HIV/AIDS.
This study seeks to provide guidelines and recommendations for companies willing to implement HIV/AIDS workplace interventions by presenting an overview of the options available and indicating where they can best invest limited resources.
SCOPE AND OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
- Background of The Study
- Objectives of The Study
- Relevance of The Study
- Problem Statement
- Research Methodology
- Limitations of The Study
- Structure of The Study
- Summary
This study will focus on one of the main stakeholders in South Africa, the business sector. In view of the above, the economy is becoming one of the most vulnerable sectors and at the same time a strategically positioned sector for controlling the impact of HIV/AIDS. The costs to businesses of not implementing effective strategies will be included in the analysis of the impact of HIV/AIDS presented in Chapter 2.
South Africa's business community is critical to controlling the disease, even as it escalates to a national emergency.
LITERATURE REVIEW AND ASSESSMENT OF THE IMPACT
- Profit VS People
- Cost of Labour
- Declining Markets
- Accelerating Markets
- The Impact Matrix
- The Burden Shift Strategy
- The Legal Framework
- Myths and Misconceptions
- Gender Discrimination
- Mainstreaming AIDS to Reduce Risk
- Breaking the Silence
- Mobilizing Organized Labour
- Summary
For example, an increase in the cost of health, life and safety insurance means higher labor costs. Because HIV/AIDS Workplace Programs are not mandatory, South African companies retain the option to do nothing. The best technique to measure the impact of HIV/AIDS on a company is to determine the HIV prevalence in the company.
By African standards, South Africa is wealthy and yet we have one of the highest HIV prevalence rates in the world.

AN ANALVSIS OF THE BUSINESS SECTORS
The Global Benchmark
The ILO's unique tripartite structure, comprising governments, employers and workers, enables it to effectively mobilize against HIV/AIDS worldwide. A pilot education and training manual to guide the implementation of the Code is currently available. Applying the special expertise of the ILO's sectoral and technical cooperation programs to specific workplace needs, particularly in education, social protection and occupational safety and health.
As a member of the ILO, South Africa has access to and support for the implementation of the ILO Code of Practice, which provides a benchmark against which the South African government, business and workers can measure the effectiveness of local interventions.
General Interventions 31
- Policy Content
- Implementation
- Role Modeling 36
HIV/AIDS lends itself to a full range of training methods designed to improve and maintain the responsiveness of the target audience. It is advisable for companies to include an awareness of HIV/AIDS in the company orientation program. The relevance of the training information must accommodate changes and new developments in HIV/AIDS.
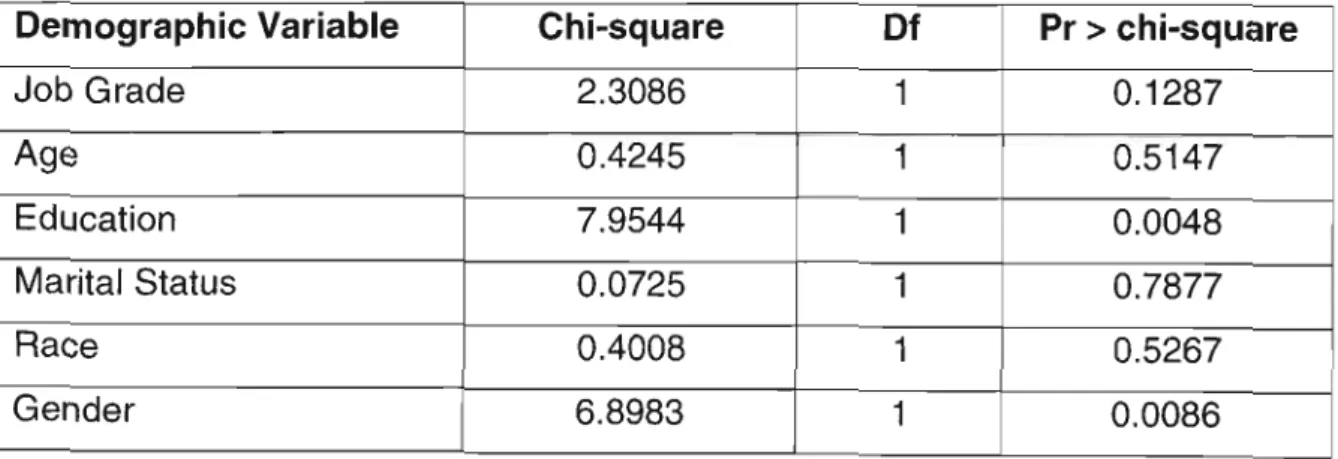
Question Fa Statistics on the number of people infected with HIV/AIDS in the workplace should be provided to staff. In terms of the primary objective, the study finds that the business sector's response to HIV/AIDS globally is proactive and purposeful, and serves to inform best practice standards. A workplace program must be targeted in terms of the knowledge, attitudes and behaviors it seeks to change.
Awareness of the company's HIV/AIDS policy and program should be included in the company's induction training. While the nature of the HIV/AIDS topic is by no means conclusive, the study remains relevant because it is placed in the context of timeless best practice. Asymptomatic: Without signs or symptoms of illness or disease (Le., the patient does not complain of any symptoms). Most people who are HIV positive are asymptomatic for five to 10 years or more.
Fa The statistics on the number of people infected with HIV/AIDS in the workplace should be communicated to the staff.
Condom Usage and Distribution 37
- The Female Condom
- Evaluation
Treatment and Testing
- Sexually Transmitted Infections 42
- HIV Treatment Strategies
The merit of workplace treatment and prevention is that they provide a temporary therapeutic intervention that can promote long-term behavior change. Ideally, clinic staff should be able to engage workers on a wide range of social issues with a clear understanding of the cultural, religious and gender dynamics of the community they serve. The benefit of the occupational health clinic as an intervention is that it provides an opportunity to address wider issues such as secondary infections, discrimination and in the long term protects the company from future losses.
All best practice guidelines consistently emphasize the need for trust in the services offered by on-site clinics. A good example of best practice at work is again found in the mining industry. In the case of BIC South Africa, while the company's HIV/AIDS program is focused on care, treatment and prevention, their key driver is education and awareness.
This approach to training can significantly reduce anxiety and fear of HIV-related workplace discrimination. As part of the workforce, peer educators are able to communicate in the same conversational language, have access to information not readily available to management, and are available as needed. The use of KAPB studies, as evidenced by the Daimler Chrysler case study, has been effective in guiding a company's policies and strategies to manage HIV/AIDS in the workplace.
Interventions must therefore meet needs in the short and medium term, while being flexible enough to accommodate changes in the long term. The analysis of existing workplace programs has clearly shown that HIV/AIDS can be managed in the workplace.
Introduction
Background
Objectives of Study
Research Design
- The Case Study Analysis 59
- The Research Sample
- The Questionnaire
It quickly became clear that the scope of the subject was immense and that the mass of information was not only vast but also available from an unmanageable range of sources. This included daily written and electronic media, literature in the form of books, journal articles, commercial and business sector magazines, business annual reports, past research, the Internet and interviews with recognized experts in the field of HIV/AIDS. The information was then filtered for relevance to the research topic and analyzed in a process of review, debate and discussion with various stakeholders.
In the absence of a control group or a single sample pretest or randomization of Company X employees, a quasi-experimental research design was used to test the emerging hypothesis. Cooper and Schindler confirm that although this design is weakened by concerns about internal validity, it is considered superior to real experiments in terms of external validity because the information obtained from a field experiment is more relevant to the sample population to which we want to generalize our findings. . Due to the extremely sensitive topic, many steps were taken to obtain permission to conduct the research, first within the company, and then also from individual participants.
A pilot survey consisting of 80 questions was conducted to test the language, comprehension and relevance of the questions. The second questionnaire included a cover letter informing potential respondents of the nature of the study and, importantly, reiterating the confidentiality of responses. It also contained a disclaimer that absolved Company X of any involvement in or responsibility for the investigation.
The first part of the questionnaire requested demographic data that was used to verify the consistency of the sample population. The open-ended questions were deliberately avoided due to the highly controversial and fluctuating nature of the topic.
Sample Population
The opinion test questions were scored based on how negative or positive the response was to HIV/AIDS. It will assess the impact of different communication methods related to the issue of HIV/AIDS, specifically the impact of interactive training on changing knowledge and attitudes before and after the training. An analysis of the knowledge questions and responses of the BEFORE and AFTER training groups shows that specific questions, especially those related to Company X's policy and HIV/AIDS program showed the most significant changes.
Should the company screen for HIV during recruitment to reduce the impact of HIV/AIDS. This study assessed the impact of HIV/AIDS on business based on literature review and case studies. It analyzed the business response in terms of HIV/AIDS workplace programs and interventions against best practice standards.
Uganda's HIV I AIDS success story - what are the critical needs, AIDS Analysis Africa, Vo!. South African Business Coalition on HIV / AIDS: Evaluation of Workplace Responses to HIV AIDS in South Africa. Corporate Response to HIV AIDS in the Workplace in the Formal African Sector: Funds of a Kenya Needs Assessment.
UNAIDS, 2000, Guidelines for the United Nations Resident Coordinator System: HIV and AIDS in the UN Workplace. I am adequately informed about the HIV/AIDS initiatives and interventions implemented by my company.
Sample Analysis 63
- Attitudinal Questions 67
Data Analysis: The Impact of Training on Knowledge
Data Analysis: The Impact of Training on Attitude
Research Conclusions
In the South African context, the business sector's response is less directed as it is hindered by a confused response from the South African government. In terms of the secondary objective, the study concludes that the one-to-one or face-to-face intervention is more successful in changing knowledge with a less significant shift in attitudes.
Recommendations
- ILO Code of Practice on HIV / AIDS & The
- Pressure on the South African Government
- Partnerships and Alliances
- Interventions
- Company Culture 86
The corporate culture must reflect and support the HIV/AIDS policy and interventions in terms of management style, communication techniques and attitude. Companies should encourage openness and transparency about HIV/AIDS by integrating it into their day-to-day business. For example, Woolworths in South Africa has launched an HIV/AIDS anti-discrimination campaign in all retail outlets with the tag line "AIDS doesn't discriminate, why should we?".
HR policies can be changed, especially for managers who have staff reporting to them, to include HIV/AIDS awareness and participation in performance appraisal training. It can hopefully inform future research into and implementation of business sectors' response to HIV/AIDS. Common opportunistic infections in people with HIV/AIDS include tuberculosis (TB), certain types of pneumonia, fungal infections, viral infections, and lymphoma.
The Port of Durban and its role in the spread of HIV in KwaZulu-Natal, AIDS Africa Analysis, vol. Gillies and Associates, Outline of an HIV/AIDS Strategy for Organizations Global Health Initiative, (2002) Private Sector Intervention: Nike. Workplace HIV I AIDS Programs: An Action Guide for Managers, Family Health International accessed at www.fhi.org.
Curbing the spread of HIV AIDS in sub-Saharan Africa: New initiatives to strengthen organizations of people living with HIV I AIDS. UNAIDS, 2000, UN System Personnel and Their Dependents Living with HIV I AIDS UNAIDS, 2000, AIDS and HIV Infection: Information for United Nations Staff and Their Families.
Practical measures to support behavioural change ,
Community outreach programmes 15
Training for factoty/labour inspectors
Training for workers who come into contact with human blood and
Prohibition for insurance purposes
Epidemiological surveillance
VoluntaIy testing
Tests and treatment after occupational exposure 20
Linkages with self-help and community-based groups
Benefits . 22
Privacy and confidentiality 23