The Education Department must make sufficient human and financial resources available for the training, supervision and monitoring of the school safety policy. A copy of the Code of Conduct is posted on the classroom bulletin board.
INTRODUCTION 1
ANALYSIS OF THE PROBLEM 2
Learners who suffer from the trauma of crime often live in their own imaginary world and do not bother in class or with their school work.
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM 3
HYPOTHESIS 3
In behavioral research, the statistical hypothesis is in most cases a null hypothesis expressed as "Ho". A hypothesis in which there is a difference between the researcher's sample statistic and the assumed value of a population parameter is known as a.
ELUCIDATION OF CONCEPTS 4
Gender 4
Education 4
The National Education Policy Act, Act No.27 of 1996 defines education as any education and training provided by an educational institution, other than training as defined in Section 1 of the Manpower Training Act, 1981, Act No.56 of 1981 ( DoE , 1996:5). Education is the event through which social values, socially determined knowledge and life skills are transferred from one person to the next (Van Rensburg, Landman & Bodenstein, 1994:417).
Learning 5
Instrumental conditioning or operant learning where a person learns to perform a response as a result of what happens after the response is given. Insight learning refers to solving a problem by understanding the relationships of different parts of the problem.
Teaching 6
According to Van der Westhuizen (1995:54) teaching is an intellectual development of the student which means the development of independent thinking. Teaching is an activity of making someone learn by example or experience (Delahunty & McDonald, 2005:703).
Crime 7
McHenry believes that teaching is the process of helping other people learn. From a legal point of view, Reid (1994:5) is of the opinion that the following statement qualifies the definition of crime: “Crime is an intentional act or omission in violation of criminal law (statuary and case law), committed without defense or justification. and sanctioned by the state as a felony or misdemeanor”.
Culture of teaching and learning 8
In such cases, the researcher had to focus on the meaning of the answers related to the topic “the effect of crime in schools on a teaching and learning culture”. The purpose of this questionnaire is to examine "The effect of crime on a culture of teaching and learning in schools".
AIMS OF THE STUDY 9
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 10
A literature study will be carried out into available and relevant literature on the effect of crime on schools.
VALUE OF THE RESEARCH 10
ANTICIPATED DISSEMINATION OF THE RESEARCH FINDINGS 10
FURTHER COURSE OF THE STUDY 11
SUMMARY 11
INTRODUCTION 13
Culture of teaching and moral dimension 18
The teacher must declare daily himself, without leaving, that his learners can take his statements home with them. If his learners are properly taught, the teacher should be the object of their affection and respect.
Culture of teaching and planning 19
An effective teaching culture is characterized by a school whose activities are well thought out, planned and purposefully implemented. To foster a culture of teaching in schools, there is a need to recognize the challenges that teachers and students now face.
CULTURE OF LEARNING 23
Culture of learning and motivation 26
Motivation is a factor that closely influences the performance of work and the overall effectiveness of the learning culture (Zulu, 2005:32). A culture of learning depends on the school's ability to differentiate motivational strategies to suit educators, learners and the community.
CAUSES OF CRIME IN SCHOOL 30
Conditions in the schools 31
Cases of teachers being shot and murdered or robbed on school grounds are regularly reported. To make the situation worse, perpetrators are often part of the school community itself (Bezuidenhout & Joubert, 2003:63).
Factors in the family 34
Cultivate co-responsibility of the parent community regarding the quality of teaching and learning. Due to the following abnormalities, the culture of teaching and learning is threatened (Reid.
The learner 44
The importance of the teacher on the intellectual and spiritual level due to the demands made by the school in this regard. Negative perceptions of the school and accompanying lack of interest, failure, underachievement and flawed processes.
The availability of alcohol and drugs 52
The longer students have been in the company of other boys or girls who have used drugs, the more likely they are to use drugs. High doses of alcohol result in a lack of judgment and inhibition, leading to student delinquency.
The educator 55
Given the appalling conditions in South African schools, teachers' fears are real, as some teachers have been stabbed, attacked and robbed during school hours (Bezuidenhout & Joubert, 2003:65). Trojanowicz and Morash argue that teachers' failure to discipline misbehaving students results in high levels of instability in some schools.
THE EFFECT OF CRIME ON LEARNERS 57
Behavioural problems 57
Love and trust relationships that these students have never had with people before are sometimes created through substance abuse. They can eventually fit in and experience closeness and security with peers who are also involved in substance abuse (Emmett & Nice.
Stress 58
According to Gwynne (1988: 19), as victims of crime, abused students often feel that they have nothing to lose by taking drugs because they are only concerned with forgetting their insecurity, fear and lack of confidence. They can eventually fit in and experience closeness and security with peers who are also involved in substance abuse (Emmett & Nice, 1996: 285).
School work 60
The previous chapters dealt with a study of the effect of crime in schools on a teaching and learning culture. The purpose of the questionnaire was to collect data regarding the effect of crime in schools on a teaching and learning culture.
THE EFFECT OF CRIME ON EDUCATORS 61
SUMMARY 62
The literature review in this educational research study provided the researcher with the tools to reach the frontier in his particular field of knowledge. The researcher used primary sources, such as the Journal of Educational Research, and secondary sources in education, for example, textbooks, educational encyclopedias and / or dictionaries, research reviews and yearbooks.
INTRODUCTION 66
PREPARATION FOR THE RESEARCH 66
Permission 66
Despite the variation, two aspects of a study are usually presented as data:. the quotations of the respondents' language. The majority of respondents claimed that the level of crime in schools has increased drastically in recent years.
Selection of the respondents 67
RESEARCH INSTRUMENT 69
- The questionnaire 69
- Construction of a questionnaire 70
- Characteristics of a good questionnaire 72
- Advantages and disadvantages of a questionnaire 74
The questionnaire was also used as a basis for profiling the nature, causes, impact and perceptions of crime in schools. Most of the questions were closed and only a few open questions were used in the educator's questionnaire.
VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY OF THE QUESTIONNAIRE 77
The majority of respondents indicated that the Department of Education (DoE) is not doing enough to reduce crime in schools. The statistical relationship between the gender, age, years of teaching experience, qualifications and their perception of the respondents.
THE PILOT STUDY 82
ADMINISTRATION OF THE QUESTIONNAIRE 84
According to Bell, the questionnaire must be accompanied by a cover letter that explains the nature and purpose of the research project and enlists the respondent's cooperation. With the above intentions of the cover letter in mind, the following practices are recommended (Ary, Jacobs & Razavieh.
PROCESSING OF DATA 85
- Descriptive statistics 85
- Inferential statistics 86
- Chi-square test 86
- Application of data 87
Questions are asked about the nature of real situations, while hypotheses are statements about how things might be. Section–4 contained open-ended questions and focused on information about educators' perceptions of the effect of crime on the culture of teaching and learning in schools.
LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY 88
ETHICAL CONSIDERATION 88
SUMMARY 89
In the above table (table 14.1), the proportion of responses in each response category (agree; disagree; unsure) is shown for the different categories of respondents'. More than fifty percent (70%) of the respondents confirmed that most educators do not experience any job satisfaction at all due to crime in schools.
INRODUCTION 92
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 92
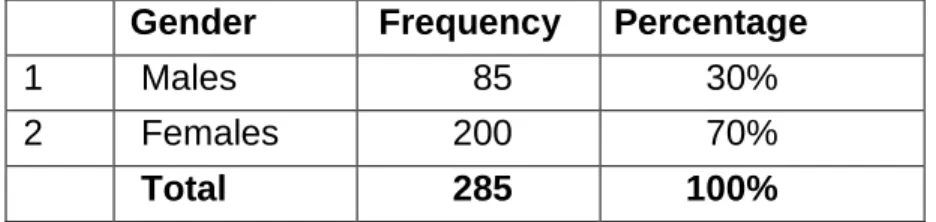
Gender of the respondents 93
Schools have more female educators than male educators and this may have contributed to the continued increase in student crime (Perumal, 2006:84). More female educators apply for primary school vacancies as they find teaching in primary schools less stressful than teaching in a secondary school (Manese, 2001:3).
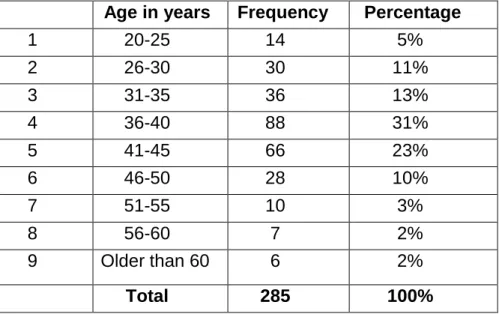
Age of the respondents 94
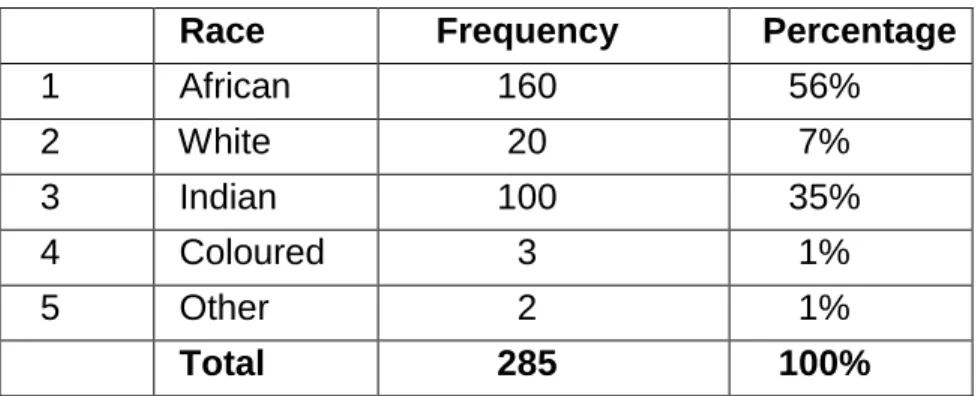
Racial grouping 95
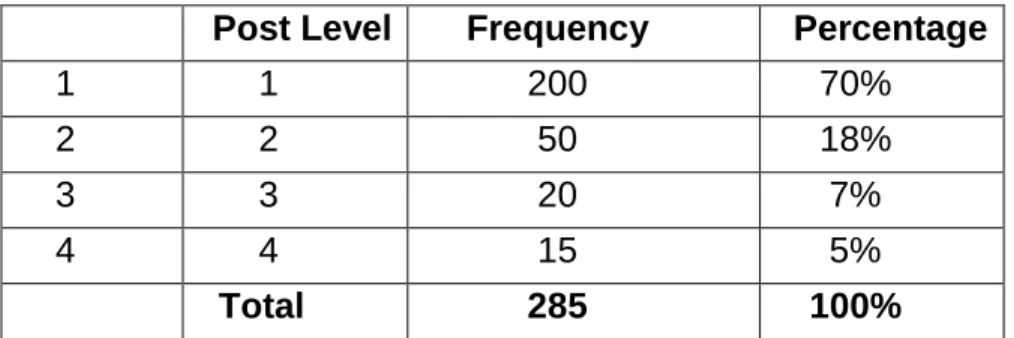
Post levels of the respondents 96
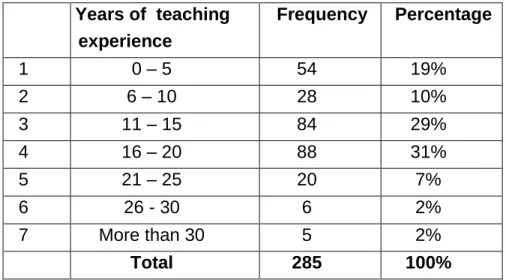
Years of teaching experience of the respondents 97
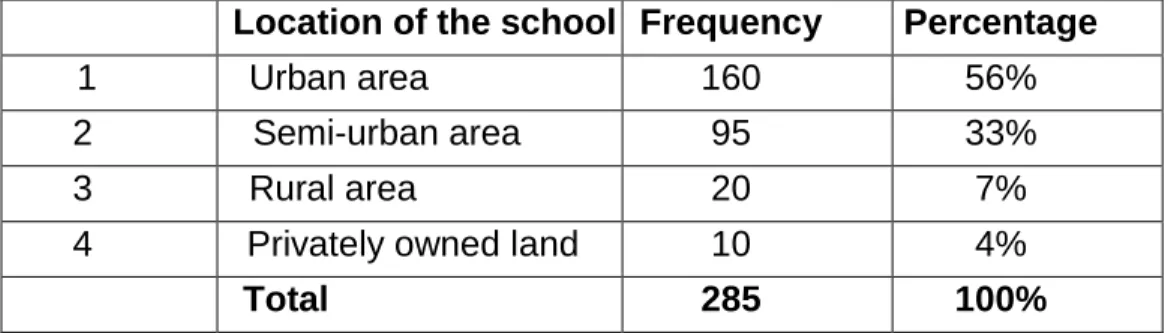
Location of the school 98
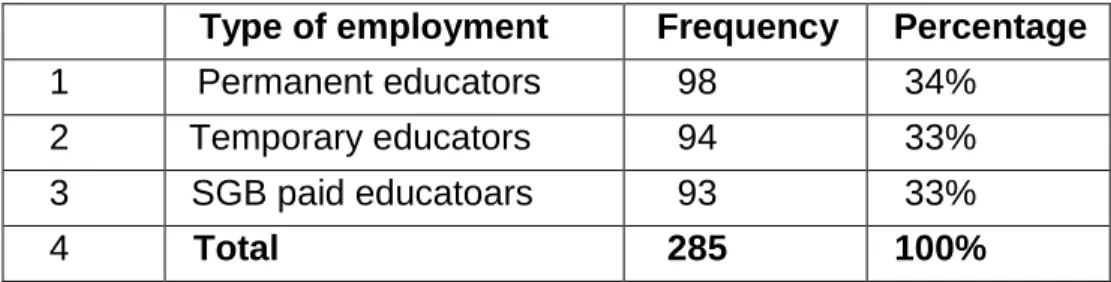
Type of employment 99
Size of the school 99
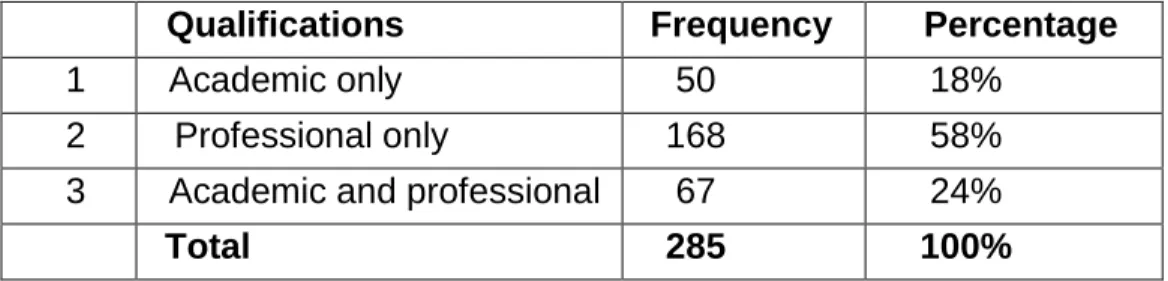
Qualifications of the respondents 100
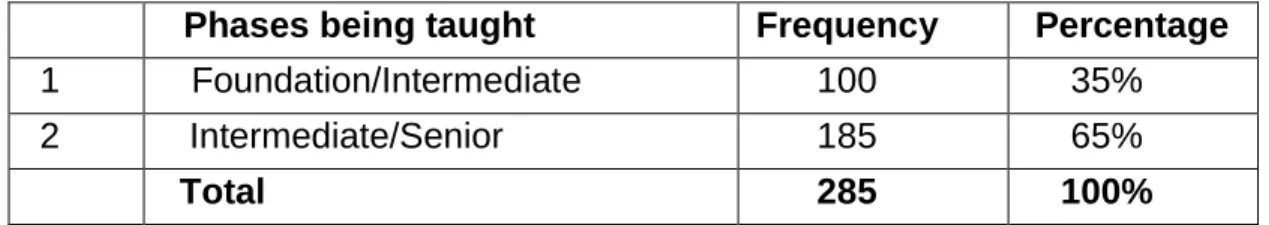
Phases being taught by the respondents 101
Causes of crime 102
More than eighty percent (89%) of the respondents who took part in the research confirmed that substance abuse affects the behavior of most students in schools. There is an awareness of the dilemma of the use of corporal punishment in schools.
Effect of crime 111
Teachers' perceptions of the causes of crime are not related to their gender, age, years of experience and qualifications. The age of the respondents and their opinion that the level of crime in schools has increased drastically over the past twelve years.
EDUCATORS’ PERCEPTIONS OF CRIME 117
Qualitative data 117
The questions to the respondents were related. for the purpose of the research, namely what effect crime in schools has on a teaching and learning culture. The themes that emerged gave an explanation of the situations experienced by educators affected by crime in schools.
INFERENTIAL STATISTICS 121
Variables 122
The dependent variable is the factor that the researcher observes and measures to determine what effect the independent variable has on it. It is the fact that appears, disappears, or varies when the researcher introduces, removes, or varies the levels of the independent variable.
THE HYPOTHESIS 123
The Chi-Square (x 2 statistical test of significance) 124
The statistical relation between the respondents’ gender, age, years of
The statistical relation between the respondents’ gender, age, years of
Almost three-quarters (74%) of respondents indicated that educators are under a heavy burden due to crime. More than eighty percent (89%) of respondents in the survey sample confirmed that substance abuse affects the behavior of most students at school.
TESTING OF HYPOTHESIS 134
SUMMARY 135
This chapter attempted to give some order to a series of information gathered from the respondents' answers to the questions in the questionnaire.
INTRODUCTION 138
- Statement of the problem 138
- Aims of the study 138
- Planning of the research 139
- Presentation and analysis of research data 139
- Findings from the literature review 140
- Findings from the empirical study 142
- Findings from the inferential statistics 144
- Acceptance of hypotheses 146
When the above situation is taken into account, most of the null hypotheses formulated for Table 14 (cf.4.3.3) will therefore be accepted because there is no significant statistical relationship (P>0.05) between the dependent and independent variables not (cf. 4.3.1). According to Table 15 (cf.4.3.4) there is only one statistically significant relationship (P<0.05) between the respondents' gender and their opinions that crime in schools causes stress for educators.
RECOMMENDATIONS 146
Initiatives on crime prevention 146
The main function of the code of conduct is to ensure the safety of students at school. A code of conduct is reviewed periodically by the school's safety committee and amended when necessary.
Workshops 149
It is recommended that further research of a quantitative and qualitative nature should be carried out on the impact of crime in schools on the culture of teaching and learning. The study was initiated to investigate the impact of crime in schools on the culture of teaching and learning.
Further research 152
CRITICISM 152
Educators from only one district, namely Pinetown District in Ethekwini Region, were used in the investigation.
FINAL REMARK 153
What cannot be endured must be healed: untying the Gordian knot of violence in South African schools. The following factors contribute to crime against teachers in your school. who lack constant parental supervision tend to misbehave).