Chapter 1 Introduction
Background of the study
Problem statement
Rationale of the study
Significance of the study
Purpose of the study
Study objectives
Research questions
Definition of terms
Conclusion
Chapter 2 Literature review
Introduction
The significance value shows that there is no significant association between HBP and most lifestyle variables. There is a high prevalence of HBP and the majority of academic staff are at risk of getting HBP if left unchecked.
Prevalence of HBP
Definition of HBP and classification of HBP
Awareness of HBP
The results of a study conducted among non-academic employees at the Niger Delta University show that non-academic employees do not have adequate knowledge of HBP (Odika, Joffa & Apiyanteide, 2011). In a study conducted among US employees, the results of the study show that about 70% knew about their BP status and about 80% had health insurance (Davila, Kuklina, Valderrama, Yoon, Rolle & Nsubuga, 2012).
Risk factors of HBP
- Social risk Factors
- Lifestyle risk factors
- Metabolicriskfactors
In a study conducted among black adults in Ha-Mothapo village, Limpopo province, the results of the study showed that the high prevalence of HBP was associated with increasing age (Sengwayo, Moraba & Motaung, 2013). The results of the study show that almost half of the scientific staff did not exercise.
Consequences of HBP
Challenges in management of HBP
Prevention of BPH is the best option, as the problem with BPH is that it cannot be completely cured and its management requires lifelong medication and lifestyle modification (Desai et al, 2009). The presence of health care models and workplace programs that address these factors may improve the control of HBP among employees (Davila et al., 2012).
Management of HBP
- Exercise
- Diet
- Medication
Physical activity has been recommended as a lifestyle change that can be used to prevent the development of HBP. Diuretics are often used in the treatment of HBP, especially in the first phase of treatment.
Conclusion
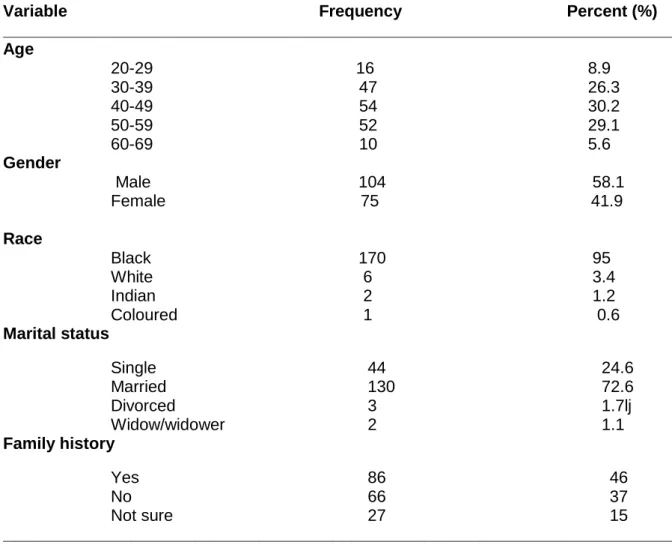
Majority of the respondents 19 (90%) indicated to be still under treatment and 2 (10%) no longer under treatment. The findings of the present study show that there is a highly significant relationship between HBP and gender, men 24 (69%) had a higher prevalence of HBP than women 11 (31%) (P = 0.000). The majority of respondents reported eating fast food most days of the week.
My research title is "prevalence of high blood pressure among academic staff of the University of Venda, South Africa". The main purpose of the study is to determine the prevalence of high blood pressure in the academic staff of the University of Venda.
Chapter 3 Methodology
Introduction
Research methodology refers to the process of data collection, data analysis and data interpretation (Cresswell, 2014). This chapter discusses the study design, study setting, population, sampling, exclusion criteria, instrumentation, instrument pre-testing, instrument validity and reliability, data collection, data analysis, ethical considerations, and dissemination.
Study design
Study setting
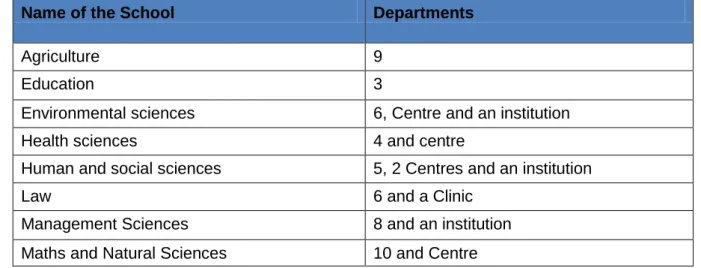
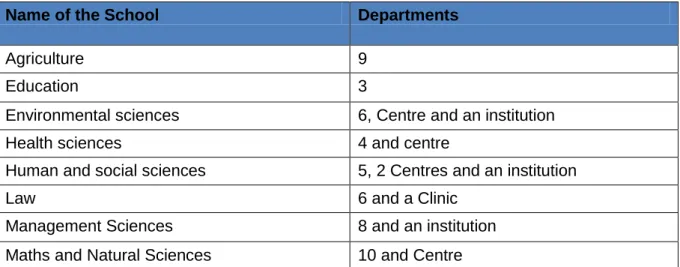
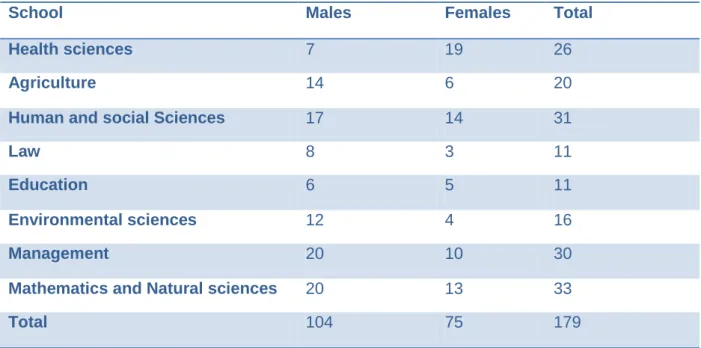
The College of Management has a large number of staff (60), followed by Social Sciences (57) and Law with the least (21).
Population
Sampling
The sampling of each school was calculated by multiplying the total male or female sample by the total sample size, divided by the total population, referenced from table 3.2 above. Population size = refers to the total number of males or females per school n= total sample size which was 179. Random sampling refers to each individual having an equal chance of being selected to be part of the study (Babbie , 2013).
The names of all the academic staff of each school were written on a small piece of paper, folded and placed in two containers, one for men and one for women. An independent person was asked to make a choice from the two containers based on the calculated number per school.
Exclusion criteria
Instrumentation
- Questionnaire
- Anthropometric instrument
Pre-test of the instrument
Data collection…
- Recruitment process
- Data collection procedure
A space was provided on the questionnaire to record the results of blood pressure, weight and height. The researcher and research assistant gave the respondents a questionnaire to fill out and then measure their blood pressure, weight and height on the same day. Respondents were given a questionnaire that they had to fill out before the blood pressure measurement and return it the same day.
The respondent stood on the scale without support with feet evenly spaced on the scale. Weight was recorded in 100 g while the subject was still standing on the scale (Ramukumba, 2012).
Data analysis
Height was measured with the subject standing upright on a stadiometer scale, with arms hanging at the side, head in an open frontal plane without touching the scale. The respondent was asked to take a deep breath and hold, and then the height was recorded to the nearest 0.5 cm (Ramukumba, 2012).
Ethical considerations
- Permission
- Informed consent form
- Privacy
- Confidentiality and anonymity
- Rights of respondents
The researcher ensured that any information obtained from the respondents during the survey remained confidential by keeping the information in a cabinet where only the researcher had access to it. The researcher fully informed the respondents about the study; for example, the nature, duration and purpose of the investigation. Respondents were also informed about the methods, processes and procedures of data collection and how the results of the survey will be used.
The researcher ensured that the respondents received information before the study, for example that the study is voluntary and that they had the right to refuse to participate in the study and that they had the right to withdraw from the study at any time without incurring any penalty (Bhattacherje, 2012 ). An information letter and an informed consent form were used to ensure that respondents would not feel compelled to participate in the study.
Validity and reliability of the study
However, the results of this study showed that there was no significant association between HBP and age (P = 0.63). The results of this study reveal that there was no significant association between HBP and exercise (P = 0.206). A study conducted among university academic staff found that there was a significant association between HBP and alcohol consumption.
A study conducted among Indian adults further showed that there is a significant association between HBP and alcohol intake (Shankarishan, Borah, Mohapatra, Ahmed & Mahanta, 2012). Ali et al. (2009) indicated that there was a significant association between HBP and BMI among female teachers in Basra.
Dissemination of results
Conclusion
Results
- Introduction
- Demographic characteristic
- HBP awareness and control…
- Risk factors associated with HBP
- Lifestyles
- Stress
- Metabolic risk
- Measurements results
- HBP and lifestyle characteristics
- HBP and stress
- HBP and metabolic risk
- Conclusion
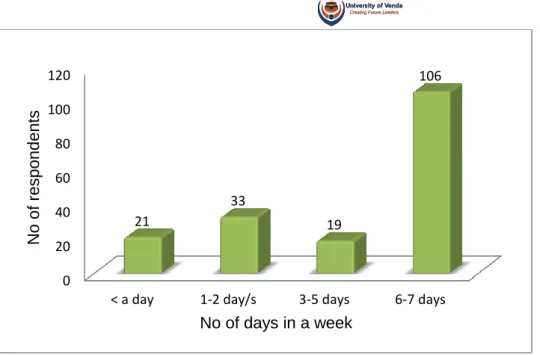
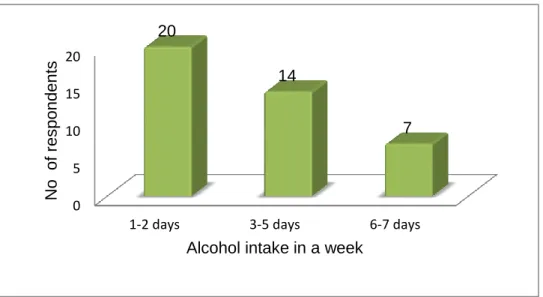
Respondents were asked whether they drink alcohol and the frequency of alcohol intake in a week among those who drink. The majority of respondents indicated that they experience stress 100(57%) and 75(43%) indicated that they do not experience stress. Respondents were asked if they had ever been told by a health professional that they were obese.
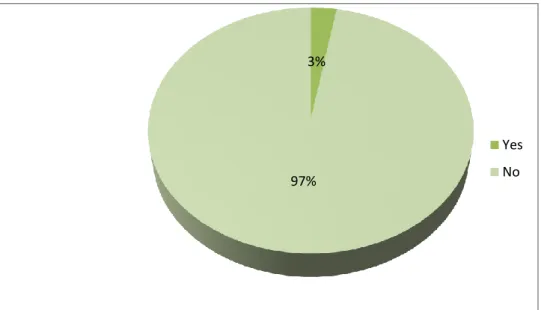
Respondents were asked if they had ever been told by a healthcare professional that they had diabetes. The results show no significant relationship between HBP and stress, frequency of stress and cause of stress.
Discussion, conclusion and recommendations
Introduction
Prevalence, awareness and control of HBP
Kumar et al., (2013) also reported a very low prevalence of HBP (4%) among school teachers in wangaral. A study conducted among teachers in Ethiopia showed that 43% of those with HBP were aware of their status (Fikadu et al., 2016). In a study conducted among adults in Benin, about 77.5% were unaware that they had HBP (Houinato, Gbary, Houehanou, Ammoussou, Segnon-Agueh, Kpozehouen & Salamon, 2012).
A study conducted among adults in Benin showed that only 1.9% had their blood pressure under control (Houinato et al., 2012). In a study conducted among workers in the United States, about 65% of those receiving treatment had
HBP and its associated risk factors
Several studies indicated that there was significant association between HBP and family history of HBP (Sikandar, 2015; Greiw, 2010; However, the results of this study revealed that there was no significant association between HBP and fruit intake among UNIVEN academic staff was not (P =0.686).Omorogiuwa et al., (2009), indicated that there was a significant association between HBP and alcohol intake among staff members of Southern University, in Nigeria.
Briasoulis et al., (2012), indicated that there was a significant association between HBP and heavy alcohol consumption among men, but there was no significant association in HBP. The results showed that there was a significant association between HBP and overweight/obesity among the indigenous Nicobarese tribe (Manimunda, Sugunan, Benegal, Balakrishna, Rao & Pesal, 2010).
Conclusions
Prevalence and associated factors of hypertension among adults at Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia: A community-based cross-sectional study. Alcohol consumption and the risk of hypertension in men and women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Role of gender and their marital status in the prevalence of hypertension in Kashmiri population.
A study on the effect of lifestyle risk factors on the prevalence of hypertension among white collar workers of Surat. Prevalence and associated risk factors of hypertension among adults in a rural community of Limpopo Province, South Africa. Prevalence of hypertension and associated risk factors in Dehui City of Jilin Province in China.
Questionnaire: The prevalence of high blood pressure among University of Venda academic staff, South Africa.
Limitations
Recommendations
The prevalence of HBP to be associated with diabetes as outcome management of diabetes prevention strategies should be implemented as a way to manage BP. Wellness campaigns should be conducted regularly to raise awareness and assist in the management of those diagnosed with HBP. A team of different health practitioners is needed to work under the supervision of a wellness coordinator to help for example a dietitian to help with diet education, biokineticist to help with exercise education, prescription and supervision, a psychologist to help with mental health programs, such as stress management programs, as the majority of staff indicated that they experience stress and a nurse or a doctor to help with medication management and education.
The Department of Sports should implement various sports activities for academic staff, and the Department of Biokinetics should expand UNIVEN's Biokinetic Clinic to encourage UNIVEN's academic staff to be physically active as a way to prevent and manage HBP. UNIVEN's cafeteria should be provided with training to prepare food that contains low fat and salt to help prevent HBP and to manage HBP.
Risk factors for hypertension in adults aged 35–64 years living in an urban slum in Nairobi, Kenya. Prevalence of elevated body mass indices and association with high blood pressure and hyperglycemia in rural areas. Baseline hypertension risk stratification in teachers of University of Peshawar, Journal of Rehman Medical Institute, 1(2): 1.
Factors associated with high blood pressure in the adult population of Kang (Kgaladi North), Botswana. Fruit and vegetable intake and risk of hypertension in middle-aged and older women. I am doing a study on "The prevalence of high blood pressure among academic staff at the University of Venda, South Africa".
The main purpose of my study is to investigate the prevalence of high blood pressure among academic staff at the University of Venda.